By using Azure services, such as the Computer Vision API and Azure Functions, companies can eliminate the need to manage individual servers, while reducing costs and utilizing the expertise that Microsoft has already developed with processing images with Cognitive Services. This example scenario specifically addresses an image-processing use case. If you have different AI needs, consider the full suite of Cognitive Services.
Architecture
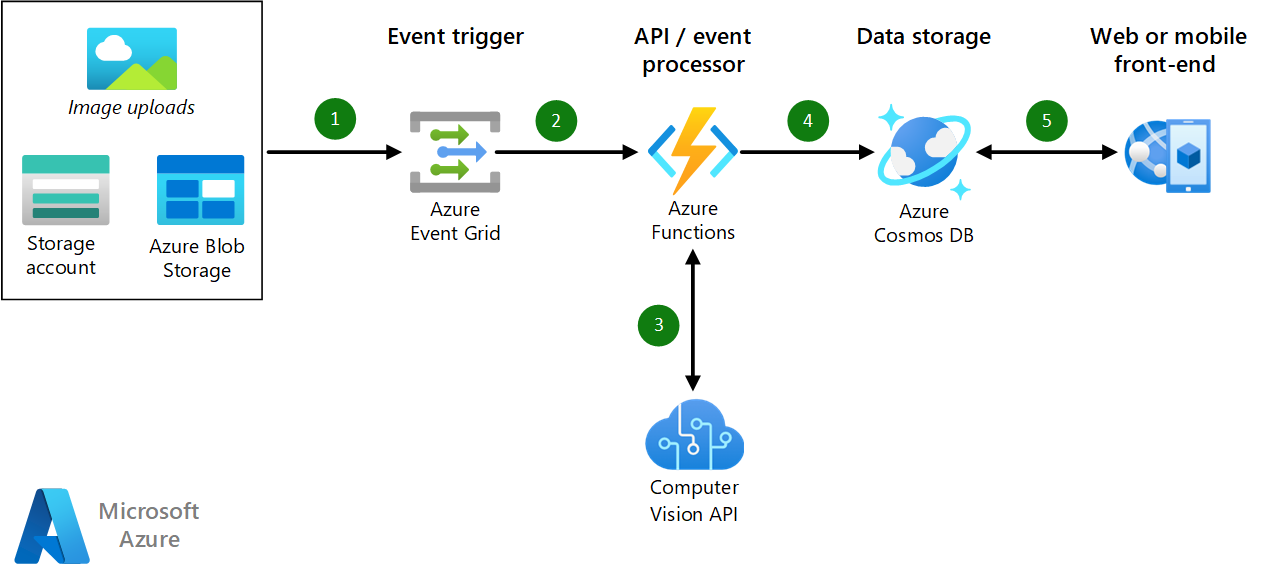
Download a Visio file of this architecture.
Workflow
This scenario covers the back-end components of a web or mobile application. Data flows through the scenario as follows:
- Adding new files (image uploads) in Blob storage triggers an event in Azure Event Grid. The uploading process can be orchestrated via the web or a mobile application. Alternatively, images can be uploaded separately to the Azure Blob storage.
- Event Grid sends a notification that triggers the Azure Functions.
- Azure Functions calls the Azure Computer Vision API to analyze the newly uploaded image. Computer Vision accesses the image via the blob URL that's parsed by Azure Functions.
- Azure Functions persists the Computer Vision API response in Azure Cosmos DB. This response includes the results of the analysis, along with the image metadata.
- The results can be consumed and reflected on the web or mobile front end. Note that this approach retrieves the results of the classification but not the uploaded image.
Components
- Computer Vision API is part of the Cognitive Services suite and is used to retrieve information about each image.
- Azure Functions provides the back-end API for the web application. This platform also provides event processing for uploaded images.
- Azure Event Grid triggers an event when a new image is uploaded to blob storage. The image is then processed with Azure functions.
- Azure Blob Storage stores all of the image files that are uploaded into the web application, as well any static files that the web application consumes.
- Azure Cosmos DB stores metadata about each image that is uploaded, including the results of the processing from Computer Vision API.
Alternatives
- Custom Vision Service. The Computer Vision API returns a set of taxonomy-based categories. If you need to process information that isn't returned by the Computer Vision API, consider the Custom Vision Service, which lets you build custom image classifiers.
- Cognitive Search (formerly Azure Search). If your use case involves querying the metadata to find images that meet specific criteria, consider using Cognitive Search. Currently in preview, Cognitive search seamlessly integrates this workflow.
- Logic Apps. If you don't need to react in real-time on added files to a blob, you might consider using Logic Apps. A logic app which can check if a file was added might be start by the recurrence trigger or sliding windows trigger.
