Resource sync
Resource sync lets you create, update, or delete resources directly on the Kubernetes cluster using Kubernetes APIs in the direct connected mode, and automatically synchronizes those changes to Azure. This article explains resource sync.
Note
As a preview feature, the technology presented in this article is subject to Supplemental Terms of Use for Microsoft Azure Previews.
The latest updates are available in the release notes.
When you deploy Azure Arc-enabled data services in direct connected mode, the deployment creates a resource sync rule. This resource sync rule ensures that the Arc resources such as SQL managed instance created or updated by directly calling the Kubernetes APIs get updated appropriately in the mapped resources in Azure and the resource metadata is continually synced back to Azure. This rule is created within the same resource group as the data controller.
Note
The resource sync rule is created by default, during the Azure Arc Data Controller deployment and is only applicable in direct connected mode.
Without the resource sync rule, the SQL managed instance is created using the following command:
az sql mi-arc create --name <name> --resource-group <group> --location <Azure location> -–subscription <subscription> --custom-location <custom-location> --storage-class-backups <RWX capable storageclass>
In this scenario, first the Azure ARM APIs are called and the mapped Azure resource is created. Once this mapped resource is created successfully, then the Kubernetes API is called to create the SQL managed instance on the Kubernetes cluster.
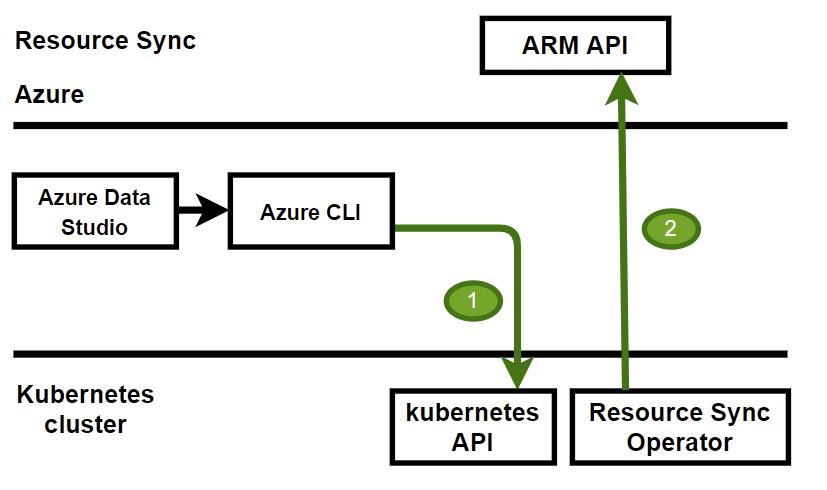
With the resource sync rule, you can use the Kubernetes API to create the Arc-enabled SQL managed instance, as follows:
az sql mi-arc create --name <name> --k8s-namespace <namespace> --use-k8s --storage-class-backups <RWX capable storageclass>
In this scenario, the SQL managed instance is directly created in the Kubernetes cluster. The resource sync rule ensures that the equivalent resource in Azure is created as well.
If the resource sync rule is deleted accidentally, you can add it back to restore the sync functionality by using the below REST API. Refer to Azure REST API reference for guidance on executing REST APIs. Please make sure to use data controller Azure resource subscription and resource group.
https://management.azure.com/subscriptions/{{subscription}}/resourcegroups/{{resource_group}}/providers/microsoft.extendedlocation/customlocations/{{custom_location_name}}/resourcesyncrules/defaultresourcesyncrule?api-version=2021-08-31-preview
"location": "{{Azure region}}",
"properties": {
"targetResourceGroup": "/subscriptions/{{subscription}}/resourcegroups/{{resource_group_of_ data_controller}}",
"priority": 100,
"selector": {
"matchLabels": {
"management.azure.com/resourceProvider": "Microsoft.AzureArcData" //Mandatory
}
}
}
}
Limitations
- Resource sync rule does not project Azure Arc Data controller. The Azure Arc Data controller must be deployed via ARM API.
- Resource sync only applies to the data services such as Arc enabled SQL managed instance, post deployment of Data controller.
- Resource sync rule does not project Azure Arc enabled PostgreSQL
- Resource sync rule does not project Azure Arc Active Directory connector
- Resource sync rule does not project Azure Arc Instance Failover Groups
Related content
Create Azure Arc data controller in direct connectivity mode using CLI
Feedback
Coming soon: Throughout 2024 we will be phasing out GitHub Issues as the feedback mechanism for content and replacing it with a new feedback system. For more information see: https://aka.ms/ContentUserFeedback.
Submit and view feedback for