Quickstart: Scale compute for dedicated SQL pool (formerly SQL DW) in Azure Synapse Analytics using T-SQL
Scale compute in dedicated SQL pools using T-SQL and SQL Server Management Studio (SSMS). Scale out compute for better performance, or scale back compute to save costs.
If you don't have an Azure subscription, create a free Azure account before you begin.
Note
This article applies to dedicated SQL pools created in Azure Synapse Analytics workspaces, dedicated SQL pools (formerly SQL DW), and dedicated SQL pools (formerly SQL DW) in connected workspaces.
Before you begin
Download and install the newest version of SQL Server Management Studio (SSMS).
Create a dedicated SQL pool if needed
This quickstart assumes you already have a dedicated SQL pool.
If needed, it is recommended to create a new dedicated SQL pool in an Azure Synapse workspace. Create an Azure Synapse workspace and then create a dedicated SQL pool using Synapse Studio. Or, you can create a legacy dedicated SQL pool (formerly SQL DW), using Quickstart: create and Connect - portal to create a dedicated SQL pool (formerly SQL DW) named mySampleDataWarehouse.
Ensure you have a firewall rule and can connect to your dedicated SQL pool from within SQL Server Management Studio (SSMS).
Connect to the server as server admin
This section uses SQL Server Management Studio (SSMS) to establish a connection to your Azure SQL server.
Open SQL Server Management Studio.
In the Connect to Server dialog box, enter the following information:
Setting Suggested value Description Server type Database engine This value is required Server name The fully qualified server name Here's an example: mySampleDataWarehouseservername.database.windows.net. Authentication SQL Server Authentication SQL Authentication is the only authentication type that is configured in this tutorial. Login The server admin account The account that you specified when you created the server. Password The password for your server admin account The password you specified when you created the server. 
Select Connect. The Object Explorer window opens in SSMS.
In Object Explorer, expand Databases. Then expand
mySampleDataWarehouseto view the objects in your new database.
View service objective
The service objective setting contains the number of data warehouse units for the dedicated SQL pool (formerly SQL DW).
To view the current data warehouse units for your dedicated SQL pool (formerly SQL DW):
Under the connection to
mySampleDataWarehouseservername.database.windows.net, expand System Databases.Right-click on the
mastersystem database and select New Query. A new query window opens.Run the following query to select from the
sys.database_service_objectivesdynamic management view.SELECT db.name AS [Database] , ds.edition AS [Edition] , ds.service_objective AS [Service Objective] FROM sys.database_service_objectives ds JOIN sys.databases db ON ds.database_id = db.database_id WHERE db.name = 'mySampleDataWarehouse';The following results show
mySampleDataWarehousehas a service objective of DW400 in theService Objectivecolumn.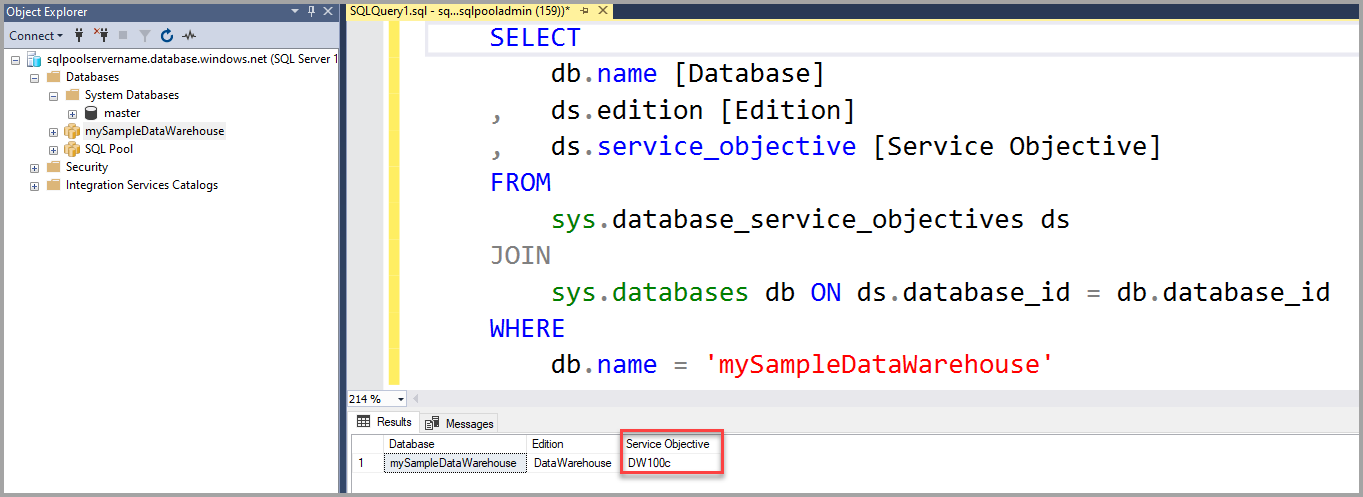
Scale compute
In dedicated SQL pool (formerly SQL DW), you can increase or decrease compute resources by adjusting data warehouse units. The Create and Connect - portal created mySampleDataWarehouse and initialized it with 400 DWUs. The following steps adjust the DWUs for mySampleDataWarehouse.
