Vorgehensweise: Erstellen und Ausführen eines Workflows mit langer Laufzeit
Eine der zentralen Features von Windows Workflow Foundation (WF) besteht darin, dass die Runtime Workflows im Leerlauf in einer Datenbank beibehalten und entladen kann. Durch die Schritte in Vorgehensweise: Ausführen eines Workflows wurden die Grundlagen für das Hosten von Workflows mithilfe einer Konsolenanwendung vorgestellt. Anhand von Beispielen wurde gezeigt, wie Workflows und Workflowlebenszyklus-Handler gestartet und Lesezeichen wiederaufgenommen werden. Um die Workflowpersistenz effektiv zu veranschaulichen, ist ein komplexerer Workflowhost erforderlich, der das Starten und Fortsetzen mehrerer Workflowinstanzen unterstützt. In diesem Schritt des Lernprogramms wird veranschaulicht, wie eine Windows-Formularhostanwendung erstellt wird, die das Starten und Fortsetzen mehrerer Workflowinstanzen und die Workflowpersistenz unterstützt sowie die Grundlage für erweiterte Funktionen wie Nachverfolgung und Versionsverwaltung bildet, die in den folgenden Schritten des Lernprogramms veranschaulicht werden.
Hinweis
In diesem und den nachfolgenden Schritten des Tutorials werden alle drei Workflowtypen aus Vorgehensweise: Erstellen eines Workflows verwendet.
So erstellen Sie die Persistenzdatenbank
Öffnen Sie SQL Server Management Studio, und stellen Sie eine Verbindung mit dem lokalen Server her, z. B. .\SQLEXPRESS. Klicken Sie mit der rechten Maustaste auf den Knoten Datenbanken auf dem lokalen Server, und wählen Sie Neue Datenbank aus. Benennen Sie die neue Datenbank WF45GettingStartedTutorial, übernehmen Sie alle anderen Werte, und wählen Sie OK aus.
Hinweis
Stellen Sie sicher, dass Sie über die Berechtigung Datenbank erstellen für den lokalen Server verfügen, bevor Sie die Datenbank erstellen.
Wählen Sie im Menü Datei die Optionen Öffnen > Datei aus. Wechseln Sie zum folgenden Ordner: C:\Windows\Microsoft.NET\Framework\v4.0.30319\sql\en
Wählen Sie die beiden folgenden Dateien aus, und klicken Sie auf Öffnen.
SqlWorkflowInstanceStoreLogic.sql
SqlWorkflowInstanceStoreSchema.sql
Wählen Sie im Menü Fenster die Option SqlWorkflowInstanceStoreSchema.sql aus. Stellen Sie sicher, dass WF45GettingStartedTutorial in der Dropdownliste Verfügbare Datenbanken ausgewählt ist, und wählen Sie aus dem Menü Abfrage die Option Ausführen aus.
Wählen Sie im Menü Fenster die Option SqlWorkflowInstanceStoreLogic.sql aus. Stellen Sie sicher, dass WF45GettingStartedTutorial in der Dropdownliste Verfügbare Datenbanken ausgewählt ist, und wählen Sie aus dem Menü Abfrage die Option Ausführen aus.
Warnung
Es ist wichtig, die vorherigen beiden Schritte in der richtigen Reihenfolge auszuführen. Wenn die Abfragen nicht in der richtigen Reihenfolge ausgeführt werden, treten Fehler auf, und die Persistenzdatenbank wird nicht richtig konfiguriert.
So fügen Sie den DurableInstancing-Assemblys den Verweis hinzu
Klicken Sie im Projektmappen-Explorer mit der rechten Maustaste auf NumberGuessWorkflowHost, und wählen Sie Verweis hinzufügen aus.
Wählen Sie in der Liste Verweis hinzufügen den Eintrag Assemblys aus, und geben Sie im Feld
DurableInstancingAssemblys durchsuchen den Namen ein. Dadurch werden die Assemblys gefiltert, sodass die gewünschten Verweise einfacher auszuwählen sind.Aktivieren Sie in der Liste Suchergebnisse die Kontrollkästchen neben System.Activities.DurableInstancing und System.Runtime.DurableInstancing, und klicken Sie auf OK.
So erstellen Sie das Hostformular für den Workflow
Klicken Sie im Projektmappen-Explorer mit der rechten Maustaste auf NumberGuessWorkflowHost, und wählen Sie Hinzufügen > Neues Element aus.
Wählen Sie in der Vorlagenliste Installiert den Eintrag Windows-Formular aus, geben Sie im Feld
WorkflowHostFormName den Namen ein, und klicken Sie auf Hinzufügen.Konfigurieren Sie die folgenden Eigenschaften für das Formular.
Eigenschaft Wert FormBorderStyle FixedSingle MaximizeBox Falsch Size 400, 420 Fügen Sie dem Formular die folgenden Steuerelemente in der angegebenen Reihenfolge hinzu, und konfigurieren Sie die Eigenschaften wie angegeben.
Control Eigenschaft: Wert Schaltfläche Name: NewGame
Location: 13, 13
Größe: 75, 23
Text: Neues SpielLabel Location: 94, 18
Text: Zahl vorschlagen zwischen 1 undComboBox Name: NumberRange
DropDownStyle: DropDownList
Elemente: 10, 100, 1.000
Location: 228, 12
Größe: 143, 21Label Location: 13, 43
Text: WorkflowtypComboBox Text: WorkflowType
DropDownStyle: DropDownList
Elemente: StateMachineNumberGuessWorkflow, FlowchartNumberGuessWorkflow, SequentialNumberGuessWorkflow
Location: 94, 40
Größe: 277, 21Label Name: WorkflowVersion
Location: 13, 362
Text: WorkflowversionGroupBox Location: 13, 67
Größe: 358, 287
Text: SpielHinweis
Wenn Sie die folgenden Steuerelemente hinzufügen, fügen Sie sie in das GroupBox-Element ein.
Control Eigenschaft: Wert Label Location: 7, 20
Text: Workflowinstanz-IDComboBox Name: InstanceId
DropDownStyle: DropDownList
Location: 121, 17
Größe: 227, 21Label Location: 7, 47
Text: VorschlagTextBox Name: Guess
Location: 50, 44
Größe: 65, 20Schaltfläche Name: EnterGuess
Location: 121, 42
Größe: 75, 23
Text: Vorschlag eingebenSchaltfläche Name: QuitGame
Location: 274, 42
Größe: 75, 23
Text: BeendenTextBox Name: WorkflowStatus
Location: 10, 73
Mehrzeilig: True
ReadOnly: True
Scrollleisten: Vertikal
Größe: 338, 208Legen Sie die AcceptButton-Eigenschaft des Formulars auf EnterGuess fest.
