Beispielszenario für Office-Skripts: Analysieren von Webdownloads
In diesem Szenario müssen Sie Downloadberichte von der Website Ihres Unternehmens analysieren. Das Ziel dieser Analyse ist es, zu ermitteln, ob der Webdatenverkehr aus dem USA oder aus anderen Teilen der Welt kommt.
Ihre Kollegen laden die Rohdaten in Ihre Arbeitsmappe hoch. Der Datensatz jeder Woche verfügt über ein eigenes Arbeitsblatt. Es gibt auch das Arbeitsblatt "Zusammenfassung " mit einer Tabelle und einem Diagramm, in dem die Trends von Woche zu Woche angezeigt werden.
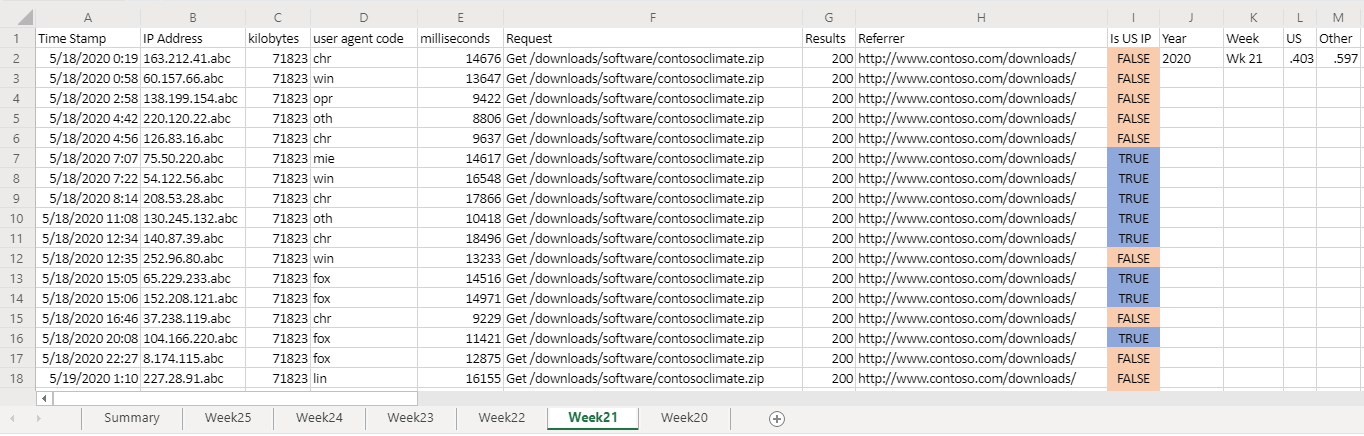
Sie entwickeln ein Skript, das wöchentliche Downloaddaten im aktiven Arbeitsblatt analysiert. Es analysiert die ip-Adresse, die jedem Download zugeordnet ist, und bestimmt, ob sie aus den USA stammt oder nicht. Die Antwort wird als boolescher Wert ("TRUE" oder "FALSE") in das Arbeitsblatt eingefügt, und die bedingte Formatierung wird auf diese Zellen angewendet. Die Ergebnisse des IP-Adressspeicherorts werden auf dem Arbeitsblatt summiert und in die Zusammenfassungstabelle kopiert.
Behandelte Skriptfähigkeiten
- Textanalyse
- Unterfunktionen in Skripts
- Bedingte Formatierung
- Tabellen
Setupanweisungen
Laden Sie die Beispielarbeitsmappe auf OneDrive herunter.
Öffnen Sie die Arbeitsmappe in Excel.
