Quickstart: Deploy a Java Spring Boot app on Azure Service Fabric
In this quickstart, you deploy a Java Spring Boot application to Azure Service Fabric by using familiar command-line tools on Linux or macOS. Azure Service Fabric is a distributed systems platform for deploying and managing microservices and containers.
Prerequisites
Download the sample
In a terminal window, run the following command to clone the Spring Boot Getting Started sample app to your local machine.
git clone https://github.com/spring-guides/gs-spring-boot.git
Build the Spring Boot application
Inside the gs-spring-boot/complete directory, run the command below to build the application
./gradlew build
Package the Spring Boot application
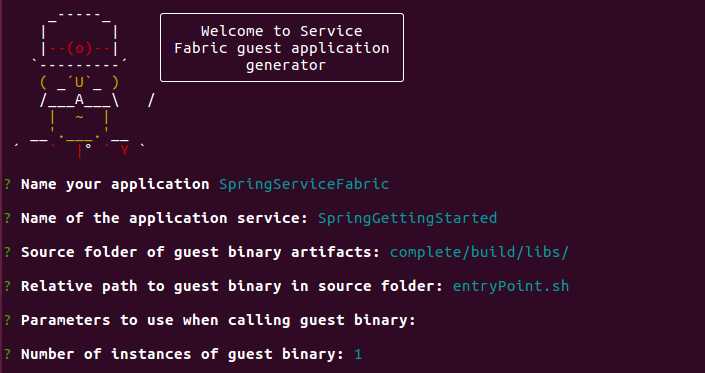
Inside the gs-spring-boot directory in your clone, run the
yo azuresfguestcommand.Enter the following details for each prompt.
In the SpringServiceFabric/SpringServiceFabric/SpringGettingStartedPkg/code folder, create a file called entryPoint.sh. Add the following code to the entryPoint.sh file.
#!/bin/bash BASEDIR=$(dirname $0) cd $BASEDIR java -jar *spring-boot*.jarAdd the Endpoints resource in the gs-spring-boot/SpringServiceFabric/SpringServiceFabric/SpringGettingStartedPkg/ServiceManifest.xml file
<Resources> <Endpoints> <Endpoint Name="WebEndpoint" Protocol="http" Port="8080" /> </Endpoints> </Resources>The ServiceManifest.xml now looks like this:
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="utf-8"?> <ServiceManifest Name="SpringGettingStartedPkg" Version="1.0.0" xmlns="http://schemas.microsoft.com/2011/01/fabric" xmlns:xsd="https://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema" xmlns:xsi="https://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance" > <ServiceTypes> <StatelessServiceType ServiceTypeName="SpringGettingStartedType" UseImplicitHost="true"> </StatelessServiceType> </ServiceTypes> <CodePackage Name="code" Version="1.0.0"> <EntryPoint> <ExeHost> <Program>entryPoint.sh</Program> <Arguments></Arguments> <WorkingFolder>CodePackage</WorkingFolder> </ExeHost> </EntryPoint> </CodePackage> <Resources> <Endpoints> <Endpoint Name="WebEndpoint" Protocol="http" Port="8080" /> </Endpoints> </Resources> </ServiceManifest>
At this stage, you have created a Service Fabric application for the Spring Boot Getting Started sample that you can deploy to Service Fabric.
Run the application locally
Start your local cluster on Ubuntu machines by running the following command:
sudo /opt/microsoft/sdk/servicefabric/common/clustersetup/devclustersetup.shIf using a Mac, start the local cluster from the Docker image (this is assuming you have followed the prerequisites to set up your local cluster for Mac).
docker run --name sftestcluster -d -p 19080:19080 -p 19000:19000 -p 25100-25200:25100-25200 -p 8080:8080 mysfclusterThe startup of the local cluster takes some time. To confirm that the cluster is fully up, access the Service Fabric Explorer at
http://localhost:19080. The five healthy nodes indicate the local cluster is up and running.
