Part 3, scaffolded Razor Pages in ASP.NET Core
Note
This isn't the latest version of this article. For the current release, see the .NET 8 version of this article.
Important
This information relates to a pre-release product that may be substantially modified before it's commercially released. Microsoft makes no warranties, express or implied, with respect to the information provided here.
For the current release, see the .NET 8 version of this article.
This tutorial examines the Razor Pages created by scaffolding in the previous tutorial.
The Create, Delete, Details, and Edit pages
Examine the Pages/Movies/Index.cshtml.cs Page Model:
using Microsoft.AspNetCore.Mvc.RazorPages;
using Microsoft.EntityFrameworkCore;
using RazorPagesMovie.Models;
namespace RazorPagesMovie.Pages.Movies;
public class IndexModel : PageModel
{
private readonly RazorPagesMovie.Data.RazorPagesMovieContext _context;
public IndexModel(RazorPagesMovie.Data.RazorPagesMovieContext context)
{
_context = context;
}
public IList<Movie> Movie { get;set; } = default!;
public async Task OnGetAsync()
{
if (_context.Movie != null)
{
Movie = await _context.Movie.ToListAsync();
}
}
}
Razor Pages are derived from PageModel. By convention, the PageModel derived class is named PageNameModel. For example, the Index page is named IndexModel.
The constructor uses dependency injection to add the RazorPagesMovieContext to the page:
public class IndexModel : PageModel
{
private readonly RazorPagesMovie.Data.RazorPagesMovieContext _context;
public IndexModel(RazorPagesMovie.Data.RazorPagesMovieContext context)
{
_context = context;
}
See Asynchronous code for more information on asynchronous programming with Entity Framework.
When a GET request is made for the page, the OnGetAsync method returns a list of movies to the Razor Page. On a Razor Page, OnGetAsync or OnGet is called to initialize the state of the page. In this case, OnGetAsync gets a list of movies and displays them.
When OnGet returns void or OnGetAsync returns Task, no return statement is used. For example, examine the Privacy Page:
using Microsoft.AspNetCore.Mvc;
using Microsoft.AspNetCore.Mvc.RazorPages;
namespace RazorPagesMovie.Pages
{
public class PrivacyModel : PageModel
{
private readonly ILogger<PrivacyModel> _logger;
public PrivacyModel(ILogger<PrivacyModel> logger)
{
_logger = logger;
}
public void OnGet()
{
}
}
}
When the return type is IActionResult or Task<IActionResult>, a return statement must be provided. For example, the Pages/Movies/Create.cshtml.cs OnPostAsync method:
public async Task<IActionResult> OnPostAsync()
{
if (!ModelState.IsValid)
{
return Page();
}
_context.Movie.Add(Movie);
await _context.SaveChangesAsync();
return RedirectToPage("./Index");
}
Examine the Pages/Movies/Index.cshtml Razor Page:
@page
@model RazorPagesMovie.Pages.Movies.IndexModel
@{
ViewData["Title"] = "Index";
}
<h1>Index</h1>
<p>
<a asp-page="Create">Create New</a>
</p>
<table class="table">
<thead>
<tr>
<th>
@Html.DisplayNameFor(model => model.Movie[0].Title)
</th>
<th>
@Html.DisplayNameFor(model => model.Movie[0].ReleaseDate)
</th>
<th>
@Html.DisplayNameFor(model => model.Movie[0].Genre)
</th>
<th>
@Html.DisplayNameFor(model => model.Movie[0].Price)
</th>
<th></th>
</tr>
</thead>
<tbody>
@foreach (var item in Model.Movie) {
<tr>
<td>
@Html.DisplayFor(modelItem => item.Title)
</td>
<td>
@Html.DisplayFor(modelItem => item.ReleaseDate)
</td>
<td>
@Html.DisplayFor(modelItem => item.Genre)
</td>
<td>
@Html.DisplayFor(modelItem => item.Price)
</td>
<td>
<a asp-page="./Edit" asp-route-id="@item.Id">Edit</a> |
<a asp-page="./Details" asp-route-id="@item.Id">Details</a> |
<a asp-page="./Delete" asp-route-id="@item.Id">Delete</a>
</td>
</tr>
}
</tbody>
</table>
Razor can transition from HTML into C# or into Razor-specific markup. When an @ symbol is followed by a Razor reserved keyword, it transitions into Razor-specific markup, otherwise it transitions into C#.
The @page directive
The @page Razor directive makes the file an MVC action, which means that it can handle requests. @page must be the first Razor directive on a page. @page and @model are examples of transitioning into Razor-specific markup. See Razor syntax for more information.
The @model directive
@page
@model RazorPagesMovie.Pages.Movies.IndexModel
The @model directive specifies the type of the model passed to the Razor Page. In the preceding example, the @model line makes the PageModel derived class available to the Razor Page. The model is used in the @Html.DisplayNameFor and @Html.DisplayFor HTML Helpers on the page.
Examine the lambda expression used in the following HTML Helper:
@Html.DisplayNameFor(model => model.Movie[0].Title)
The DisplayNameFor HTML Helper inspects the Title property referenced in the lambda expression to determine the display name. The lambda expression is inspected rather than evaluated. That means there is no access violation when model, model.Movie, or model.Movie[0] is null or empty. When the lambda expression is evaluated, for example, with @Html.DisplayFor(modelItem => item.Title), the model's property values are evaluated.
The layout page
Select the menu links RazorPagesMovie, Home, and Privacy. Each page shows the same menu layout. The menu layout is implemented in the Pages/Shared/_Layout.cshtml file.
Open and examine the Pages/Shared/_Layout.cshtml file.
Layout templates allow the HTML container layout to be:
- Specified in one place.
- Applied in multiple pages in the site.
Find the @RenderBody() line. RenderBody is a placeholder where all the page-specific views show up, wrapped in the layout page. For example, select the Privacy link and the Pages/Privacy.cshtml view is rendered inside the RenderBody method.
ViewData and layout
Consider the following markup from the Pages/Movies/Index.cshtml file:
@page
@model RazorPagesMovie.Pages.Movies.IndexModel
@{
ViewData["Title"] = "Index";
}
The preceding highlighted markup is an example of Razor transitioning into C#. The { and } characters enclose a block of C# code.
The PageModel base class contains a ViewData dictionary property that can be used to pass data to a View. Objects are added to the ViewData dictionary using a key value pattern. In the preceding sample, the Title property is added to the ViewData dictionary.
The Title property is used in the Pages/Shared/_Layout.cshtml file. The following markup shows the first few lines of the _Layout.cshtml file.
