Extract, transform, and load (ETL) at scale
Extract, transform, and load (ETL) is the process by which data is acquired from various sources. The data is collected in a standard location, cleaned, and processed. Ultimately, the data is loaded into a datastore from which it can be queried. Legacy ETL processes import data, clean it in place, and then store it in a relational data engine. With Azure HDInsight, a wide variety of Apache Hadoop environment components support ETL at scale.
The use of HDInsight in the ETL process is summarized by this pipeline:
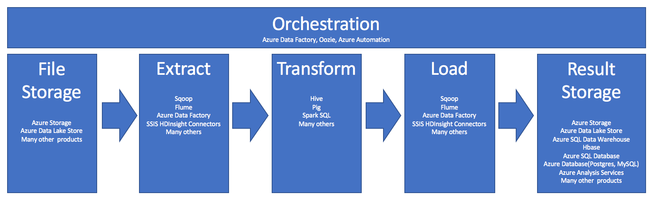
The following sections explore each of the ETL phases and their associated components.
Orchestration
Orchestration spans across all phases of the ETL pipeline. ETL jobs in HDInsight often involve several different products working in conjunction with each other. For example:
- You might use Apache Hive to clean a portion of the data, and Apache Pig to clean another portion.
- You might use Azure Data Factory to load data into Azure SQL Database from Azure Data Lake Store.
Orchestration is needed to run the appropriate job at the appropriate time.
Apache Oozie
Apache Oozie is a workflow coordination system that manages Hadoop jobs. Oozie runs within an HDInsight cluster and is integrated with the Hadoop stack. Oozie supports Hadoop jobs for Apache Hadoop MapReduce, Pig, Hive, and Sqoop. You can use Oozie to schedule jobs that are specific to a system, such as Java programs or shell scripts.
For more information, see Use Apache Oozie with Apache Hadoop to define and run a workflow on HDInsight. See also, Operationalize the data pipeline.
Azure Data Factory
Azure Data Factory provides orchestration capabilities in the form of platform as a service (PaaS). Azure Data Factory is a cloud-based data integration service. It allows you to create data-driven workflows for orchestrating and automating data movement and data transformation.
Use Azure Data Factory to:
- Create and schedule data-driven workflows. These pipelines ingest data from disparate data stores.
- Process and transform the data by using compute services such as HDInsight or Hadoop. You can also use Spark, Azure Data Lake Analytics, Azure Batch, or Azure Machine Learning for this step.
- Publish output data to data stores, such as Azure Synapse Analytics, for BI applications to consume.
For more information on Azure Data Factory, see the documentation.
Ingest file storage and result storage
Source data files are typically loaded into a location on Azure Storage or Azure Data Lake Storage. The files are usually in a flat format, like CSV. But, they can be in any format.
Azure Storage
Azure Storage has specific adaptability targets. See Scalability and performance targets for Blob storage for more information. For most analytic nodes, Azure Storage scales best when dealing with many smaller files. As long as you're within your account limits, Azure Storage guarantees the same performance, no matter how large the files are. You can store terabytes of data and still get consistent performance. This statement is true whether you're using a subset or all of the data.
Azure Storage has several types of blobs. An append blob is a great option for storing web logs or sensor data.
Multiple blobs can be distributed across many servers to scale out access to them. But a single blob is only served by a single server. Although blobs can be logically grouped in blob containers, there are no partitioning implications from this grouping.
Azure Storage has a WebHDFS API layer for the blob storage. All HDInsight services can access files in Azure Blob storage for data cleaning and data processing. This is similar to how those services would use Hadoop Distributed File System (HDFS).
Data is typically ingested into Azure Storage through PowerShell, the Azure Storage SDK, or AzCopy.
Azure Data Lake Storage
Azure Data Lake Storage is a managed, hyperscale repository for analytics data. It's compatible with and uses a design paradigm that's similar to HDFS. Data Lake Storage offers unlimited adaptability for total capacity and the size of individual files. It's a good choice when working with large files, because they can be stored across multiple nodes. Partitioning data in Data Lake Storage is done behind the scenes. You get massive throughput to run analytic jobs with thousands of concurrent executors that efficiently read and write hundreds of terabytes of data.
