Note
Access to this page requires authorization. You can try signing in or changing directories.
Access to this page requires authorization. You can try changing directories.
Microsoft Authenticator provides another level of security to your Microsoft Entra work or school account or your Microsoft account. It's available for Android and iOS. With the Microsoft Authenticator app, users can authenticate in a passwordless way during sign-in. They can also use it as a verification option during self-service password reset (SSPR) or multifactor authentication (MFA) events.
Microsoft Authenticator supports passkey, passwordless sign in, and MFA by using notifications and verification codes.
- Users can sign in with a passkey in the Authenticator app and complete phishing-resistant authentication with their biometric sign-in or device PIN.
- Users can set up Authenticator notifications and sign in with Authenticator instead of their username and password.
- Users can receive an MFA request on their mobile device, and approve or deny the sign-in attempt from their phone.
- They can also use an OATH verification code in the Authenticator app and enter it in a sign-in interface.
For more information, see Enable passwordless sign-in with the Microsoft Authenticator.
Note
Android users with Company Portal versions below 2111 (5.0.5333.0) can't register Authenticator until they update their Company Portal application to a newer version.
Authenticator is a free passkey solution that lets users do passwordless phishing-resistant authentications from their own phones. Some key benefits to using passkeys in the Authenticator app:
- Passkeys can be easily deployed at scale. Then passkeys are available on a user's phone for both mobile device management (MDM) and bring your own device (BYOD) scenarios.
- Passkeys in Authenticator come at no more cost and travel with the user wherever they go.
- Passkeys in Authenticator are device-bound which ensures the passkey doesn't leave the device on which it was created.
- Users stay up-to-date with latest passkey innovation based upon open WebAuthn standards.
- Enterprises can layer other capabilities on top of authentication flows such as Federal Information Processing Standards (FIPS) 140 compliance.
Passkeys in the Authenticator app are device-bound to ensure that they never leave the device they were created on. On an iOS device, Authenticator uses the Secure Enclave to create the passkey. On Android, we create the passkey in the Secure Element on devices that support it, or fall back to the Trusted Execution Environment (TEE).
When attestation is enabled in the Passkey (FIDO2) policy, Microsoft Entra ID attempts to verify the legitimacy of the security key model or passkey provider where the passkey is being created. When a user registers a passkey in Authenticator, attestation verifies that the legitimate Microsoft Authenticator app created the passkey by using Apple and Google services. Here are details for how attestation works for each platform:
iOS: Authenticator attestation uses the iOS App Attest service to ensure the legitimacy of the Authenticator app before registering the passkey.
Android:
- For Play Integrity attestation, Authenticator attestation uses the Play Integrity API to ensure the legitimacy of the Authenticator app before registering the passkey.
- For Key attestation, Authenticator attestation uses key attestation by Android to verify that the passkey being registered is hardware-backed.
Note
For both iOS and Android, Authenticator attestation relies upon Apple and Google services to verify the authenticity of the Authenticator app. Heavy service usage can make passkey registration fail, and users may need to try again. If Apple and Google services are down, Authenticator attestation blocks registration that requires attestation until services are restored. To monitor the status of Google Play Integrity service, see Google Play Status Dashboard. To monitor the status of the iOS App Attest service, see System Status.
For more information about how to configure attestation, see How to enable passkeys in Microsoft Authenticator for Microsoft Entra ID.
Instead of seeing a prompt for a password after entering a username, users who enable phone sign-in from the Authenticator app sees a message to enter a number in their app. When the correct number is selected, the sign-in process is complete.
