Tutorial: Use a Linux VM system-assigned managed identity to access Azure Storage
Managed identities for Azure resources is a feature of Microsoft Entra ID. Each of the Azure services that support managed identities for Azure resources are subject to their own timeline. Make sure you review the availability status of managed identities for your resource and known issues before you begin.
This tutorial shows you how to use a system-assigned managed identity for a Linux virtual machine (VM) to access Azure Storage. You learn how to:
- Create a storage account
- Create a blob container in a storage account
- Grant the Linux VM's Managed Identity access to an Azure Storage container
- Get an access token and use it to call Azure Storage
Prerequisites
- If you're not familiar with the managed identities for Azure resources feature, see this overview.
- If you don't have an Azure account, sign up for a free account before you continue.
- To perform the required resource creation and role management, your account needs "Owner" permissions at the appropriate scope (your subscription or resource group). If you need assistance with role assignment, see Assign Azure roles to manage access to your Azure subscription resources.
To run the CLI script examples in this tutorial, you have two options:
- Use Azure Cloud Shell either from the Azure portal, or via the Try It button, located in the top-right corner of each code block.
- Install the latest version of CLI 2.0 (2.0.23 or later) if you prefer to use a local CLI console.
Create a storage account
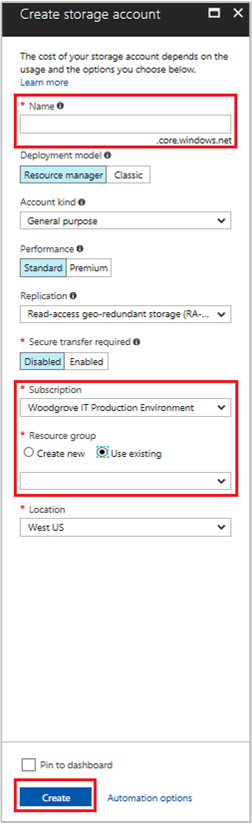
In this section, you create a storage account.
Select the + Create a resource button found on the upper left-hand corner of the Azure portal.
Select Storage, then Storage account - blob, file, table, queue.
Under Name, enter a name for the storage account.
Deployment model and Account kind should be set to Resource manager and Storage (general purpose v1).
Ensure the Subscription and Resource Group match the ones you specified when you created your VM in the previous step.
Select Create.
Create a blob container and upload a file to the storage account
Files require blob storage so you need to create a blob container in which to store the file. You then upload a file to the blob container in the new storage account.
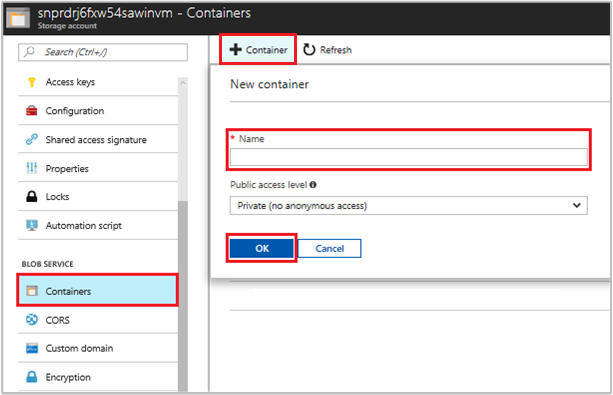
Navigate back to your newly created storage account.
Under Blob Service, select Containers.
Select + Container on the top of the page.
Under New container, enter a name for the container and under Public access level keep the default value.
Using an editor of your choice, create a file titled hello world.txt on your local machine. Open the file and add the text (without the quotes) "Hello world! :)" and then save it.
