Integrate API Management in an internal virtual network with Application Gateway
APPLIES TO: Developer | Premium
You can configure Azure API Management in a virtual network in internal mode, which makes it accessible only within the virtual network. Azure Application Gateway is a platform as a service (PaaS) that acts as a Layer-7 load balancer. It acts as a reverse-proxy service and provides among its offerings Azure Web Application Firewall (WAF).
By combining API Management provisioned in an internal virtual network with the Application Gateway front end, you can:
- Use the same API Management resource for consumption by both internal consumers and external consumers.
- Use a single API Management resource and have a subset of APIs defined in API Management available for external consumers.
- Provide a turnkey way to switch access to API Management from the public internet on and off.
For architectural guidance, see:
- Basic enterprise integration: Reference architecture
- API Management landing zone accelerator: Reference architecture and design guidance
Note
This article has been updated to use the Application Gateway WAF_v2 SKU.
Prerequisites
Note
We recommend that you use the Azure Az PowerShell module to interact with Azure. See Install Azure PowerShell to get started. To learn how to migrate to the Az PowerShell module, see Migrate Azure PowerShell from AzureRM to Az.
To follow the steps described in this article, you must have:
An active Azure subscription
If you don't have an Azure subscription, create an Azure free account before you begin.
Certificates
- Personal Information Exchange (PFX) files for API Management's custom host names: gateway, developer portal, and management endpoint.
- A Certificate (CER) file for the root certificate of the PFX certificates.
For more information, see Certificates for the back end. For testing purposes, optionally generate self-signed certificates.
The latest version of Azure PowerShell
Scenario
In this article, you learn how to use a single API Management instance for internal and external consumers and make it act as a single front end for both on-premises and cloud APIs. You create an API Management instance of the newer single-tenant version 2 (stv2) type. You learn how to use public and private listeners in Application Gateway. You understand how to expose only a subset of your APIs for external consumption by using routing functionality available in Application Gateway. In the example, the APIs are highlighted in green.
In the first setup example, all your APIs are managed only from within your virtual network. Internal consumers can access all your internal and external APIs. Traffic never goes out to the internet. High-performance connectivity can be delivered via Azure ExpressRoute circuits. In the example, the internal consumers are highlighted in orange.
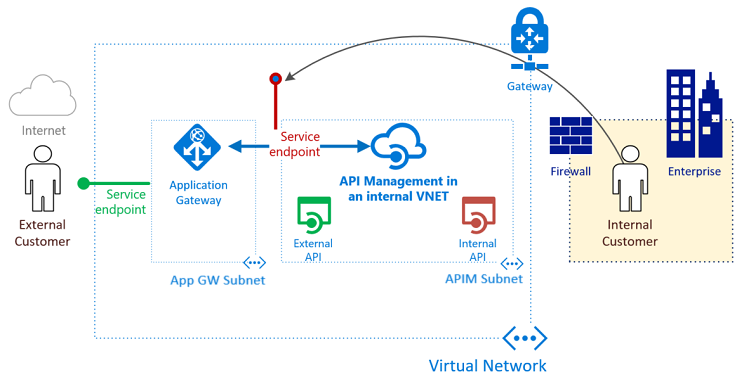
What is required to integrate API Management and Application Gateway?
- Back-end server pool: This server pool is the internal virtual IP address of API Management.
- Back-end server pool settings: Every pool has settings like port, protocol, and cookie-based affinity. These settings are applied to all servers within the pool.
- Front-end port: This public port is opened on the application gateway. Traffic that hits it gets redirected to one of the back-end servers.
- Listener: The listener has a front-end port, a protocol (Http or Https, these values are case sensitive), and the Transport Layer Security (TLS) certificate name (if configuring TLS offload).
- Rule: The rule binds a listener to a back-end server pool.
- Custom health probe: Application Gateway, by default, uses IP address-based probes to figure out which servers in
BackendAddressPoolare active. API Management only responds to requests with the correct host header, so the default probes fail. You define a custom health probe to help the application gateway determine that the service is alive and should forward requests. - Custom domain certificates: To access API Management from the internet, create Domain Name System (DNS) records to map its host names to the Application Gateway front-end IP address. This mapping ensures that the Host header and certificate sent to API Management are valid. In this example, we use three certificates. They're for API Management's gateway (the back end), the developer portal, and the management endpoint.