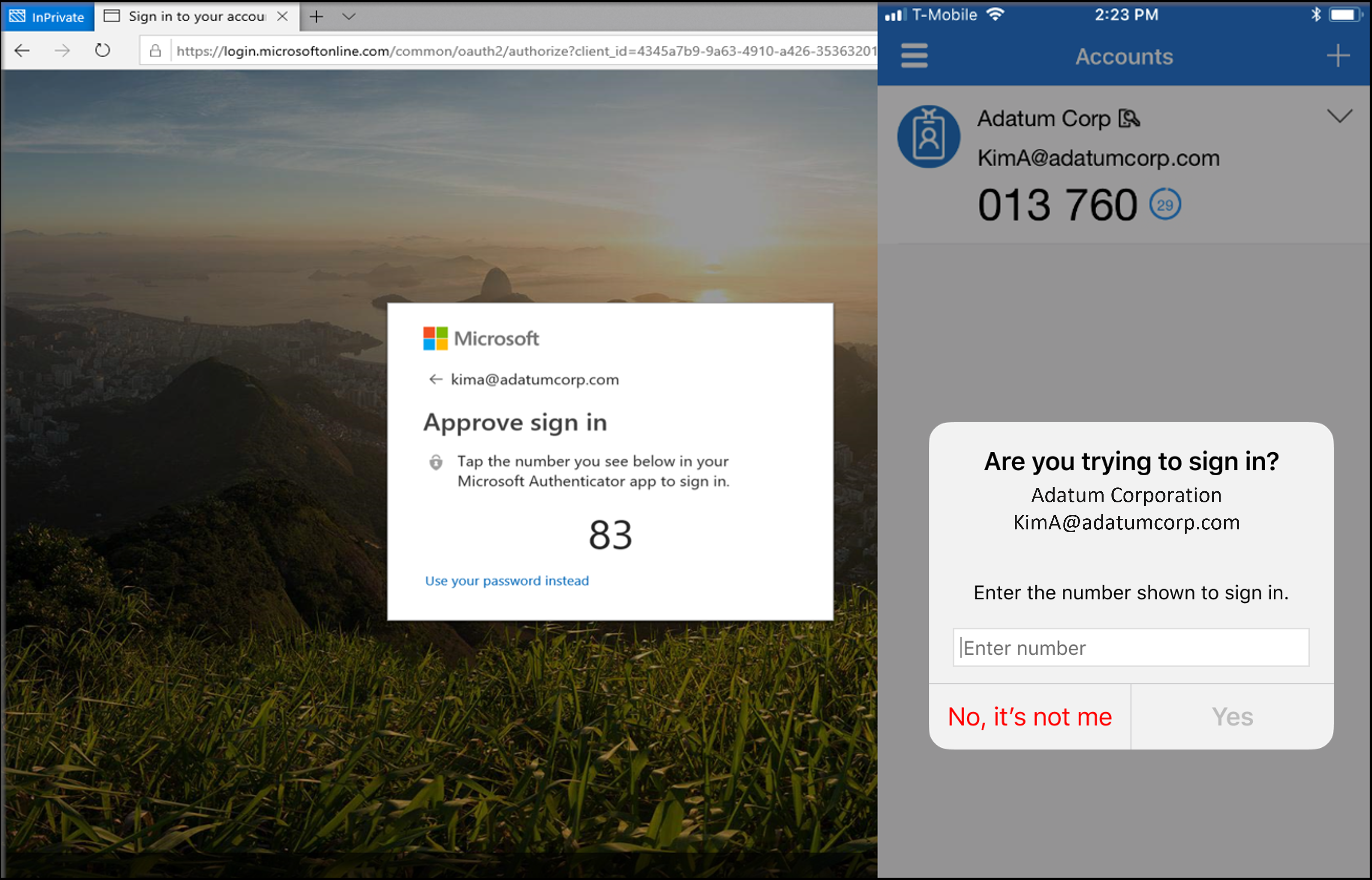
This authentication method provides a high level of security, and removes the need for the user to provide a password at sign-in.
To get started with passwordless sign-in, see Enable passwordless sign-in with the Microsoft Authenticator.
The Authenticator app can help prevent unauthorized access to accounts and stop fraudulent transactions by pushing a notification to your smartphone or tablet. Users view the notification, and if it's legitimate, select Verify. Otherwise, they can select Deny.