Open the gs-spring-boot/SpringServiceFabric folder.
Run the following command to connect to your local cluster.
sfctl cluster select --endpoint http://localhost:19080Run the install.sh script.
./install.shOpen your favorite web browser and access the application by accessing
http://localhost:8080.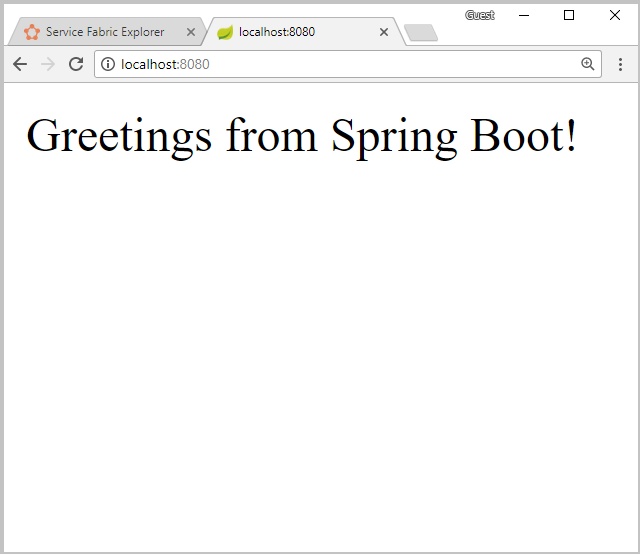
You can now access the Spring Boot application that was deployed to a Service Fabric cluster.
For more information, see the Spring Boot Getting Started sample on the Spring website.
Scale applications and services in a cluster
Services can be scaled across a cluster to accommodate for a change in load on the services. You scale a service by changing the number of instances running in the cluster. There are many ways of scaling your services, for example, you can use scripts or commands from Service Fabric CLI (sfctl). The following steps use Service Fabric Explorer.
Service Fabric Explorer runs in all Service Fabric clusters and can be accessed from a browser by browsing to the cluster's HTTP management port (19080); for example, http://localhost:19080.
To scale the web front-end service, do the following:
Open Service Fabric Explorer in your cluster - for example,
http://localhost:19080.Select the ellipsis (...) next to the fabric:/SpringServiceFabric/SpringGettingStarted node in the treeview and select Scale Service.

You can now choose to scale the number of instances of the service.
Change the number to 3 and select Scale Service.
An alternative way to scale the service using command line is as follows.
# Connect to your local cluster sfctl cluster select --endpoint https://<ConnectionIPOrURL>:19080 --pem <path_to_certificate> --no-verify # Run Bash command to scale instance count for your service sfctl service update --service-id 'SpringServiceFabric~SpringGettingStarted' --instance-count 3 --statelessSelect the fabric:/SpringServiceFabric/SpringGettingStarted node in the tree-view and expand the partition node (represented by a GUID).
