Deploy Azure IoT Operations Preview extensions to a Kubernetes cluster
Important
Azure IoT Operations Preview – enabled by Azure Arc is currently in PREVIEW. You shouldn't use this preview software in production environments.
See the Supplemental Terms of Use for Microsoft Azure Previews for legal terms that apply to Azure features that are in beta, preview, or otherwise not yet released into general availability.
Deploy Azure IoT Operations Preview to a Kubernetes cluster using the Azure CLI. Once you have Azure IoT Operations deployed, then you can use the Azure IoT Orchestrator Preview service to manage and deploy other workloads to your cluster.
Prerequisites
Cloud resources:
An Azure subscription.
Azure access permissions. At a minimum, have Contributor permissions in your Azure subscription. Depending on the deployment feature flag status you select, you might also need Microsoft/Authorization/roleAssignments/write permissions for the resource group that contains your Arc-enabled Kubernetes cluster. You can make a custom role in Azure role-based access control or assign a built-in role that grants this permission. For more information, see Azure built-in roles for General.
If you don't have role assignment write permissions, you can still deploy Azure IoT Operations by disabling some features. This approach is discussed in more detail in the Deploy extensions section of this article.
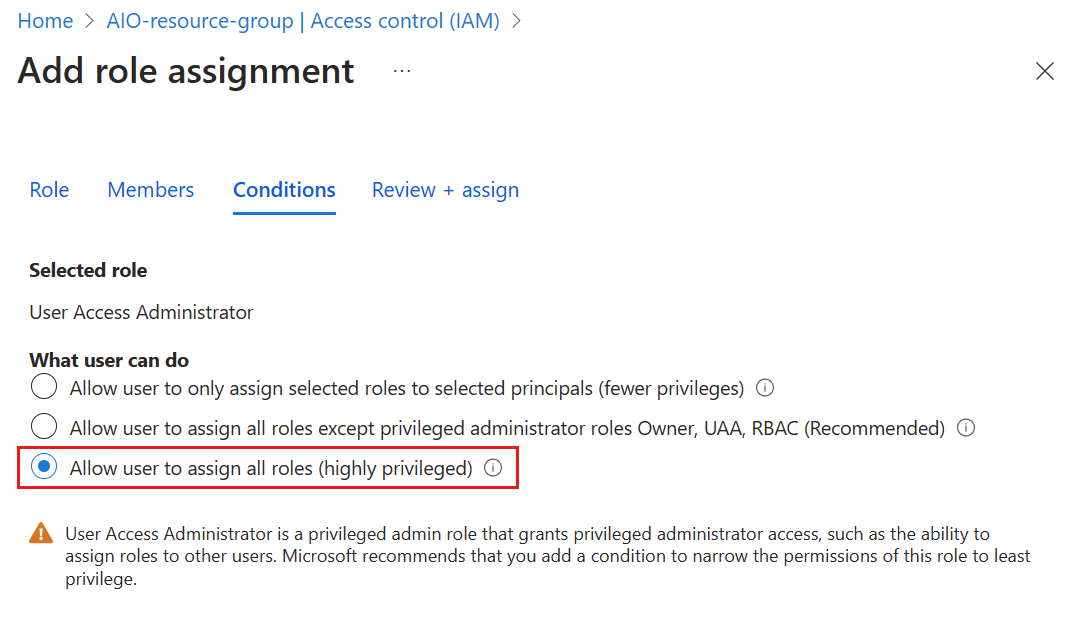
In the Azure CLI, use the az role assignment create command to give permissions. For example,
az role assignment create --assignee sp_name --role "Role Based Access Control Administrator" --scope subscriptions/00000000-0000-0000-0000-000000000000/resourceGroups/MyResourceGroupIn the Azure portal, you're prompted to restrict access using conditions when you assign privileged admin roles to a user or principal. For this scenario, select the Allow user to assign all roles condition in the Add role assignment page.
An Azure Key Vault that has the Permission model set to Vault access policy. You can check this setting in the Access configuration section of an existing key vault. If you need to create a new key vault, use the az keyvault create command:
az keyvault create --enable-rbac-authorization false --name "<KEYVAULT_NAME>" --resource-group "<RESOURCE_GROUP>"
Development resources:
Azure CLI installed on your development machine. For more information, see How to install the Azure CLI. This scenario requires Azure CLI version 2.46.0 or higher. Use
az --versionto check your version andaz upgradeto update if necessary.The Azure IoT Operations extension for Azure CLI. Use the following command to add the extension or update it to the latest version:
az extension add --upgrade --name azure-iot-ops
A cluster host:
An Azure Arc-enabled Kubernetes cluster. If you don't have one, follow the steps in Prepare your Azure Arc-enabled Kubernetes cluster.
If you've already deployed Azure IoT Operations to your cluster, uninstall those resources before continuing. For more information, see Update a deployment.
Azure IoT Operations should work on any CNCF-conformant kubernetes cluster. Currently, Microsoft only supports K3s on Ubuntu Linux and WSL, or AKS Edge Essentials on Windows. Using Ubuntu in Windows Subsystem for Linux (WSL) is the simplest way to get a Kubernetes cluster for testing.
