Better together Windows Server and Azure Management
Windows Server together with Microsoft Azure cloud management capabilities allows you to get even more out of your Windows Server investments.
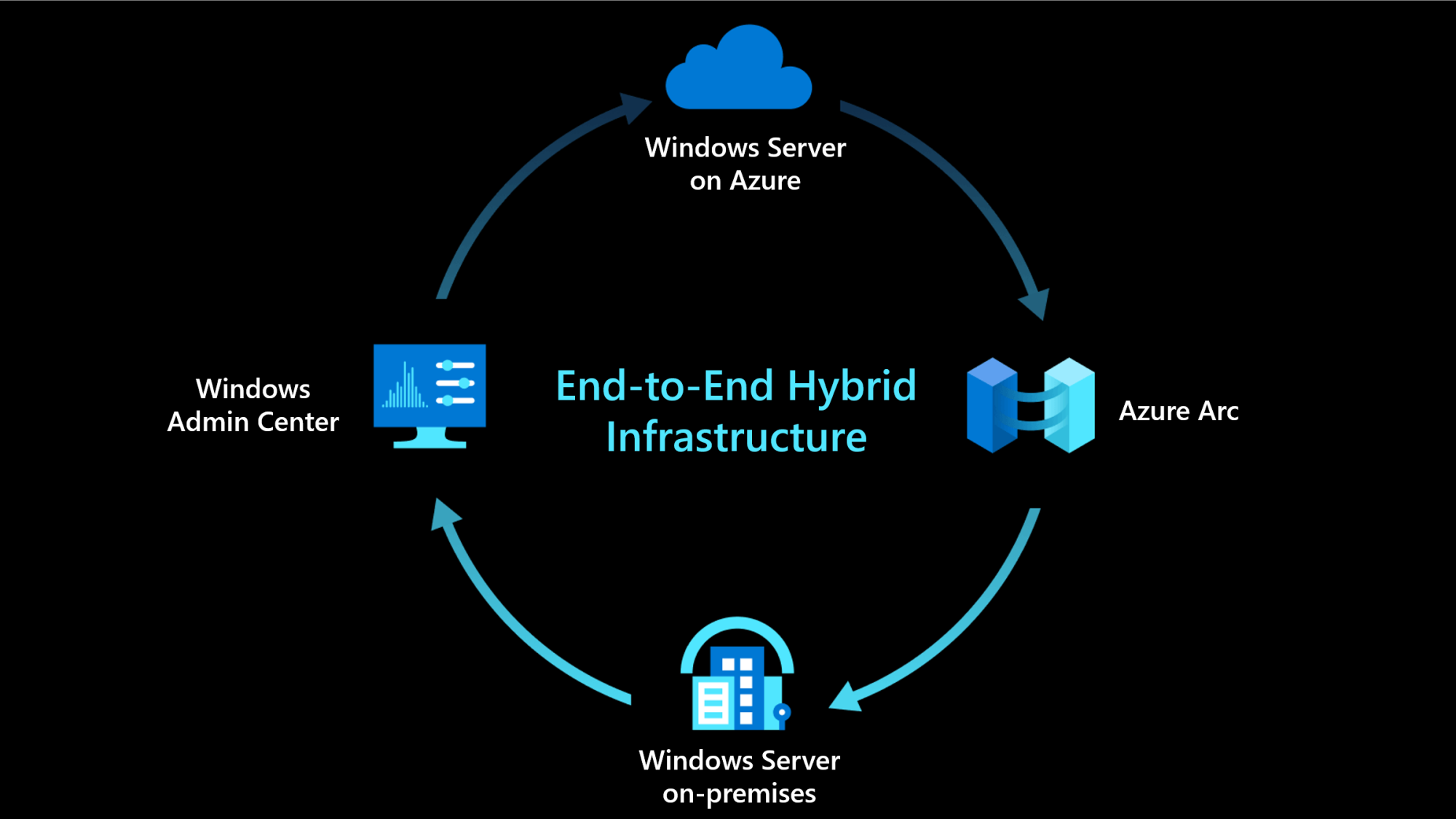
Cloud operations for Windows Server in a hybrid and multi-cloud environment
When you connect Windows Server running on-premises or multi-cloud environment to Azure, it enables the following integration:
| Operations function | Description |
|---|---|
| Govern | |
| Azure Policy | Assign Azure Policy guest configurations to audit settings inside Windows Server. |
| Azure Tags | Use tags to organize your Windows Server machines, Azure resources, and management hierarchy |
| Protect | |
| Microsoft Defender for Cloud | Protect non-Azure servers with Microsoft Defender for Endpoint, included through Microsoft Defender for Cloud, for threat detection, for vulnerability management, and to proactively monitor for potential security threats. Microsoft Defender for Cloud presents the alerts and remediation suggestions from the threats detected. |
| Microsoft Sentinel | Machines connected to Arc-enabled servers can be configured with Microsoft Sentinel to collect security-related events and correlate them with other data sources. |
| Azure Backup | Azure Backup service uses the Microsoft Azure Recovery Services (MARS) agent to back up and restore files, folders, and the volume or system state from an on-premises computer to Azure, helping to protect you from accidental or malicious deletions, corruption, and ransomware. |
| Azure Site Recovery | Site Recovery replicates workloads running on physical and virtual machines (VMs) from a primary site to a secondary location or Microsoft Azure. When an outage occurs at your primary site, you fail over to secondary location, and access apps from there. After the primary location is running again, you can fail back to it. |
| Configure | |
| Azure Automation | Automate frequent and time-consuming management tasks using PowerShell and Python runbooks. Assess configuration changes about installed software, Microsoft services, Windows registry and files, and Linux daemons using Change Tracking and Inventory. Use Update Management to manage operating system updates for your Windows and Linux servers. |
| Azure Automanage (preview) | Automate onboarding and configuration of a set of Azure services when you use Automanage Machine for Arc-enabled servers. |
| VM extensions | Provides post-deployment configuration and automation tasks using supported Arc-enabled servers VM extensions for your non-Azure Windows or Linux machine. |
