This article describes known issues and errors you may encounter when upgrading Azure Kubernetes Service (AKS) Arc deployments to the newest release. You can also review known issues with Windows Admin Center and when installing AKS on Azure Stack HCI.
After a successful upgrade, older versions of PowerShell are not removed
Older versions of PowerShell are not removed.
To work around this issue, you can run this script to uninstall older PowerShell versions.
Certificate renewal pod is in a crash loop state
After upgrading or up-scaling the target cluster, the certificate renewal pod is now in a crash loop state. It's expecting a cert tattoo yaml file from the path /etc/Kubernetes/pki. The configuration file is present in the control plane node VMs but not on worker node VMs.
Note
This issue is fixed after the April 2022 release.
To resolve this issue, manually copy the cert tattoo file from the control plane node to each of the worker nodes.
Copy the file from control plane VM to your host machine current directory.
ssh clouduser@<comtrol-plane-vm-ip> -i (get-mocconfig).sshprivatekey sudo cp /etc/kubernetes/pki/cert-tattoo-kubelet.yaml ~/ sudo chown clouduser cert-tattoo-kubelet.yaml sudo chgrp clouduser cert-tattoo-kubelet.yaml (change file permissions here so that scp works) scp -i (get-mocconfig).sshprivatekey clouduser@<comtrol-plane-vm-ip>:~/cert*.yaml .\Copy the file from host machine to the worker node VM.
scp -i (get-mocconfig).sshprivatekey .\cert-tattoo-kubelet.yaml clouduser@<workernode-vm-ip>:~/cert-tattoo-kubelet.yamlSet the owner and group information on this file back to root if it not already set to root.
ssh clouduser@<workernode-vm-ip> -i (get-mocconfig).sshprivatekey sudo cp ~/cert-tattoo-kubelet.yaml /etc/kubernetes/pki/cert-tattoo-kubelet.yaml (copies the cert file to correct location) sudo chown root cert-tattoo-kubelet.yaml sudo chgrp root cert-tattoo-kubelet.yamlRepeat steps 2 and 3 for each of your worker nodes.
Nodeagent leaking ports when unable to join cloudagent due to expired token when cluster not upgraded for more than 60 days
When a cluster has not been upgraded for more than 60 days, the node agent fails to start during a node agent restart because of token expiry. This failure causes the agents to be in the starting phase. Continuous attempts to join the cloudagent may exhaust the supply of ports on the host. The status for the following command is Starting.
Get-Service wssdagent | Select-Object -Property Name, Status
Expected behavior: The node agent should be in the starting phase, which constantly tries to join the cloud agent, exhausting the ports.
To resolve the issue, stop the wssdagent from running. Since the service is in the starting phase, it may prevent you from stopping the service. If so, kill the process before attempting to stop the service.
Confirm the wssdagent is in starting phase.
Get-Service wssdagent | Select-Object -Property Name, StatusKill the process.
kill -Name wssdagent -ForceStop the service.
Stop-Service wssdagent -Force
Note
Even after stopping the service, the wssdagent process appears to start in a few seconds for a couple of times before stopping. Before proceeding to the next step, make sure the following command returns an error on all the nodes.
Get-Process -Name wssdagent
PS C:\WINDOWs\system32 Get-process -Name wssdagent
Get-process : Cannot find a process with the name "wssdaqent". Verify the process name and call the cmdlet again.
At line: 1 char: 1
+ Get-process -Name wssdagent
+ ~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~
+ Categorylnfo : ObjectNotFound: (wssdagent:String) [Get-Process], ProcessCommandException
+ FullyQua1ifiedErrorId : NoProcess FoundForGivenName , Microsoft.PowerShell.Commands.Getprocesscommand
Repeat steps 1, 2, and 3 at each node of the HCI cluster that has this issue.
After confirming the wssdagent is not running, start the cloudagent if it isn't running.
Start-ClusterGroup -Name (Get-MocConfig).clusterRoleName
Confirm the cloudagent is up and running.
Get-ClusterGroup -Name (Get-MocConfig).clusterRoleNameRun the following command to fix the wssdagent:
Repair-MocOnce this command completes, the wssdagent should be in running state.
