Run Apache Hive queries using the Data Lake tools for Visual Studio
Learn how to use the Data Lake tools for Visual Studio to query Apache Hive. The Data Lake tools allow you to easily create, submit, and monitor Hive queries to Apache Hadoop on Azure HDInsight.
Prerequisites
An Apache Hadoop cluster on HDInsight. For information about creating this item, see Create Apache Hadoop cluster in Azure HDInsight using Resource Manager template.
Visual Studio. The steps in this article use Visual Studio 2019.
HDInsight tools for Visual Studio or Azure Data Lake tools for Visual Studio. For information on installing and configuring the tools, see Install Data Lake Tools for Visual Studio.
Run Apache Hive queries using the Visual Studio
You have two options for creating and running Hive queries:
- Create ad-hoc queries.
- Create a Hive application.
Create an ad-hoc Hive query
Ad hoc queries can be executed in either Batch or Interactive mode.
Launch Visual Studio and select Continue without code.
From Server Explorer, right-click Azure, select Connect to Microsoft Azure Subscription..., and complete the sign in process.
Expand HDInsight, right-click the cluster where you want to run the query, and then select Write a Hive Query.
Enter the following hive query:
SELECT * FROM hivesampletable;Select Execute. The execution mode defaults to Interactive.
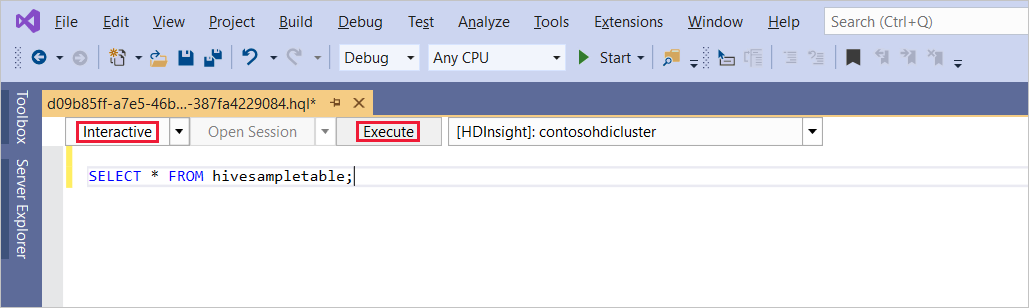
To run the same query in Batch mode, toggle the drop-down list from Interactive to Batch. The execution button changes from Execute to Submit.
The Hive editor supports IntelliSense. Data Lake Tools for Visual Studio supports loading remote metadata when you edit your Hive script. For example, if you type
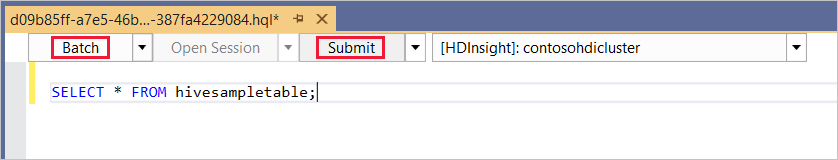
SELECT * FROM, IntelliSense lists all the suggested table names. When a table name is specified, IntelliSense lists the column names. The tools support most Hive DML statements, subqueries, and built-in UDFs. IntelliSense suggests only the metadata of the cluster that is selected in the HDInsight toolbar.In the query toolbar (the area below the query tab and above the query text), either select Submit, or select the pulldown arrow next to Submit and choose Advanced from the pulldown list. If you select the latter option,
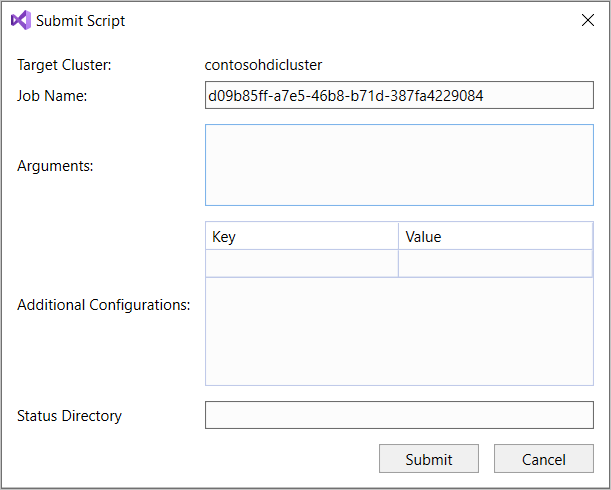
If you selected the advanced submit option, configure Job Name, Arguments, Additional Configurations, and Status Directory in the Submit Script dialog box. Then select Submit.
Create a Hive application
To run a Hive query by creating a Hive application, follow these steps:
Open Visual Studio.
In the Start window, select Create a new project.
In the Create a new project window, in the Search for templates box, enter Hive. Then choose Hive Application and select Next.