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="en">
<head>
<meta charset="utf-8" />
<meta name="viewport" content="width=device-width, initial-scale=1.0" />
<title>@ViewData["Title"] - RazorPagesMovie</title>
<link rel="stylesheet" href="~/lib/bootstrap/dist/css/bootstrap.min.css" />
<link rel="stylesheet" href="~/css/site.css" asp-append-version="true" />
<link rel="stylesheet" href="~/RazorPagesMovie.styles.css" asp-append-version="true" />
Update the layout
Change the
<title>element in thePages/Shared/_Layout.cshtmlfile to display Movie rather than RazorPagesMovie.<!DOCTYPE html> <html lang="en"> <head> <meta charset="utf-8" /> <meta name="viewport" content="width=device-width, initial-scale=1.0" /> <title>@ViewData["Title"] - Movie</title>Find the following anchor element in the
Pages/Shared/_Layout.cshtmlfile.<a class="navbar-brand" asp-area="" asp-page="/Index">RazorPagesMovie</a>Replace the preceding element with the following markup:
<a class="navbar-brand" asp-page="/Movies/Index">RpMovie</a>The preceding anchor element is a Tag Helper. In this case, it's the Anchor Tag Helper. The
asp-page="/Movies/Index"Tag Helper attribute and value creates a link to the/Movies/IndexRazor Page. Theasp-areaattribute value is empty, so the area isn't used in the link. See Areas for more information.Save the changes and test the app by selecting the RpMovie link. See the _Layout.cshtml file in GitHub if you have any problems.
Test the Home, RpMovie, Create, Edit, and Delete links. Each page sets the title, which you can see in the browser tab. When you bookmark a page, the title is used for the bookmark.
Note
You may not be able to enter decimal commas in the Price field. To support jQuery validation for non-English locales that use a comma (",") for a decimal point, and non US-English date formats, you must take steps to globalize the app. See this GitHub issue 4076 for instructions on adding decimal comma.
The Layout property is set in the Pages/_ViewStart.cshtml file:
@{
Layout = "_Layout";
}
The preceding markup sets the layout file to Pages/Shared/_Layout.cshtml for all Razor files under the Pages folder. See Layout for more information.
The Create page model
Examine the Pages/Movies/Create.cshtml.cs page model:
using Microsoft.AspNetCore.Mvc;
using Microsoft.AspNetCore.Mvc.RazorPages;
using RazorPagesMovie.Models;
namespace RazorPagesMovie.Pages.Movies
{
public class CreateModel : PageModel
{
private readonly RazorPagesMovie.Data.RazorPagesMovieContext _context;
public CreateModel(RazorPagesMovie.Data.RazorPagesMovieContext context)
{
_context = context;
}
public IActionResult OnGet()
{
return Page();
}
[BindProperty]
public Movie Movie { get; set; } = default!;
// To protect from overposting attacks, see https://aka.ms/RazorPagesCRUD
public async Task<IActionResult> OnPostAsync()
{
if (!ModelState.IsValid || _context.Movie == null || Movie == null)
{
return Page();
}
_context.Movie.Add(Movie);
await _context.SaveChangesAsync();
return RedirectToPage("./Index");
}
}
}
The OnGet method initializes any state needed for the page. The Create page doesn't have any state to initialize, so Page is returned. Later in the tutorial, an example of OnGet initializing state is shown. The Page method creates a PageResult object that renders the Create.cshtml page.
The Movie property uses the [BindProperty] attribute to opt-in to model binding. When the Create form posts the form values, the ASP.NET Core runtime binds the posted values to the Movie model.
The OnPostAsync method is run when the page posts form data:
public async Task<IActionResult> OnPostAsync()
{
if (!ModelState.IsValid)
{
return Page();
}
_context.Movie.Add(Movie);
await _context.SaveChangesAsync();
return RedirectToPage("./Index");
}
If there are any model errors, the form is redisplayed, along with any form data posted. Most model errors can be caught on the client-side before the form is posted. An example of a model error is posting a value for the date field that cannot be converted to a date. Client-side validation and model validation are discussed later in the tutorial.
If there are no model errors:
- The data is saved.
- The browser is redirected to the Index page.
The Create Razor Page
Examine the Pages/Movies/Create.cshtml Razor Page file:
@page
@model RazorPagesMovie.Pages.Movies.CreateModel
@{
ViewData["Title"] = "Create";
}
<h1>Create</h1>
<h4>Movie</h4>
<hr />
<div class="row">
<div class="col-md-4">
<form method="post">
<div asp-validation-summary="ModelOnly" class="text-danger"></div>
<div class="form-group">
<label asp-for="Movie.Title" class="control-label"></label>
<input asp-for="Movie.Title" class="form-control" />
<span asp-validation-for="Movie.Title" class="text-danger"></span>
</div>
<div class="form-group">
<label asp-for="Movie.ReleaseDate" class="control-label"></label>
<input asp-for="Movie.ReleaseDate" class="form-control" />
<span asp-validation-for="Movie.ReleaseDate" class="text-danger"></span>
</div>
<div class="form-group">
<label asp-for="Movie.Genre" class="control-label"></label>
<input asp-for="Movie.Genre" class="form-control" />
<span asp-validation-for="Movie.Genre" class="text-danger"></span>
</div>
<div class="form-group">
<label asp-for="Movie.Price" class="control-label"></label>
<input asp-for="Movie.Price" class="form-control" />
<span asp-validation-for="Movie.Price" class="text-danger"></span>
</div>
<div class="form-group">
<input type="submit" value="Create" class="btn btn-primary" />
</div>
</form>
</div>
</div>
<div>
<a asp-page="Index">Back to List</a>
</div>
@section Scripts {
@{await Html.RenderPartialAsync("_ValidationScriptsPartial");}
}
Visual Studio displays the following tags in a distinctive bold font used for Tag Helpers:
<form method="post"><div asp-validation-summary="ModelOnly" class="text-danger"></div><label asp-for="Movie.Title" class="control-label"></label><input asp-for="Movie.Title" class="form-control" /><span asp-validation-for="Movie.Title" class="text-danger"></span>
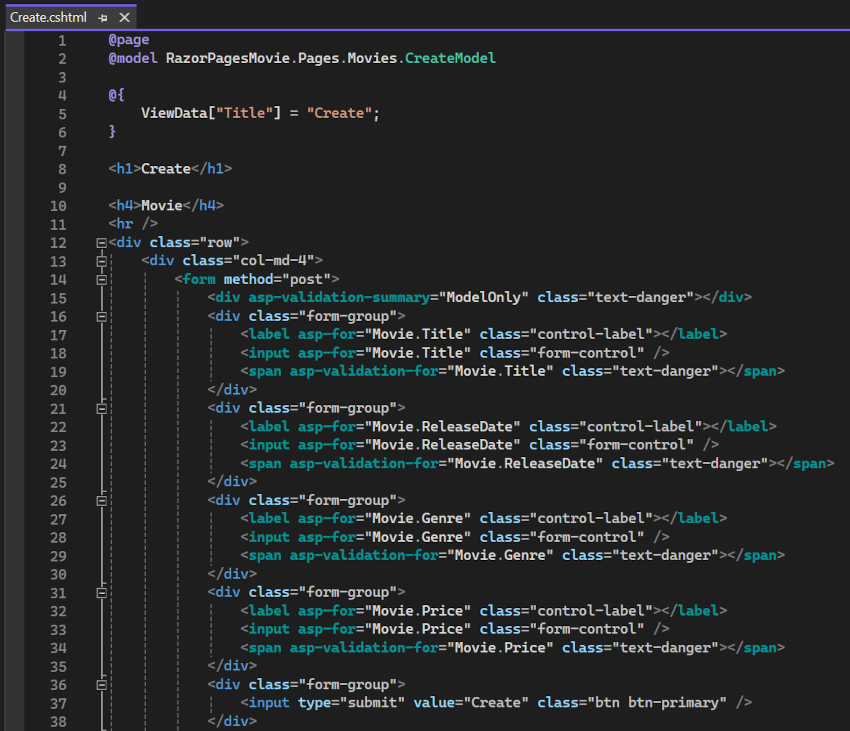
The <form method="post"> element is a Form Tag Helper. The Form Tag Helper automatically includes an antiforgery token.