Get-Service wssdagent | Select-Object -Property Name, Status
MOC agents don't start after an upgrade failure
When AKS-HCI fails to upgrade from the May release to the June release, the expectation is that AKS-HCI should revert to the May release and continue to function. But it leaves MOC agents in a stopped state, and manual attempts to start the agent don't activate them.
Note
This issue is only relevant when upgrading from the May release to the June release.
Steps to reproduce
- Install AKS-HCI PowerShell module version 1.1.36.
- Upgrade AKS-HCI. If the upgrade fails, AKS-HCI falls back to May, but MOC agents are down.
Expected behavior
If the Aks-Hci upgrade fails, the expectation is that AksHci reverts to the previous release and continues to function without any issues.
Symptoms
Mismatch between Aks-Hci version and MOC version
Get-AksHciVersion: 1.0.10.10513Get-MocVersion: 1.0.11.10707
Mismatch between Get-MocVersion and wssdcloudagent.exe version
Get-MocVersion indicates that the June build is installed while the wssdcloudagent.exe version indicates that the May build is installed.
MOC agent services image path has deployment ID parameter
Run the following command to show the image path for the cloud agent:
reg query "HKLM\System\CurrentControlSet\Services\wssdcloudagent"
Example output
"C:\Program Files\AksHci\wssdcloudagent.exe" --service --basedir "base dir" --cloudagentfqdn "cloudagent fqdn" --dotfolderpath "dot folder path" --objectdatastore "data store" --clusterresourcename "cluster name" --certificatevalidityfactor 1 --deploymentid "deployment id"
Use the following command to show the image path for the node agent: reg query "HKLM\System\CurrentControlSet\Services\wssdagent"
Example output
"C:\Program Files\AksHci\wssdagent.exe" --service --basedir "base dir" --cloudloginfile "cloud login file path" --dotfolderpath "dotfolder path" --nodeagentfqdn "node fqdn" --objectdatastore "object data store" --wssdproviderspec "provider spec" --deploymentid "deployment id"
To mitigate the issue, run the following PowerShell cmdlets:
Set-ItemProperty -Path "HKLM:\System\CurrentControlSet\Services\wssdcloudagent" -Name ImagePath -Value 'above cloud agent image path without the deployment id'
Set-ItemProperty -Path "HKLM:\System\CurrentControlSet\Services\wssdagent" -Name ImagePath -Value 'above node agent image path without the deployment id'
During an upgrade, custom node taints, roles, and labels are lost
When upgrading, you may lose all custom taints, roles, and labels that you added to your worker nodes. Since AKS is a managed service, adding custom taints, labels, and roles when performed outside the provided PowerShell cmdlets or Windows Admin Center is not supported.
To work around this issue, run the New-AksHciNodePool cmdlet to correctly create a node pool with taints for your worker nodes.
AKS Arc goes out-of-policy if a workload cluster hasn't been created in 60 days
If you created a management cluster but haven't deployed a workload cluster in the first 60 days, you'll be blocked from creating one, because it's now out-of-policy. In this situation, when you run Update-AksHci, the update process is blocked with the error Waiting for deployment 'AksHci Billing Operator' to be ready. If you run Sync-AksHciBilling, it returns successful output. However, if you run Get-AksHciBillingStatus, the connection status is OutofPolicy.
If you haven't deployed a workload cluster in 60 days, the billing goes out of policy.
The only way to fix this issue is to redeploy with a clean installation.
vNIC goes missing after a machine reboot
Note
This issue is fixed in the May 2022 release and later.
If Azure Stack HCI nodes are rebooted one after the other, some of the virtual machines lose the vNICs attached to them. This loss of vNICs causes the VMs to lose network connectivity, and the cluster falls into a bad state.
To Reproduce
- Reboot one Azure Stack HCI node.
- Wait for the node to complete the reboot. The node needs to be marked
Upin the failover cluster. - Reboot the other nodes.
- Repeat.
Expected behavior The cluster state should be healthy. All the VMs should have NICs attached to them.
In order to resolve the problem, use the MOC commands to add the vNIC to the VM.
- Get vNIC name for the VM.
(Get-MocVirtualMachine -group <group> -name <vmname>).virtualmachineproperties.networkprofile.networkinterfaces
or
mocctl.exe compute vm get --name <vmname> --group <group>
- Connect the vNIC to the VM.