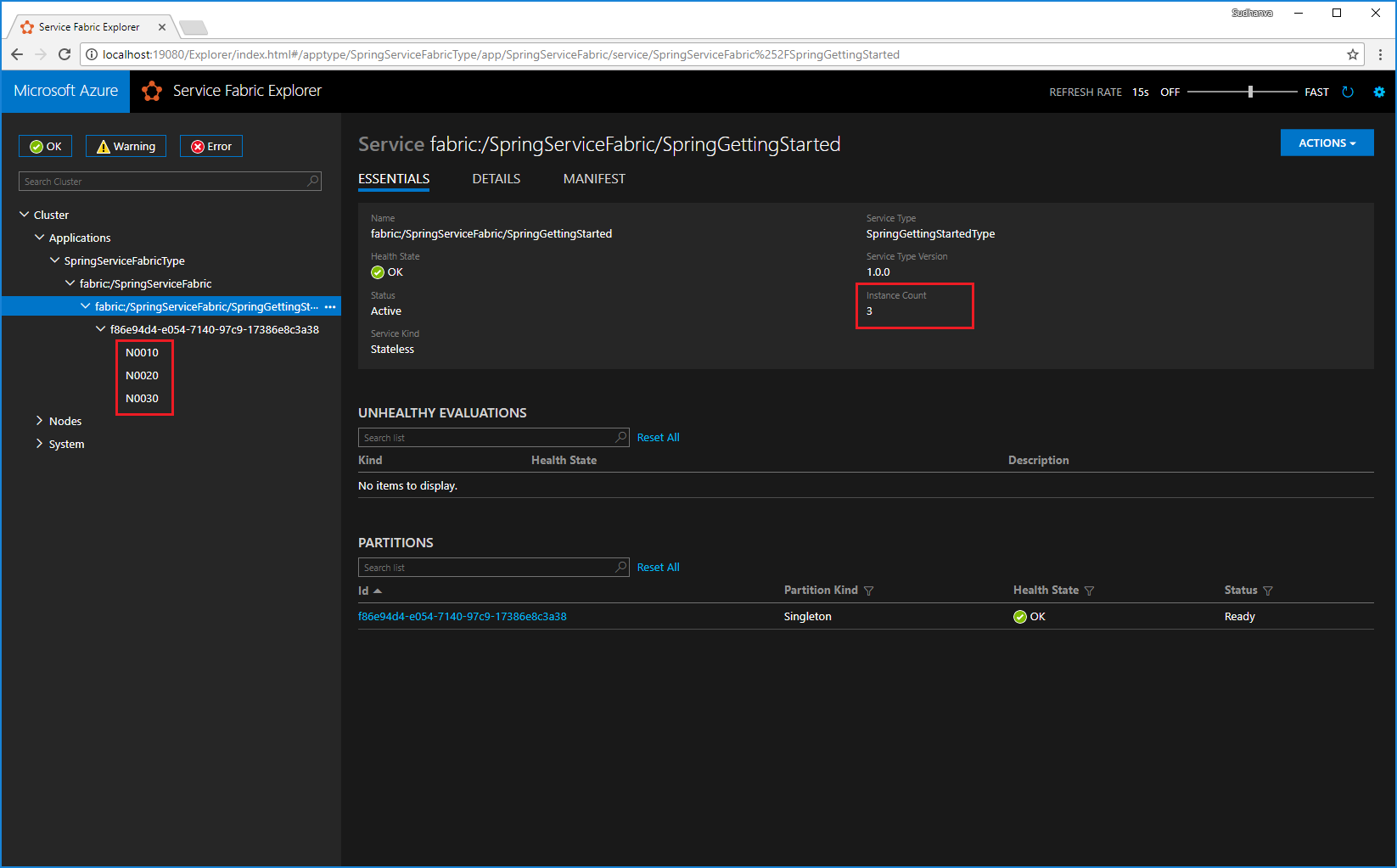
The service has three instances, and the tree view shows which nodes the instances run on.
Through this simple management task, you've doubled the resources available for the front-end service to process user load. It's important to understand that you don't need multiple instances of a service for it to run reliably. If a service fails, Service Fabric makes sure that a new service instance runs in the cluster.
Fail over services in a cluster
To demonstrate service failover, a node restart is simulated by using Service Fabric Explorer. Ensure only one instance of your service is running.
Open Service Fabric Explorer in your cluster - for example,
http://localhost:19080.Select the ellipsis (...) next to the node running the instance of your service and Restart the node.