Note
Starting in August, 2023, anomalous sign-ins don't generate notifications, similarly to how sign-ins from unfamiliar locations don't generate notifications. To approve an anomalous sign-in, users can open Microsoft Authenticator, or Authenticator Lite in a relevant companion app like Outlook. Then they can either pull down to refresh or tap Refresh, and approve the request.

In China, the Notification through mobile app method on Android devices doesn't work because as Google play services (including push notifications) are blocked in the region. However, iOS notifications do work. For Android devices, alternate authentication methods should be made available for those users.
The Authenticator app can be used as a software token to generate an OATH verification code. After entering your username and password, you enter the code provided by the Authenticator app into the sign-in interface. The verification code provides a second form of authentication.
Note
OATH verification codes generated by Authenticator aren't supported for certificate-based authentication.
Users can have a combination of up to five OATH hardware tokens or authenticator applications, such as the Authenticator app, configured for use at any time.
Consistent with the guidelines outlined in National Institute of Standards and Technologies (NIST) Special Publication 800-63B, authenticators used by US government agencies are required to use FIPS 140 validated cryptography. This guideline helps US government agencies meet the requirements of Executive Order (EO) 14028. Additionally, this guideline helps other regulated industries such as healthcare organizations working with Electronic Prescriptions for Controlled Substances (EPCS) meet their regulatory requirements.
FIPS 140 is a US government standard that defines minimum security requirements for cryptographic modules in information technology products and systems. The Cryptographic Module Validation Program (CMVP) maintains the testing against the FIPS 140 standard.
Beginning with version 6.6.8, Microsoft Authenticator for iOS uses the native Apple CoreCrypto module for FIPS validated cryptography on Apple iOS FIPS 140 compliant devices. All Microsoft Entra authentications using phishing-resistant device-bound passkeys, push multifactor authentications (MFA), passwordless phone sign-in (PSI), and time-based one-time passcodes (TOTP) use the FIPS cryptography.
For more information about the FIPS 140 validated cryptographic modules that are used and compliant iOS devices, see Apple iOS security certifications.
Beginning with version 6.2409.6094 on Microsoft Authenticator for Android, all authentications in Microsoft Entra ID, including passkeys, are considered FIPS-compliant. Authenticator uses the wolfSSL Inc. cryptographic module to achieve FIPS 140, Security Level 1 compliance on Android devices. For more information about the certification, see Cryptographic Module Validation Program.
Users can access Security info (see the URLs in the next section) or by selecting Security info from MyAccount to manage and add more Microsoft Authenticator registrations. Specific icons are used to differentiate whether the Microsoft Authenticator registration is passwordless phone sign-in or MFA.
| Authenticator registration type | Icon |
|---|---|
| Microsoft Authenticator: Passwordless phone sign-in | |
| Microsoft Authenticator: (Notification/Code) |
| Cloud | Security info URL |
|---|---|
| Azure commercial (includes Government Community Cloud (GCC)) | https://aka.ms/MySecurityInfo |
| Azure for US Government (includes GCC High and DoD) | https://aka.ms/MySecurityInfo-us |
Microsoft continuously updates Authenticator to maintain a high level of security. To ensure that your users are getting the best experience possible, we recommend having them continuously update their Authenticator App. In the case of critical security updates, app versions that aren't up-to-date may not work, and may block users from completing their authentication. If a user is using a version of the app that isn't supported, they're prompted to upgrade to the latest version before they proceed to sign in.
Microsoft also periodically retires older versions of the Authenticator App to maintain a high security bar for your organization. If a user's device doesn't support modern versions of Microsoft Authenticator, they can't sign in with the app. We recommend they sign in with an OATH verification code in Microsoft Authenticator to complete MFA.
To get started with passkeys, see How to enable passkeys in Microsoft Authenticator for Microsoft Entra ID.
For more information about passwordless sign-in, see Enable passwordless sign-in with the Microsoft Authenticator.
Learn more about configuring authentication methods using the Microsoft Graph REST API.