High Availability with SQL Managed Instance enabled by Azure Arc
SQL Managed Instance enabled by Azure Arc is deployed on Kubernetes as a containerized application. It uses Kubernetes constructs such as stateful sets and persistent storage to provide built-in:
- Health monitoring
- Failure detection
- Automatic fail over to maintain service health.
For increased reliability, you can also configure SQL Managed Instance enabled by Azure Arc to deploy with extra replicas in a high availability configuration. The Arc data services data controller manages:
- Monitoring
- Failure detection
- Automatic failover
Arc-enabled data service provides this service without user intervention. The service:
- Sets up the availability group
- Configures database mirroring endpoints
- Adds databases to the availability group
- Coordinates failover and upgrade.
This document explores both types of high availability.
SQL Managed Instance enabled by Azure Arc provides different levels of high availability depending on whether the SQL managed instance was deployed as a General Purpose service tier or Business Critical service tier.
High availability in General Purpose service tier
In the General Purpose service tier, there is only one replica available, and the high availability is achieved via Kubernetes orchestration. For instance, if a pod or node containing the managed instance container image crashes, Kubernetes attempts to stand up another pod or node, and attach to the same persistent storage. During this time, the SQL managed instance is unavailable to the applications. Applications need to reconnect and retry the transaction when the new pod is up. If load balancer is the service type used, then applications can reconnect to the same primary endpoint and Kubernetes will redirect the connection to the new primary. If the service type is nodeport then the applications will need to reconnect to the new IP address.
Verify built-in high availability
To verify the build-in high availability provided by Kubernetes, you can:
- Delete the pod of an existing managed instance
- Verify that Kubernetes recovers from this action
During recover, Kubernetes bootstraps another pod and attaches the persistent storage.
Prerequisites
- Kubernetes cluster requires shared, remote storage
- A SQL Managed Instance enabled by Azure Arc deployed with one replica (default)
View the pods.
kubectl get pods -n <namespace of data controller>Delete the managed instance pod.
kubectl delete pod <name of managed instance>-0 -n <namespace of data controller>For example
user@pc:/# kubectl delete pod sql1-0 -n arc pod "sql1-0" deletedView the pods to verify that the managed instance is recovering.
kubectl get pods -n <namespace of data controller>For example:
user@pc:/# kubectl get pods -n arc NAME READY STATUS RESTARTS AGE sql1-0 2/3 Running 0 22s
After all containers within the pod recover, you can connect to the managed instance.
High availability in Business Critical service tier
In the Business Critical service tier, in addition to what is natively provided by Kubernetes orchestration, SQL Managed Instance for Azure Arc provides a contained availability group. The contained availability group is built on SQL Server Always On technology. It provides higher levels of availability. SQL Managed Instance enabled by Azure Arc deployed with Business Critical service tier can be deployed with either 2 or 3 replicas. These replicas are always kept in sync with each other.
With contained availability groups, any pod crashes or node failures are transparent to the application. The contained availability group provides at least one other pod that has all the data from the primary and is ready to take on connections.
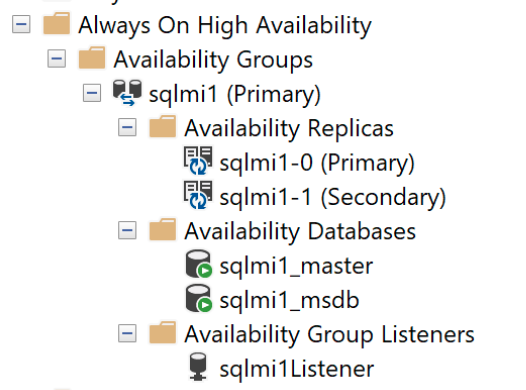
Contained availability groups
An availability group binds one or more user databases into a logical group so that when there is a failover, the entire group of databases fails over to the secondary replica as a single unit. An availability group only replicates data in the user databases but not the data in system databases such as logins, permissions, or agent jobs. A contained availability group includes metadata from system databases such as msdb and master databases. When logins are created or modified in the primary replica, they're automatically also created in the secondary replicas. Similarly, when an agent job is created or modified in the primary replica, the secondary replicas also receive those changes.
SQL Managed Instance enabled by Azure Arc takes this concept of contained availability group and adds Kubernetes operator so these can be deployed and managed at scale.
Capabilities that contained availability groups enable:
When deployed with multiple replicas, a single availability group named with the same name as the Arc enabled SQL managed instance is created. By default, contained AG has three replicas, including primary. All CRUD operations for the availability group are managed internally, including creating the availability group or joining replicas to the availability group created. You can't create more availability groups in an instance.