The scaffolding engine creates Razor markup for each field in the model, except the ID, similar to the following:
<div asp-validation-summary="ModelOnly" class="text-danger"></div>
<div class="form-group">
<label asp-for="Movie.Title" class="control-label"></label>
<input asp-for="Movie.Title" class="form-control" />
<span asp-validation-for="Movie.Title" class="text-danger"></span>
</div>
The Validation Tag Helpers (<div asp-validation-summary and <span asp-validation-for) display validation errors. Validation is covered in more detail later in this series.
The Label Tag Helper (<label asp-for="Movie.Title" class="control-label"></label>) generates the label caption and [for] attribute for the Title property.
The Input Tag Helper (<input asp-for="Movie.Title" class="form-control">) uses the DataAnnotations attributes and produces HTML attributes needed for jQuery Validation on the client-side.
For more information on Tag Helpers such as <form method="post">, see Tag Helpers in ASP.NET Core.
Next steps
The Create, Delete, Details, and Edit pages
Examine the Pages/Movies/Index.cshtml.cs Page Model:
using Microsoft.AspNetCore.Mvc.RazorPages;
using Microsoft.EntityFrameworkCore;
using RazorPagesMovie.Models;
namespace RazorPagesMovie.Pages.Movies;
public class IndexModel : PageModel
{
private readonly RazorPagesMovie.Data.RazorPagesMovieContext _context;
public IndexModel(RazorPagesMovie.Data.RazorPagesMovieContext context)
{
_context = context;
}
public IList<Movie> Movie { get;set; } = default!;
public async Task OnGetAsync()
{
if (_context.Movie != null)
{
Movie = await _context.Movie.ToListAsync();
}
}
}
Razor Pages are derived from PageModel. By convention, the PageModel derived class is named PageNameModel. For example, the Index page is named IndexModel.
The constructor uses dependency injection to add the RazorPagesMovieContext to the page:
public class IndexModel : PageModel
{
private readonly RazorPagesMovie.Data.RazorPagesMovieContext _context;
public IndexModel(RazorPagesMovie.Data.RazorPagesMovieContext context)
{
_context = context;
}
See Asynchronous code for more information on asynchronous programming with Entity Framework.
When a GET request is made for the page, the OnGetAsync method returns a list of movies to the Razor Page. On a Razor Page, OnGetAsync or OnGet is called to initialize the state of the page. In this case, OnGetAsync gets a list of movies and displays them.
When OnGet returns void or OnGetAsync returns Task, no return statement is used. For example, examine the Privacy Page:
using Microsoft.AspNetCore.Mvc;
using Microsoft.AspNetCore.Mvc.RazorPages;
namespace RazorPagesMovie.Pages
{
public class PrivacyModel : PageModel
{
private readonly ILogger<PrivacyModel> _logger;
public PrivacyModel(ILogger<PrivacyModel> logger)
{
_logger = logger;
}
public void OnGet()
{
}
}
}
When the return type is IActionResult or Task<IActionResult>, a return statement must be provided. For example, the Pages/Movies/Create.cshtml.cs OnPostAsync method:
public async Task<IActionResult> OnPostAsync()
{
if (!ModelState.IsValid)
{
return Page();
}
_context.Movie.Add(Movie);
await _context.SaveChangesAsync();
return RedirectToPage("./Index");
}
Examine the Pages/Movies/Index.cshtml Razor Page:
@page
@model RazorPagesMovie.Pages.Movies.IndexModel
@{
ViewData["Title"] = "Index";
}
<h1>Index</h1>
<p>
<a asp-page="Create">Create New</a>
</p>
<table class="table">
<thead>
<tr>
<th>
@Html.DisplayNameFor(model => model.Movie[0].Title)
</th>
<th>
@Html.DisplayNameFor(model => model.Movie[0].ReleaseDate)
</th>
<th>
@Html.DisplayNameFor(model => model.Movie[0].Genre)
</th>
<th>
@Html.DisplayNameFor(model => model.Movie[0].Price)
</th>
<th></th>
</tr>
</thead>
<tbody>
@foreach (var item in Model.Movie) {
<tr>
<td>
@Html.DisplayFor(modelItem => item.Title)
</td>
<td>
@Html.DisplayFor(modelItem => item.ReleaseDate)
</td>
<td>
@Html.DisplayFor(modelItem => item.Genre)
</td>
<td>
@Html.DisplayFor(modelItem => item.Price)
</td>
<td>
<a asp-page="./Edit" asp-route-id="@item.Id">Edit</a> |
<a asp-page="./Details" asp-route-id="@item.Id">Details</a> |
<a asp-page="./Delete" asp-route-id="@item.Id">Delete</a>
</td>
</tr>
}
</tbody>
</table>
Razor can transition from HTML into C# or into Razor-specific markup. When an @ symbol is followed by a Razor reserved keyword, it transitions into Razor-specific markup, otherwise it transitions into C#.
The @page directive
The @page Razor directive makes the file an MVC action, which means that it can handle requests. @page must be the first Razor directive on a page. @page and @model are examples of transitioning into Razor-specific markup. See Razor syntax for more information.
The @model directive
@page
@model RazorPagesMovie.Pages.Movies.IndexModel
The @model directive specifies the type of the model passed to the Razor Page. In the preceding example, the @model line makes the PageModel derived class available to the Razor Page. The model is used in the @Html.DisplayNameFor and @Html.DisplayFor HTML Helpers on the page.
Examine the lambda expression used in the following HTML Helper:
@Html.DisplayNameFor(model => model.Movie[0].Title)
The DisplayNameFor HTML Helper inspects the Title property referenced in the lambda expression to determine the display name. The lambda expression is inspected rather than evaluated. That means there is no access violation when model, model.Movie, or model.Movie[0] is null or empty. When the lambda expression is evaluated, for example, with @Html.DisplayFor(modelItem => item.Title), the model's property values are evaluated.
The layout page
Select the menu links RazorPagesMovie, Home, and Privacy. Each page shows the same menu layout. The menu layout is implemented in the Pages/Shared/_Layout.cshtml file.
Open and examine the Pages/Shared/_Layout.cshtml file.
Layout templates allow the HTML container layout to be:
- Specified in one place.
- Applied in multiple pages in the site.
Find the @RenderBody() line. RenderBody is a placeholder where all the page-specific views show up, wrapped in the layout page. For example, select the Privacy link and the Pages/Privacy.cshtml view is rendered inside the RenderBody method.
ViewData and layout
Consider the following markup from the Pages/Movies/Index.cshtml file:
@page
@model RazorPagesMovie.Pages.Movies.IndexModel
@{
ViewData["Title"] = "Index";
}
The preceding highlighted markup is an example of Razor transitioning into C#. The { and } characters enclose a block of C# code.
