Hi @Pavel Zhdanov ,
I set in backend new roles for some user and want update online user roles without relogin.
You can create a Custom Authorization Handler and use the Authorize attribute with role. Check the following sample:
Create Custom AuthorizationHandler:
public class RolesAuthorizationHandler : AuthorizationHandler<RolesAuthorizationRequirement>, IAuthorizationHandler
{
protected override Task HandleRequirementAsync(AuthorizationHandlerContext context,
RolesAuthorizationRequirement requirement)
{
if (context.User == null || !context.User.Identity.IsAuthenticated)
{
context.Fail();
return Task.CompletedTask;
}
var validRole = false;
if (requirement.AllowedRoles == null ||
requirement.AllowedRoles.Any() == false)
{
validRole = true;
}
else
{
var claims = context.User.Claims;
var userName = claims.FirstOrDefault(c => c.Type == "UserName").Value;
var roles = requirement.AllowedRoles;
//get user list from database
#region
var userlist = new Users().GetUsers();
#endregion
validRole = userlist.Where(p => roles.Contains(p.Role) && p.UserName == userName).Any();
}
if (validRole)
{
context.Succeed(requirement);
}
else
{
context.Fail();
}
return Task.CompletedTask;
}
}
Then register it in the ConfigureService method:
public void ConfigureServices(IServiceCollection services)
{
services.AddAuthentication("CookieAuthentication")