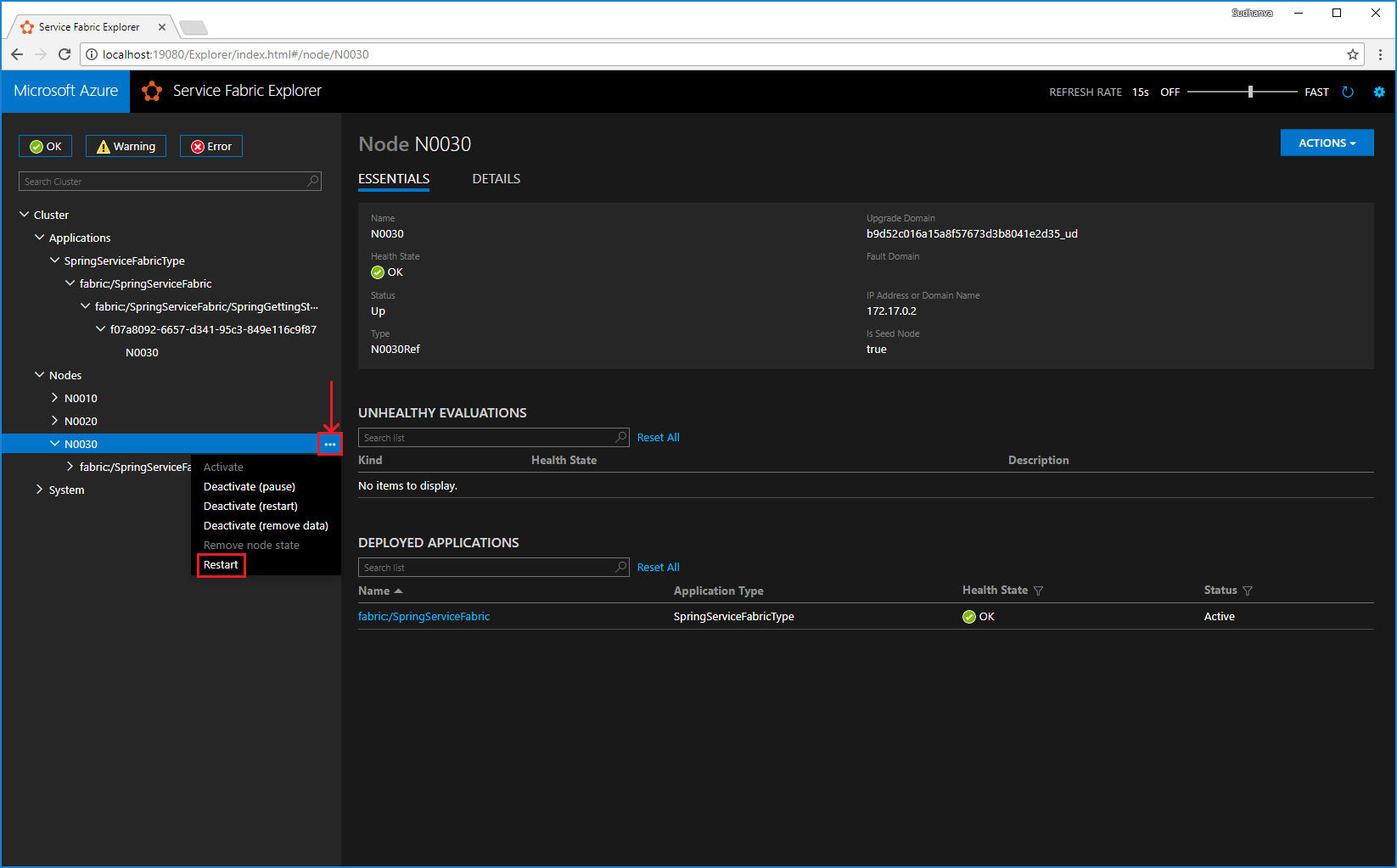
The instance of your service is moved to a different node and your application has no downtime.
Next steps
In this quickstart, you learned how to:
- Deploy a Spring Boot application to Service Fabric
- Deploy the application to your local cluster
- Scale out the application across multiple nodes
- Perform failover of your service with no hit to availability
To learn more about working with Java apps in Service Fabric, continue to the tutorial for Java apps.
Feedback
Coming soon: Throughout 2024 we will be phasing out GitHub Issues as the feedback mechanism for content and replacing it with a new feedback system. For more information see: https://aka.ms/ContentUserFeedback.
Submit and view feedback for