Use the Azure IoT Operations extension for Azure CLI to verify that your cluster host is configured correctly for deployment by using the verify-host command on the cluster host:
az iot ops verify-host
Deploy extensions
Use the Azure CLI to deploy Azure IoT Operations components to your Arc-enabled Kubernetes cluster.
Sign in to Azure CLI interactively with a browser even if you already signed in before. If you don't sign in interactively, you might get an error that says Your device is required to be managed to access your resource when you continue to the next step to deploy Azure IoT Operations.
az loginNote
If you're using GitHub Codespaces in a browser,
az loginreturns a localhost error in the browser window after logging in. To fix, either:- Open the codespace in VS Code desktop, and then run
az loginin the terminal. This opens a browser window where you can log in to Azure. - Or, after you get the localhost error on the browser, copy the URL from the browser and use
curl <URL>in a new terminal tab. You should see a JSON response with the message "You have logged into Microsoft Azure!".
- Open the codespace in VS Code desktop, and then run
Deploy Azure IoT Operations to your cluster. Use optional flags to customize the az iot ops init command to fit your scenario.
By default, the
az iot ops initcommand takes the following actions, some of which require that the principal signed in to the CLI has elevated permissions:- Set up a service principal and app registration to give your cluster access to the key vault.
- Configure TLS certificates.
- Configure a secrets store on your cluster that connects to the key vault.
- Deploy the Azure IoT Operations resources.
az iot ops init --cluster <CLUSTER_NAME> --resource-group <RESOURCE_GROUP> --kv-id <KEYVAULT_ID>If you don't have Microsoft.Authorization/roleAssignment/write permissions in the resource group, add the
--disable-rsync-rulesfeature flag. This flag disables the resource sync rules on the deployment.If you want to use an existing service principal and app registration instead of allowing
initto create new ones, include the--sp-app-id,--sp-object-id, and--sp-secretparameters. For more information, see Configure service principal and Key Vault manually.After the deployment is complete, you can use az iot ops check to evaluate IoT Operations service deployment for health, configuration, and usability. The check command can help you find problems in your deployment and configuration.
az iot ops checkYou can also check the configurations of topic maps, QoS, and message routes by adding the
--detail-level 2parameter for a verbose view.
Configure cluster network (AKS EE)
On AKS Edge Essentials clusters, enable inbound connections to Azure IoT MQ Preview broker and configure port forwarding:
Enable a firewall rule for port 8883:
New-NetFirewallRule -DisplayName "Azure IoT MQ" -Direction Inbound -Protocol TCP -LocalPort 8883 -Action AllowRun the following command and make a note of the IP address for the service called
aio-mq-dmqtt-frontend:kubectl get svc aio-mq-dmqtt-frontend -n azure-iot-operations -o jsonpath='{.status.loadBalancer.ingress[0].ip}'Enable port forwarding for port 8883. Replace
<aio-mq-dmqtt-frontend IP address>with the IP address you noted in the previous step:netsh interface portproxy add v4tov4 listenport=8883 listenaddress=0.0.0.0 connectport=8883 connectaddress=<aio-mq-dmqtt-frontend IP address>
View resources in your cluster
While the deployment is in progress, you can watch the resources being applied to your cluster. You can use kubectl commands to observe changes on the cluster or, since the cluster is Arc-enabled, you can use the Azure portal.
To view the pods on your cluster, run the following command:
kubectl get pods -n azure-iot-operations
It can take several minutes for the deployment to complete. Rerun the get pods command to refresh your view.
To view your cluster on the Azure portal, use the following steps:
In the Azure portal, navigate to the resource group that contains your cluster.
From the Overview of the resource group, select the name of your cluster.
On your cluster, select Extensions from the menu.
You can see that your cluster is running extensions of the type microsoft.iotoperations.x, which is the group name for all of the Azure IoT Operations components and the orchestration service.
There's also an extension called akvsecretsprovider. This extension is the secrets provider that you configured and installed on your cluster with the
az iot ops initcommand. You might delete and reinstall the Azure IoT Operations components during testing, but keep the secrets provider extension on your cluster.
Tip
You can run az iot ops check to assess health and configurations of deployed AIO workloads. By default, MQ including cloud connectors are assessed and you can specifiy the service with --ops-service --svc.
Update a deployment
Currently, there's no support for updating an existing Azure IoT Operations deployment. Instead, start with a clean cluster for a new deployment.
If you want to delete the Azure IoT Operations deployment on your cluster so that you can redeploy to it, navigate to your cluster on the Azure portal. Select the extensions of the type microsoft.iotoperations.x and microsoft.deviceregistry.assets, then select Uninstall. Keep the secrets provider on your cluster, as that is a prerequisite for deployment and not included in a fresh deployment.
Next steps
If your components need to connect to Azure endpoints like SQL or Fabric, learn how to Manage secrets for your Azure IoT Operations Preview deployment.
Feedback
Coming soon: Throughout 2024 we will be phasing out GitHub Issues as the feedback mechanism for content and replacing it with a new feedback system. For more information see: https://aka.ms/ContentUserFeedback.
Submit and view feedback for