To change data warehouse units:
Right-click on the
mastersystem database and select New Query.Use the ALTER DATABASE T-SQL statement to modify the service objective. Run the following query to change the service objective to DW300.
ALTER DATABASE mySampleDataWarehouse MODIFY (SERVICE_OBJECTIVE = 'DW300c');
Monitor scale change request
To see the progress of the previous change request, you can use the WAITFORDELAY T-SQL syntax to poll the sys.dm_operation_status dynamic management view (DMV).
To poll for the service object change status:
Right-click on the
mastersystem database and select New Query.Run the following query to poll the sys.dm_operation_status DMV.
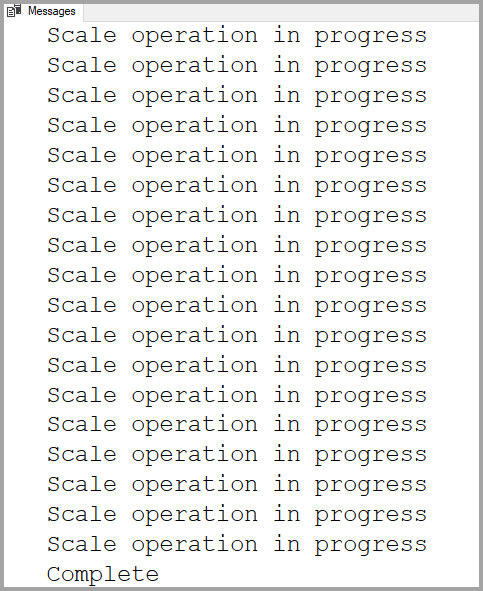
WHILE ( SELECT TOP 1 state_desc FROM sys.dm_operation_status WHERE 1=1 AND resource_type_desc = 'Database' AND major_resource_id = 'mySampleDataWarehouse' AND operation = 'ALTER DATABASE' ORDER BY start_time DESC ) = 'IN_PROGRESS' BEGIN RAISERROR('Scale operation in progress',0,0) WITH NOWAIT; WAITFOR DELAY '00:00:05'; END PRINT 'Complete';The resulting output shows a log of the polling of the status.
Check dedicated SQL pool (formerly SQL DW) state
When a dedicated SQL pool (formerly SQL DW) is paused, you can't connect to it with T-SQL. To see the current state of the dedicated SQL pool (formerly SQL DW), you can use a PowerShell cmdlet. For an example, see Check dedicated SQL pool (formerly SQL DW) state - PowerShell.
Check operation status
To return information about various management operations on your dedicated SQL pool (formerly SQL DW), run the following query on the sys.dm_operation_status DMV. For example, it returns the operation and the state of the operation, which is IN_PROGRESS or COMPLETED.
SELECT *
FROM
sys.dm_operation_status
WHERE
resource_type_desc = 'Database'
AND
major_resource_id = 'mySampleDataWarehouse';
Next steps
You've now learned how to scale compute for your dedicated SQL pool (formerly SQL DW). To learn more about Azure Synapse Analytics, continue to the tutorial for loading data.
Feedback
Coming soon: Throughout 2024 we will be phasing out GitHub Issues as the feedback mechanism for content and replacing it with a new feedback system. For more information see: https://aka.ms/ContentUserFeedback.
Submit and view feedback for