Expose the developer portal and management endpoint externally through Application Gateway
In this article, we also expose the developer portal and the management endpoint to external audiences through the application gateway. Extra steps are needed to create a listener, probe, settings, and rules for each endpoint. All details are provided in their respective steps.
If you use Microsoft Entra ID or third-party authentication, enable the cookie-based session affinity feature in Application Gateway.
Warning
To prevent Application Gateway WAF from breaking the download of OpenAPI specifications in the developer portal, disable the firewall rule 942200 - "Detects MySQL comment-/space-obfuscated injections and backtick termination".
Application Gateway WAF rules that might break the portal's functionality include:
920300,920330,931130,942100,942110,942180,942200,942260,942340,942370for the administrative mode942200,942260,942370,942430,942440for the published portal
Setting Variables
Throughout this guide, you need to define several variables. Naming is based on the Cloud Adoption Framework abbreviation guidance.
# These variables must be changed.
$subscriptionId = "00000000-0000-0000-0000-000000000000" # GUID of your Azure subscription
$domain = "contoso.net" # The custom domain for your certificate
$apimServiceName = "apim-contoso" # API Management service instance name, must be globally unique
$apimDomainNameLabel = $apimServiceName # Domain name label for API Management's public IP address, must be globally unique
$apimAdminEmail = "admin@contoso.net" # Administrator's email address - use your email address
$gatewayHostname = "api.$domain" # API gateway host
$portalHostname = "portal.$domain" # API developer portal host
$managementHostname = "management.$domain" # API management endpoint host
$baseCertPath = "C:\Users\Contoso\" # The base path where all certificates are stored
$trustedRootCertCerPath = "${baseCertPath}trustedroot.cer" # Full path to contoso.net trusted root .cer file
$gatewayCertPfxPath = "${baseCertPath}gateway.pfx" # Full path to api.contoso.net .pfx file
$portalCertPfxPath = "${baseCertPath}portal.pfx" # Full path to portal.contoso.net .pfx file
$managementCertPfxPath = "${baseCertPath}management.pfx" # Full path to management.contoso.net .pfx file
$gatewayCertPfxPassword = "certificatePassword123" # Password for api.contoso.net pfx certificate
$portalCertPfxPassword = "certificatePassword123" # Password for portal.contoso.net pfx certificate
$managementCertPfxPassword = "certificatePassword123" # Password for management.contoso.net pfx certificate
# These variables may be changed.
$resGroupName = "rg-apim-agw" # Resource group name that will hold all assets
$location = "West US" # Azure region that will hold all assets
$apimOrganization = "Contoso" # Organization name
$appgwName = "agw-contoso" # The name of the Application Gateway
Create a resource group for Resource Manager
To create a resource group for Azure Resource Manager:
Sign in to Azure.
Connect-AzAccountAuthenticate with your credentials.
Select the subscription you want.
Get-AzSubscription -Subscriptionid $subscriptionId | Select-AzSubscriptionCreate a resource group. You can skip this step if you're using an existing resource group.
New-AzResourceGroup -Name $resGroupName -Location $location
Resource Manager requires that all resource groups specify a location. This location is used as the default for resources in that resource group. Make sure that all commands to create an application gateway use the same resource group.
Create a virtual network and a subnet for the application gateway
The following example shows how to create a virtual network by using Resource Manager. The virtual network in this example consists of separate subnets for Application Gateway and API Management.
Set the Application Gateway IP addresses.
Note
As there will be public and private listeners, we need a public and a private IP address. The static, public IP address must be created whereas the private IP address must be selected from the subnet that is associated with the application gateway. The private IP address has been selected arbitrarily.
$appGatewayExternalIP = New-AzPublicIpAddress -ResourceGroupName $resGroupName -name "pip-ag" -location $location -AllocationMethod Static -Sku Standard -Force $appGatewayInternalIP = "10.0.0.100" [String[]]$appGwNsgDestIPs = $appGatewayInternalIP, $appGatewayExternalIP.IpAddressCreate a network security group (NSG) and NSG rules for the Application Gateway subnet.
