Deployment and Migration: System Center 2012 SP1 Explained – App Controller for VM and Cloud Service Deployment (Part 14 of 19) by Yung Chou
In Part 14 of the Deployment and Migration Blog Series, Yung Chou goes into detail on the configuration of System Center 2012 SP1 App Controller and Security settings in Virtual Machine Manager so that you can connect your On-Premises management toolset to Azure and manage both environments. I am including a brief snippet directly from Yung’s post below, but you will definitely want to go directly to his post to read the entire article.
One essential characteristics of cloud computing is a self-service mechanism. Both NIST SP 800-145 and Chou’s 5-3-2 Principle have discussed well. The self-servicing capability is essential since not only it reduces support cost fundamentally, but making it easy for a user to consume provided services will continually promote the usage and ultimately accelerate the ROI.  In System Center 2012 SP1, App Controller is the self-service vehicle for managing a hybrid cloud based on SCVMM, Windows Azure, and 3rd party hosting services.
In System Center 2012 SP1, App Controller is the self-service vehicle for managing a hybrid cloud based on SCVMM, Windows Azure, and 3rd party hosting services.
This article assumes a reader is familiar with System Center 2012 SP1, and particularly System Center Virtual Machine Manager (SCVMM) and App Controller. Those who are new to System Center 2012 SP1 should first download and install at least SCVMM 2012 SP1and App Controller 2012 SP1 from https://aka.ms/2012 to better follow the presented content.
Role-Based Security Model for Delegating Authority
The concept of a role-based security model in SCVMM is to package security settings and policies on who can do what, and how much on an object into a single concept, the so-called user role. The idea of a user role is to define a job function which a user performs as opposed to simply offering a logical group of selected user accounts.
To delegate authority, a user role is set with tasks, scope, and quotas based on a target business role and assigned responsibilities. The members of a user role are then with the authority to carry out specific tasks on authorized objects for performing a defined business function. For instance, a first-tier help desk support may perform a few specific diagnostic operations on a VM or service, but not debugging, storing, or redeploying it, while a datacenter administrator as an escalation path for the first-tier help desk can do all. In this case, a help desk support and an escalation engineer are to be defined as two user roles for delegating authority.
User-Role Defined in SCVMM Settings
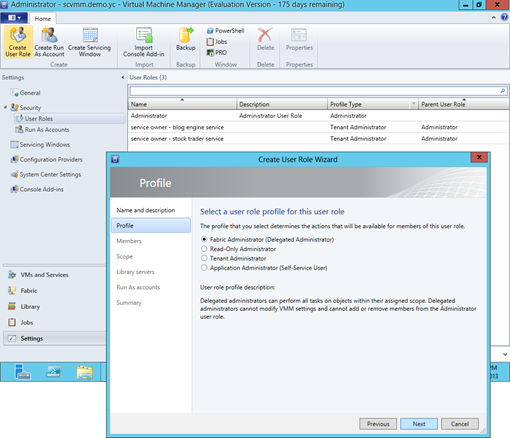
Operationally, creating a user role is to configure a profile which include membership, scope, resources, credentials, etc. A user role defines who can do what and how much on an authorized resource. And in essence a defined user role is a policy imposed on those who are assigned with this role, i.e. having a membership of this role.
To set up a user role in SCVMM, use the admin console and go to Setting workspace followed by clicking Create User Role from the ribbon as shown below. There are four user roles profiles available in SCVMM 2012 SP1. Each profile includes membership, scope, accessible networks and resources, allowed operations, etc.
- A Fabric Administrator or a Delegated Administrator can perform all tasks on objects within assigned scope. This role however can change neither VMM settings, nor the Administrator user role membership. The scope of this role include all services deployed and host groups added into SCVMM admin console.
….
Harold Wong