The PageModel base class contains a ViewData dictionary property that can be used to pass data to a View. Objects are added to the ViewData dictionary using a key value pattern. In the preceding sample, the Title property is added to the ViewData dictionary.
The Title property is used in the Pages/Shared/_Layout.cshtml file. The following markup shows the first few lines of the _Layout.cshtml file.
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="en">
<head>
<meta charset="utf-8" />
<meta name="viewport" content="width=device-width, initial-scale=1.0" />
<title>@ViewData["Title"] - RazorPagesMovie</title>
<link rel="stylesheet" href="~/lib/bootstrap/dist/css/bootstrap.min.css" />
<link rel="stylesheet" href="~/css/site.css" asp-append-version="true" />
<link rel="stylesheet" href="~/RazorPagesMovie.styles.css" asp-append-version="true" />
The line @*Markup removed for brevity.*@ is a Razor comment. Unlike HTML comments <!-- -->, Razor comments are not sent to the client. See MDN web docs: Getting started with HTML for more information.
Update the layout
Change the
<title>element in thePages/Shared/_Layout.cshtmlfile to display Movie rather than RazorPagesMovie.<!DOCTYPE html> <html lang="en"> <head> <meta charset="utf-8" /> <meta name="viewport" content="width=device-width, initial-scale=1.0" /> <title>@ViewData["Title"] - Movie</title>Find the following anchor element in the
Pages/Shared/_Layout.cshtmlfile.<a class="navbar-brand" asp-area="" asp-page="/Index">RazorPagesMovie</a>Replace the preceding element with the following markup:
<a class="navbar-brand" asp-page="/Movies/Index">RpMovie</a>The preceding anchor element is a Tag Helper. In this case, it's the Anchor Tag Helper. The
asp-page="/Movies/Index"Tag Helper attribute and value creates a link to the/Movies/IndexRazor Page. Theasp-areaattribute value is empty, so the area isn't used in the link. See Areas for more information.Save the changes and test the app by selecting the RpMovie link. See the _Layout.cshtml file in GitHub if you have any problems.
Test the Home, RpMovie, Create, Edit, and Delete links. Each page sets the title, which you can see in the browser tab. When you bookmark a page, the title is used for the bookmark.
Note
You may not be able to enter decimal commas in the Price field. To support jQuery validation for non-English locales that use a comma (",") for a decimal point, and non US-English date formats, you must take steps to globalize the app. See this GitHub issue 4076 for instructions on adding decimal comma.
The Layout property is set in the Pages/_ViewStart.cshtml file:
@{
Layout = "_Layout";
}
The preceding markup sets the layout file to Pages/Shared/_Layout.cshtml for all Razor files under the Pages folder. See Layout for more information.
The Create page model
Examine the Pages/Movies/Create.cshtml.cs page model:
using Microsoft.AspNetCore.Mvc;
using Microsoft.AspNetCore.Mvc.RazorPages;
using RazorPagesMovie.Models;
namespace RazorPagesMovie.Pages.Movies
{
public class CreateModel : PageModel
{
private readonly RazorPagesMovie.Data.RazorPagesMovieContext _context;
public CreateModel(RazorPagesMovie.Data.RazorPagesMovieContext context)
{
_context = context;
}
public IActionResult OnGet()
{
return Page();
}
[BindProperty]
public Movie Movie { get; set; } = default!;
// To protect from overposting attacks, see https://aka.ms/RazorPagesCRUD
public async Task<IActionResult> OnPostAsync()
{
if (!ModelState.IsValid || _context.Movie == null || Movie == null)
{
return Page();
}
_context.Movie.Add(Movie);
await _context.SaveChangesAsync();
return RedirectToPage("./Index");
}
}
}
The OnGet method initializes any state needed for the page. The Create page doesn't have any state to initialize, so Page is returned. Later in the tutorial, an example of OnGet initializing state is shown. The Page method creates a PageResult object that renders the Create.cshtml page.
The Movie property uses the [BindProperty] attribute to opt-in to model binding. When the Create form posts the form values, the ASP.NET Core runtime binds the posted values to the Movie model.
The OnPostAsync method is run when the page posts form data:
public async Task<IActionResult> OnPostAsync()
{
if (!ModelState.IsValid)
{
return Page();
}
_context.Movie.Add(Movie);
await _context.SaveChangesAsync();
return RedirectToPage("./Index");
}
If there are any model errors, the form is redisplayed, along with any form data posted. Most model errors can be caught on the client-side before the form is posted. An example of a model error is posting a value for the date field that cannot be converted to a date. Client-side validation and model validation are discussed later in the tutorial.
If there are no model errors:
- The data is saved.
- The browser is redirected to the Index page.
The Create Razor Page
Examine the Pages/Movies/Create.cshtml Razor Page file:
@page
@model RazorPagesMovie.Pages.Movies.CreateModel
@{
ViewData["Title"] = "Create";
}
<h1>Create</h1>
<h4>Movie</h4>
<hr />
<div class="row">
<div class="col-md-4">
<form method="post">
<div asp-validation-summary="ModelOnly" class="text-danger"></div>
<div class="form-group">
<label asp-for="Movie.Title" class="control-label"></label>
<input asp-for="Movie.Title" class="form-control" />
<span asp-validation-for="Movie.Title" class="text-danger"></span>
</div>
<div class="form-group">
<label asp-for="Movie.ReleaseDate" class="control-label"></label>
<input asp-for="Movie.ReleaseDate" class="form-control" />
<span asp-validation-for="Movie.ReleaseDate" class="text-danger"></span>
</div>
<div class="form-group">
<label asp-for="Movie.Genre" class="control-label"></label>
<input asp-for="Movie.Genre" class="form-control" />
<span asp-validation-for="Movie.Genre" class="text-danger"></span>
</div>
<div class="form-group">
<label asp-for="Movie.Price" class="control-label"></label>
<input asp-for="Movie.Price" class="form-control" />
<span asp-validation-for="Movie.Price" class="text-danger"></span>
</div>
<div class="form-group">
<input type="submit" value="Create" class="btn btn-primary" />
</div>
</form>
</div>
</div>
<div>
<a asp-page="Index">Back to List</a>
</div>
@section Scripts {
@{await Html.RenderPartialAsync("_ValidationScriptsPartial");}
}
Visual Studio displays the following tags in a distinctive bold font used for Tag Helpers:
<form method="post"><div asp-validation-summary="ModelOnly" class="text-danger"></div><label asp-for="Movie.Title" class="control-label"></label><input asp-for="Movie.Title" class="form-control" /><span asp-validation-for="Movie.Title" class="text-danger"></span>
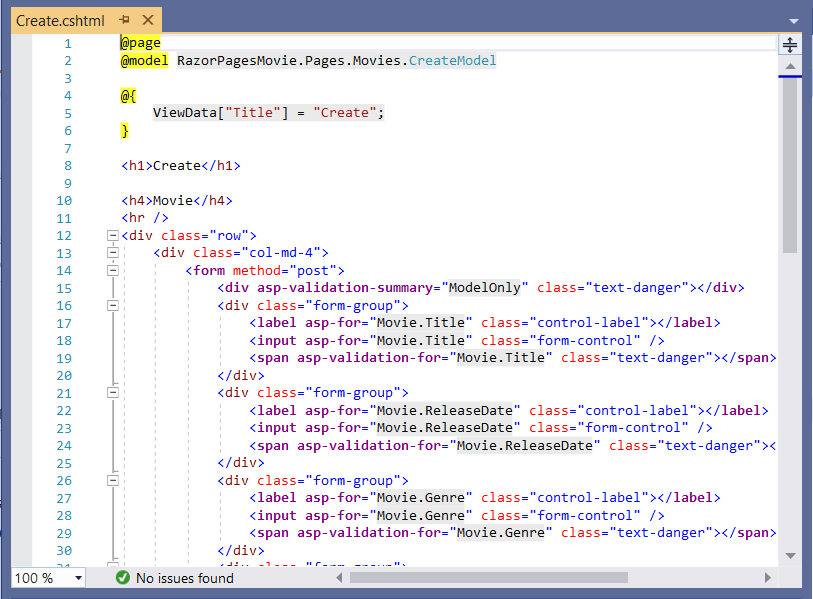
The <form method="post"> element is a Form Tag Helper. The Form Tag Helper automatically includes an antiforgery token.