Wählen Sie auf der Registerkarte Automatisierendie Option Neues Skript aus, und fügen Sie das folgende Skript in den Editor ein.
function main(workbook: ExcelScript.Workbook) { /* Get the Summary worksheet and table. * End the script early if either object is not in the workbook. */ let summaryWorksheet = workbook.getWorksheet("Summary"); if (!summaryWorksheet) { console.log("The script expects a worksheet named \"Summary\". Please download the correct template and try again."); return; } let summaryTable = summaryWorksheet.getTable("Table1"); if (!summaryTable) { console.log("The script expects a summary table named \"Table1\". Please download the correct template and try again."); return; } // Get the current worksheet. let currentWorksheet = workbook.getActiveWorksheet(); if (currentWorksheet.getName().toLocaleLowerCase().indexOf("week") !== 0) { console.log("Please switch worksheet to one of the weekly data sheets and try again.") return; } // Get the values of the active range of the active worksheet. let logRange = currentWorksheet.getUsedRange(); if (logRange.getColumnCount() !== 8) { console.log(`Verify that you are on the correct worksheet. Either the week's data has been already processed or the content is incorrect. The following columns are expected: ${[ "Time Stamp", "IP Address", "kilobytes", "user agent code", "milliseconds", "Request", "Results", "Referrer" ]}`); return; } // Get the range that will contain TRUE/FALSE if the IP address is from the United States (US). let isUSColumn = logRange .getLastColumn() .getOffsetRange(0, 1); // Get the values of all the US IP addresses. let ipRange = workbook.getWorksheet("USIPAddresses").getUsedRange(); let ipRangeValues = ipRange.getValues() as number[][]; let logRangeValues = logRange.getValues() as string[][]; // Remove the first row. let topRow = logRangeValues.shift(); console.log(`Analyzing ${logRangeValues.length} entries.`); // Create a new array to contain the boolean representing if this is a US IP address. let newCol: (boolean | string)[][] = []; // Go through each row in worksheet and add Boolean. for (let i = 0; i < logRangeValues.length; i++) { let curRowIP = logRangeValues[i][1]; if (findIP(ipRangeValues, ipAddressToInteger(curRowIP)) > 0) { newCol.push([true]); } else { newCol.push([false]); } } // Remove the empty column header and add proper heading. newCol = [["Is US IP"], ...newCol]; // Write the result to the spreadsheet. console.log(`Adding column to indicate whether IP belongs to US region or not at address: ${isUSColumn.getAddress()}`); console.log(newCol.length); console.log(newCol); isUSColumn.setValues(newCol); // Call the local function to add summary data to the worksheet. addSummaryData(); // Call the local function to apply conditional formatting. applyConditionalFormatting(isUSColumn); // Autofit columns. currentWorksheet.getUsedRange().getFormat().autofitColumns(); // Get the calculated summary data. let summaryRangeValues = currentWorksheet.getRange("J2:M2").getValues(); // Add the corresponding row to the summary table. summaryTable.addRow(null, summaryRangeValues[0]); console.log("Complete."); return; /** * A function to add summary data on the worksheet. */ function addSummaryData() { // Add a summary row and table. let summaryHeader = [["Year", "Week", "US", "Other"]]; let countTrueFormula = "=COUNTIF(" + isUSColumn.getAddress() + ', "=TRUE")/' + (newCol.length - 1); let countFalseFormula = "=COUNTIF(" + isUSColumn.getAddress() + ', "=FALSE")/' + (newCol.length - 1); let summaryContent = [ [ '=TEXT(A2,"YYYY")', '=TEXTJOIN(" ", FALSE, "Wk", WEEKNUM(A2))', countTrueFormula, countFalseFormula ] ]; let summaryHeaderRow = currentWorksheet.getRange("J1:M1"); let summaryContentRow = currentWorksheet.getRange("J2:M2"); console.log("2"); summaryHeaderRow.setValues(summaryHeader); console.log("3"); summaryContentRow.setValues(summaryContent); console.log("4"); let formats = [[".000", ".000"]]; summaryContentRow .getOffsetRange(0, 2) .getResizedRange(0, -2).setNumberFormats(formats); } } /** * Apply conditional formatting based on TRUE/FALSE values of the Is US IP column. */ function applyConditionalFormatting(isUSColumn: ExcelScript.Range) { // Add conditional formatting to the new column. let conditionalFormatTrue = isUSColumn.addConditionalFormat( ExcelScript.ConditionalFormatType.cellValue ); let conditionalFormatFalse = isUSColumn.addConditionalFormat( ExcelScript.ConditionalFormatType.cellValue ); // Set TRUE to light blue and FALSE to light orange. conditionalFormatTrue.getCellValue().getFormat().getFill().setColor("#8FA8DB"); conditionalFormatTrue.getCellValue().setRule({ formula1: "=TRUE", operator: ExcelScript.ConditionalCellValueOperator.equalTo }); conditionalFormatFalse.getCellValue().getFormat().getFill().setColor("#F8CCAD"); conditionalFormatFalse.getCellValue().setRule({ formula1: "=FALSE", operator: ExcelScript.ConditionalCellValueOperator.equalTo }); } /** * Translate an IP address into an integer. * @param ipAddress: IP address to verify. */ function ipAddressToInteger(ipAddress: string): number { // Split the IP address into octets. let octets = ipAddress.split("."); // Create a number for each octet and do the math to create the integer value of the IP address. let fullNum = // Define an arbitrary number for the last octet. 111 + parseInt(octets[2]) * 256 + parseInt(octets[1]) * 65536 + parseInt(octets[0]) * 16777216; return fullNum; } /** * Return the row number where the ip address is found. * @param ipLookupTable IP look-up table. * @param n IP address to number value. */ function findIP(ipLookupTable: number[][], n: number): number { for (let i = 0; i < ipLookupTable.length; i++) { if (ipLookupTable[i][0] <= n && ipLookupTable[i][1] >= n) { return i; } } return -1; }Benennen Sie das Skript in Analyze Web Downloads (Webdownloads analysieren ) um, und speichern Sie es.
Ausführen des Skripts
Navigieren Sie zu einem der Arbeitsblätter der Woche** , und führen Sie das Skript Analyze Web Downloads (Webdownloads analysieren ) aus. Das Skript wendet die bedingte Formatierung und Positionskennzeichnung auf dem aktuellen Blatt an. Außerdem wird das Arbeitsblatt Zusammenfassung aktualisiert.
Vor dem Ausführen des Skripts
Nach dem Ausführen des Skripts
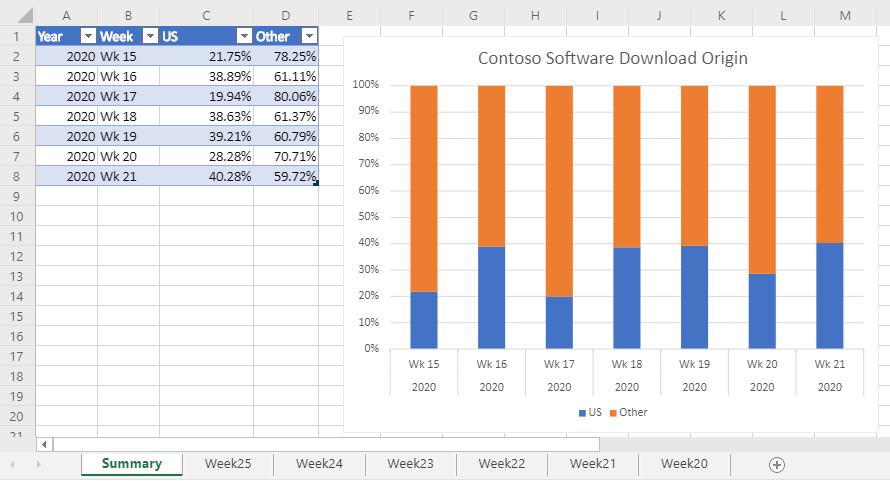
Office Scripts
Feedback
Bald verfügbar: Im Laufe des Jahres 2024 werden wir GitHub-Issues stufenweise als Feedbackmechanismus für Inhalte abbauen und durch ein neues Feedbacksystem ersetzen. Weitere Informationen finden Sie unter https://aka.ms/ContentUserFeedback.
Feedback senden und anzeigen für