Im folgenden Beispiel wird das abgeschlossene Formular dargestellt.
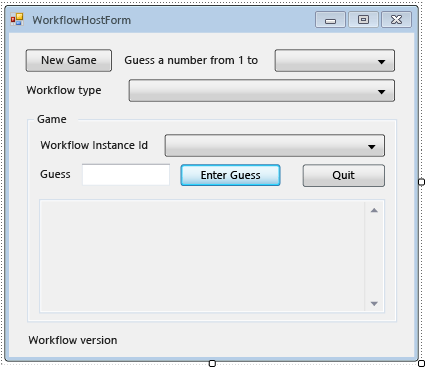
So fügen Sie die Eigenschaften und Hilfsmethoden des Formulars hinzu
Durch die Schritte in diesem Abschnitt werden der Formularklasse Eigenschaften und Hilfsmethoden hinzugefügt, die die Benutzeroberfläche des Formulars so konfigurieren, dass sie das Ausführen und Fortsetzen der Workflows zum Schätzen von Zahlen unterstützen.
Klicken Sie im Projektmappen-Explorer mit der rechten Maustaste auf WorkflowHostForm, und wählen Sie Code anzeigen aus.
Fügen Sie die folgenden
using-Anweisungen (oderImports-Anweisungen) mit den anderenusing-Anweisungen (oderImports-Anweisungen) am Anfang der Datei hinzu.Imports System.Activities Imports System.Activities.DurableInstancing Imports System.Data.SqlClient Imports System.IO Imports System.Windows.Formsusing System.Activities; using System.Activities.DurableInstancing; using System.Data.SqlClient; using System.IO; using System.Windows.Forms;Fügen Sie der WorkflowHostForm-Klasse die folgenden Memberdeklarationen hinzu.
Const connectionString = "Server=.\SQLEXPRESS;Initial Catalog=WF45GettingStartedTutorial;Integrated Security=SSPI" Dim store As SqlWorkflowInstanceStore Dim workflowStarting As Booleanconst string connectionString = "Server=.\\SQLEXPRESS;Initial Catalog=WF45GettingStartedTutorial;Integrated Security=SSPI"; SqlWorkflowInstanceStore store; bool workflowStarting;Hinweis
Wenn Ihre Verbindungszeichenfolge abweicht, aktualisieren Sie
connectionString, damit sie auf Ihre Datenbank verweist.Fügen Sie der
WorkflowInstanceId-Klasse eineWorkflowFormHost-Eigenschaft hinzu.Public ReadOnly Property WorkflowInstanceId() As Guid Get If InstanceId.SelectedIndex = -1 Then Return Guid.Empty Else Return New Guid(InstanceId.SelectedItem.ToString()) End If End Get End Propertypublic Guid WorkflowInstanceId { get { return InstanceId.SelectedIndex == -1 ? Guid.Empty : (Guid)InstanceId.SelectedItem; } }Das Kombinationsfeld
InstanceIdzeigt eine Liste der persistenten Workflowinstanz-IDs an, und dieWorkflowInstanceId-Eigenschaft gibt den aktuell ausgewählten Workflow zurück.Fügen Sie einen Handler für das
Load-Ereignis des Formulars hinzu. Um den Handler hinzuzufügen, wechseln Sie für das Formular zur Entwurfsansicht, klicken Sie oben im Fenster Eigenschaften auf das Symbol Ereignisse, und doppelklicken Sie auf Laden.Private Sub WorkflowHostForm_Load(sender As Object, e As EventArgs) Handles Me.Load End Subprivate void WorkflowHostForm_Load(object sender, EventArgs e) { }Fügen Sie
WorkflowHostForm_Loadden folgenden Code hinzu.' Initialize the store and configure it so that it can be used for ' multiple WorkflowApplication instances. store = New SqlWorkflowInstanceStore(connectionString) WorkflowApplication.CreateDefaultInstanceOwner(store, Nothing, WorkflowIdentityFilter.Any) ' Set default ComboBox selections. NumberRange.SelectedIndex = 0 WorkflowType.SelectedIndex = 0 ListPersistedWorkflows()// Initialize the store and configure it so that it can be used for // multiple WorkflowApplication instances. store = new SqlWorkflowInstanceStore(connectionString); WorkflowApplication.CreateDefaultInstanceOwner(store, null, WorkflowIdentityFilter.Any); // Set default ComboBox selections. NumberRange.SelectedIndex = 0; WorkflowType.SelectedIndex = 0; ListPersistedWorkflows();Beim Laden des Formulars geschieht Folgendes:
SqlWorkflowInstanceStorewird konfiguriert, der Bereich und die Kombinationsfelder für den Workflowtyp werden auf die Standardwerte festgelegt, und die persistenten Workflowinstanzen werden dem KombinationsfeldInstanceIdhinzugefügt.Fügen Sie einen
SelectedIndexChanged-Handler fürInstanceIdhinzu. Um den Handler hinzuzufügen, wechseln Sie für das Formular zur Entwurfsansicht, wählen Sie das KombinationsfeldInstanceIdaus, klicken Sie oben im Fenster Eigenschaften auf das Symbol Ereignisse, und doppelklicken Sie auf SelectedIndexChanged.Private Sub InstanceId_SelectedIndexChanged(sender As Object, e As EventArgs) Handles InstanceId.SelectedIndexChanged End Subprivate void InstanceId_SelectedIndexChanged(object sender, EventArgs e) { }Fügen Sie
InstanceId_SelectedIndexChangedden folgenden Code hinzu. Sobald der Benutzer über das Kombinationsfeld einen Workflow auswählt, wird das Statusfenster von diesem Handler aktualisiert.If InstanceId.SelectedIndex = -1 Then Return End If ' Clear the status window. WorkflowStatus.Clear() ' Get the workflow version and display it. ' If the workflow is just starting then this info will not ' be available in the persistence store so do not try and retrieve it. If Not workflowStarting Then Dim instance As WorkflowApplicationInstance = _ WorkflowApplication.GetInstance(WorkflowInstanceId, store) WorkflowVersion.Text = _ WorkflowVersionMap.GetIdentityDescription(instance.DefinitionIdentity) ' Unload the instance. instance.Abandon() End Ifif (InstanceId.SelectedIndex == -1) { return; } // Clear the status window. WorkflowStatus.Clear(); // Get the workflow version and display it. // If the workflow is just starting then this info will not // be available in the persistence store so do not try and retrieve it. if (!workflowStarting) { WorkflowApplicationInstance instance = WorkflowApplication.GetInstance(this.WorkflowInstanceId, store); WorkflowVersion.Text = WorkflowVersionMap.GetIdentityDescription(instance.DefinitionIdentity); // Unload the instance. instance.Abandon(); }Fügen Sie der Formularklasse die folgende