The scaffolding engine creates Razor markup for each field in the model, except the ID, similar to the following:
<div asp-validation-summary="ModelOnly" class="text-danger"></div>
<div class="form-group">
<label asp-for="Movie.Title" class="control-label"></label>
<input asp-for="Movie.Title" class="form-control" />
<span asp-validation-for="Movie.Title" class="text-danger"></span>
</div>
The Validation Tag Helpers (<div asp-validation-summary and <span asp-validation-for) display validation errors. Validation is covered in more detail later in this series.
The Label Tag Helper (<label asp-for="Movie.Title" class="control-label"></label>) generates the label caption and [for] attribute for the Title property.
The Input Tag Helper (<input asp-for="Movie.Title" class="form-control">) uses the DataAnnotations attributes and produces HTML attributes needed for jQuery Validation on the client-side.
For more information on Tag Helpers such as <form method="post">, see Tag Helpers in ASP.NET Core.
Next steps
The Create, Delete, Details, and Edit pages
Examine the Pages/Movies/Index.cshtml.cs Page Model:
using Microsoft.AspNetCore.Mvc.RazorPages;
using Microsoft.EntityFrameworkCore;
using RazorPagesMovie.Models;
namespace RazorPagesMovie.Pages.Movies
{
public class IndexModel : PageModel
{
private readonly RazorPagesMovie.Data.RazorPagesMovieContext _context;
public IndexModel(RazorPagesMovie.Data.RazorPagesMovieContext context)
{
_context = context;
}
public IList<Movie> Movie { get;set; } = default!;
public async Task OnGetAsync()
{
if (_context.Movie != null)
{
Movie = await _context.Movie.ToListAsync();
}
}
}
}
Razor Pages are derived from PageModel. By convention, the PageModel derived class is named PageNameModel. For example, the Index page is named IndexModel.
The constructor uses dependency injection to add the RazorPagesMovieContext to the page:
public class IndexModel : PageModel
{
private readonly RazorPagesMovie.Data.RazorPagesMovieContext _context;
public IndexModel(RazorPagesMovie.Data.RazorPagesMovieContext context)
{
_context = context;
}
See Asynchronous code for more information on asynchronous programming with Entity Framework.
When a request is made for the page, the OnGetAsync method returns a list of movies to the Razor Page. On a Razor Page, OnGetAsync or OnGet is called to initialize the state of the page. In this case, OnGetAsync gets a list of movies and displays them.
When OnGet returns void or OnGetAsync returns Task, no return statement is used. For example, examine the Privacy Page:
using Microsoft.AspNetCore.Mvc;
using Microsoft.AspNetCore.Mvc.RazorPages;
namespace RazorPagesMovie.Pages
{
public class PrivacyModel : PageModel
{
private readonly ILogger<PrivacyModel> _logger;
public PrivacyModel(ILogger<PrivacyModel> logger)
{
_logger = logger;
}
public void OnGet()
{
}
}
}
When the return type is IActionResult or Task<IActionResult>, a return statement must be provided. For example, the Pages/Movies/Create.cshtml.cs OnPostAsync method:
public async Task<IActionResult> OnPostAsync()
{
if (!ModelState.IsValid || _context.Movie == null || Movie == null)
{
return Page();
}
_context.Movie.Add(Movie);
await _context.SaveChangesAsync();
return RedirectToPage("./Index");
}
Examine the Pages/Movies/Index.cshtml Razor Page:
@page
@model RazorPagesMovie.Pages.Movies.IndexModel
@{
ViewData["Title"] = "Index";
}
<h1>Index</h1>
<p>
<a asp-page="Create">Create New</a>
</p>
<table class="table">
<thead>
<tr>
<th>
@Html.DisplayNameFor(model => model.Movie[0].Title)
</th>
<th>
@Html.DisplayNameFor(model => model.Movie[0].ReleaseDate)
</th>
<th>
@Html.DisplayNameFor(model => model.Movie[0].Genre)
</th>
<th>
@Html.DisplayNameFor(model => model.Movie[0].Price)
</th>
<th></th>
</tr>
</thead>
<tbody>
@foreach (var item in Model.Movie) {
<tr>
<td>
@Html.DisplayFor(modelItem => item.Title)
</td>
<td>
@Html.DisplayFor(modelItem => item.ReleaseDate)
</td>
<td>
@Html.DisplayFor(modelItem => item.Genre)
</td>
<td>
@Html.DisplayFor(modelItem => item.Price)
</td>
<td>
<a asp-page="./Edit" asp-route-id="@item.ID">Edit</a> |
<a asp-page="./Details" asp-route-id="@item.ID">Details</a> |
<a asp-page="./Delete" asp-route-id="@item.ID">Delete</a>
</td>
</tr>
}
</tbody>
</table>
Razor can transition from HTML into C# or into Razor-specific markup. When an @ symbol is followed by a Razor reserved keyword, it transitions into Razor-specific markup, otherwise it transitions into C#.
The @page directive
The @page Razor directive makes the file an MVC action, which means that it can handle requests. @page must be the first Razor directive on a page. @page and @model are examples of transitioning into Razor-specific markup. See Razor syntax for more information.
The @model directive
@page
@model RazorPagesMovie.Pages.Movies.IndexModel
The @model directive specifies the type of the model passed to the Razor Page. In the preceding example, the @model line makes the PageModel derived class available to the Razor Page. The model is used in the @Html.DisplayNameFor and @Html.DisplayFor HTML Helpers on the page.
Examine the lambda expression used in the following HTML Helper:
@Html.DisplayNameFor(model => model.Movie[0].Title)
The DisplayNameFor HTML Helper inspects the Title property referenced in the lambda expression to determine the display name. The lambda expression is inspected rather than evaluated. That means there is no access violation when model, model.Movie, or model.Movie[0] is null or empty. When the lambda expression is evaluated, for example, with @Html.DisplayFor(modelItem => item.Title), the model's property values are evaluated.