$appGwRule1 = New-AzNetworkSecurityRuleConfig -Name appgw-in -Description "AppGw inbound" ` -Access Allow -Protocol * -Direction Inbound -Priority 100 -SourceAddressPrefix ` GatewayManager -SourcePortRange * -DestinationAddressPrefix * -DestinationPortRange 65200-65535 $appGwRule2 = New-AzNetworkSecurityRuleConfig -Name appgw-in-internet -Description "AppGw inbound Internet" ` -Access Allow -Protocol "TCP" -Direction Inbound -Priority 110 -SourceAddressPrefix ` Internet -SourcePortRange * -DestinationAddressPrefix $appGwNsgDestIPs -DestinationPortRange 443 $appGwNsg = New-AzNetworkSecurityGroup -ResourceGroupName $resGroupName -Location $location -Name ` "nsg-agw" -SecurityRules $appGwRule1, $appGwRule2Create a network security group (NSG) and NSG rules for the API Management subnet. API Management stv2 requires several specific NSG rules.
$apimRule1 = New-AzNetworkSecurityRuleConfig -Name APIM-Management -Description "APIM inbound" ` -Access Allow -Protocol Tcp -Direction Inbound -Priority 100 -SourceAddressPrefix ApiManagement ` -SourcePortRange * -DestinationAddressPrefix VirtualNetwork -DestinationPortRange 3443 $apimRule2 = New-AzNetworkSecurityRuleConfig -Name AllowAppGatewayToAPIM -Description "Allows inbound App Gateway traffic to APIM" ` -Access Allow -Protocol Tcp -Direction Inbound -Priority 110 -SourceAddressPrefix "10.0.0.0/24" ` -SourcePortRange * -DestinationAddressPrefix "10.0.1.0/24" -DestinationPortRange 443 $apimRule3 = New-AzNetworkSecurityRuleConfig -Name AllowAzureLoadBalancer -Description "Allows inbound Azure Infrastructure Load Balancer traffic to APIM" ` -Access Allow -Protocol Tcp -Direction Inbound -Priority 120 -SourceAddressPrefix AzureLoadBalancer ` -SourcePortRange * -DestinationAddressPrefix "10.0.1.0/24" -DestinationPortRange 6390 $apimRule4 = New-AzNetworkSecurityRuleConfig -Name AllowKeyVault -Description "Allows outbound traffic to Azure Key Vault" ` -Access Allow -Protocol Tcp -Direction Outbound -Priority 100 -SourceAddressPrefix "10.0.1.0/24" ` -SourcePortRange * -DestinationAddressPrefix AzureKeyVault -DestinationPortRange 443 $apimNsg = New-AzNetworkSecurityGroup -ResourceGroupName $resGroupName -Location $location -Name ` "nsg-apim" -SecurityRules $apimRule1, $apimRule2, $apimRule3, $apimRule4Assign the address range 10.0.0.0/24 to the subnet variable to be used for Application Gateway while you create a virtual network.
$appGatewaySubnet = New-AzVirtualNetworkSubnetConfig -Name "appGatewaySubnet" -NetworkSecurityGroup $appGwNsg -AddressPrefix "10.0.0.0/24"Assign the address range 10.0.1.0/24 to the subnet variable to be used for API Management while you create a virtual network.
$apimSubnet = New-AzVirtualNetworkSubnetConfig -Name "apimSubnet" -NetworkSecurityGroup $apimNsg -AddressPrefix "10.0.1.0/24"Create a virtual network named vnet-contoso. Use the prefix 10.0.0.0/16 with subnets 10.0.0.0/24 and 10.0.1.0/24.
$vnet = New-AzVirtualNetwork -Name "vnet-contoso" -ResourceGroupName $resGroupName ` -Location $location -AddressPrefix "10.0.0.0/16" -Subnet $appGatewaySubnet,$apimSubnetAssign subnet variables for the next steps.
$appGatewaySubnetData = $vnet.Subnets[0] $apimSubnetData = $vnet.Subnets[1]
Create an API Management instance inside a virtual network
The following example shows how to create an API Management instance in a virtual network configured for internal access only.
API Management stv2 requires a public IP with a unique
DomainNameLabel.$apimPublicIpAddressId = New-AzPublicIpAddress -ResourceGroupName $resGroupName -name "pip-apim" -location $location ` -AllocationMethod Static -Sku Standard -Force -DomainNameLabel $apimDomainNameLabelCreate an API Management virtual network object by using the subnet
$apimSubnetDatayou created.$apimVirtualNetwork = New-AzApiManagementVirtualNetwork -SubnetResourceId $apimSubnetData.IdCreate an API Management instance inside the virtual network. This example creates the service in the Developer service tier. Substitute a unique name for your API Management instance.