In the Configure your new project window, enter a Project name, select or create a Location for the new project, and then select Create.
Open the Script.hql file that is created with this project, and paste in the following HiveQL statements:
set hive.execution.engine=tez; DROP TABLE log4jLogs; CREATE EXTERNAL TABLE log4jLogs (t1 string, t2 string, t3 string, t4 string, t5 string, t6 string, t7 string) ROW FORMAT DELIMITED FIELDS TERMINATED BY ' ' STORED AS TEXTFILE LOCATION '/example/data/'; SELECT t4 AS sev, COUNT(*) AS count FROM log4jLogs WHERE t4 = '[ERROR]' AND INPUT__FILE__NAME LIKE '%.log' GROUP BY t4;These statements do the following actions:
DROP TABLE: Deletes the table if it exists.CREATE EXTERNAL TABLE: Creates a new 'external' table in Hive. External tables only store the table definition in Hive. (The data is left in the original location.)Note
External tables should be used when you expect the underlying data to be updated by an external source, such as a MapReduce job or an Azure service.
Dropping an external table does not delete the data, only the table definition.
ROW FORMAT: Tells Hive how the data is formatted. In this case, the fields in each log are separated by a space.STORED AS TEXTFILE LOCATION: Tells Hive that the data is stored in the example/data directory, and that it's stored as text.SELECT: Selects a count of all rows where columnt4contains the value[ERROR]. This statement returns a value of3, because three rows contain this value.INPUT__FILE__NAME LIKE '%.log': Tells Hive to only return data from files ending in .log. This clause restricts the search to the sample.log file that contains the data.
From the query file toolbar (which has a similar appearance to the ad-hoc query toolbar), select the HDInsight cluster that you want to use for this query. Then change Interactive to Batch (if necessary) and select Submit to run the statements as a Hive job.
The Hive Job Summary appears and displays information about the running job. Use the Refresh link to refresh the job information, until the Job Status changes to Completed.
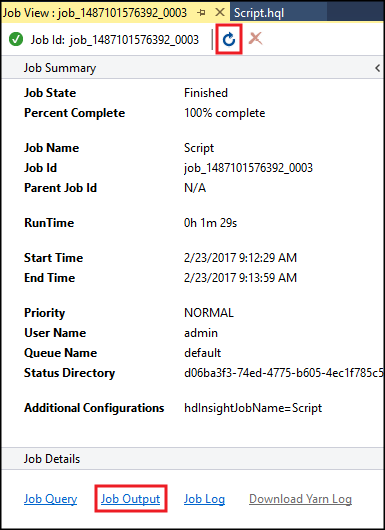
Select Job Output to view the output of this job. It displays
[ERROR] 3, which is the value returned by this query.
Additional example
The following example relies on the log4jLogs table created in the previous procedure, Create a Hive application.
From Server Explorer, right-click your cluster and select Write a Hive Query.
Enter the following hive query:
set hive.execution.engine=tez; CREATE TABLE IF NOT EXISTS errorLogs (t1 string, t2 string, t3 string, t4 string, t5 string, t6 string, t7 string) STORED AS ORC; INSERT OVERWRITE TABLE errorLogs SELECT t1, t2, t3, t4, t5, t6, t7 FROM log4jLogs WHERE t4 = '[ERROR]' AND INPUT__FILE__NAME LIKE '%.log';These statements do the following actions:
CREATE TABLE IF NOT EXISTS: Creates a table if it doesn't already exist. Because theEXTERNALkeyword isn't used, this statement creates an internal table. Internal tables are stored in the Hive data warehouse and are managed by Hive.Note
Unlike
EXTERNALtables, dropping an internal table also deletes the underlying data.STORED AS ORC: Stores the data in optimized row columnar (ORC) format. ORC is a highly optimized and efficient format for storing Hive data.INSERT OVERWRITE ... SELECT: Selects rows from thelog4jLogstable that contain[ERROR], then inserts the data into theerrorLogstable.
Change Interactive to Batch if necessary, then select Submit.
To verify that the job created the table, go to Server Explorer and expand Azure > HDInsight. Expand your HDInsight cluster, and then expand Hive Databases > default. The errorLogs table and the log4jLogs table are listed.
Next steps
As you can see, the HDInsight tools for Visual Studio provide an easy way to work with Hive queries on HDInsight.
For general information about Hive in HDInsight, see What is Apache Hive and HiveQL on Azure HDInsight?
For information about other ways you can work with Hadoop on HDInsight, see Use MapReduce in Apache Hadoop on HDInsight
For more information about the HDInsight tools for Visual Studio, seeUse Data Lake Tools for Visual Studio to connect to Azure HDInsight and run Apache Hive queries
Feedback
Coming soon: Throughout 2024 we will be phasing out GitHub Issues as the feedback mechanism for content and replacing it with a new feedback system. For more information see: https://aka.ms/ContentUserFeedback.
Submit and view feedback for