The layout page
Select the menu links RazorPagesMovie, Home, and Privacy. Each page shows the same menu layout. The menu layout is implemented in the Pages/Shared/_Layout.cshtml file.
Open and examine the Pages/Shared/_Layout.cshtml file.
Layout templates allow the HTML container layout to be:
- Specified in one place.
- Applied in multiple pages in the site.
Find the @RenderBody() line. RenderBody is a placeholder where all the page-specific views show up, wrapped in the layout page. For example, select the Privacy link and the Pages/Privacy.cshtml view is rendered inside the RenderBody method.
ViewData and layout
Consider the following markup from the Pages/Movies/Index.cshtml file:
@page
@model RazorPagesMovie.Pages.Movies.IndexModel
@{
ViewData["Title"] = "Index";
}
The preceding highlighted markup is an example of Razor transitioning into C#. The { and } characters enclose a block of C# code.
The PageModel base class contains a ViewData dictionary property that can be used to pass data to a View. Objects are added to the ViewData dictionary using a key value pattern. In the preceding sample, the Title property is added to the ViewData dictionary.
The Title property is used in the Pages/Shared/_Layout.cshtml file. The following markup shows the first few lines of the _Layout.cshtml file.
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="en">
<head>
<meta charset="utf-8" />
<meta name="viewport" content="width=device-width, initial-scale=1.0" />
<title>@ViewData["Title"] - RazorPagesMovie</title>
@*Markup removed for brevity.*@
<link rel="stylesheet" href="~/lib/bootstrap/dist/css/bootstrap.css" />
The line @*Markup removed for brevity.*@ is a Razor comment. Unlike HTML comments <!-- -->, Razor comments are not sent to the client. See MDN web docs: Getting started with HTML for more information.
Update the layout
Change the
<title>element in thePages/Shared/_Layout.cshtmlfile to display Movie rather than RazorPagesMovie.<!DOCTYPE html> <html lang="en"> <head> <meta charset="utf-8" /> <meta name="viewport" content="width=device-width, initial-scale=1.0" /> <title>@ViewData["Title"] - Movie</title>Find the following anchor element in the
Pages/Shared/_Layout.cshtmlfile.<a class="navbar-brand" asp-area="" asp-page="/Index">RazorPagesMovie</a>Replace the preceding element with the following markup:
<a class="navbar-brand" asp-page="/Movies/Index">RpMovie</a>The preceding anchor element is a Tag Helper. In this case, it's the Anchor Tag Helper. The
asp-page="/Movies/Index"Tag Helper attribute and value creates a link to the/Movies/IndexRazor Page. Theasp-areaattribute value is empty, so the area isn't used in the link. See Areas for more information.Save the changes and test the app by selecting the RpMovie link. See the _Layout.cshtml file in GitHub if you have any problems.
Test the Home, RpMovie, Create, Edit, and Delete links. Each page sets the title, which you can see in the browser tab. When you bookmark a page, the title is used for the bookmark.
Note
You may not be able to enter decimal commas in the Price field. To support jQuery validation for non-English locales that use a comma (",") for a decimal point, and non US-English date formats, you must take steps to globalize the app. See this GitHub issue 4076 for instructions on adding decimal comma.
The Layout property is set in the Pages/_ViewStart.cshtml file:
@{
Layout = "_Layout";
}
The preceding markup sets the layout file to Pages/Shared/_Layout.cshtml for all Razor files under the Pages folder. See Layout for more information.
The Create page model
Examine the Pages/Movies/Create.cshtml.cs page model:
using Microsoft.AspNetCore.Mvc;
using Microsoft.AspNetCore.Mvc.RazorPages;
using RazorPagesMovie.Models;
namespace RazorPagesMovie.Pages.Movies
{
public class CreateModel : PageModel
{
private readonly RazorPagesMovie.Data.RazorPagesMovieContext _context;
public CreateModel(RazorPagesMovie.Data.RazorPagesMovieContext context)
{
_context = context;
}
public IActionResult OnGet()
{
return Page();
}
[BindProperty]
public Movie Movie { get; set; } = default!;
// To protect from overposting attacks, see https://aka.ms/RazorPagesCRUD
public async Task<IActionResult> OnPostAsync()
{
if (!ModelState.IsValid || _context.Movie == null || Movie == null)
{
return Page();
}
_context.Movie.Add(Movie);
await _context.SaveChangesAsync();
return RedirectToPage("./Index");
}
}
}
The OnGet method initializes any state needed for the page. The Create page doesn't have any state to initialize, so Page is returned. Later in the tutorial, an example of OnGet initializing state is shown. The Page method creates a PageResult object that renders the Create.cshtml page.
The Movie property uses the [BindProperty] attribute to opt-in to model binding. When the Create form posts the form values, the ASP.NET Core runtime binds the posted values to the Movie model.
The OnPostAsync method is run when the page posts form data:
public async Task<IActionResult> OnPostAsync()
{
if (!ModelState.IsValid || _context.Movie == null || Movie == null)
{
return Page();
}
_context.Movie.Add(Movie);
await _context.SaveChangesAsync();
return RedirectToPage("./Index");
}
If there are any model errors, the form is redisplayed, along with any form data posted. Most model errors can be caught on the client-side before the form is posted. An example of a model error is posting a value for the date field that cannot be converted to a date. Client-side validation and model validation are discussed later in the tutorial.
If there are no model errors:
- The data is saved.
- The browser is redirected to the Index page.
The Create Razor Page
Examine the Pages/Movies/Create.cshtml Razor Page file:
@page
@model RazorPagesMovie.Pages.Movies.CreateModel
@{
ViewData["Title"] = "Create";
}
<h1>Create</h1>
<h4>Movie</h4>
<hr />
<div class="row">
<div class="col-md-4">
<form method="post">
<div asp-validation-summary="ModelOnly" class="text-danger"></div>
<div class="form-group">
<label asp-for="Movie.Title" class="control-label"></label>
<input asp-for="Movie.Title" class="form-control" />
<span asp-validation-for="Movie.Title" class="text-danger"></span>
</div>
<div class="form-group">
<label asp-for="Movie.ReleaseDate" class="control-label"></label>
<input asp-for="Movie.ReleaseDate" class="form-control" />
<span asp-validation-for="Movie.ReleaseDate" class="text-danger"></span>
</div>
<div class="form-group">
<label asp-for="Movie.Genre" class="control-label"></label>
<input asp-for="Movie.Genre" class="form-control" />
<span asp-validation-for="Movie.Genre" class="text-danger"></span>
</div>
<div class="form-group">
<label asp-for="Movie.Price" class="control-label"></label>
<input asp-for="Movie.Price" class="form-control" />
<span asp-validation-for="Movie.Price" class="text-danger"></span>
</div>
<div class="form-group">
<input type="submit" value="Create" class="btn btn-primary" />
</div>
</form>
</div>
</div>
<div>
<a asp-page="Index">Back to List</a>
</div>
@section Scripts {
@{await Html.RenderPartialAsync("_ValidationScriptsPartial");}
}
Visual Studio displays the following tags in a distinctive bold font used for Tag Helpers:
<form method="post"><div asp-validation-summary="ModelOnly" class="text-danger"></div><label asp-for="Movie.Title" class="control-label"></label><input asp-for="Movie.Title" class="form-control" /><span asp-validation-for="Movie.Title" class="text-danger"></span>

The <form method="post"> element is a Form Tag Helper. The Form Tag Helper automatically includes an antiforgery token.