ListPersistedWorkflows-Methode hinzu.Private Sub ListPersistedWorkflows() Using localCon As New SqlConnection(connectionString) Dim localCmd As String = _ "SELECT [InstanceId] FROM [System.Activities.DurableInstancing].[Instances] ORDER BY [CreationTime]" Dim cmd As SqlCommand = localCon.CreateCommand() cmd.CommandText = localCmd localCon.Open() Using reader As SqlDataReader = cmd.ExecuteReader(CommandBehavior.CloseConnection) While (reader.Read()) ' Get the InstanceId of the persisted Workflow. Dim id As Guid = Guid.Parse(reader(0).ToString()) InstanceId.Items.Add(id) End While End Using End Using End Subusing (var localCon = new SqlConnection(connectionString)) { string localCmd = "SELECT [InstanceId] FROM [System.Activities.DurableInstancing].[Instances] ORDER BY [CreationTime]"; SqlCommand cmd = localCon.CreateCommand(); cmd.CommandText = localCmd; localCon.Open(); using (SqlDataReader reader = cmd.ExecuteReader(CommandBehavior.CloseConnection)) { while (reader.Read()) { // Get the InstanceId of the persisted Workflow. Guid id = Guid.Parse(reader[0].ToString()); InstanceId.Items.Add(id); } } }ListPersistedWorkflowsfragt den Instanzspeicher für persistente Workflowinstanzen ab und fügt dem KombinationsfeldcboInstanceIddie Instanz-IDs hinzu.Fügen Sie der Formularklasse die folgende
UpdateStatus-Methode und den entsprechenden Delegaten hinzu. Durch diese Methode wird das Statusfenster auf dem Formular mit dem Status des derzeit ausgeführten Workflows aktualisiert.Private Delegate Sub UpdateStatusDelegate(msg As String) Public Sub UpdateStatus(msg As String) ' We may be on a different thread so we need to ' make this call using BeginInvoke. If InvokeRequired Then BeginInvoke(New UpdateStatusDelegate(AddressOf UpdateStatus), msg) Else If Not msg.EndsWith(vbCrLf) Then msg = msg & vbCrLf End If WorkflowStatus.AppendText(msg) ' Ensure that the newly added status is visible. WorkflowStatus.SelectionStart = WorkflowStatus.Text.Length WorkflowStatus.ScrollToCaret() End If End Subprivate delegate void UpdateStatusDelegate(string msg); public void UpdateStatus(string msg) { // We may be on a different thread so we need to // make this call using BeginInvoke. if (InvokeRequired) { BeginInvoke(new UpdateStatusDelegate(UpdateStatus), msg); } else { if (!msg.EndsWith("\r\n")) { msg += "\r\n"; } WorkflowStatus.AppendText(msg); WorkflowStatus.SelectionStart = WorkflowStatus.Text.Length; WorkflowStatus.ScrollToCaret(); } }Fügen Sie der Formularklasse die folgende
GameOver-Methode und den entsprechenden Delegaten hinzu. Sobald ein Workflow abgeschlossen ist, wird die Formular-Benutzeroberfläche durch diese Methode aktualisiert. Dazu wird die Instanz-ID des abgeschlossenen Workflows aus dem Kombinationsfeld InstanceId entfernt.Private Delegate Sub GameOverDelegate() Private Sub GameOver() If InvokeRequired Then BeginInvoke(New GameOverDelegate(AddressOf GameOver)) Else ' Remove this instance from the InstanceId combo box. InstanceId.Items.Remove(InstanceId.SelectedItem) InstanceId.SelectedIndex = -1 End If End Subprivate delegate void GameOverDelegate(); private void GameOver() { if (InvokeRequired) { BeginInvoke(new GameOverDelegate(GameOver)); } else { // Remove this instance from the combo box. InstanceId.Items.Remove(InstanceId.SelectedItem); InstanceId.SelectedIndex = -1; } }
So konfigurieren Sie den Instanzspeicher, die Handler für den Workflowlebenszyklus und Erweiterungen
Fügen Sie der Formularklasse eine
ConfigureWorkflowApplication-Methode hinzu.Private Sub ConfigureWorkflowApplication(wfApp As WorkflowApplication) End Subprivate void ConfigureWorkflowApplication(WorkflowApplication wfApp) { }Durch diese Methode wird
WorkflowApplicationkonfiguriert und die gewünschten Erweiterungen sowie Handler für die Lebenszyklusereignisse des Workflows werden hinzugefügt.Geben Sie in
ConfigureWorkflowApplicationdenSqlWorkflowInstanceStorefürWorkflowApplicationan.' Configure the persistence store. wfApp.InstanceStore = store// Configure the persistence store. wfApp.InstanceStore = store;Als Nächstes erstellen Sie eine
StringWriter-Instanz und fügen sie derExtensions-Auflistung vonWorkflowApplicationhinzu. WennStringWriterden Erweiterungen hinzugefügt wird, zeichnet er alleWriteLine-Aktivitätsausgaben auf. Sobald der Workflow im Leerlauf ist, kann dieWriteLineAusgabe ausStringWriterextrahiert und im Formular angezeigt werden.' Add a StringWriter to the extensions. This captures the output ' from the WriteLine activities so we can display it in the form. Dim sw As New StringWriter() wfApp.Extensions.Add(sw)// Add a StringWriter to the extensions. This captures the output // from the WriteLine activities so we can display it in the form. var sw = new StringWriter(); wfApp.Extensions.Add(sw);Fügen Sie folgenden Handler für das