$apimService = New-AzApiManagement -ResourceGroupName $resGroupName -Location $location -Name $apimServiceName -Organization $apimOrganization ` -AdminEmail $apimAdminEmail -VirtualNetwork $apimVirtualNetwork -VpnType "Internal" -Sku "Developer" -PublicIpAddressId $apimPublicIpAddressId.Id
It can take between 30 and 40 minutes to create and activate an API Management instance in this tier. After the previous command succeeds, see DNS configuration required to access internal virtual network API Management service to confirm access to it.
Set up custom domain names in API Management
To set up custom domain names in API Management:
Initialize the following variables with the details of the certificates with private keys for the domains and the trusted root certificate. In this example, we use
api.contoso.net,portal.contoso.net, andmanagement.contoso.net.$certGatewayPwd = ConvertTo-SecureString -String $gatewayCertPfxPassword -AsPlainText -Force $certPortalPwd = ConvertTo-SecureString -String $portalCertPfxPassword -AsPlainText -Force $certManagementPwd = ConvertTo-SecureString -String $managementCertPfxPassword -AsPlainText -ForceCreate and set the
Hostnameconfiguration objects for the API Management endpoints.$gatewayHostnameConfig = New-AzApiManagementCustomHostnameConfiguration -Hostname $gatewayHostname ` -HostnameType Proxy -PfxPath $gatewayCertPfxPath -PfxPassword $certGatewayPwd $portalHostnameConfig = New-AzApiManagementCustomHostnameConfiguration -Hostname $portalHostname ` -HostnameType DeveloperPortal -PfxPath $portalCertPfxPath -PfxPassword $certPortalPwd $managementHostnameConfig = New-AzApiManagementCustomHostnameConfiguration -Hostname $managementHostname ` -HostnameType Management -PfxPath $managementCertPfxPath -PfxPassword $certManagementPwd $apimService.ProxyCustomHostnameConfiguration = $gatewayHostnameConfig $apimService.PortalCustomHostnameConfiguration = $portalHostnameConfig $apimService.ManagementCustomHostnameConfiguration = $managementHostnameConfig Set-AzApiManagement -InputObject $apimService
Configure a private zone for DNS resolution in the virtual network
To configure a private DNS zone for DNS resolution in the virtual network:
Create a private DNS zone and link the virtual network.
$myZone = New-AzPrivateDnsZone -Name $domain -ResourceGroupName $resGroupName $link = New-AzPrivateDnsVirtualNetworkLink -ZoneName $domain ` -ResourceGroupName $resGroupName -Name "mylink" ` -VirtualNetworkId $vnet.idCreate A-records for the custom domain host names that map to the private IP address of API Management.
$apimIP = $apimService.PrivateIPAddresses[0] New-AzPrivateDnsRecordSet -Name api -RecordType A -ZoneName $domain ` -ResourceGroupName $resGroupName -Ttl 3600 ` -PrivateDnsRecords (New-AzPrivateDnsRecordConfig -IPv4Address $apimIP) New-AzPrivateDnsRecordSet -Name portal -RecordType A -ZoneName $domain ` -ResourceGroupName $resGroupName -Ttl 3600 ` -PrivateDnsRecords (New-AzPrivateDnsRecordConfig -IPv4Address $apimIP) New-AzPrivateDnsRecordSet -Name management -RecordType A -ZoneName $domain ` -ResourceGroupName $resGroupName -Ttl 3600 ` -PrivateDnsRecords (New-AzPrivateDnsRecordConfig -IPv4Address $apimIP)
Create application gateway configuration
All configuration items must be set up before you create the application gateway. The following steps create the configuration items that are needed for an Application Gateway resource.
Create an Application Gateway IP configuration named gatewayIP01. When Application Gateway starts, it picks up an IP address from the subnet configured and routes network traffic to the IP addresses in the back-end IP pool. Keep in mind that each instance takes one IP address.
$gipconfig = New-AzApplicationGatewayIPConfiguration -Name "gatewayIP01" -Subnet $appGatewaySubnetDataConfigure the same frontend port for the public and private IP endpoint. This port is the one that users connect to. By using the same port for both we ensure that internal and external requests can be made to the same port.