Connect-MocNetworkInterface -name <vnicname> -group <group> -virtualMachineName <vmname>
or
mocctl.exe compute vm nic add --name <vnicname> --vm-name <vmname> --group <group>
- If the vNIC connect command fails, try disconnect and connect again. Following is the command for vNIC disconnect.
Disconnect-MocNetworkInterface -name <vnicname> -group <group> -virtualMachineName <vmname>
or
mocctl.exe compute vm nic remove --name <vnicname> --vm-name <vmname> --group <group>
When upgrading a deployment, some pods might be stuck at 'waiting for static pods to have a ready condition'
Pods stuck at waiting for static pods to have a ready condition.
To release the pods and resolve this issue, you should restart kubelet. To view the NotReady node with the static pods, run the following command:
kubectl get nodes -o wide
To get more information on the faulty node, run the following command:
kubectl describe node <IP of the node>
Use SSH to log into the NotReady node by running the following command:
ssh -i <path of the private key file> administrator@<IP of the node>
Then, to restart kubelet, run the following command:
/etc/.../kubelet restart
Running an upgrade results in the error: 'Error occurred while fetching platform upgrade information'
When running an upgrade in Windows Admin Center, the following error occurred:
Error occurred while fetching platform upgrade information. RemoteException: No match was found for the specified search criteria and module name 'AksHci'. Try Get-PSRepository to see all available registered module repositories.
This error message typically occurs when AKS on Azure Stack HCI is deployed in an environment that has a proxy configured. Currently, Windows Admin Center doesn't have support to install modules in a proxy environment.
To resolve this error, set up AKS on Azure Stack HCI using the proxy PowerShell command.
When upgrading a Kubernetes cluster with an Open Policy Agent, the upgrade process hangs
When upgrading Kubernetes clusters with an Open Policy Agent (OPA), such as OPA GateKeeper, the process may hang and be unable to complete. This issue can occur because the policy agent is configured to prevent pulling container images from private registries.
To resolve this issue, if you upgrade clusters deployed with an OPA, make sure that your policies allow for pulling images from Azure Container Registry. For an AKS on Azure Stack HCI upgrade, you should add the following endpoint in your policy's list: ecpacr.azurecr.io.
Update of host OS HCI to HCIv2 breaks AKS on Azure Stack HCI installation: OutOfCapacity
Running an OS update on a host with an AKS on Azure Stack HCI deployment can cause the deployment to enter a bad state and fail day two operations. The MOC NodeAgent Services may fail to start on updated hosts. All MOC calls to the nodes fail.
Note
This issue only happens occasionally.
To reproduce: When you update a cluster with an existing AKS deployment from HCI to HCIv2, an AKS operation such as New-AksHciCluster may fail. The error message states that the MOC nodes are OutOfCapacity. For example:
System.Collections.Hashtable.generic_non_zero1 [Error: failed to create nic test-load-balancer-whceb-nic for machinetest-load-balancer-whceb: unable to create VM network interface: failed to create network interface test-load-balancer-whceb-nic in resource group clustergroup-test: rpc error: code = Unknown desc = Location 'MocLocation' doesn't expose any nodes to create VNIC 'test-load-balancer-whceb-nic' on: OutOfCapacity]
To resolve this issue, start the wssdagent Moc NodeAgent Service on the affected nodes. This will solve the issue, and bring the deployment back to a good state. Run the following command:
Get-ClusterNode -ErrorAction Stop | ForEach-Object { Invoke-Command -ComputerName $_ -ScriptBlock { Start-Service wssdagent -WarningAction:SilentlyContinue } }
Upgrade of target cluster gets stuck with one or more nodes in an old Kubernetes version
After running Update-AksHciCluster, the upgrade process stalls.
Run the following command to check if there is a machine with PHASE Deleting that is running the previous Kubernetes version that you are upgrading from.
kubectl get machines -o wide --kubeconfig (Get-KvaConfig).kubeconfig
If there is a machine with PHASE Deleting and VERSION matching the previous Kubernetes version, proceed with the following steps.
To address this problem, you need the following pieces of information:
- Kubernetes version to which you're upgrading your workload cluster.
- IP address of the node that is stuck.
To find this information, run the following cmdlet and command. By default, the cmdlet Get-AksHciCredential writes the kubeconfig to ~/.kube/config. If you specify a different location for your workload cluster kubeconfig when calling Get-AksHciCredential, you will need to provide that location to kubectl as another argument. For example, kubectl get nodes -o wide --kubeconfig <path to workload cluster kubeconfig>.