Completed-Ereignis hinzu. Sobald ein Workflow erfolgreich abgeschlossen ist, wird die Anzahl der Durchläufe zum Schätzen der Zahl im Statusfenster angezeigt. Bei Beendigung des Workflows werden die Ausnahmeinformationen, die zur Beendigung geführt haben, angezeigt. Am Ende des Handlers wird dieGameOver-Methode aufgerufen, durch die der abgeschlossene Workflow aus der Workflowliste entfernt wird.wfApp.Completed = _ Sub(e As WorkflowApplicationCompletedEventArgs) If e.CompletionState = ActivityInstanceState.Faulted Then UpdateStatus($"Workflow Terminated. Exception: {e.TerminationException.GetType().FullName}{vbCrLf}{e.TerminationException.Message}") ElseIf e.CompletionState = ActivityInstanceState.Canceled Then UpdateStatus("Workflow Canceled.") Else Dim turns As Integer = Convert.ToInt32(e.Outputs("Turns")) UpdateStatus($"Congratulations, you guessed the number in {turns} turns.") End If GameOver() End SubwfApp.Completed = delegate(WorkflowApplicationCompletedEventArgs e) { if (e.CompletionState == ActivityInstanceState.Faulted) { UpdateStatus($"Workflow Terminated. Exception: {e.TerminationException.GetType().FullName}\r\n{e.TerminationException.Message}"); } else if (e.CompletionState == ActivityInstanceState.Canceled) { UpdateStatus("Workflow Canceled."); } else { int turns = Convert.ToInt32(e.Outputs["Turns"]); UpdateStatus($"Congratulations, you guessed the number in {turns} turns."); } GameOver(); };Fügen Sie den folgenden
Aborted-Handler undOnUnhandledException-Handler hinzu. DieGameOver-Methode wird nicht vomAborted-Handler aufgerufen, da eine Workflowinstanz beim Abbruch nicht beendet wird. Es besteht keine Möglichkeit, die Instanz zu einem späteren Zeitpunkt fortzusetzen.wfApp.Aborted = _ Sub(e As WorkflowApplicationAbortedEventArgs) UpdateStatus($"Workflow Aborted. Exception: {e.Reason.GetType().FullName}{vbCrLf}{e.Reason.Message}") End Sub wfApp.OnUnhandledException = _ Function(e As WorkflowApplicationUnhandledExceptionEventArgs) UpdateStatus($"Unhandled Exception: {e.UnhandledException.GetType().FullName}{vbCrLf}{e.UnhandledException.Message}") GameOver() Return UnhandledExceptionAction.Terminate End FunctionwfApp.Aborted = delegate(WorkflowApplicationAbortedEventArgs e) { UpdateStatus($"Workflow Aborted. Exception: {e.Reason.GetType().FullName}\r\n{e.Reason.Message}"); }; wfApp.OnUnhandledException = delegate(WorkflowApplicationUnhandledExceptionEventArgs e) { UpdateStatus($"Unhandled Exception: {e.UnhandledException.GetType().FullName}\r\n{e.UnhandledException.Message}"); GameOver(); return UnhandledExceptionAction.Terminate; };Fügen Sie den folgenden
PersistableIdle-Handler hinzu. Dieser Handler ruft die hinzugefügteStringWriterErweiterung ab, extrahiert die Ausgabe aus denWriteLine-Aktivitäten und zeigt sie im Statusfenster an.wfApp.PersistableIdle = _ Function(e As WorkflowApplicationIdleEventArgs) ' Send the current WriteLine outputs to the status window. Dim writers = e.GetInstanceExtensions(Of StringWriter)() For Each writer In writers UpdateStatus(writer.ToString()) Next Return PersistableIdleAction.Unload End FunctionwfApp.PersistableIdle = delegate(WorkflowApplicationIdleEventArgs e) { // Send the current WriteLine outputs to the status window. var writers = e.GetInstanceExtensions<StringWriter>(); foreach (var writer in writers) { UpdateStatus(writer.ToString()); } return PersistableIdleAction.Unload; };Die PersistableIdleAction-Enumeration besitzt drei Werte: None, Persist und Unload. Persist bewirkt, dass der Workflow persistent gespeichert wird, jedoch nicht, dass der Workflow entladen wird. Unload bewirkt, dass der Workflow persistent gespeichert und entladen wird.
Im folgenden Beispiel ist die abgeschlossene
ConfigureWorkflowApplication-Methode dargestellt.Private Sub ConfigureWorkflowApplication(wfApp As WorkflowApplication) ' Configure the persistence store. wfApp.InstanceStore = store ' Add a StringWriter to the extensions. This captures the output ' from the WriteLine activities so we can display it in the form. Dim sw As New StringWriter() wfApp.Extensions.Add(sw) wfApp.Completed = _ Sub(e As WorkflowApplicationCompletedEventArgs) If e.CompletionState = ActivityInstanceState.Faulted Then UpdateStatus($"Workflow Terminated. Exception: {e.TerminationException.GetType().FullName}{vbCrLf}{e.TerminationException.Message}") ElseIf e.CompletionState = ActivityInstanceState.Canceled Then UpdateStatus("Workflow Canceled.") Else Dim turns As Integer = Convert.ToInt32(e.Outputs("Turns")) UpdateStatus($"Congratulations, you guessed the number in {turns} turns.") End If GameOver() End Sub wfApp.Aborted = _ Sub(e As WorkflowApplicationAbortedEventArgs) UpdateStatus($"Workflow Aborted. Exception: {e.Reason.GetType().FullName}{vbCrLf}{e.Reason.Message}") End Sub wfApp.OnUnhandledException = _ Function(e As WorkflowApplicationUnhandledExceptionEventArgs) UpdateStatus($"Unhandled Exception: {e.UnhandledException.GetType().FullName}{vbCrLf}{e.UnhandledException.Message}") GameOver() Return UnhandledExceptionAction.Terminate End Function wfApp.PersistableIdle = _ Function(e As WorkflowApplicationIdleEventArgs) ' Send the current WriteLine outputs to the status window. Dim writers = e.GetInstanceExtensions(Of StringWriter)() For Each writer In writers UpdateStatus(writer.ToString()) Next Return PersistableIdleAction.Unload End Function End Subprivate void ConfigureWorkflowApplication(WorkflowApplication wfApp) { // Configure the persistence store. wfApp.InstanceStore = store; // Add a StringWriter to the extensions. This captures the output // from the WriteLine activities so we can display it in the form. var sw = new StringWriter(); wfApp.Extensions.Add(sw); wfApp.Completed = delegate(WorkflowApplicationCompletedEventArgs