$fp01 = New-AzApplicationGatewayFrontendPort -Name "port01" -Port 443Configure two frontend IP addresses - one public and one private. The private IP address is taken from the application gateway subnet, which was the first to be created at index 0.
$fipconfig01 = New-AzApplicationGatewayFrontendIPConfig ` -Name "gateway-public-ip" -PublicIPAddress $appGatewayExternalIP $fipconfig02 = New-AzApplicationGatewayFrontendIPConfig ` -Name "gateway-private-ip" -PrivateIPAddress $appGatewayInternalIP ` -Subnet $vnet.Subnets[0]Configure the certificates for the application gateway. They're used to decrypt and reencrypt the traffic that passes through.
Note
Application Gateway supports defining custom TLS options, disabling certain TLS protocol versions, and specifying cipher suites and the order of preference. To learn more about configurable TLS options, see the TLS policy overview.
$certGateway = New-AzApplicationGatewaySslCertificate -Name "gatewaycert" ` -CertificateFile $gatewayCertPfxPath -Password $certGatewayPwd $certPortal = New-AzApplicationGatewaySslCertificate -Name "portalcert" ` -CertificateFile $portalCertPfxPath -Password $certPortalPwd $certManagement = New-AzApplicationGatewaySslCertificate -Name "managementcert" ` -CertificateFile $managementCertPfxPath -Password $certManagementPwdCreate the HTTP listeners for the application gateway. Assign the front-end IP configuration, port, and TLS/SSL certificates to them.
# Public/external listeners $gatewayListener = New-AzApplicationGatewayHttpListener -Name "gatewaylistener" ` -Protocol "Https" -FrontendIPConfiguration $fipconfig01 -FrontendPort $fp01 ` -SslCertificate $certGateway -HostName $gatewayHostname -RequireServerNameIndication true $portalListener = New-AzApplicationGatewayHttpListener -Name "portallistener" ` -Protocol "Https" -FrontendIPConfiguration $fipconfig01 -FrontendPort $fp01 ` -SslCertificate $certPortal -HostName $portalHostname -RequireServerNameIndication true $managementListener = New-AzApplicationGatewayHttpListener -Name "managementlistener" ` -Protocol "Https" -FrontendIPConfiguration $fipconfig01 -FrontendPort $fp01 ` -SslCertificate $certManagement -HostName $managementHostname -RequireServerNameIndication true # Private/internal listeners $gatewayListenerPrivate = New-AzApplicationGatewayHttpListener -Name "gatewaylistener-private" ` -Protocol "Https" -FrontendIPConfiguration $fipconfig02 -FrontendPort $fp01 ` -SslCertificate $certGateway -HostName $gatewayHostname -RequireServerNameIndication true $portalListenerPrivate = New-AzApplicationGatewayHttpListener -Name "portallistener-private" ` -Protocol "Https" -FrontendIPConfiguration $fipconfig02 -FrontendPort $fp01 ` -SslCertificate $certPortal -HostName $portalHostname -RequireServerNameIndication true $managementListenerPrivate = New-AzApplicationGatewayHttpListener -Name "managementlistener-private" ` -Protocol "Https" -FrontendIPConfiguration $fipconfig02 -FrontendPort $fp01 ` -SslCertificate $certManagement -HostName $managementHostname -RequireServerNameIndication trueCreate custom probes to the API Management
ContosoApigateway domain endpoint. The path/status-0123456789abcdefis a default health endpoint hosted on all instances of API Management. Setapi.contoso.netas a custom probe host name to secure it with the TLS/SSL certificate.Note
The host name
contosoapi.azure-api.netis the default proxy host name configured when a service namedcontosoapiis created in public Azure.$apimGatewayProbe = New-AzApplicationGatewayProbeConfig -Name "apimgatewayprobe" ` -Protocol "Https" -HostName $gatewayHostname -Path "/status-0123456789abcdef" ` -Interval 30 -Timeout 120 -UnhealthyThreshold 8 $apimPortalProbe = New-AzApplicationGatewayProbeConfig -Name "apimportalprobe" ` -Protocol "Https" -HostName $portalHostname -Path "/signin" ` -Interval 60 -Timeout 300 -UnhealthyThreshold 8 $apimManagementProbe = New-AzApplicationGatewayProbeConfig -Name "apimmanagementprobe" ` -Protocol "Https" -HostName $managementHostname -Path "/ServiceStatus" ` -Interval 60 -Timeout 300 -UnhealthyThreshold 8Configure the backend certificates' trusted root certificate. This certificate verifies the authenticity of the backend certificates.