All databases are automatically added to the availability group, including all user and system databases like
masterandmsdb. This capability provides a single-system view across the availability group replicas. Notice bothcontainedag_masterandcontainedag_msdbdatabases if you connect directly to the instance. Thecontainedag_*databases represent themasterandmsdbinside the availability group.An external endpoint is automatically provisioned for connecting to databases within the availability group. This endpoint
<managed_instance_name>-external-svcplays the role of the availability group listener.
Deploy SQL Managed Instance enabled by Azure Arc with multiple replicas using Azure portal
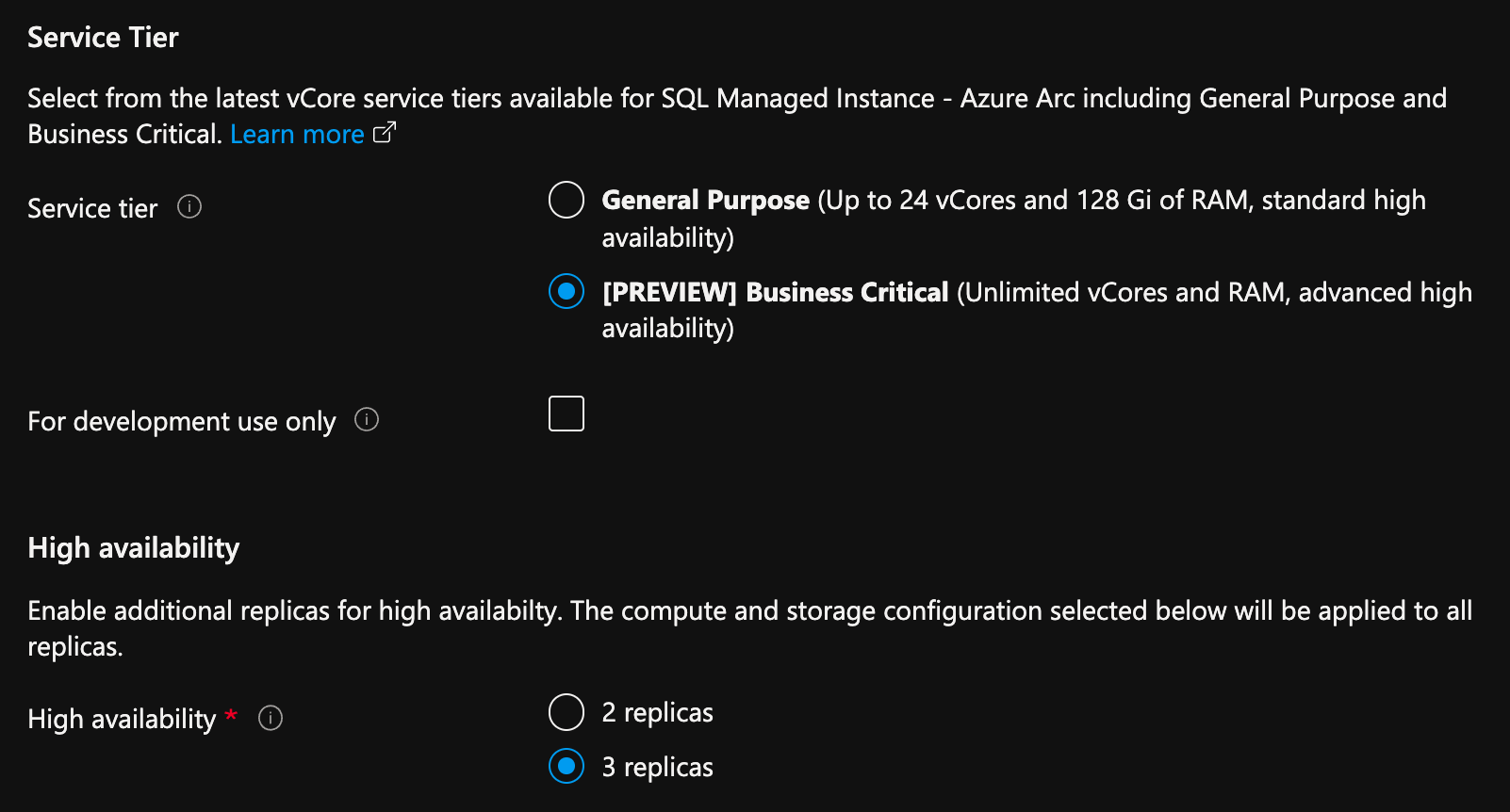
From Azure portal, on the create SQL Managed Instance enabled by Azure Arc page:
- Select Configure Compute + Storage under Compute + Storage. The portal shows advanced settings.
