Create threat protection policies in Defender for Cloud Apps
Microsoft Defender for Cloud Apps provides policy-driven mechanisms to help manage your users' behavior in the cloud. Policies enable you to detect and identify:
- Violations
- Risky behavior
- Suspicious data points and activities
There are four different policy categories. These are:
- Access control
- Threat detection
- Cloud discovery
- DLP
Work with threat protection policies
Threat protection policies are designed to help you:
- Identify high-risk use
- Identify cloud security issues
- Detect abnormal user behavior
- Prevent threats in sanctioned apps
The following screenshot displays the high severity threat detection policies that are available by default.
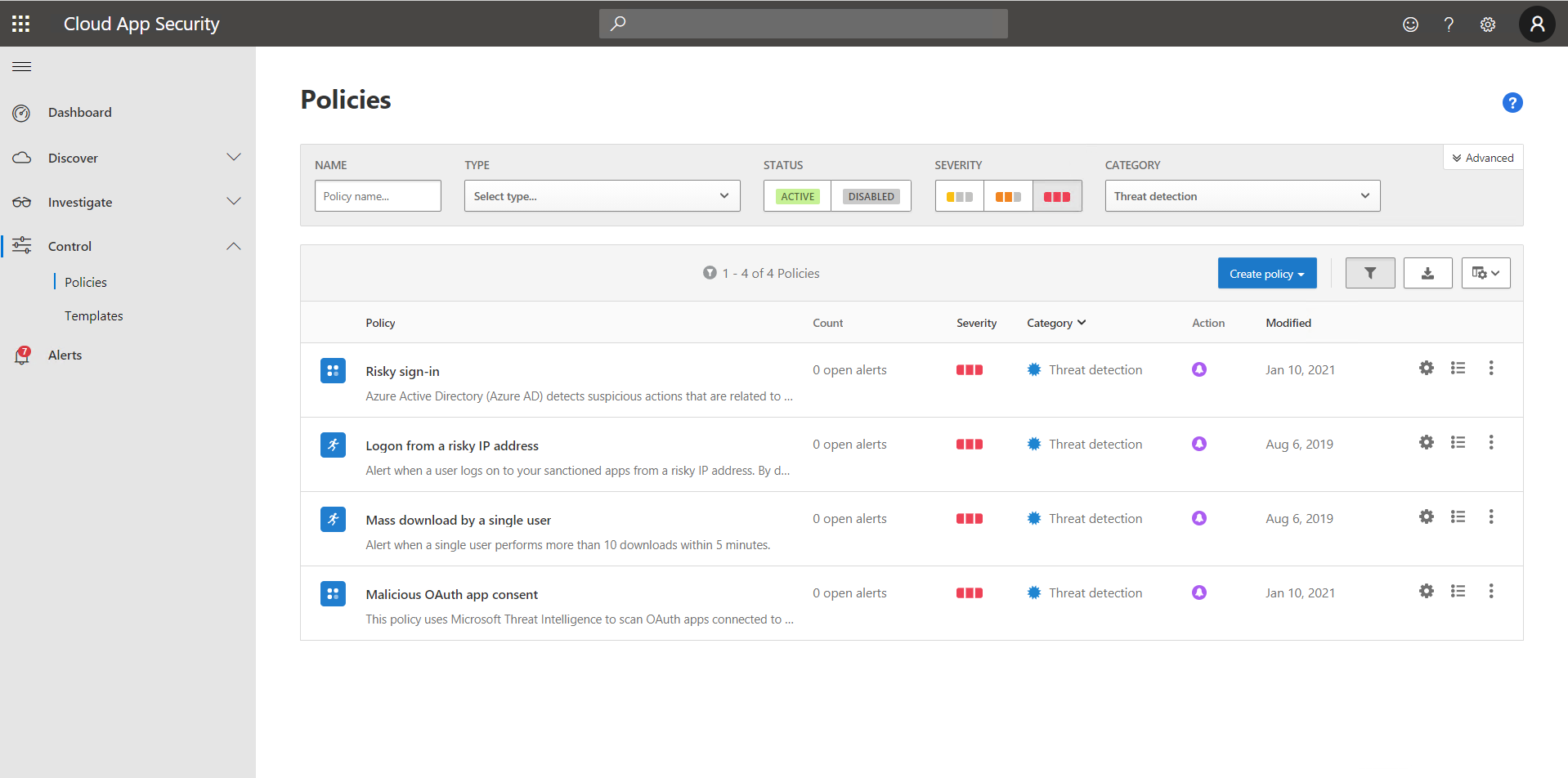
When establishing threat protection policies, there are three types of policies you can implement, described in the following table.