$trustedRootCert = New-AzApplicationGatewayTrustedRootCertificate ` -Name "allowlistcert1" -CertificateFile $trustedRootCertCerPathConfigure HTTP backend settings for the application gateway, including a timeout limit for backend requests, after which they're canceled. This value is different from the probe timeout.
$apimPoolGatewaySetting = New-AzApplicationGatewayBackendHttpSettings -Name "apimPoolGatewaySetting" ` -Port 443 -Protocol "Https" -CookieBasedAffinity "Disabled" -Probe $apimGatewayProbe ` -TrustedRootCertificate $trustedRootCert -PickHostNameFromBackendAddress -RequestTimeout 180 $apimPoolPortalSetting = New-AzApplicationGatewayBackendHttpSettings -Name "apimPoolPortalSetting" ` -Port 443 -Protocol "Https" -CookieBasedAffinity "Disabled" -Probe $apimPortalProbe ` -TrustedRootCertificate $trustedRootCert -PickHostNameFromBackendAddress -RequestTimeout 180 $apimPoolManagementSetting = New-AzApplicationGatewayBackendHttpSettings -Name "apimPoolManagementSetting" ` -Port 443 -Protocol "Https" -CookieBasedAffinity "Disabled" -Probe $apimManagementProbe ` -TrustedRootCertificate $trustedRootCert -PickHostNameFromBackendAddress -RequestTimeout 180Configure a backend IP address pool for each API Management endpoint by using its respective domain name.
$apimGatewayBackendPool = New-AzApplicationGatewayBackendAddressPool -Name "gatewaybackend" ` -BackendFqdns $gatewayHostname $apimPortalBackendPool = New-AzApplicationGatewayBackendAddressPool -Name "portalbackend" ` -BackendFqdns $portalHostname $apimManagementBackendPool = New-AzApplicationGatewayBackendAddressPool -Name "managementbackend" ` -BackendFqdns $managementHostnameCreate routing rules for the application gateway to use basic routing.
# Public/external gateway rules $gatewayRule = New-AzApplicationGatewayRequestRoutingRule -Name "gatewayrule" ` -RuleType Basic -HttpListener $gatewayListener -BackendAddressPool $apimGatewayBackendPool ` -BackendHttpSettings $apimPoolGatewaySetting -Priority 10 $portalRule = New-AzApplicationGatewayRequestRoutingRule -Name "portalrule" ` -RuleType Basic -HttpListener $portalListener -BackendAddressPool $apimPortalBackendPool ` -BackendHttpSettings $apimPoolPortalSetting -Priority 20 $managementRule = New-AzApplicationGatewayRequestRoutingRule -Name "managementrule" ` -RuleType Basic -HttpListener $managementListener -BackendAddressPool $apimManagementBackendPool ` -BackendHttpSettings $apimPoolManagementSetting -Priority 30 # Private/internal gateway rules $gatewayRulePrivate = New-AzApplicationGatewayRequestRoutingRule -Name "gatewayrule-private" ` -RuleType Basic -HttpListener $gatewayListenerPrivate -BackendAddressPool $apimGatewayBackendPool ` -BackendHttpSettings $apimPoolGatewaySetting -Priority 11 $portalRulePrivate = New-AzApplicationGatewayRequestRoutingRule -Name "portalrule-private" ` -RuleType Basic -HttpListener $portalListenerPrivate -BackendAddressPool $apimPortalBackendPool ` -BackendHttpSettings $apimPoolPortalSetting -Priority 21 $managementRulePrivate = New-AzApplicationGatewayRequestRoutingRule -Name "managementrule-private" ` -RuleType Basic -HttpListener $managementListenerPrivate -BackendAddressPool $apimManagementBackendPool ` -BackendHttpSettings $apimPoolManagementSetting -Priority 31Tip
Change
-RuleTypeand routing to restrict access to certain pages of the developer portal.Configure the number of instances and size for the application gateway. In this example, we use WAF_v2 SKU for increased security of the API Management resource.
Use a minimum of two instances (Capacity) for production workloads. You might want to use only one instance for nonproduction scenarios or for general experimentation. For more information, see Azure Application Gateway pricing.
