Migrate PostgreSQL database to Azure Arc-enabled PostgreSQL server
This document describes the steps to get your existing PostgreSQL database (one that not hosted in Azure Arc-enabled Data Services) into your Azure Arc-enabled PostgreSQL server.
Note
As a preview feature, the technology presented in this article is subject to Supplemental Terms of Use for Microsoft Azure Previews.
The latest updates are available in the release notes.
Considerations
Azure Arc-enabled PostgreSQL server is the community version of PostgreSQL. So any tool that works on PostgreSQL outside of Azure Arc should work with Azure Arc-enabled PostgreSQL server.
As such, with the set of tools you use today for Postgres, you should be able to:
- Backup your Postgres database from your instance hosted outside of Azure Arc
- Restore it in your Azure Arc-enabled PostgreSQL server
What will be left for you to do is:
- reset the server parameters
- reset the security contexts: recreate users, roles, and reset permissions...
To do this backup/restore operation, you can use any tool that is capable of doing backup/restore for Postgres. For example:
- Azure Data Studio and its Postgres extension
pgclipgAdminpg_dumppg_restorepsql- ...
Example
Let's illustrate those steps using the pgAdmin tool.
Consider the following setup:
Source:
A Postgres server running on premises on a bare metal server and named JEANYDSRV. It is of version 14 and hosts a database named MyOnPremPostgresDB that has one table T1 which has 1 row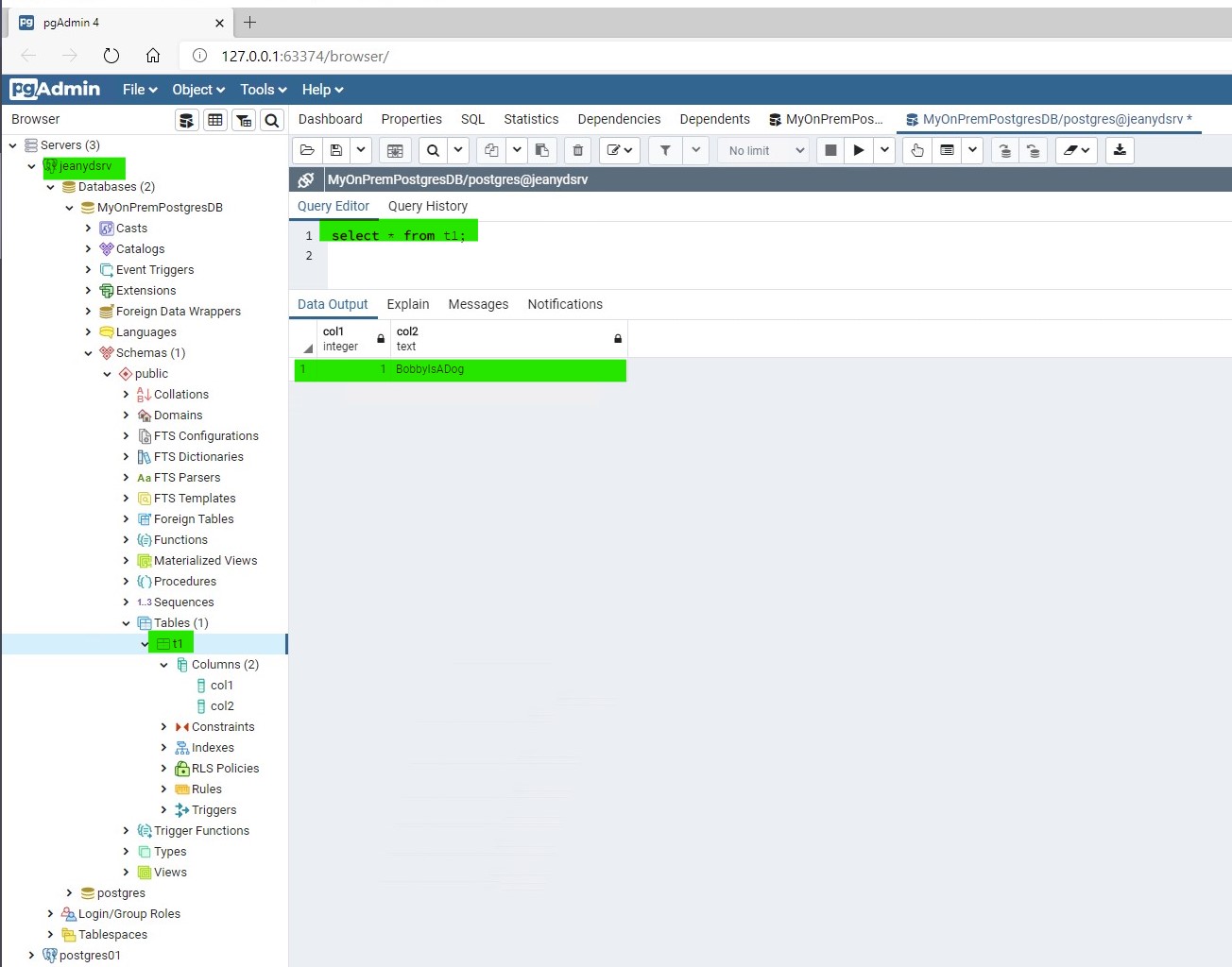
Destination:
A Postgres server running in an Azure Arc environment and named postgres01. It is of version 14. It does not have any database except the standard Postgres database.