Get-AksHciCredential -name <workload cluster name>
kubectl get nodes -o wide
The node that needs to be fixed should show STATUS Ready,SchedulingDisabled. If you see a node with this status, use the INTERNAL-IP of this node as the IP address value in the following command below. Use the Kubernetes version you are upgrading to as the version value; this should match the VERSION value from the node with ROLES control-plane,master. Be sure to include the full value for the Kubernetes version, including the v, for example v1.22.6.
ssh -i (Get-MocConfig).sshPrivateKey -o StrictHostKeyChecking=no clouduser@<IP address> sudo crictl pull ecpacr.azurecr.io/kube-proxy:<Kubernetes version>
After running this ssh command, the remaining nodes with the old Kubernetes version should be deleted and the upgrade will proceed.
Update of host OS HCI to HCIv2 breaks AKS on Azure Stack HCI installation: Cannot reach management cluster
Running an OS update on a host with an AKS on Azure Stack HCI deployment can cause the deployment to enter a bad state, which renders the management cluster's API server unreachable and fails day two operations. The kube-vip pod cannot apply the VIP configuration to the interface, and as a result the VIP is unreachable.
To reproduce: Update a cluster with an existing AKS HCI deployment from HCI to HCIv2. Then try running commands that attempt to reach the management cluster such as Get-AksHciCluster. Any operations that attempt to reach the management cluster fails with errors such as:
PS C:\Users\wolfpack> Get-AksHciCluster
C:\Program Files\AksHci\kvactl.exe cluster list --kubeconfig="C:\ClusterStorage\Volume1\Msk8s\WorkingDir\1.0.8.10223\kubeconfig-mgmt" System.Collections.Hashtable.generic_non_zero 1 [Error: failed to connect to the cluster: action failed after 9
attempts: Get "https://10.193.237.5:6443/api?timeout=10s": net/http: request canceled while waiting for connection
(Client.Timeout exceeded while awaiting headers)]
At C:\Program Files\WindowsPowerShell\Modules\Kva\1.0.22\Common.psm1:2164 char:9
+ throw $errMessage
+ ~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~
+ CategoryInfo : OperationStopped: (C:\Program File...iting headers)]:String) [], RuntimeException
+ FullyQualifiedErrorId : C:\Program Files\AksHci\kvactl.exe cluster list --kubeconfig="C:\ClusterStorage\Volume1\Msk8s\WorkingDir\1.0.8.10223\kubeconfig-mgmt" System.Collections.Hashtable.generic_non_zero 1 [Error: failed to connect to the cluster: action failed after 9 attempts: Get "https://10.193.237.5:6443/api?timeout=10s": net/http: request canceled while waiting for connection (Client.Timeout exceeded while awaiting headers)]
To resolve this issue: restart the kube-vip container to bring the deployment back to a good state.
- Get the
kube-vipcontainer ID:
ssh -i (Get-AksHciConfig).Moc.sshPrivateKey clouduser@<ip> "sudo crictl ls | grep 'kube-vip'"
The output should look something like this, with the container ID being the first value 4a49a5158a5f8. For example:
4a49a5158a5f8 7751a28bb5ce1 28 minutes ago Running kube-vip 1 cf9681f921a55
- Restart the Restart the container:
ssh -i (Get-AksHciConfig).Moc.sshPrivateKey clouduser@<ip> "sudo crictl stop <Container ID>"
When running Update-AksHci, the update process was stuck at 'Waiting for deployment 'AksHci Billing Operator' to be ready'
This status message appears when running the Update-AksHci PowerShell cmdlet.
Review the following root causes to resolve the issue:
Reason one: During the update of the AksHci Billing Operator, the operator incorrectly marked itself as out of policy. To resolve this issue, open a new PowerShell window and run Sync-AksHciBilling. You should see the billing operation continue within the next 20-30 minutes.
Reason two: The management cluster VM may be out of memory, which causes the API server to be unreachable and makes all commands from Get-AksHciCluster, billing, and update, time out. As a workaround, set the management cluster VM to 32 GB in Hyper-V, and reboot it.