Data is usually ingested into Data Lake Storage through Azure Data Factory. You can also use Data Lake Storage SDKs, the AdlCopy service, Apache DistCp, or Apache Sqoop. The service you choose depends on where the data is. If it's in an existing Hadoop cluster, you might use Apache DistCp, the AdlCopy service, or Azure Data Factory. For data in Azure Blob storage, you might use Azure Data Lake Storage .NET SDK, Azure PowerShell, or Azure Data Factory.
Data Lake Storage is optimized for event ingestion through Azure Event Hubs.
Considerations for both storage options
For uploading datasets in the terabyte range, network latency can be a major problem. This is particularly true if the data is coming from an on-premises location. In such cases, you can use these options:
Azure ExpressRoute: Create private connections between Azure datacenters and your on-premises infrastructure. These connections provide a reliable option for transferring large amounts of data. For more information, see Azure ExpressRoute documentation.
Data upload from hard disk drives: You can use Azure Import/Export service to ship hard disk drives with your data to an Azure datacenter. Your data is first uploaded to Azure Blob storage. You can then use Azure Data Factory or the AdlCopy tool to copy data from Azure Blob storage to Data Lake Storage.
Azure Synapse Analytics
Azure Synapse Analytics is an appropriate choice to store prepared results. You can use Azure HDInsight to perform those services for Azure Synapse Analytics.
Azure Synapse Analytics is a relational database store optimized for analytic workloads. It scales based on partitioned tables. Tables can be partitioned across multiple nodes. The nodes are selected at the time of creation. They can scale after the fact, but that's an active process that might require data movement. For more information, see Manage compute in Azure Synapse Analytics.
Apache HBase
Apache HBase is a key/value store available in Azure HDInsight. It's an open-source, NoSQL database that's built on Hadoop and modeled after Google BigTable. HBase provides performant random access and strong consistency for large amounts of unstructured and semi-structured data.
Because HBase is a schemaless database, you don't need to define columns and data types before you use them. Data is stored in the rows of a table, and is grouped by column family.
The open-source code scales linearly to handle petabytes of data on thousands of nodes. HBase relies on data redundancy, batch processing, and other features that are provided by distributed applications in the Hadoop environment.
HBase is a good destination for sensor and log data for future analysis.
HBase adaptability is dependent on the number of nodes in the HDInsight cluster.
Azure SQL databases
Azure offers three PaaS relational databases:
- Azure SQL Database is an implementation of Microsoft SQL Server. For more information on performance, see Tuning Performance in Azure SQL Database.
- Azure Database for MySQL is an implementation of Oracle MySQL.
- Azure Database for PostgreSQL is an implementation of PostgreSQL.
Add more CPU and memory to scale up these products. You can also choose to use premium disks with the products for better I/O performance.
Azure Analysis Services
Azure Analysis Services is an analytical data engine used in decision support and business analytics. It provides the analytical data for business reports and client applications such as Power BI. The analytical data also works with Excel, SQL Server Reporting Services reports, and other data visualization tools.
Scale analysis cubes by changing tiers for each individual cube. For more information, see Azure Analysis Services pricing.
Extract and load
After the data exists in Azure, you can use many services to extract and load it into other products. HDInsight supports Sqoop and Flume.
Apache Sqoop
Apache Sqoop is a tool designed for efficiently transferring data between structured, semi-structured, and unstructured data sources.
Sqoop uses MapReduce to import and export the data, to provide parallel operation and fault tolerance.
Apache Flume
Apache Flume is a distributed, reliable, and available service for efficiently collecting, aggregating, and moving large amounts of log data. Its flexible architecture is based on streaming data flows. Flume is robust and fault-tolerant with tunable reliability mechanisms. It has many failover and recovery mechanisms. Flume uses a simple extensible data model that allows for online, analytic application.
Apache Flume can't be used with Azure HDInsight. But, an on-premises Hadoop installation can use Flume to send data to either Azure Blob storage or Azure Data Lake Storage. For more information, see Using Apache Flume with HDInsight.
Transform
After data exists in the chosen location, you need to clean it, combine it, or prepare it for a specific usage pattern. Hive, Pig, and Spark SQL are all good choices for that kind of work. They're all supported on HDInsight.
Next steps
Feedback
Coming soon: Throughout 2024 we will be phasing out GitHub Issues as the feedback mechanism for content and replacing it with a new feedback system. For more information see: https://aka.ms/ContentUserFeedback.
Submit and view feedback for