.AddCookie("CookieAuthentication", config =>
{
config.Cookie.Name = "UserLoginCookie"; // Name of cookie
config.LoginPath = "/Login/UserLogin"; // Path for the redirect to user login page
config.AccessDeniedPath = "/Login/UserAccessDenied";
config.Cookie.SameSite = SameSiteMode.Lax;
config.Cookie.HttpOnly = true;
// Here we set the cookie to be only send over an HTTPS connection.
config.Cookie.SecurePolicy = CookieSecurePolicy.None;
config.Events = new Microsoft.AspNetCore.Authentication.Cookies.CookieAuthenticationEvents()
{
OnRedirectToAccessDenied = ctx =>
{
ctx.Response.Redirect("/Login/UserAccessDenied?code=401");
return Task.CompletedTask;
}
};
});
services.AddScoped<IAuthorizationHandler, RolesAuthorizationHandler>();
services.AddControllersWithViews();
}
In the Login controller, after user login success, add the role claims:
[HttpPost]
public ActionResult UserLogin([Bind] Users userModel)
{
//Get User list
#region
var userlist = ...
#endregion
var user = userlist.Where(u => u.UserName.ToLower() == userModel.UserName.ToLower()).FirstOrDefault();
if (user != null)
{
var userClaims = new List<Claim>()
{
new Claim("UserName", user.UserName),
new Claim(ClaimTypes.Name, user.Name),
new Claim(ClaimTypes.Email, user.EmailId),
new Claim(ClaimTypes.DateOfBirth, user.DateOfBirth),
new Claim(ClaimTypes.Role, user.Role)
};
var userIdentity = new ClaimsIdentity(userClaims, "User Identity");