| Policy type | Use |
|---|---|
| Activity policy | Enable you to monitor user activities, or identify unexpectedly high rates of a specific activity |
| Anomaly detection policy | Enable you to identify unusual activities on your cloud. Detection is based on configured risk factors. Anomaly detection policies are only available for OAuth apps that are authorized in your Microsoft Entra ID |
| OAuth app policy | Enable you to determine which permissions an OAuth app requested and to automatically approve or revoke that permission |
Activity policies
Activity policies are designed to monitor defined user activities, or to identify high rates of a specific activity. Once you create an activity detection policy, it starts to generate alerts.
Important
Defender for Cloud Apps disables policies that trigger more than 50,000 matches per day, for 3 out of the last 7 days.
Defender for Cloud Apps provides two activity policies by default. These are:
Log on from a risky IP address. Alert when a user logs on to your sanctioned apps from a risky IP address. By default, the Risky IP address category contains addresses that have IP address tags of Anonymous proxy, TOR, or Botnet.
Tip
You can add more IP addresses to this category in the IP address ranges settings page.
Mass download by a single user. Alert when a single user performs more than 10 downloads within 5 minutes.
To create an activity policy, use the following procedure:
In Defender for Cloud Apps, select Control, select Policies, and then select Create policy.
In the Create policy list, select Activity policy.
Enter the following information:
Policy name
Policy severity (choose between Low, Medium, and High)
Category is already defined as Threat detection
Optionally, enter a description
In the Create filters for the policy section, select Single activity or Repeated activity.
Then select filter options. You can filter on many properties, including the following:
- Activity type
- Administrative activity
- App
- Applied action
- Device
- Files and folders
- IP address
- Location
- Potential malware detected
- User
In the Alerts section, optionally select the Create an alert for each matching event with the policy's severity check box. Then you can enable an alert by email or text message (or both) for each matching event. You'll need to define the email addresses and phone numbers in the appropriate text boxes.
Finally, in the Governance section, choose the actions you want to perform on All apps and any specifically listed apps. These actions include: Notify user, Suspend user, Require user to sign in again.
When all settings are configured, select Create.
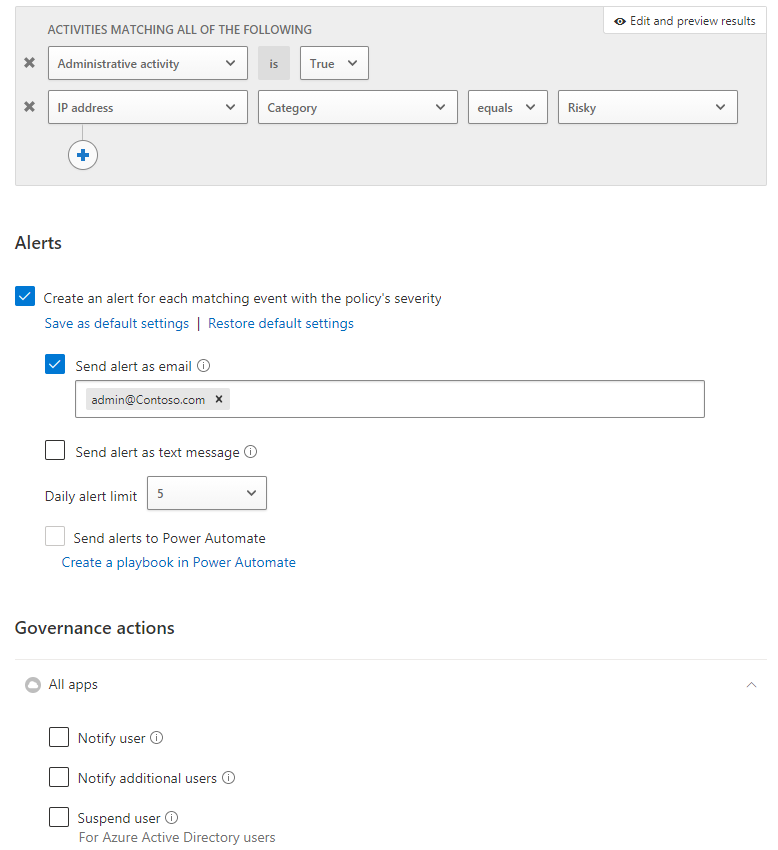
For example, the following screenshot displays the settings for an activity policy where:
Administrative activity is true
IP address category is risky
Anomaly detection policies
Anomaly detection policies are designed to analyze user and entity behavior. In Defender for Cloud Apps, Anomaly detection policies are automatically enabled by default, so you don't need to create any.