- Under Service tier, select Business Critical.
- Check the "For development use only", if using for development purposes.
- Under High availability, select either 2 replicas or 3 replicas.
Deploy with multiple replicas using Azure CLI
When a SQL Managed Instance enabled by Azure Arc is deployed in Business Critical service tier, the deployment creates multiple replicas. The setup and configuration of contained availability groups among those instances is automatically done during provisioning.
For instance, the following command creates a managed instance with 3 replicas.
Indirectly connected mode:
az sql mi-arc create -n <instanceName> --k8s-namespace <namespace> --use-k8s --tier <tier> --replicas <number of replicas>
Example:
az sql mi-arc create -n sqldemo --k8s-namespace my-namespace --use-k8s --tier BusinessCritical --replicas 3
Directly connected mode:
az sql mi-arc create --name <name> --resource-group <group> --location <Azure location> –subscription <subscription> --custom-location <custom-location> --tier <tier> --replicas <number of replicas>
Example:
az sql mi-arc create --name sqldemo --resource-group rg --location uswest2 –subscription xxxxxxx-xxxx-xxxx-xxxx-xxxxxxxxxxxx --custom-location private-location --tier BusinessCritical --replcias 3
By default, all the replicas are configured in synchronous mode. This means any updates on the primary instance are synchronously replicated to each of the secondary instances.
View and monitor high availability status
Once the deployment is complete, connect to the primary endpoint from SQL Server Management Studio.
Verify and retrieve the endpoint of the primary replica, and connect to it from SQL Server Management Studio.
For instance, if the SQL instance was deployed using service-type=loadbalancer, run the below command to retrieve the endpoint to connect to:
az sql mi-arc list --k8s-namespace my-namespace --use-k8s
or
kubectl get sqlmi -A
Get the primary and secondary endpoints and AG status
Use the kubectl describe sqlmi or az sql mi-arc show commands to view the primary and secondary endpoints, and high availability status.
Example:
kubectl describe sqlmi sqldemo -n my-namespace
or
az sql mi-arc show --name sqldemo --k8s-namespace my-namespace --use-k8s
Example output:
"status": {
"endpoints": {
"logSearchDashboard": "https://10.120.230.404:5601/app/kibana#/discover?_a=(query:(language:kuery,query:'custom_resource_name:sqldemo'))",
"metricsDashboard": "https://10.120.230.46:3000/d/40q72HnGk/sql-managed-instance-metrics?var-hostname=sqldemo-0",
"mirroring": "10.15.100.150:5022",
"primary": "10.15.100.150,1433",
"secondary": "10.15.100.156,1433"
},