$sku = New-AzApplicationGatewaySku -Name "WAF_v2" -Tier "WAF_v2" -Capacity 2Configure the WAF mode.
Tip
For a short period during setup and to test your firewall rules, you might want to configure "Detection" mode, which monitors and logs threat alerts but doesn't block traffic. You can then make any updates to firewall rules before transitioning to "Prevention" mode, which blocks intrusions and attacks that the rules detect.
$config = New-AzApplicationGatewayWebApplicationFirewallConfiguration -Enabled $true -FirewallMode "Prevention"Because TLS 1.0 currently is the default, set the application gateway to use one of the recent TLS 1.2 policy.
$policy = New-AzApplicationGatewaySslPolicy -PolicyType Predefined -PolicyName AppGwSslPolicy20220101
Create an application gateway
Create an application gateway with all the configuration objects from the preceding steps. It can take 15 minutes to create an instance.
$appgw = New-AzApplicationGateway ` -Name $appgwName ` -ResourceGroupName $resGroupName ` -Location $location ` -Sku $sku ` -SslPolicy $policy ` -SslCertificates $certGateway, $certPortal, $certManagement ` -TrustedRootCertificate $trustedRootCert ` -BackendAddressPools $apimGatewayBackendPool, $apimPortalBackendPool, $apimManagementBackendPool ` -BackendHttpSettingsCollection $apimPoolGatewaySetting, $apimPoolPortalSetting, $apimPoolManagementSetting ` -GatewayIpConfigurations $gipconfig ` -FrontendIpConfigurations $fipconfig01, $fipconfig02 ` -FrontendPorts $fp01 ` -HttpListeners $gatewayListener, $portalListener, $managementListener, $gatewayListenerPrivate, $portalListenerPrivate, $managementListenerPrivate ` -RequestRoutingRules $gatewayRule, $portalRule, $managementRule, $gatewayRulePrivate, $portalRulePrivate, $managementRulePrivate ` -Probes $apimGatewayProbe, $apimPortalProbe, $apimManagementProbe ` -WebApplicationFirewallConfig $configConfirm the health status of the API Management back ends.
Get-AzApplicationGatewayBackendHealth -Name $appgwName -ResourceGroupName $resGroupName
Ensure that the health status of each back-end pool is Healthy. If you need to troubleshoot an unhealthy back end or a back end with unknown health status, see Troubleshoot back-end health issues in Application Gateway.
Create DNS records to access API Management endpoints from the internet
After the application gateway is created, configure communication to API Management from the internet. Create DNS A-records that map each of the API Management endpoint host names that you configured to the application gateway's static public IP address. In this article, example host names are api.contoso.net, portal.contoso.net, and management.contoso.net.
Connectivity verification
For quick testing purposes, consider temporarily amending your computer's hosts file with entries that map the application gateway's public IP address to the API Management endpoint host names:
- Modify the hosts files. For example, if the application gateway's public IP is
172.203.129.101, the entry may be172.203.129.101 api.contoso.net. - Execute a curl command against API Management's status endpoint (the same path that was used for the health probe earlier):
curl -v https://api.contoso.net/status-0123456789abcdefThis should return a200 Service Operationalstatus, which indicates successful communication to API Management through Application Gateway.
DNS considerations
The Application Gateway now has private and public pathways. Using the same domains and ports creates a split-brain DNS situation in which an external DNS resolver should be set to resolve api.contoso.net to the application gateway's external IP address whereas an internal DNS resolver should resolve the same domain to the application gateway's internal IP address. This setup provides an advantage in that applications don't need to alter domain or port for internal or external targeting of applications and APIs. The responsibility for targeting is appropriately deferred to the DNS resolvers.
Summary
API Management configured in a virtual network provides a single gateway interface for all configured APIs, whether they're hosted on-premises or in the cloud. Integrating Application Gateway with API Management provides you with the flexibility to selectively enable particular APIs to be accessible on the internet. Integration also provides a WAF as a front end to your API Management instance.
Next steps
Set up using an Azure Resource Manager template
Learn more about Application Gateway:
Learn more about API Management and virtual networks:
Feedback
Coming soon: Throughout 2024 we will be phasing out GitHub Issues as the feedback mechanism for content and replacing it with a new feedback system. For more information see: https://aka.ms/ContentUserFeedback.
Submit and view feedback for