| Monitor | |
| Azure Monitor | Monitor the connected machine guest operating system performance, and discover application components to monitor their processes and dependencies with other resources using VM insights. Collect other log data, such as performance data and events, from the operating system or workload(s) running on the machine with the Log Analytics agent. This data is stored in a Log Analytics workspace. |
| Extend and connect | |
| Microsoft Entra ID | Connect your on-premises Windows Server Active Directory to Microsoft Entra ID to create a hybrid identity. Managed identities for Azure Arc-enabled servers provides servers with an automatically managed identity in Microsoft Entra ID. You can use this identity to authenticate to any service that supports Microsoft Entra authentication, without having credentials in your code. |
| Azure Extended Network | Make Azure VMs look like your on-premises network with Azure Extended Network. Windows Admin Center can set up a site-to-site VPN and extend your on-premises IP addresses into your Azure vNet to let you more easily migrate workloads into Azure without breaking dependencies on IP addresses. |
| Azure Network Adapter | Connect your on-premises servers to an Azure Virtual Network with Azure Network Adapter. Let Windows Admin Center simplify setting up a point-to-site VPN from an on-premises server into an Azure virtual network. |
| Azure File Sync | Sync your file server with the cloud by using Azure File Sync. Sync files on this server with Azure file shares. Keep all your files local or use cloud tiering to free up space and cache only the most frequently used files on the server, tiering cold data to the cloud. Data in the cloud can be backed up, eliminating the need to worry about on-premises server backup. Additionally, multi-site-sync can keep a set of files in sync across multiple servers. |
| Storage Replica | Use synchronous or asynchronous block-based replication to a VM in Azure using Storage Replica. You can configure block-based or volume-based replication on a server-to-server level using Storage Replica to a secondary server or VM. Windows Admin Center allows you to create an Azure VM specifically for your replication target, helping you to right-size and correctly configure storage on a new Azure VM. For more info, see Server-to-server replication with Storage Replica. |
Learn more about Azure Arc-enabled server at What is Azure Arc-enabled server and how to connect Windows Server to Azure hybrid services using Windows Admin Center.