Reason three: The AksHci Billing Operator may be out of storage space, which is due to a bug in the Microsoft SQL configuration settings. The lack of storage space may be causing the upgrade to stop responding. To work around this issue, manually resize the billing pod
pvcusing the following steps.Run the following command to edit the pod settings:
kubectl edit pvc mssql-data-claim --kubeconfig (Get-AksHciConfig).Kva.kubeconfig -n azure-arcWhen Notepad or another editor opens with a YAML file, edit the line for storage from 100Mi to 5Gi:
spec: resources: requests: **storage: 5Gi**Check the status of the billing deployment using the following command:
kubectl get deployments/billing-manager-deployment --kubeconfig (Get-AksHciConfig).Kva.kubeconfig -n azure-arc
When upgrading AKS on Azure Stack HCI from the February 2022 Update to April 2022 Update, the CSI deployment disappears and causes the upgrade to stall
When you upgrade clusters from the AKS on Azure Stack HCI February 2022 Update to the April 2022 Update, the update may be stuck upgrading for an indefinite period of time. There may be be pods stuck in either the Terminating or CrashLoopBackoff state.
You may see that some of the AksHci CSI addon resources are missing. These resources pods deployed using the csi-akshcicsi-controller or from the csi-akshcicsi-node daemonset.
The AksHci CSI addon in the February 2022 Update contained a change to the CSI driver spec that can sometimes leave the addon's resources in an unresponsive state during upgrade. The CSI driver's .spec.fsGroupPolicy was set to a new value even though it is an immutable field. Since the field is immutable, the driver spec does not update. A consequence of this is that the other AksHci CSI addon resources might not fully get reconciled. All of the CSI resources would be recreated.
To manually resolve the issue, the CSI driver can be manually deleted. Once you have removed it, the cloud-operator reconciles the AksHci CSI addon within the 10 minutes and recreate the driver along with the rest of the missing addon resources.
kubectl --kubeconfig $(Get-AksHciConfig).Kva.kubeconfig delete csidriver disk.csi.akshci.com`
Windows Admin Center update dashboard doesn't refresh after successful updates
After a successful upgrade, the Windows Admin Center update dashboard still shows the previous version.
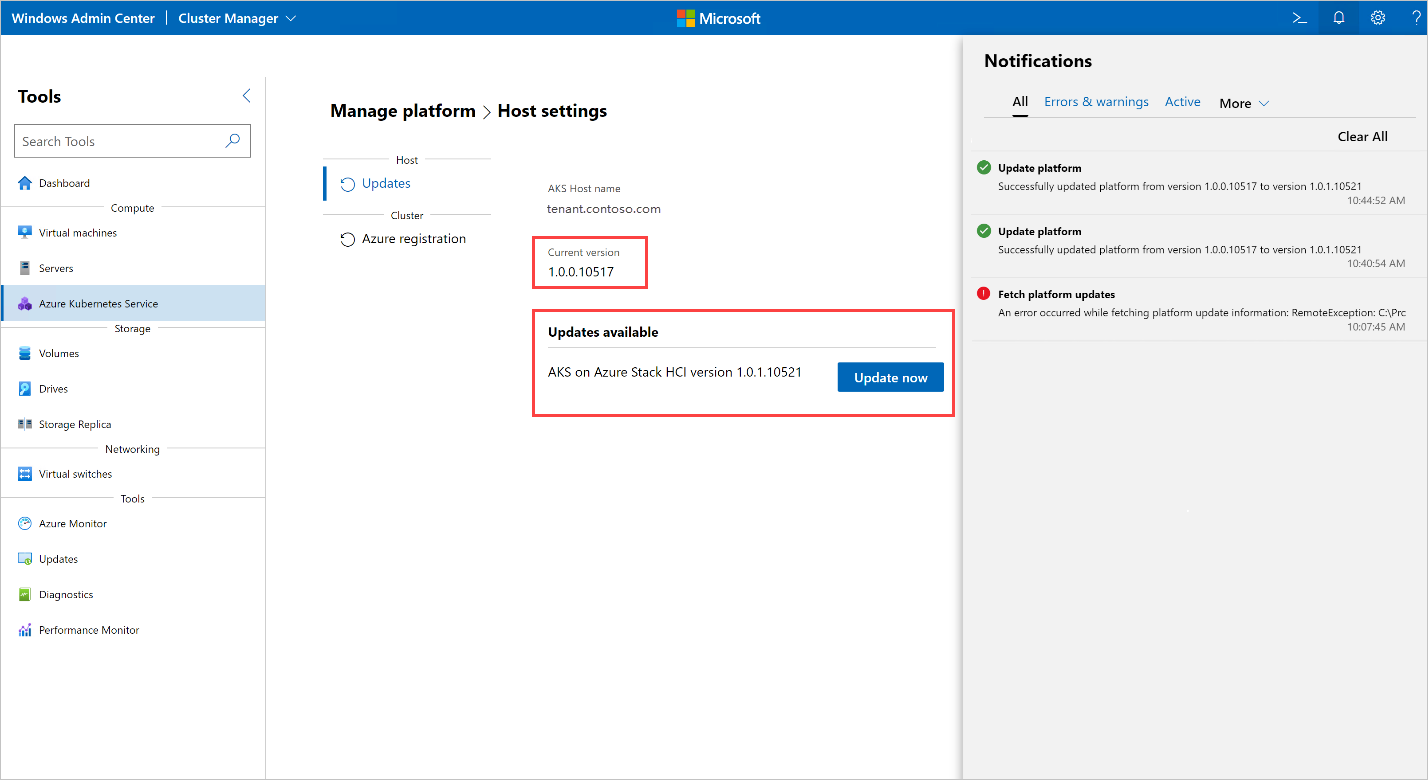
Refresh the browser to fix this issue.