e) { if (e.CompletionState == ActivityInstanceState.Faulted) { UpdateStatus($"Workflow Terminated. Exception: {e.TerminationException.GetType().FullName}\r\n{e.TerminationException.Message}"); } else if (e.CompletionState == ActivityInstanceState.Canceled) { UpdateStatus("Workflow Canceled."); } else { int turns = Convert.ToInt32(e.Outputs["Turns"]); UpdateStatus($"Congratulations, you guessed the number in {turns} turns."); } GameOver(); }; wfApp.Aborted = delegate(WorkflowApplicationAbortedEventArgs e) { UpdateStatus($"Workflow Aborted. Exception: {e.Reason.GetType().FullName}\r\n{e.Reason.Message}"); }; wfApp.OnUnhandledException = delegate(WorkflowApplicationUnhandledExceptionEventArgs e) { UpdateStatus($"Unhandled Exception: {e.UnhandledException.GetType().FullName}\r\n{e.UnhandledException.Message}"); GameOver(); return UnhandledExceptionAction.Terminate; }; wfApp.PersistableIdle = delegate(WorkflowApplicationIdleEventArgs e) { // Send the current WriteLine outputs to the status window. var writers = e.GetInstanceExtensions<StringWriter>(); foreach (var writer in writers) { UpdateStatus(writer.ToString()); } return PersistableIdleAction.Unload; }; }
So aktivieren Sie das Starten und Fortsetzen mehrerer Workflowtypen
Um eine Workflowinstanz fortzusetzen, muss der Host die Workflowdefinition bereitstellen. In diesem Lernprogramm werden drei Workflowtypen verwendet, von denen in den folgenden Schritten mehrere Versionen vorgestellt werden. WorkflowIdentity ermöglicht einer Hostanwendung, einer persistenten Workflowinstanz Identifikationsinformationen zuzuordnen. Die Schritte in diesem Abschnitt veranschaulichen das Erstellen einer Hilfsprogrammklasse, die das Zuordnen der Workflowidentität von einer persistenten Workflowinstanz zur entsprechenden Workflowdefinition unterstützt. Weitere Informationen zu WorkflowIdentity und der Versionsverwaltung finden Sie unter Verwenden von WorkflowIdentity und Versionsverwaltung.
Klicken Sie im Projektmappen-Explorer mit der rechten Maustaste auf NumberGuessWorkflowHost, und wählen Sie Hinzufügen > Klasse aus. Geben Sie im Feld Name die Bezeichnung
WorkflowVersionMapein, und klicken Sie auf OK.Fügen Sie die folgenden
using-Anweisungen (oderImports-Anweisungen) mit den anderenusing-Anweisungen (oderImports-Anweisungen) am Anfang der Datei hinzu.Imports System.Activities Imports NumberGuessWorkflowActivitiesusing System.Activities; using NumberGuessWorkflowActivities;Ersetzen Sie die Deklaration der
WorkflowVersionMap-Klasse durch die folgende Deklaration.Public Module WorkflowVersionMap Dim map As Dictionary(Of WorkflowIdentity, Activity) ' Current version identities. Public StateMachineNumberGuessIdentity As WorkflowIdentity Public FlowchartNumberGuessIdentity As WorkflowIdentity Public SequentialNumberGuessIdentity As WorkflowIdentity Sub New() map = New Dictionary(Of WorkflowIdentity, Activity) ' Add the current workflow version identities. StateMachineNumberGuessIdentity = New WorkflowIdentity With { .Name = "StateMachineNumberGuessWorkflow", .Version = New Version(1, 0, 0, 0) } FlowchartNumberGuessIdentity = New WorkflowIdentity With { .Name = "FlowchartNumberGuessWorkflow", .Version = New Version(1, 0, 0, 0) } SequentialNumberGuessIdentity = New WorkflowIdentity With { .Name = "SequentialNumberGuessWorkflow", .Version = New Version(1, 0, 0, 0) } map.Add(StateMachineNumberGuessIdentity, New StateMachineNumberGuessWorkflow()) map.Add(FlowchartNumberGuessIdentity, New FlowchartNumberGuessWorkflow()) map.Add(SequentialNumberGuessIdentity, New SequentialNumberGuessWorkflow()) End Sub Public Function GetWorkflowDefinition(identity As WorkflowIdentity) As Activity Return map(identity) End Function Public Function GetIdentityDescription(identity As WorkflowIdentity) As String Return identity.ToString() End Function End Modulepublic static class WorkflowVersionMap { static Dictionary<WorkflowIdentity, Activity> map; // Current version identities. static public WorkflowIdentity StateMachineNumberGuessIdentity; static public WorkflowIdentity FlowchartNumberGuessIdentity; static public WorkflowIdentity SequentialNumberGuessIdentity; static WorkflowVersionMap() { map = new Dictionary<WorkflowIdentity, Activity>(); // Add the current workflow version identities. StateMachineNumberGuessIdentity = new WorkflowIdentity { Name = "StateMachineNumberGuessWorkflow", Version = new Version(1, 0, 0, 0) }; FlowchartNumberGuessIdentity = new WorkflowIdentity { Name = "FlowchartNumberGuessWorkflow", Version = new Version(1, 0, 0, 0) }; SequentialNumberGuessIdentity = new WorkflowIdentity { Name = "SequentialNumberGuessWorkflow", Version = new Version(1, 0, 0, 0) }; map.Add(StateMachineNumberGuessIdentity, new StateMachineNumberGuessWorkflow()); map.Add(FlowchartNumberGuessIdentity, new FlowchartNumberGuessWorkflow()); map.Add(SequentialNumberGuessIdentity, new SequentialNumberGuessWorkflow()); } public static Activity GetWorkflowDefinition(WorkflowIdentity identity) { return map[identity]; } public static string GetIdentityDescription(WorkflowIdentity identity) { return identity.ToString(); } }WorkflowVersionMapenthält drei Workflowidentitäten, die den drei Workflowdefinitionen aus diesem Lernprogramm zugeordnet werden, und wird in den folgenden Abschnitten beim Starten und Fortsetzen von Workflows verwendet.