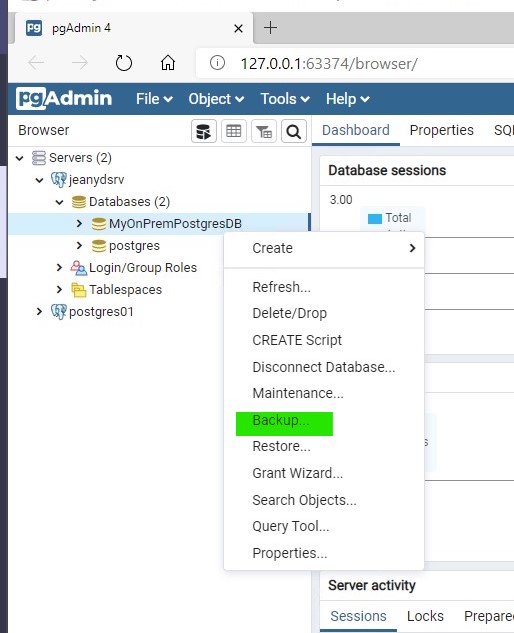
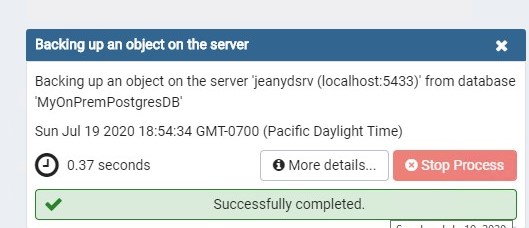
Take a backup of the source database on premises
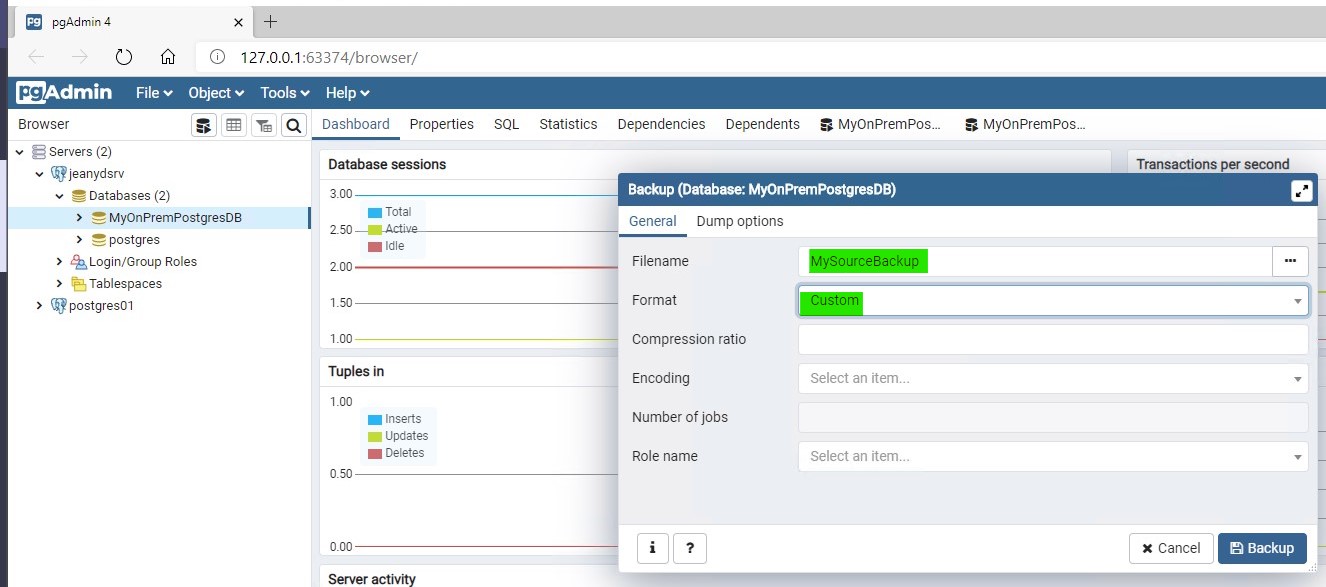
Configure it:
- Give it a file name: MySourceBackup
- Set the format to Custom
The backup completes successfully:
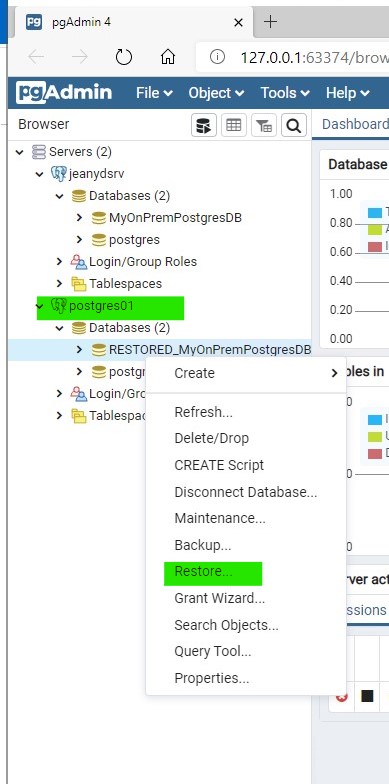
Create an empty database on the destination system in your Azure Arc-enabled PostgreSQL server
Note
To register a Postgres instance in the pgAdmin tool, you need to you use public IP of your instance in your Kubernetes cluster and set the port and security context appropriately. You will find these details on the psql endpoint line after running the following command:
az postgres server-arc endpoint list -n postgres01 --k8s-namespace <namespace> --use-k8s
That returns an output like:
{
"instances": [
{
"endpoints": [
"Description": "PostgreSQL Instance",
"Endpoint": "postgresql://postgres:<replace with password>@12.345.123.456:1234"
},
{
"Description": "Log Search Dashboard",
"Endpoint": "https://12.345.123.456:12345/kibana/app/kibana#/discover?_a=(query:(language:kuery,query:'custom_resource_name:\"postgres01\"'))"
},
{
"Description": "Metrics Dashboard",