Important
Defender for Cloud Apps has an initial learning period of seven days during which not all anomaly detection alerts are raised.
Defender for Cloud Apps scans user activity to help identify anomalous behavior. Risks are evaluated by reviewing over 30 risk indicators, grouped into the following risk factors:
- Risky IP address
- Login failures
- Admin activity
- Inactive accounts
- Location
- Impossible travel
- Device and user agent
- Activity rate
Defender for Cloud Apps raises security alerts as needed when it detects risky behavior. Although you don't create Anomaly detection policies, you can review the existing policies in the Defender for Cloud Apps portal. Select Control in the navigation pane, and then select Policies. In the TYPE list, select only Anomaly detection policy.
The following Anomaly policies are available:
- Activity from anonymous IP addresses
- Activity from infrequent country
- Activity from suspicious IP addresses
- Activity performed by terminated user
- Impossible travel
- Leaked credentials
- Multiple VM creation activities
- Multiple delete VM activities
- Multiple failed login attempts
- Multiple storage deletion activities
- Data exfiltration to unsanctioned apps
- Malware detection
- Ransomware activity
- Risky sign-in
- Suspicious OAuth app file download activities
- Suspicious email deletion activity
- Suspicious inbox forwarding
- Suspicious inbox manipulation rules
- Unusual addition of credentials to an OAuth app
- Unusual administrative activity
- Unusual file deletion activity
- Unusual file download
- Unusual file share activity
- Unusual impersonated activity
Note
For a complete description of these policies, review the following document: Anomaly detection policies
Although you do not create anomaly detection policies, you can edit the following properties of these policies:
Scope. Select which users and groups you want to monitor. The default is all users and groups.
Alerts. Change the alert actions and contact details. By default, no alerts actions are enabled.
Governance actions. Update the governance actions for All apps or specific apps listed. By default, no governance actions are selected.
Note
You can configure additional properties of some policies, including sensitivity and severity.
OAuth app policies
Your users might choose to install OAuth apps within your organization without your knowledge. OAuth apps use a delegated authorization model. This delegation allows the app to obtain access to a user's data following user consent.
Important
Defender for Cloud Apps only identifies apps that request delegated permissions.
Give that some, perhaps most, users do not closely review the apps' request for permissions, these apps can pose a security risk to your organization. You can use OAuth app policies to determine which permissions each app requested. You can also determine which users authorized those apps for access to Office 365, Google Workspace, and Salesforce data.
By using policies, you can mark those granted permissions as either approved or banned.
Note
Marking them as banned revokes permissions for each app for each user that authorized the app.
To create an OAuth app policy, use the following procedure:
In Defender for Cloud Apps, select Control, select Policies, and then select Create policy.
In the Create policy list, select OAuth app policy.
Enter the following information:
- Policy name
- Policy severity (choose between Low, Medium, and High)
Tip
You cannot modify the severity of OAuth app anomaly detection policies.
- Category is already defined as Threat detection
- Optionally, enter a description
- In the Create filters for the policy section, select filter options. You can filter on the following properties:
- App
- App state
- Community use
- Permission level
- Permissions
- Published
- User
- In the Alerts section, optionally select the Create an alert for each matching event with the policy's severity check box. Then you can enable an alert by email or text message (or both) for each matching event. You'll need to define the email addresses and phone numbers in the appropriate text boxes.
- Finally, in the Governance actions section, choose the actions you want to perform on listed apps.
When all settings are configured, select Create.