This article briefly describes the steps for running Turbostream on a virtual machine (VM) that's deployed on Azure. It also presents the performance results of running TurboStream on Azure.
Turbostream is advanced simulation software that's based on a computational fluid dynamics (CFD) solver. It can run on high-speed GPUs and on conventional CPUs.
The software enables high-fidelity methods, like unsteady full-annulus simulations, to be used as part of the routine design process.
Turbostream is used by NASA and in the design of aircraft engines, turbomachinery, and gas turbines.
Why deploy Turbostream on Azure?
- Modern and diverse compute options to meet the needs of your workloads
- The flexibility of virtualization without the need to buy and maintain physical hardware
- Rapid provisioning
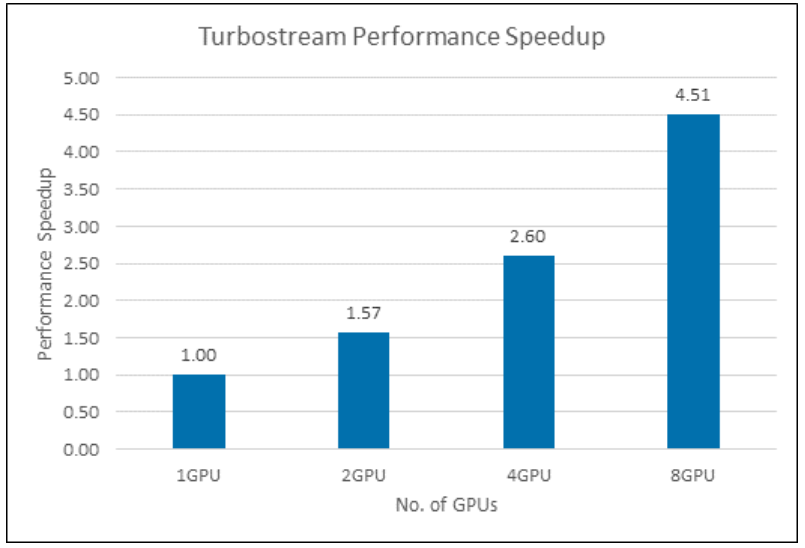
- With an eight-GPU configuration, a performance increase of 4.51 times that of a single GPU
Architecture
Download a Visio file of this architecture.
Components
- Azure Virtual Machines is used to create a Linux VM. For information about deploying the VM and installing the drivers, see Linux VMs on Azure.
- Azure Virtual Network is
used to create a private network infrastructure in the cloud.
- Network security groups are used to restrict access to the VM.
- A public IP address connects the internet to the VM.
- A physical solid-state drive (SSD) is used for storage.
Compute sizing and drivers
The performance tests of Turbostream used an ND_A100_v4 VM running Linux. The following table provides details about the VM.
| VM size | vCPU | Memory (GiB) | SSD (GiB) | GPUs | GPU memory (GiB) | Maximum data disks |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Standard_ND96asr_v4 | 96 | 900 | 6,000 | 8 A100 | 40 | 32 |
Required drivers
To take advantage of the GPU capabilities of ND_A100_v4 VMs, you need to install NVIDIA GPU drivers.
To use AMD processors on ND_A100_v4 VMs, you need to install AMD drivers.
Turbostream installation
Before you install Turbostream, you need to deploy and connect a Linux VM and install the required NVIDIA and AMD drivers.
Important
NVIDIA Fabric Manager installation is required for VMs that use NVLink or NVSwitch. ND_A100_v4 VMs use NVLink.
For information about deploying the VM and installing the drivers, see Run a Linux VM on Azure.
You can install Turbostream by signing in to ExaVault as a customer. The downloadable files include documentation, a release package, a license file, and a test simulation package (scaling_test.zip). For more information, contact Turbostream.
Turbostream performance results
Four simulations were tested, as described in the following table.
| Model number | Number of grid nodes (millions) |
|---|---|
| 1 | 6 |
| 2 | 12 |
| 3 | 24 |
| 4 | 48 |
The following table describes the performance results. Performance is the number of grid nodes processed per second. Relative performance is relative to the performance described in the first line of the table.
| Model number | Number of GPUs | Time (seconds, average of 200 iterations) | Performance | Relative performance |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 1* | 0.0743 | 80,753,701.21 | 1 |
| 2 | 2* | 0.0944 | 127,118,644.1 | 1.57 |
| 3 | 4* | 0.1145 | 209,606,986.9 | 2.60 |
| 4 | 8 | 0.1319 | 363,912,054.6 | 4.51 |
* In these cases, the number of GPUs was artificially limited. The Standard_ND96asr_v4 VM has eight GPUs.
The relative performance increases are presented graphically here:
Additional notes about tests
The following table provides details about the operating system and the NVIDIA drivers that were used for testing.
| OS version | OS architecture | GPU driver version | CUDA version |
|---|---|---|---|
| CentOS Linux release 8.1.1911 (Core) | x86-64 | 470.57.02 | 11.4 |
Azure cost
The following table presents the elapsed time. You can use this time and the Azure VM hourly cost for the NDA100v4 VM to calculate costs. For the current hourly cost, see Linux Virtual Machines Pricing.
Only simulation runtime is included in the reported time. Application installation time isn't included.
You can use the Azure pricing calculator to estimate the costs for your configuration.
| VM size | GPUs | Elapsed time (seconds) |
|---|---|---|
| Standard_ND96asr_v4 | 8 A100 | 196.10 |
Summary
- Turbostream was successfully tested on the ND_A100_v4 VM.
- Performance with eight GPUs is 4.51 times faster than the performance with one GPU.
Contributors
This article is maintained by Microsoft. It was originally written by the following contributors.
Principal authors:
- Hari Bagudu | Senior Manager
- Gauhar Junnarkar | Principal Program Manager
- Vinod Pamulapati | HPC Performance Engineer
Other contributors:
- Mick Alberts | Technical Writer
- Guy Bursell | Director Business Strategy
- Sachin Rastogi | Manager
To see non-public LinkedIn profiles, sign in to LinkedIn.
Next steps
- GPU-optimized virtual machine sizes
- Virtual machines on Azure
- Virtual networks and virtual machines on Azure
- Learning path: Run high-performance computing (HPC) applications on Azure