When using PowerShell to upgrade, an excess number of Kubernetes configuration secrets is created on a cluster
The June 1.0.1.10628 build of AKS on Azure Stack HCI creates an excess number of Kubernetes configuration secrets in the cluster. The upgrade path from the June 1.0.1.10628 release to the July 1.0.2.10723 release was improved to clean up the extra Kubernetes secrets. However, in some cases during upgrading, the secrets were still not cleaned up, and therefore, the upgrade process fails.
If you experience this issue, run the following steps:
Save the script below as a file named fix_leaked_secrets.ps1:
upgparam ( [Parameter(Mandatory=$true)] [string] $ClusterName, [Parameter(Mandatory=$true)] [string] $ManagementKubeConfigPath ) $ControlPlaneHostName = kubectl get nodes --kubeconfig $ManagementKubeConfigPath -o=jsonpath='{.items[0].metadata.name}' "Hostname is: $ControlPlaneHostName" $leakedSecretPath1 = "$ClusterName-template-secret-akshci-cc" $leakedSecretPath2 = "$ClusterName-moc-kms-plugin" $leakedSecretPath3 = "$ClusterName-kube-vip" $leakedSecretPath4 = "$ClusterName-template-secret-akshc" $leakedSecretPath5 = "$ClusterName-linux-template-secret-akshci-cc" $leakedSecretPath6 = "$ClusterName-windows-template-secret-akshci-cc" $leakedSecretNameList = New-Object -TypeName 'System.Collections.ArrayList'; $leakedSecretNameList.Add($leakedSecretPath1) | Out-Null $leakedSecretNameList.Add($leakedSecretPath2) | Out-Null $leakedSecretNameList.Add($leakedSecretPath3) | Out-Null $leakedSecretNameList.Add($leakedSecretPath4) | Out-Null $leakedSecretNameList.Add($leakedSecretPath5) | Out-Null $leakedSecretNameList.Add($leakedSecretPath6) | Out-Null foreach ($leakedSecretName in $leakedSecretNameList) { "Deleting secrets with the prefix $leakedSecretName" $output = kubectl --kubeconfig $ManagementKubeConfigPath exec etcd-$ControlPlaneHostName -n kube-system -- sh -c "ETCDCTL_API=3 etcdctl --cacert /etc/kubernetes/pki/etcd/ca.crt --key /etc/kubernetes/pki/etcd/server.key --cert /etc/kubernetes/pki/etcd/server.crt del /registry/secrets/default/$leakedSecretName --prefix=true" "Deleted: $output" }Next, run the following command using the fix_secret_leak.ps1 file you saved:
.\fix_secret_leak.ps1 -ClusterName (Get-AksHciConfig).Kva.KvaName -ManagementKubeConfigPath (Get-AksHciConfig).Kva.KubeconfigFinally, use the following PowerShell command to repeat the upgrade process:
Update-AksHci
Next steps
If you continue to run into problems when you're using AKS Arc, you can file bugs through GitHub.