"highAvailability": {
"healthState": "OK",
"mirroringCertificate": "-----BEGIN CERTIFICATE-----\n...\n-----END CERTIFICATE-----"
},
"observedGeneration": 1,
"readyReplicas": "2/2",
"state": "Ready"
}
You can connect to the primary endpoint with SQL Server Management Studio and verify DMVs as:
SELECT * FROM sys.dm_hadr_availability_replica_states
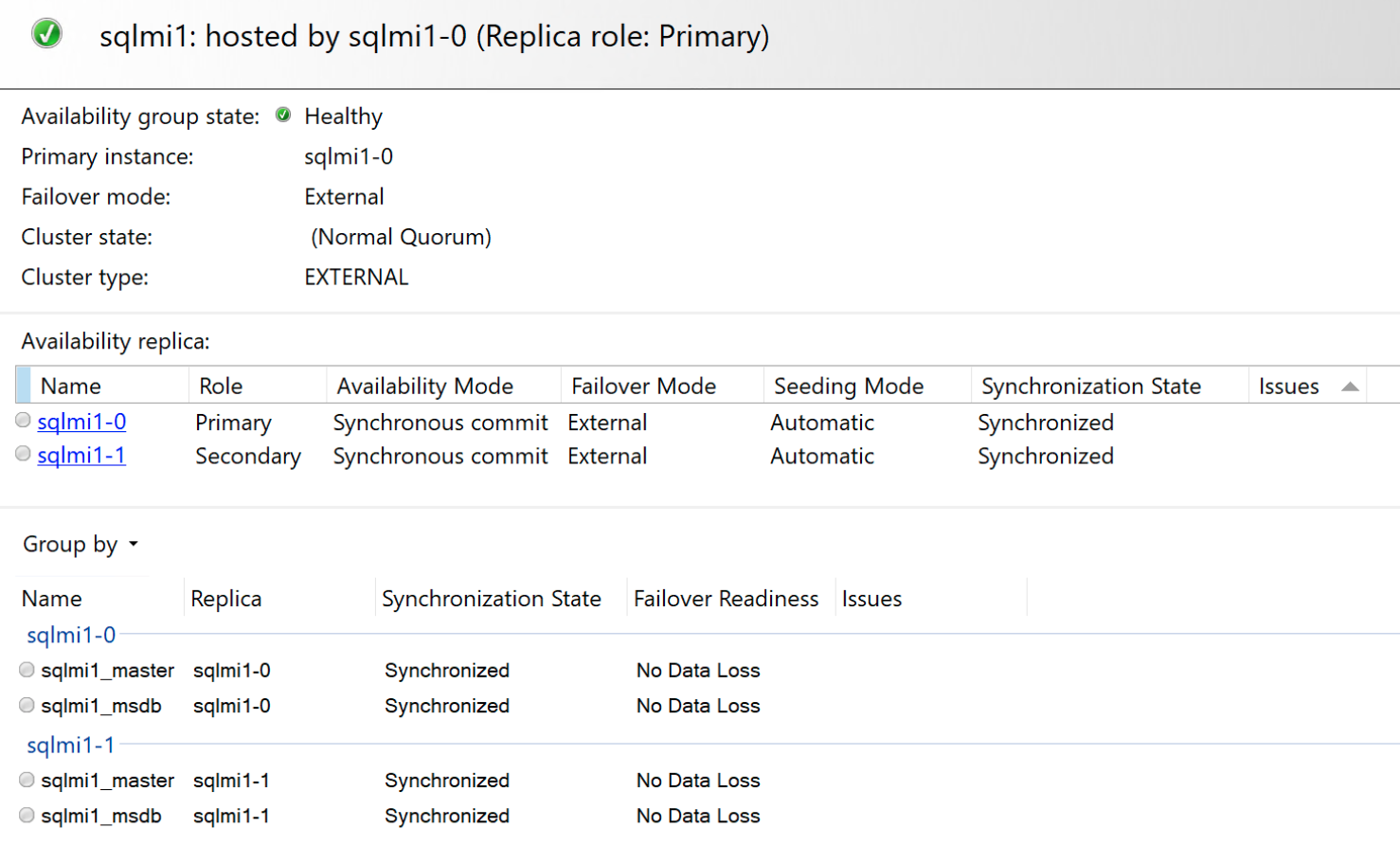
And the Contained Availability Dashboard:
Failover scenarios
Unlike SQL Server Always On availability groups, the contained availability group is a managed high availability solution. Hence, the failover modes are limited compared to the typical modes available with SQL Server Always On availability groups.
Deploy Business Critical service tier SQL managed instances in either two-replica configuration or three replica configuration. The effects of failures and the subsequent recoverability are different with each configuration. A three replica instance provides a higher level of availability and recovery, than a two replica instance.
In a two replica configuration, when both the node states are SYNCHRONIZED, if the primary replica becomes unavailable, the secondary replica is automatically promoted to primary. When the failed replica becomes available, it is updated with all the pending changes. If there are connectivity issues between the replicas, then the primary replica may not commit any transactions as every transaction needs to be committed on both replicas before a success is returned back on the primary.
In a three replica configuration, a transaction needs to commit in at least 2 of the 3 replicas before returning a success message back to the application. In the event of a failure, one of the secondaries is automatically promoted to primary while Kubernetes attempts to recover the failed replica. When the replica becomes available, it is automatically joined back with the contained availability group and pending changes are synchronized. If there are connectivity issues between the replicas, and more than 2 replicas are out of sync, primary replica won't commit any transactions.
Note
It is recommended to deploy a Business Critical SQL Managed Instance in a three replica configuration than a two replica configuration to achieve near-zero data loss.
To fail over from the primary replica to one of the secondaries, for a planned event, run the following command:
If you connect to primary, you can use following T-SQL to fail over the SQL instance to one of the secondaries:
ALTER AVAILABILITY GROUP current SET (ROLE = SECONDARY);
If you connect to the secondary, you can use following T-SQL to promote the desired secondary to primary replica.