Cloud operations for Windows Server on Azure
When you run Windows Server on Azure, it enables the following integration:
| Operations function | Description |
|---|---|
| Govern | |
| Azure Policy | Assign Azure Policy guest configurations to audit settings inside the machine. |
| Azure Tags | Use tags to organize your Windows Servers and Azure resources and management hierarchy |
| Protect | |
| Microsoft Defender for Cloud | Protect non-Azure servers with Microsoft Defender for Endpoint, included through Microsoft Defender for Cloud, for threat detection, for vulnerability management, and to proactively monitor for potential security threats. Microsoft Defender for Cloud presents the alerts and remediation suggestions from the threats detected. |
| Microsoft Sentinel | Windows Server machines running in Azure can be configured with Microsoft Sentinel to collect security-related events and correlate them with other data sources. |
| Azure Backup | Azure Backup provides independent and isolated backups to guard against unintended destruction of the data on your VMs. Backups are stored in a Recovery Services vault with built-in management of recovery points. |
| Azure Site Recovery | Site Recovery replicates workloads running on Azure virtual machines (VMs) from the primary Azure region to another Azure region. When an outage occurs at the primary Azure region, you fail over to the other Azure region, and access apps from there. After the primary Azure region is running again, you can fail back to it. |
| Azure confidential computing | Azure confidential computing offers confidential VMs. Confidential VMs are for tenants with high security and confidentiality requirements. These VMs provide a strong, hardware-enforced boundary to help meet your security needs. You can use confidential VMs for migrations without making changes to your code, with the platform protecting your VM's state from being read or modified. |
| Configure | |
| Azure Automation | Automate frequent and time-consuming management tasks using PowerShell and Python runbooks. Assess configuration changes about installed software, Microsoft services, Windows registry and files, and Linux daemons using Change Tracking and Inventory. Use Update Management to manage operating system updates for your Windows and Linux servers. |
| Azure Automanage (preview) | Automate onboarding and configuration of a set of Azure services when you use Azure Automanage for Windows Server. Hotpatching is a new way to install updates on supported Windows Server Azure Edition virtual machines (VMs) that doesn’t require a reboot after installation SMB over QUIC offers an "SMB VPN" for telecommuters, mobile device users, and branch offices, providing secure, reliable connectivity to edge file servers over untrusted networks like the Internet. To learn more about SMB over QUIC and how to configure SMB over QUIC, see SMB over QUIC. |
| VM extensions | Azure virtual machine (VM) extensions are small applications that provide post-deployment configuration and automation tasks on Azure VMs. For example, if a virtual machine requires software installation, antivirus protection, or the ability to run a script inside it, you can use a VM extension. |
| Windows Admin Center in the Azure portal | Use Windows Admin Center (preview) in the Azure portal to manage the Windows Server operating system inside an Azure VM. Manage operating system functions from the Azure portal as well as work with files in the VM without using Remote Desktop or PowerShell. |
| VM Run Command | The Run Command feature uses the virtual machine (VM) agent to run PowerShell scripts within an Azure Windows VM. |
| Monitor | |
| Azure Monitor | Monitor the connected machine guest operating system performance, and discover application components to monitor their processes and dependencies with other resources using VM insights. Collect other log data, such as performance data and events, from the operating system or workload(s) running on the machine with the Log Analytics agent. This data is stored in a Log Analytics workspace. |
| Extend and connect | |
| Microsoft Entra ID | Connect your on-premises Windows Server Active Directory to Microsoft Entra ID to create a hybrid identity. Managed identities for Azure virtual machines provides Azure services with an automatically managed identity in Microsoft Entra ID. You can use this identity to authenticate to any service that supports Microsoft Entra authentication, without having credentials in your code. Improve the security of Windows virtual machines (VMs) in Azure by integrating with Microsoft Entra authentication. You can now use Microsoft Entra ID as a core authentication platform to remotely connect using the Remote Desktop Protocol (RDP) into Windows Server (starting with Windows Server 2019 Datacenter edition) or Windows 10 (starting with version 1809). |
Learn more about Windows Server on Azure at Windows virtual machines in Azure and how to migrate Windows Server to Azure at Azure Migrate.
Feedback
Coming soon: Throughout 2024 we will be phasing out GitHub Issues as the feedback mechanism for content and replacing it with a new feedback system. For more information see: https://aka.ms/ContentUserFeedback.
Submit and view feedback for