Scenario details
This scenario is relevant for businesses that need to process images.
Potential applications include classifying images for a fashion website, analyzing text and images for insurance claims, or understanding telemetry data from game screenshots. Traditionally, companies would need to develop expertise in machine learning models, train the models, and finally run the images through their custom process to get the data out of the images.
Potential use cases
This solution is ideal for the retail, game, finance, and insurance industries. Other relevant use cases include:
Classifying images on a fashion website. Image classification can be used by sellers while uploading pictures of products on the platform for sale. They can then automate the consequent manual tagging involved. The customers can also search through the visual impression of the products.
Classifying telemetry data from screenshots of games. The classification of video games from screenshots is evolving into a relevant problem in social media, coupled with computer vision. For example, when Twitch streamers play different games in succession, they might skip manually updating their stream information. Failure to update stream information could result in the misclassification of streams in user searches and might lead to the loss of potential viewership for both the content creators and the streaming platforms. While introducing novel games, a custom model route could be helpful to introduce the capability to detect novel images from those games.
Classifying images for insurance claims. Image classification can help reduce the time and cost of claims processing and underwriting. It could help analyze natural-disaster damage, vehicle-damage, and identify residential and commercial properties.
Considerations
These considerations implement the pillars of the Azure Well-Architected Framework, which is a set of guiding tenets that can be used to improve the quality of a workload. For more information, see Microsoft Azure Well-Architected Framework.
Consider these points when implementing this solution:
Scalability
The majority of the components used in this example scenario are managed services that will automatically scale. A couple of notable exceptions: Azure Functions has a limit of a maximum of 200 instances. If you need to scale beyond this limit, consider multiple regions or app plans.
You can provision Azure Cosmos DB to autoscale in Azure Cosmos DB for NoSQL only. If you plan to use other APIs, see guidance on estimating your requirements in Request units. To fully take advantage of the scaling in Azure Cosmos DB, understand how partition keys work in Azure Cosmos DB.
NoSQL databases frequently trade consistency (in the sense of the CAP theorem) for availability, scalability, and partitioning. In this example scenario, a key-value data model is used and transaction consistency is rarely needed as most operations are by definition atomic. Additional guidance to Choose the right data store is available in the Azure Architecture Center. If your implementation requires high consistency, you can choose your consistency level in Azure Cosmos DB.
For general guidance on designing scalable solutions, see the performance efficiency checklist in the Azure Architecture Center.
Security
Security provides assurances against deliberate attacks and the abuse of your valuable data and systems. For more information, see Overview of the security pillar.
Managed identities for Azure resources are used to provide access to other resources internal to your account and then assigned to your Azure Functions. Only allow access to the requisite resources in those identities to ensure that nothing extra is exposed to your functions (and potentially to your customers).
For general guidance on designing secure solutions, see the Azure Security Documentation.
Resiliency
All of the components in this scenario are managed, so at a regional level they are all resilient automatically.
For general guidance on designing resilient solutions, see Designing resilient applications for Azure.
Cost optimization
Cost optimization is about looking at ways to reduce unnecessary expenses and improve operational efficiencies. For more information, see Overview of the cost optimization pillar.
To explore the cost of running this scenario, all of the services are pre-configured in the cost calculator. To see how the pricing would change for your particular use case, change the appropriate variables to match your expected traffic.
We have provided three sample cost profiles based on amount of traffic (we assume all images are 100 kb in size):
- Small: this pricing example correlates to processing < 5000 images a month.
- Medium: this pricing example correlates to processing 500,000 images a month.
- Large: this pricing example correlates to processing 50 million images a month.
Contributors
This article is maintained by Microsoft. It was originally written by the following contributors.
Principal authors:
- David Stanford | Principal Program Manager
- Ashish Chauhan | Senior Solution Architect
Next steps
Product documentation
- What is Computer Vision?
- AI enrichment in Azure Cognitive Search
- Introduction to Azure Functions
- What is Azure Event Grid?
- Introduction to Azure Blob storage
- Welcome to Azure Cosmos DB
For a guided learning path, see:
- Build a serverless web app in Azure
- Classify images with the Custom Vision service
- Use AI to recognize objects in images by using the Custom Vision service
- Classify endangered bird species with Custom Vision
- Classify images with the Microsoft Custom Vision Service
- Detect objects in images with the Custom Vision service
Before deploying this example scenario in a production environment, review recommended practices for optimizing the performance and reliability of Azure Functions.
Related resources
AI enrichment with image and natural language processing in Azure Cognitive Search