"Endpoint": "https://12.345.123.456:12345/grafana/d/postgres-metrics?var-Namespace=arc3&var-Name=postgres01"
}
],
"engine": "PostgreSql",
"name": "postgres01"
}
],
"namespace": "arc"
}
Let's name the destination database RESTORED_MyOnPremPostgresDB.
Restore the database in your Arc setup
Configure the restore:
Point to the file that contains the backup to restore: MySourceBackup
Keep the format set to Custom or tar
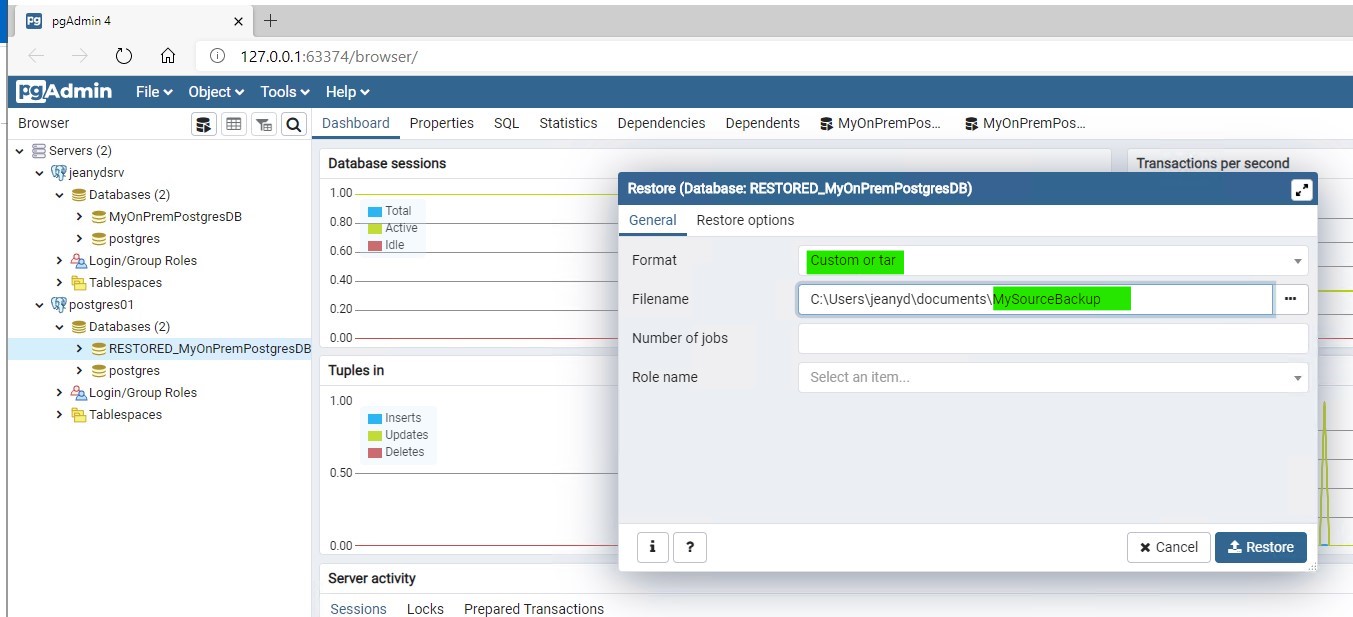
Click Restore.
The restore is successful.
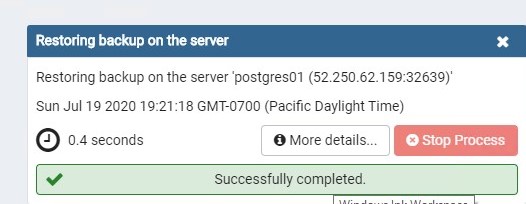
Verify that the database was successfully restored in your Azure Arc-enabled PostgreSQL server
Use either of the following methods:
From pgAdmin:
Expand the Postgres instance hosted in your Azure Arc setup. You will see the table in the database that you have restored and when you select the data it shows the same row as that it has in the on-premises instance:
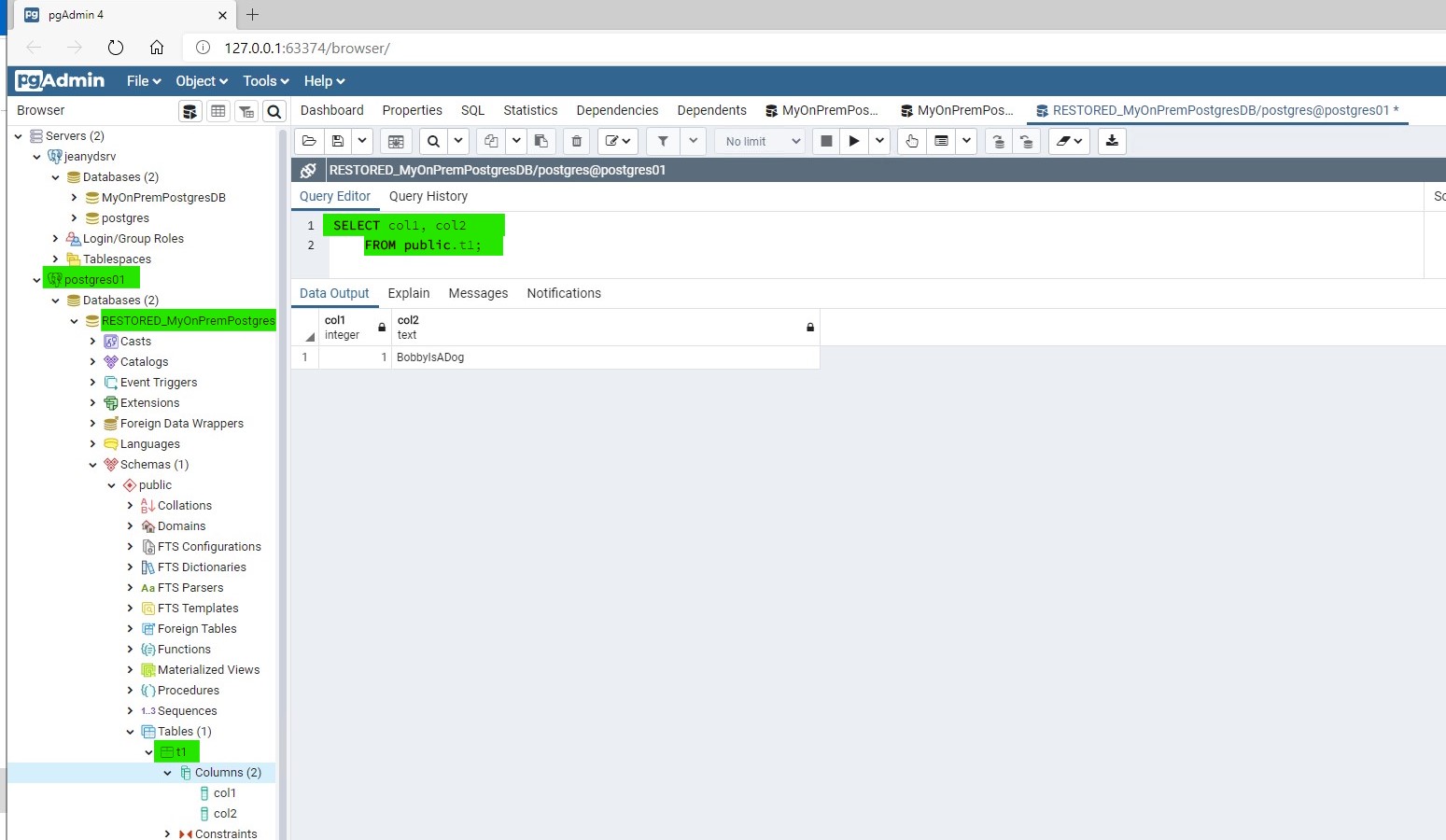
From psql inside your Azure Arc setup:
Within your Arc setup you can use psql to connect to your Postgres instance, set the database context to RESTORED_MyOnPremPostgresDB and query the data:
List the end points to help form your