The scaffolding engine creates Razor markup for each field in the model, except the ID, similar to the following:
<div asp-validation-summary="ModelOnly" class="text-danger"></div>
<div class="form-group">
<label asp-for="Movie.Title" class="control-label"></label>
<input asp-for="Movie.Title" class="form-control" />
<span asp-validation-for="Movie.Title" class="text-danger"></span>
</div>
The Validation Tag Helpers (<div asp-validation-summary and <span asp-validation-for) display validation errors. Validation is covered in more detail later in this series.
The Label Tag Helper (<label asp-for="Movie.Title" class="control-label"></label>) generates the label caption and [for] attribute for the Title property.
The Input Tag Helper (<input asp-for="Movie.Title" class="form-control">) uses the DataAnnotations attributes and produces HTML attributes needed for jQuery Validation on the client-side.
For more information on Tag Helpers such as <form method="post">, see Tag Helpers in ASP.NET Core.
Next steps
The Create, Delete, Details, and Edit pages
Examine the Pages/Movies/Index.cshtml.cs Page Model:
// Unused usings removed.
using Microsoft.AspNetCore.Mvc.RazorPages;
using Microsoft.EntityFrameworkCore;
using RazorPagesMovie.Models;
using System.Collections.Generic;
using System.Threading.Tasks;
namespace RazorPagesMovie.Pages.Movies
{
public class IndexModel : PageModel
{
private readonly RazorPagesMovie.Data.RazorPagesMovieContext _context;
public IndexModel(RazorPagesMovie.Data.RazorPagesMovieContext context)
{
_context = context;
}
public IList<Movie> Movie { get;set; }
public async Task OnGetAsync()
{
Movie = await _context.Movie.ToListAsync();
}
}
}
Razor Pages are derived from PageModel. By convention, the PageModel-derived class is named <PageName>Model. The constructor uses dependency injection to add the RazorPagesMovieContext to the page:
public class IndexModel : PageModel
{
private readonly RazorPagesMovie.Data.RazorPagesMovieContext _context;
public IndexModel(RazorPagesMovie.Data.RazorPagesMovieContext context)
{
_context = context;
}
See Asynchronous code for more information on asynchronous programming with Entity Framework.
When a request is made for the page, the OnGetAsync method returns a list of movies to the Razor Page. On a Razor Page, OnGetAsync or OnGet is called to initialize the state of the page. In this case, OnGetAsync gets a list of movies and displays them.
When OnGet returns void or OnGetAsync returns Task, no return statement is used. For example the Privacy Page:
public class PrivacyModel : PageModel
{
private readonly ILogger<PrivacyModel> _logger;
public PrivacyModel(ILogger<PrivacyModel> logger)
{
_logger = logger;
}
public void OnGet()
{
}
}
When the return type is IActionResult or Task<IActionResult>, a return statement must be provided. For example, the Pages/Movies/Create.cshtml.cs OnPostAsync method:
public async Task<IActionResult> OnPostAsync()
{
if (!ModelState.IsValid)
{
return Page();
}
_context.Movie.Add(Movie);
await _context.SaveChangesAsync();
return RedirectToPage("./Index");
}
}
Examine the Pages/Movies/Index.cshtml Razor Page:
@page
@model RazorPagesMovie.Pages.Movies.IndexModel
@{
ViewData["Title"] = "Index";
}
<h1>Index</h1>
<p>
<a asp-page="Create">Create New</a>
</p>
<table class="table">
<thead>
<tr>
<th>
@Html.DisplayNameFor(model => model.Movie[0].Title)
</th>
<th>
@Html.DisplayNameFor(model => model.Movie[0].ReleaseDate)
</th>
<th>
@Html.DisplayNameFor(model => model.Movie[0].Genre)
</th>
<th>
@Html.DisplayNameFor(model => model.Movie[0].Price)
</th>
<th></th>
</tr>
</thead>
<tbody>
@foreach (var item in Model.Movie) {
<tr>
<td>
@Html.DisplayFor(modelItem => item.Title)
</td>
<td>
@Html.DisplayFor(modelItem => item.ReleaseDate)
</td>
<td>
@Html.DisplayFor(modelItem => item.Genre)
</td>
<td>
@Html.DisplayFor(modelItem => item.Price)
</td>
<td>
<a asp-page="./Edit" asp-route-id="@item.ID">Edit</a> |
<a asp-page="./Details" asp-route-id="@item.ID">Details</a> |
<a asp-page="./Delete" asp-route-id="@item.ID">Delete</a>
</td>
</tr>
}
</tbody>
</table>
Razor can transition from HTML into C# or into Razor-specific markup. When an @ symbol is followed by a Razor reserved keyword, it transitions into Razor-specific markup, otherwise it transitions into C#.
The @page directive
The @page Razor directive makes the file an MVC action, which means that it can handle requests. @page must be the first Razor directive on a page. @page and @model are examples of transitioning into Razor-specific markup. See Razor syntax for more information.
The @model directive
@page
@model RazorPagesMovie.Pages.Movies.IndexModel
The @model directive specifies the type of the model passed to the Razor Page. In the preceding example, the @model line makes the PageModel-derived class available to the Razor Page. The model is used in the @Html.DisplayNameFor and @Html.DisplayFor HTML Helpers on the page.
Examine the lambda expression used in the following HTML Helper:
@Html.DisplayNameFor(model => model.Movie[0].Title)
The DisplayNameFor HTML Helper inspects the Title property referenced in the lambda expression to determine the display name. The lambda expression is inspected rather than evaluated. That means there is no access violation when model, model.Movie, or model.Movie[0] is null or empty. When the lambda expression is evaluated, for example, with @Html.DisplayFor(modelItem => item.Title), the model's property values are evaluated.
The layout page
Select the menu links RazorPagesMovie, Home, and Privacy. Each page shows the same menu layout. The menu layout is implemented in the Pages/Shared/_Layout.cshtml file.
Open and examine the Pages/Shared/_Layout.cshtml file.
Layout templates allow the HTML container layout to be:
- Specified in one place.
- Applied in multiple pages in the site.
Find the @RenderBody() line. RenderBody is a placeholder where all the page-specific views show up, wrapped in the layout page. For example, select the Privacy link and the Pages/Privacy.cshtml view is rendered inside the RenderBody method.
ViewData and layout
Consider the following markup from the Pages/Movies/Index.cshtml file:
@page
@model RazorPagesMovie.Pages.Movies.IndexModel
@{
ViewData["Title"] = "Index";
}
The preceding highlighted markup is an example of Razor transitioning into C#. The { and } characters enclose a block of C# code.
The PageModel base class contains a ViewData dictionary property that can be used to pass data to a View. Objects are added to the ViewData dictionary using a key value pattern. In the preceding sample, the Title property is added to the ViewData dictionary.
The Title property is used in the Pages/Shared/_Layout.cshtml file. The following markup shows the first few lines of the _Layout.cshtml file.