So starten Sie einen neuen Workflow
Fügen Sie einen
Click-Handler fürNewGamehinzu. Um den Handler hinzuzufügen, wechseln Sie zur Entwurfsansicht für das Formular, und doppelklicken Sie aufNewGame. EinNewGame_Click-Handler wird hinzugefügt, und die Ansicht wechselt zur Codeansicht für das Formular. Sobald der Benutzer auf diese Schaltfläche klickt, wird ein neuer Workflow gestartet.Private Sub NewGame_Click(sender As Object, e As EventArgs) Handles NewGame.Click End Subprivate void NewGame_Click(object sender, EventArgs e) { }Fügen Sie dem Click-Handler folgenden Code hinzu. Durch diesen Code wird ein Wörterbuch mit Eingabeargumenten für den Workflow erstellt, die nach Argumentnamen geordnet sind. Das Wörterbuch verfügt über einen Eintrag, der den Bereich der zufällig generierten Zahl enthält, die vom Bereichskombinationsfeld abgerufen wird.
Dim inputs As New Dictionary(Of String, Object)() inputs.Add("MaxNumber", Convert.ToInt32(NumberRange.SelectedItem))var inputs = new Dictionary<string, object>(); inputs.Add("MaxNumber", Convert.ToInt32(NumberRange.SelectedItem));Als Nächstes fügen Sie den folgenden Code hinzu, durch den der Workflow gestartet wird.
WorkflowIdentityund die Workflowdefinition, die dem Typ des ausgewählten Workflows entspricht, werden mithilfe derWorkflowVersionMap-Hilfsklasse abgerufen. Anschließend wird eine neueWorkflowApplication-Instanz mithilfe von Workflowdefinition,WorkflowIdentityund des Wörterbuchs mit Eingabeargumenten erstellt.Dim identity As WorkflowIdentity = Nothing Select Case WorkflowType.SelectedItem.ToString() Case "SequentialNumberGuessWorkflow" identity = WorkflowVersionMap.SequentialNumberGuessIdentity Case "StateMachineNumberGuessWorkflow" identity = WorkflowVersionMap.StateMachineNumberGuessIdentity Case "FlowchartNumberGuessWorkflow" identity = WorkflowVersionMap.FlowchartNumberGuessIdentity End Select Dim wf As Activity = WorkflowVersionMap.GetWorkflowDefinition(identity) Dim wfApp = New WorkflowApplication(wf, inputs, identity)WorkflowIdentity identity = null; switch (WorkflowType.SelectedItem.ToString()) { case "SequentialNumberGuessWorkflow": identity = WorkflowVersionMap.SequentialNumberGuessIdentity; break; case "StateMachineNumberGuessWorkflow": identity = WorkflowVersionMap.StateMachineNumberGuessIdentity; break; case "FlowchartNumberGuessWorkflow": identity = WorkflowVersionMap.FlowchartNumberGuessIdentity; break; }; Activity wf = WorkflowVersionMap.GetWorkflowDefinition(identity); WorkflowApplication wfApp = new WorkflowApplication(wf, inputs, identity);Als Nächstes fügen Sie den folgenden Code hinzu, durch den der Workflowliste der Workflow hinzugefügt und die Versionsinformationen des Workflows für das Formular angezeigt werden.
' Add the workflow to the list and display the version information. workflowStarting = True InstanceId.SelectedIndex = InstanceId.Items.Add(wfApp.Id) WorkflowVersion.Text = identity.ToString() workflowStarting = False// Add the workflow to the list and display the version information. workflowStarting = true; InstanceId.SelectedIndex = InstanceId.Items.Add(wfApp.Id); WorkflowVersion.Text = identity.ToString(); workflowStarting = false;Rufen Sie
ConfigureWorkflowApplicationauf, um den Instanzspeicher, die Erweiterungen und die Workflowlebenszyklus-Handler für dieseWorkflowApplication-Instanz zu konfigurieren.' Configure the instance store, extensions, and ' workflow lifecycle handlers. ConfigureWorkflowApplication(wfApp)// Configure the instance store, extensions, and // workflow lifecycle handlers. ConfigureWorkflowApplication(wfApp);Rufen Sie abschließend
Runauf.' Start the workflow. wfApp.Run()// Start the workflow. wfApp.Run();Im folgenden Beispiel ist der abgeschlossene
NewGame_Click-Handler dargestellt.Private Sub NewGame_Click(sender As Object, e As EventArgs) Handles NewGame.Click ' Start a new workflow. Dim inputs As New Dictionary(Of String, Object)() inputs.Add("MaxNumber", Convert.ToInt32(NumberRange.SelectedItem)) Dim identity As WorkflowIdentity = Nothing Select Case WorkflowType.SelectedItem.ToString() Case "SequentialNumberGuessWorkflow" identity = WorkflowVersionMap.SequentialNumberGuessIdentity Case "StateMachineNumberGuessWorkflow" identity = WorkflowVersionMap.StateMachineNumberGuessIdentity Case "FlowchartNumberGuessWorkflow" identity = WorkflowVersionMap.FlowchartNumberGuessIdentity End Select Dim wf As Activity = WorkflowVersionMap.GetWorkflowDefinition(identity) Dim wfApp = New WorkflowApplication(wf, inputs, identity) ' Add the workflow to the list and display the version information. workflowStarting = True InstanceId.SelectedIndex = InstanceId.Items.Add(wfApp.Id) WorkflowVersion.Text = identity.ToString() workflowStarting = False ' Configure the instance store, extensions, and ' workflow lifecycle handlers. ConfigureWorkflowApplication(wfApp) ' Start the workflow. wfApp.Run() End Subprivate void NewGame_Click(object sender, EventArgs e) { var inputs = new Dictionary<string, object>(); inputs.Add("MaxNumber", Convert.ToInt32(NumberRange.SelectedItem)); WorkflowIdentity identity = null; switch (WorkflowType.SelectedItem.ToString()) { case "SequentialNumberGuessWorkflow": identity = WorkflowVersionMap.SequentialNumberGuessIdentity; break; case "StateMachineNumberGuessWorkflow": identity = WorkflowVersionMap.StateMachineNumberGuessIdentity; break; case "FlowchartNumberGuessWorkflow": identity = WorkflowVersionMap.FlowchartNumberGuessIdentity; break; }; Activity wf = WorkflowVersionMap.GetWorkflowDefinition(identity); var wfApp = new WorkflowApplication(wf, inputs, identity); // Add the workflow to the list and display the version information. workflowStarting = true; InstanceId.SelectedIndex = InstanceId.Items.Add(wfApp.Id); WorkflowVersion.Text = identity.ToString(); workflowStarting = false; // Configure the instance store, extensions, and // workflow lifecycle handlers. ConfigureWorkflowApplication(wfApp); // Start the workflow. wfApp.Run(); }
So setzen Sie einen Workflow fort
Fügen Sie einen
Click-Handler fürEnterGuesshinzu. Um den Handler hinzuzufügen, wechseln Sie zur Entwurfsansicht für das Formular, und doppelklicken Sie aufEnterGuess. Sobald der Benutzer auf diese Schaltfläche klickt, wird ein Workflow fortgesetzt.Private Sub EnterGuess_Click(sender As Object, e As EventArgs) Handles EnterGuess.Click End Subprivate void EnterGuess_Click(object sender, EventArgs e) { }Fügen Sie den folgenden Code hinzu, um sicherzustellen, dass ein Workflow in der Workflowliste ausgewählt ist und dass der Schätzwert des Benutzers gültig ist.