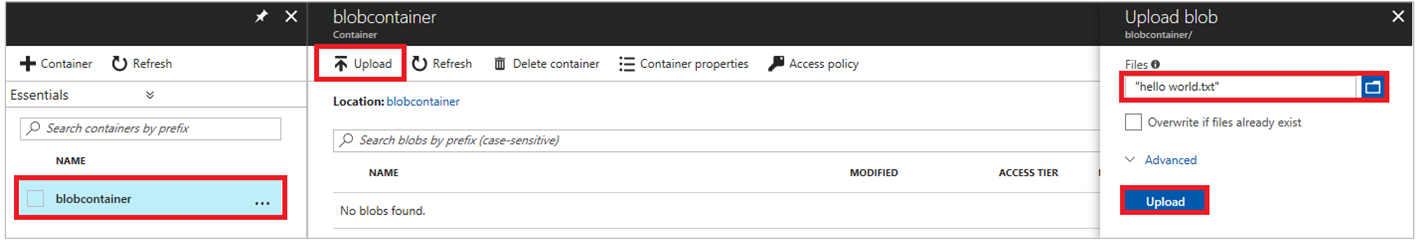
Upload the file to the newly created container by clicking on the container name, then Upload
In the Upload blob pane, under Files, select the folder icon and browse to the file hello_world.txt on your local machine, select the file, then select Upload.
Grant your VM access to an Azure Storage container
You can use the VM's managed identity to retrieve the data in the Azure storage blob. Managed identities for Azure resources, can be used to authenticate to resources that support Microsoft Entra authentication. Grant access by assigning the storage-blob-data-reader role to the managed-identity at the scope of the resource group that contains your storage account.
For detailed steps, see Assign Azure roles using the Azure portal.
Note
For more information on the various roles that you can use to grant permissions to storage review Authorize access to blobs and queues using Microsoft Entra ID
Get an access token and use it to call Azure Storage
Azure Storage natively supports Microsoft Entra authentication, so it can directly accept access tokens obtained using a Managed Identity. This is part of Azure Storage's integration with Microsoft Entra ID, and is different from supplying credentials on the connection string.
To complete the following steps, you need to work from the VM created earlier and you need an SSH client to connect to it. If you are using Windows, you can use the SSH client in the Windows Subsystem for Linux. If you need assistance configuring your SSH client's keys, see How to Use SSH keys with Windows on Azure, or How to create and use an SSH public and private key pair for Linux VMs in Azure.
In the Azure portal, navigate to Virtual Machines, go to your Linux virtual machine, then from the Overview page select Connect. Copy the string to connect to your VM.
Connect to the VM with the SSH client of your choice.
In the terminal window, use CURL to make a request to the local Managed Identity endpoint to get an access token for Azure Storage.
curl 'http://169.254.169.254/metadata/identity/oauth2/token?api-version=2018-02-01&resource=https%3A%2F%2Fstorage.azure.com%2F' -H Metadata:trueNow use the access token to access Azure Storage, for example to read the contents of the sample file which you previously uploaded to the container. Replace the values of
<STORAGE ACCOUNT>,<CONTAINER NAME>, and<FILE NAME>with the values you specified earlier, and<ACCESS TOKEN>with the token returned in the previous step.curl https://<STORAGE ACCOUNT>.blob.core.windows.net/<CONTAINER NAME>/<FILE NAME> -H "x-ms-version: 2017-11-09" -H "Authorization: Bearer <ACCESS TOKEN>"The response contains the contents of the file:
Hello world! :)
Alternatively, you could also store the token in a variable and pass it to the second command as shown:
# Run the first curl command and capture its output in a variable
access_token=$(curl 'http://169.254.169.254/metadata/identity/oauth2/token?api-version=2018-02-01&resource=https%3A%2F%2Fstorage.azure.com%2F' -H Metadata:true | jq -r '.access_token')
# Run the second curl command with the access token
curl "https://<STORAGE ACCOUNT>.blob.core.windows.net/<CONTAINER NAME>/<FILE NAME>" \
-H "x-ms-version: 2017-11-09" \
-H "Authorization: Bearer $access_token"
Next steps
In this tutorial, you learned how enable a Linux VM system-assigned managed identity to access Azure Storage. To learn more about Azure Storage see:
Feedback
Coming soon: Throughout 2024 we will be phasing out GitHub Issues as the feedback mechanism for content and replacing it with a new feedback system. For more information see: https://aka.ms/ContentUserFeedback.
Submit and view feedback for