var userPrincipal = new ClaimsPrincipal(new[] { userIdentity });
HttpContext.SignInAsync(userPrincipal);
return RedirectToAction("Index", "Home");
}
return View(user);
}
Apply the Authorize attribute on the action method:
[Authorize(Roles = "Admin")]
public ActionResult UsersPolicy()
{
var uses = new Users();
return View("Users", uses.GetUsers());
}
[Authorize(Roles = "User")]
public ActionResult UsersRole()
{
var uses = new Users();
return View("Users", uses.GetUsers());
}
The result as below:
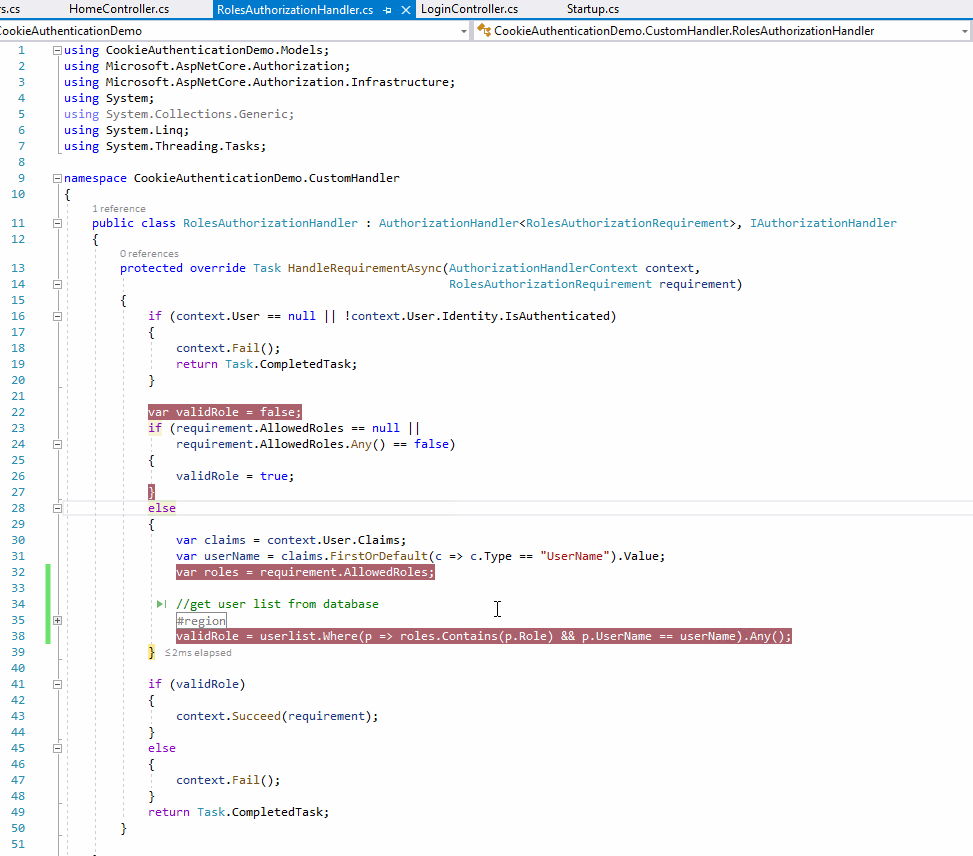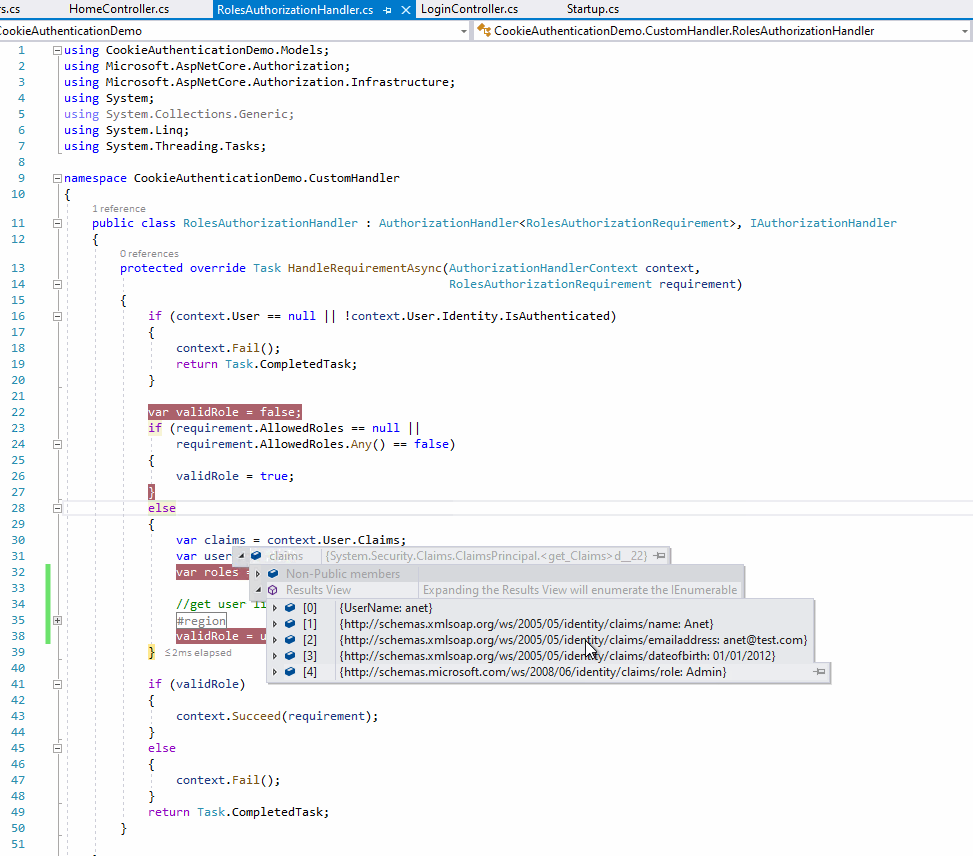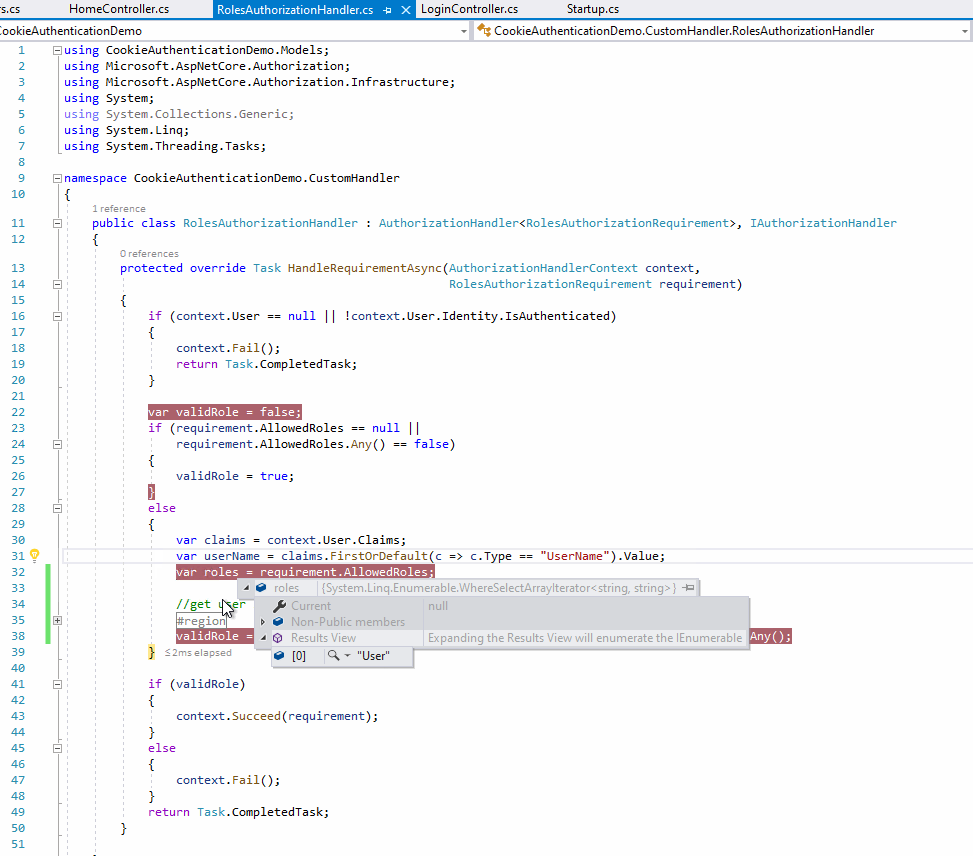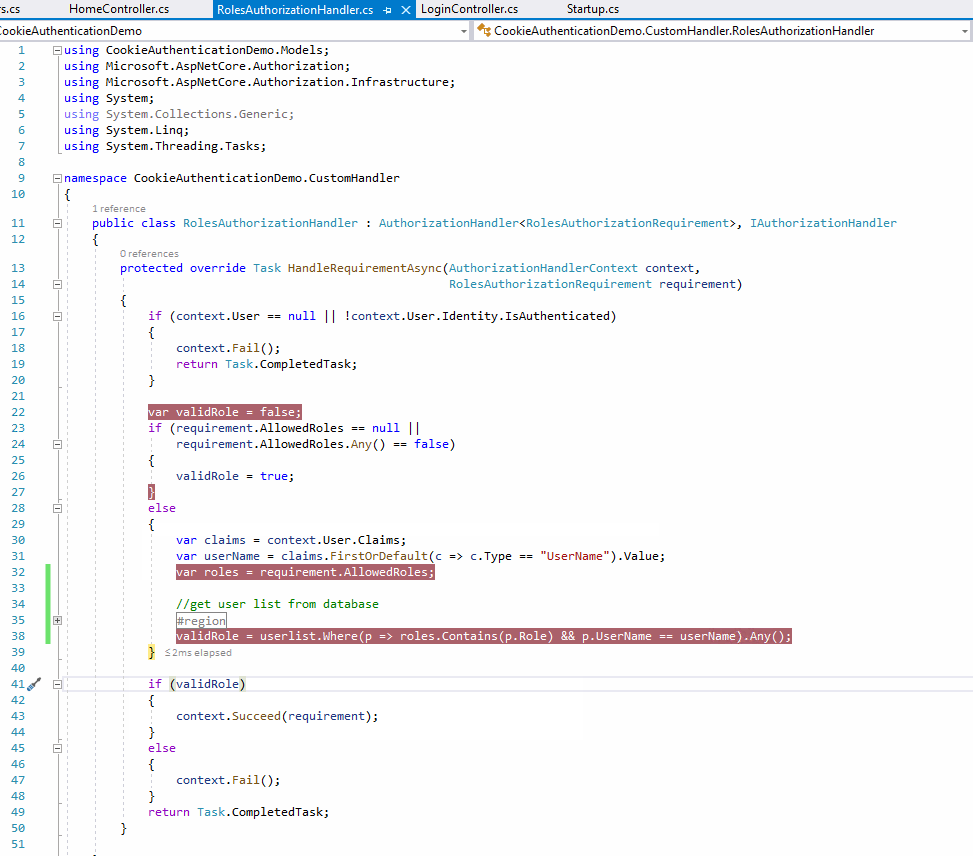
From the above screenshot, when the user login, we can see the current user's role is Admin (from the claims variable), and the action allowed role is User, but since we have changed the User's role to User, then we can see the validRole variable is true, so the login user can continue access the action method without re-login .
Reference: Policy-Based And Role-Based Authorization In ASP.NET Core 3.0 Using Custom Handler.
If the answer is helpful, please click "Accept Answer" and upvote it.
Note: Please follow the steps in our documentation to enable e-mail notifications if you want to receive the related email notification for this thread.
Best regards,
Dillion