psqlconnection string:az postgres server-arc endpoint list -n postgres01 --k8s-namespace <namespace> --use-k8s{ "instances": [ { "endpoints": [ "Description": "PostgreSQL Instance", "Endpoint": "postgresql://postgres:<replace with password>@12.345.123.456:1234" }, { "Description": "Log Search Dashboard", "Endpoint": "https://12.345.123.456:12345/kibana/app/kibana#/discover?_a=(query:(language:kuery,query:'custom_resource_name:\"postgres01\"'))" }, { "Description": "Metrics Dashboard", "Endpoint": "https://12.345.123.456:12345/grafana/d/postgres-metrics?var-Namespace=arc3&var-Name=postgres01" } ], "engine": "PostgreSql", "name": "postgres01" } ], "namespace": "arc" }From your
psqlconnection string use the-dparameter to indicate the database name. With the below command, you will be prompted for the password:psql -d RESTORED_MyOnPremPostgresDB -U postgres -h 10.0.0.4 -p 32639psqlconnects.Password for user postgres: psql (10.12 (Ubuntu 10.12-0ubuntu0.18.04.1), server 12.3 (Debian 12.3-1.pgdg100+1)) WARNING: psql major version 10, server major version 12. Some psql features might not work. SSL connection (protocol: TLSv1.3, cipher: TLS_AES_256_GCM_SHA384, bits: 256, compression: off) Type "help" for help. RESTORED_MyOnPremPostgresDB=#Select the table and you'll see the data that you restored from the on-premises Postgres instance:
RESTORED_MyOnPremPostgresDB=# select * from t1;col1 | col2 ------+------------- 1 | BobbyIsADog (1 row)
Note
- It is not possible today to "onboard into Azure Arc" an existing Postgres instance that would running on premises or in any other cloud. In other words, it is not possible to install some sort of "Azure Arc agent" on your existing Postgres instance to make it a Postgres setup enabled by Azure Arc. Instead, you need to create a new Postgres instance and transfer data into it. You may use the technique shown above to do this or you may use any ETL tool of your choice.
*In these documents, skip the sections Sign in to the Azure portal, and Create an Azure Database for PostgreSQL. Implement the remaining steps in your Azure Arc deployment. Those sections are specific to the Azure Database for PostgreSQL server offered as a PaaS service in the Azure cloud but the other parts of the documents are directly applicable to your Azure Arc-enabled PostgreSQL server.
Feedback
Coming soon: Throughout 2024 we will be phasing out GitHub Issues as the feedback mechanism for content and replacing it with a new feedback system. For more information see: https://aka.ms/ContentUserFeedback.
Submit and view feedback for