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html>
<head>
<meta charset="utf-8" />
<meta name="viewport" content="width=device-width, initial-scale=1.0" />
<title>@ViewData["Title"] - RazorPagesMovie</title>
@*Markup removed for brevity.*@
The line @*Markup removed for brevity.*@ is a Razor comment. Unlike HTML comments <!-- -->, Razor comments are not sent to the client. See MDN web docs: Getting started with HTML for more information.
Update the layout
Change the
<title>element in thePages/Shared/_Layout.cshtmlfile to display Movie rather than RazorPagesMovie.<!DOCTYPE html> <html lang="en"> <head> <meta charset="utf-8" /> <meta name="viewport" content="width=device-width, initial-scale=1.0" /> <title>@ViewData["Title"] - Movie</title>Find the following anchor element in the
Pages/Shared/_Layout.cshtmlfile.<a class="navbar-brand" asp-area="" asp-page="/Index">RazorPagesMovie</a>Replace the preceding element with the following markup:
<a class="navbar-brand" asp-page="/Movies/Index">RpMovie</a>The preceding anchor element is a Tag Helper. In this case, it's the Anchor Tag Helper. The
asp-page="/Movies/Index"Tag Helper attribute and value creates a link to the/Movies/IndexRazor Page. Theasp-areaattribute value is empty, so the area isn't used in the link. See Areas for more information.Save the changes and test the app by selecting the RpMovie link. See the _Layout.cshtml file in GitHub if you have any problems.
Test the Home, RpMovie, Create, Edit, and Delete links. Each page sets the title, which you can see in the browser tab. When you bookmark a page, the title is used for the bookmark.
Note
You may not be able to enter decimal commas in the Price field. To support jQuery validation for non-English locales that use a comma (",") for a decimal point, and non US-English date formats, you must take steps to globalize the app. See this GitHub issue 4076 for instructions on adding decimal comma.
The Layout property is set in the Pages/_ViewStart.cshtml file:
@{
Layout = "_Layout";
}
The preceding markup sets the layout file to Pages/Shared/_Layout.cshtml for all Razor files under the Pages folder. See Layout for more information.
The Create page model
Examine the Pages/Movies/Create.cshtml.cs page model:
using Microsoft.AspNetCore.Mvc;
using Microsoft.AspNetCore.Mvc.RazorPages;
using RazorPagesMovie.Models;
using System;
using System.Threading.Tasks;
namespace RazorPagesMovie.Pages.Movies
{
public class CreateModel : PageModel
{
private readonly RazorPagesMovie.Data.RazorPagesMovieContext _context;
public CreateModel(RazorPagesMovie.Data.RazorPagesMovieContext context)
{
_context = context;
}
public IActionResult OnGet()
{
return Page();
}
[BindProperty]
public Movie Movie { get; set; }
public async Task<IActionResult> OnPostAsync()
{
if (!ModelState.IsValid)
{
return Page();
}
_context.Movie.Add(Movie);
await _context.SaveChangesAsync();
return RedirectToPage("./Index");
}
}
}
The OnGet method initializes any state needed for the page. The Create page doesn't have any state to initialize, so Page is returned. Later in the tutorial, an example of OnGet initializing state is shown. The Page method creates a PageResult object that renders the Create.cshtml page.
The Movie property uses the [BindProperty] attribute to opt-in to model binding. When the Create form posts the form values, the ASP.NET Core runtime binds the posted values to the Movie model.
The OnPostAsync method is run when the page posts form data:
public async Task<IActionResult> OnPostAsync()
{
if (!ModelState.IsValid)
{
return Page();
}
_context.Movie.Add(Movie);
await _context.SaveChangesAsync();
return RedirectToPage("./Index");
}
If there are any model errors, the form is redisplayed, along with any form data posted. Most model errors can be caught on the client-side before the form is posted. An example of a model error is posting a value for the date field that cannot be converted to a date. Client-side validation and model validation are discussed later in the tutorial.
If there are no model errors:
- The data is saved.
- The browser is redirected to the Index page.
The Create Razor Page
Examine the Pages/Movies/Create.cshtml Razor Page file:
@page
@model RazorPagesMovie.Pages.Movies.CreateModel
@{
ViewData["Title"] = "Create";
}
<h1>Create</h1>
<h4>Movie</h4>
<hr />
<div class="row">
<div class="col-md-4">
<form method="post">
<div asp-validation-summary="ModelOnly" class="text-danger"></div>
<div class="form-group">
<label asp-for="Movie.Title" class="control-label"></label>
<input asp-for="Movie.Title" class="form-control" />
<span asp-validation-for="Movie.Title" class="text-danger"></span>
</div>
<div class="form-group">
<label asp-for="Movie.ReleaseDate" class="control-label"></label>
<input asp-for="Movie.ReleaseDate" class="form-control" />
<span asp-validation-for="Movie.ReleaseDate" class="text-danger"></span>
</div>
<div class="form-group">
<label asp-for="Movie.Genre" class="control-label"></label>
<input asp-for="Movie.Genre" class="form-control" />
<span asp-validation-for="Movie.Genre" class="text-danger"></span>
</div>
<div class="form-group">
<label asp-for="Movie.Price" class="control-label"></label>
<input asp-for="Movie.Price" class="form-control" />
<span asp-validation-for="Movie.Price" class="text-danger"></span>
</div>
<div class="form-group">
<input type="submit" value="Create" class="btn btn-primary" />
</div>
</form>
</div>
</div>
<div>
<a asp-page="Index">Back to List</a>
</div>
@section Scripts {
@{await Html.RenderPartialAsync("_ValidationScriptsPartial");}
}
Visual Studio displays the following tags in a distinctive bold font used for Tag Helpers:
<form method="post"><div asp-validation-summary="ModelOnly" class="text-danger"></div><label asp-for="Movie.Title" class="control-label"></label><input asp-for="Movie.Title" class="form-control" /><span asp-validation-for="Movie.Title" class="text-danger"></span>

The <form method="post"> element is a Form Tag Helper. The Form Tag Helper automatically includes an antiforgery token.
The scaffolding engine creates Razor markup for each field in the model, except the ID, similar to the following:
<div asp-validation-summary="ModelOnly" class="text-danger"></div>
<div class="form-group">
<label asp-for="Movie.Title" class="control-label"></label>
<input asp-for="Movie.Title" class="form-control" />
<span asp-validation-for="Movie.Title" class="text-danger"></span>
</div>
The Validation Tag Helpers (<div asp-validation-summary and <span asp-validation-for) display validation errors. Validation is covered in more detail later in this series.
The Label Tag Helper (<label asp-for="Movie.Title" class="control-label"></label>) generates the label caption and [for] attribute for the Title property.
The Input Tag Helper (<input asp-for="Movie.Title" class="form-control">) uses the DataAnnotations attributes and produces HTML attributes needed for jQuery Validation on the client-side.
For more information on Tag Helpers such as <form method="post">, see Tag Helpers in ASP.NET Core.
Next steps
ASP.NET Core
Feedback
Coming soon: Throughout 2024 we will be phasing out GitHub Issues as the feedback mechanism for content and replacing it with a new feedback system. For more information see: https://aka.ms/ContentUserFeedback.
Submit and view feedback for