If WorkflowInstanceId = Guid.Empty Then MessageBox.Show("Please select a workflow.") Return End If Dim userGuess As Integer If Not Int32.TryParse(Guess.Text, userGuess) Then MessageBox.Show("Please enter an integer.") Guess.SelectAll() Guess.Focus() Return End Ifif (WorkflowInstanceId == Guid.Empty) { MessageBox.Show("Please select a workflow."); return; } int guess; if (!Int32.TryParse(Guess.Text, out guess)) { MessageBox.Show("Please enter an integer."); Guess.SelectAll(); Guess.Focus(); return; }Rufen Sie anschließend die
WorkflowApplicationInstanceder resistenten Workflowinstanz ab.WorkflowApplicationInstancestellt eine persistente Workflowinstanz dar, die noch keiner Workflowdefinition zugeordnet wurde. DieDefinitionIdentityvonWorkflowApplicationInstanceenthält dieWorkflowIdentityder persistenten Workflowinstanz. In diesem Lernprogramm wird dieWorkflowVersionMapHilfsklasse verwendet, umWorkflowIdentityder richtigen Workflowdefinition zuzuordnen. Beim Abrufen der Workflowdefinition wird anhand der richtigen Workflowdefinition eineWorkflowApplicationerstellt.Dim instance As WorkflowApplicationInstance = _ WorkflowApplication.GetInstance(WorkflowInstanceId, store) ' Use the persisted WorkflowIdentity to retrieve the correct workflow ' definition from the dictionary. Dim wf As Activity = _ WorkflowVersionMap.GetWorkflowDefinition(instance.DefinitionIdentity) ' Associate the WorkflowApplication with the correct definition Dim wfApp As New WorkflowApplication(wf, instance.DefinitionIdentity)WorkflowApplicationInstance instance = WorkflowApplication.GetInstance(WorkflowInstanceId, store); // Use the persisted WorkflowIdentity to retrieve the correct workflow // definition from the dictionary. Activity wf = WorkflowVersionMap.GetWorkflowDefinition(instance.DefinitionIdentity); // Associate the WorkflowApplication with the correct definition var wfApp = new WorkflowApplication(wf, instance.DefinitionIdentity);Sobald
WorkflowApplicationerstellt wird, konfigurieren Sie den Instanzspeicher, die Handler des Workflowlebenszyklus und die Erweiterungen, indem SieConfigureWorkflowApplicationaufrufen. Diese Schritte müssen bei jeder Erstellung einer neuenWorkflowApplicationausgeführt werden, und zwar bevor die Workflowinstanz inWorkflowApplicationgeladen wird. Nachdem der Workflow geladen wurde, wird er mit der Schätzung des Benutzers fortgesetzt.' Configure the extensions and lifecycle handlers. ' Do this before the instance is loaded. Once the instance is ' loaded it is too late to add extensions. ConfigureWorkflowApplication(wfApp) ' Load the workflow. wfApp.Load(instance) ' Resume the workflow. wfApp.ResumeBookmark("EnterGuess", userGuess)// Configure the extensions and lifecycle handlers. // Do this before the instance is loaded. Once the instance is // loaded it is too late to add extensions. ConfigureWorkflowApplication(wfApp); // Load the workflow. wfApp.Load(instance); // Resume the workflow. wfApp.ResumeBookmark("EnterGuess", guess);Löschen Sie abschließend den Eintrag im Textfeld, und bereiten Sie das Formular für die Eingabe eines anderen Schätzwerts vor.
' Clear the Guess textbox. Guess.Clear() Guess.Focus()// Clear the Guess textbox. Guess.Clear(); Guess.Focus();Im folgenden Beispiel ist der abgeschlossene
EnterGuess_Click-Handler dargestellt.Private Sub EnterGuess_Click(sender As Object, e As EventArgs) Handles EnterGuess.Click If WorkflowInstanceId = Guid.Empty Then MessageBox.Show("Please select a workflow.") Return End If Dim userGuess As Integer If Not Int32.TryParse(Guess.Text, userGuess) Then MessageBox.Show("Please enter an integer.") Guess.SelectAll() Guess.Focus() Return End If Dim instance As WorkflowApplicationInstance = _ WorkflowApplication.GetInstance(WorkflowInstanceId, store) ' Use the persisted WorkflowIdentity to retrieve the correct workflow ' definition from the dictionary. Dim wf As Activity = _ WorkflowVersionMap.GetWorkflowDefinition(instance.DefinitionIdentity) ' Associate the WorkflowApplication with the correct definition Dim wfApp As New WorkflowApplication(wf, instance.DefinitionIdentity) ' Configure the extensions and lifecycle handlers. ' Do this before the instance is loaded. Once the instance is ' loaded it is too late to add extensions. ConfigureWorkflowApplication(wfApp) ' Load the workflow. wfApp.Load(instance) ' Resume the workflow. wfApp.ResumeBookmark("EnterGuess", userGuess) ' Clear the Guess textbox. Guess.Clear() Guess.Focus() End Subprivate void EnterGuess_Click(object sender, EventArgs e) { if (WorkflowInstanceId == Guid.Empty) { MessageBox.Show("Please select a workflow."); return; } int guess; if (!Int32.TryParse(Guess.Text, out guess)) { MessageBox.Show("Please enter an integer."); Guess.SelectAll(); Guess.Focus(); return; } WorkflowApplicationInstance instance = WorkflowApplication.GetInstance(WorkflowInstanceId, store); // Use the persisted WorkflowIdentity to retrieve the correct workflow // definition from the dictionary. Activity wf = WorkflowVersionMap.GetWorkflowDefinition(instance.DefinitionIdentity); // Associate the WorkflowApplication with the correct definition var wfApp = new WorkflowApplication(wf, instance.DefinitionIdentity); // Configure the extensions and lifecycle handlers. // Do this before the instance is loaded. Once the instance is // loaded it is too late to add extensions. ConfigureWorkflowApplication(wfApp); // Load the workflow. wfApp.Load(instance); // Resume the workflow. wfApp.ResumeBookmark("EnterGuess", guess); // Clear the Guess textbox. Guess.Clear(); Guess.Focus(); }