ALTER AVAILABILITY GROUP current SET (ROLE = PRIMARY);
Preferred primary replica
You can also set a specific replica to be the primary replica using AZ CLI as follows:
az sql mi-arc update --name <sqlinstance name> --k8s-namespace <namespace> --use-k8s --preferred-primary-replica <replica>
Example:
az sql mi-arc update --name sqldemo --k8s-namespace my-namespace --use-k8s --preferred-primary-replica sqldemo-3
Note
Kubernetes will attempt to set the preferred replica, however it is not guaranteed.
Restoring a database onto a multi-replica instance
Additional steps are required to restore a database into an availability group. The following steps demonstrate how to restore a database into a managed instance and add it to an availability group.
Expose the primary instance external endpoint by creating a new Kubernetes service.
Determine the pod that hosts the primary replica. Connect to the managed instance and run:
SELECT @@SERVERNAMEThe query returns the pod that hosts the primary replica.
Create the Kubernetes service to the primary instance by running the following command if your Kubernetes cluster uses
NodePortservices. Replace<podName>with the name of the server returned at previous step,<serviceName>with the preferred name for the Kubernetes service created.kubectl -n <namespaceName> expose pod <podName> --port=1533 --name=<serviceName> --type=NodePortFor a LoadBalancer service, run the same command, except that the type of the service created is
LoadBalancer. For example:kubectl -n <namespaceName> expose pod <podName> --port=1533 --name=<serviceName> --type=LoadBalancerHere is an example of this command run against Azure Kubernetes Service, where the pod hosting the primary is
sql2-0:kubectl -n arc-cluster expose pod sql2-0 --port=1533 --name=sql2-0-p --type=LoadBalancerGet the IP of the Kubernetes service created:
kubectl get services -n <namespaceName>Restore the database to the primary instance endpoint.
Add the database backup file into the primary instance container.
kubectl cp <source file location> <pod name>:var/opt/mssql/data/<file name> -c <serviceName> -n <namespaceName>Example
kubectl cp /home/WideWorldImporters-Full.bak sql2-1:var/opt/mssql/data/WideWorldImporters-Full.bak -c arc-sqlmi -n arcRestore the database backup file by running the command below.
RESTORE DATABASE test FROM DISK = '/var/opt/mssql/data/<file name>.bak' WITH MOVE '<database name>' to '/var/opt/mssql/data/<file name>.mdf' ,MOVE '<database name>' to '/var/opt/mssql/data/<file name>_log.ldf' ,RECOVERY, REPLACE, STATS = 5; GOExample
RESTORE Database WideWorldImporters FROM DISK = '/var/opt/mssql/data/WideWorldImporters-Full.BAK' WITH MOVE 'WWI_Primary' TO '/var/opt/mssql/data/WideWorldImporters.mdf', MOVE 'WWI_UserData' TO '/var/opt/mssql/data/WideWorldImporters_UserData.ndf', MOVE 'WWI_Log' TO '/var/opt/mssql/data/WideWorldImporters.ldf', MOVE 'WWI_InMemory_Data_1' TO '/var/opt/mssql/data/WideWorldImporters_InMemory_Data_1', RECOVERY, REPLACE, STATS = 5; GOAdd the database to the availability group.
For the database to be added to the AG, it must run in full recovery mode and a log backup has to be taken. Run the TSQL statements below to add the restored database into the availability group.
ALTER DATABASE <databaseName> SET RECOVERY FULL; BACKUP DATABASE <databaseName> TO DISK='<filePath>' ALTER AVAILABILITY GROUP containedag ADD DATABASE <databaseName>The following example adds a database named
WideWorldImportersthat was restored on the instance:ALTER DATABASE WideWorldImporters SET RECOVERY FULL; BACKUP DATABASE WideWorldImporters TO DISK='/var/opt/mssql/data/WideWorldImporters.bak' ALTER AVAILABILITY GROUP containedag ADD DATABASE WideWorldImporters
Important
As a best practice, you should delete the Kubernetes service created above by running this command:
kubectl delete svc sql2-0-p -n arc
Limitations
SQL Managed Instance enabled by Azure Arc availability groups has the same limitations as Big Data Cluster availability groups. For more information, see Deploy SQL Server Big Data Cluster with high availability.
Related content
Learn more about Features and Capabilities of SQL Managed Instance enabled by Azure Arc
Feedback
Coming soon: Throughout 2024 we will be phasing out GitHub Issues as the feedback mechanism for content and replacing it with a new feedback system. For more information see: https://aka.ms/ContentUserFeedback.
Submit and view feedback for