So beenden Sie einen Workflow
Fügen Sie einen
Click-Handler fürQuitGamehinzu. Um den Handler hinzuzufügen, wechseln Sie zur Entwurfsansicht für das Formular, und doppelklicken Sie aufQuitGame. Sobald der Benutzer auf diese Schaltfläche klickt, wird der aktuell ausgewählte Workflow beendet.Private Sub QuitGame_Click(sender As Object, e As EventArgs) Handles QuitGame.Click End Subprivate void QuitGame_Click(object sender, EventArgs e) { }Fügen Sie dem
QuitGame_Click-Handler folgenden Code hinzu. Durch diesen Code wird zuerst überprüft, ob in der Workflowliste ein Workflow ausgewählt ist. Anschließend lädt er die persistente Instanz in eineWorkflowApplicationInstance, ermittelt anhand vonDefinitionIdentitydie richtige Workflowdefinition und initialisiert dieWorkflowApplication. Als Nächstes werden die Erweiterungen und die Workflowlebenszyklus-Handler mit einem Aufruf vonConfigureWorkflowApplicationkonfiguriert. SobaldWorkflowApplicationkonfiguriert ist, wird sie geladen, undTerminatewird aufgerufen.If WorkflowInstanceId = Guid.Empty Then MessageBox.Show("Please select a workflow.") Return End If Dim instance As WorkflowApplicationInstance = _ WorkflowApplication.GetInstance(WorkflowInstanceId, store) ' Use the persisted WorkflowIdentity to retrieve the correct workflow ' definition from the dictionary. Dim wf As Activity = WorkflowVersionMap.GetWorkflowDefinition(instance.DefinitionIdentity) ' Associate the WorkflowApplication with the correct definition. Dim wfApp As New WorkflowApplication(wf, instance.DefinitionIdentity) ' Configure the extensions and lifecycle handlers. ConfigureWorkflowApplication(wfApp) ' Load the workflow. wfApp.Load(instance) ' Terminate the workflow. wfApp.Terminate("User resigns.")if (WorkflowInstanceId == Guid.Empty) { MessageBox.Show("Please select a workflow."); return; } WorkflowApplicationInstance instance = WorkflowApplication.GetInstance(WorkflowInstanceId, store); // Use the persisted WorkflowIdentity to retrieve the correct workflow // definition from the dictionary. Activity wf = WorkflowVersionMap.GetWorkflowDefinition(instance.DefinitionIdentity); // Associate the WorkflowApplication with the correct definition var wfApp = new WorkflowApplication(wf, instance.DefinitionIdentity); // Configure the extensions and lifecycle handlers ConfigureWorkflowApplication(wfApp); // Load the workflow. wfApp.Load(instance); // Terminate the workflow. wfApp.Terminate("User resigns.");
So erstellen Sie die Anwendung und führen sie aus
Doppelklicken Sie im Projektmappen-Explorer auf Program.cs oder Module1.vb, um den Code anzuzeigen.
Fügen Sie die folgende
using-Anweisung (oderImports-Anweisung) mit den anderenusing-Anweisungen (oderImports-Anweisungen) am Anfang der Datei hinzu.Imports System.Windows.Formsusing System.Windows.Forms;Entfernen oder kommentieren Sie den vorhandenen Workflowhostingcode aus Vorgehensweise: Ausführen eines Workflows aus, und ersetzen Sie ihn durch den folgenden Code.
Sub Main() Application.EnableVisualStyles() Application.Run(New WorkflowHostForm()) End Substatic void Main(string[] args) { Application.EnableVisualStyles(); Application.Run(new WorkflowHostForm()); }Klicken Sie im Projektmappen-Explorer mit der rechten Maustaste auf NumberGuessWorkflowHost, und wählen Sie Eigenschaften aus. Geben Sie auf der Registerkarte Anwendung für Ausgabetyp den Typ Windows-Anwendung an. Dieser Schritt ist optional, wird er jedoch nicht ausgeführt, wird zusätzlich zum Formular das Konsolenfenster angezeigt.
Drücken Sie STRG+UMSCHALT+B, um die Anwendung zu erstellen.
Stellen Sie sicher, dass NumberGuessWorkflowHost als Startanwendung festgelegt ist, und drücken Sie STRG+F5, um die Anwendung zu starten.
Wählen Sie einen Bereich für das Ratespiel und den zu startenden Workflowtyp aus, und klicken Sie auf Neues Spiel. Geben Sie im Feld Vorschlag einen Schätzwert ein, und klicken Sie auf Starten, um die Zahl zu senden. Beachten Sie, dass die Ausgabe der
WriteLine-Aktivitäten auf dem Formular angezeigt wird.Starten Sie mehrere Workflows mit verschiedenen Workflowtypen und Zahlenbereichen, geben Sie einige Schätzwerte ein, und wechseln Sie zwischen den Workflows, indem Sie sie aus der Liste Workflowinstanz-ID auswählen.
Wenn Sie zu einem neuen Workflow wechseln, werden die vorherigen Schätzwerte und der Workflowverlauf nicht im Statusfenster angezeigt. Der Status ist nicht verfügbar, weil er nicht erfasst wurde und nirgends gespeichert ist. Im nächsten Schritt des Tutorials Vorgehensweise: Erstellen eines benutzerdefinierten Überwachungsteilnehmers erstellen Sie einen benutzerdefinierten Überwachungsteilnehmer, von dem diese Informationen gespeichert werden.
Feedback
Bald verfügbar: Im Laufe des Jahres 2024 werden wir GitHub-Issues stufenweise als Feedbackmechanismus für Inhalte abbauen und durch ein neues Feedbacksystem ersetzen. Weitere Informationen finden Sie unter https://aka.ms/ContentUserFeedback.
Feedback senden und anzeigen für
