Azure Arc-enabled Kubernetes agent overview
Azure Arc-enabled Kubernetes provides a centralized, consistent control plane to manage policy, governance, and security across Kubernetes clusters in different environments.
Azure Arc agents are deployed on Kubernetes clusters when you connect them to Azure Arc. This article provides an overview of these agents.
Deploy agents to your cluster
Most on-premises datacenters enforce strict network rules that prevent inbound communication on the network boundary firewall. Azure Arc-enabled Kubernetes works with these restrictions by not requiring inbound ports on the firewall. Azure Arc agents require outbound communication to a set list of network endpoints.
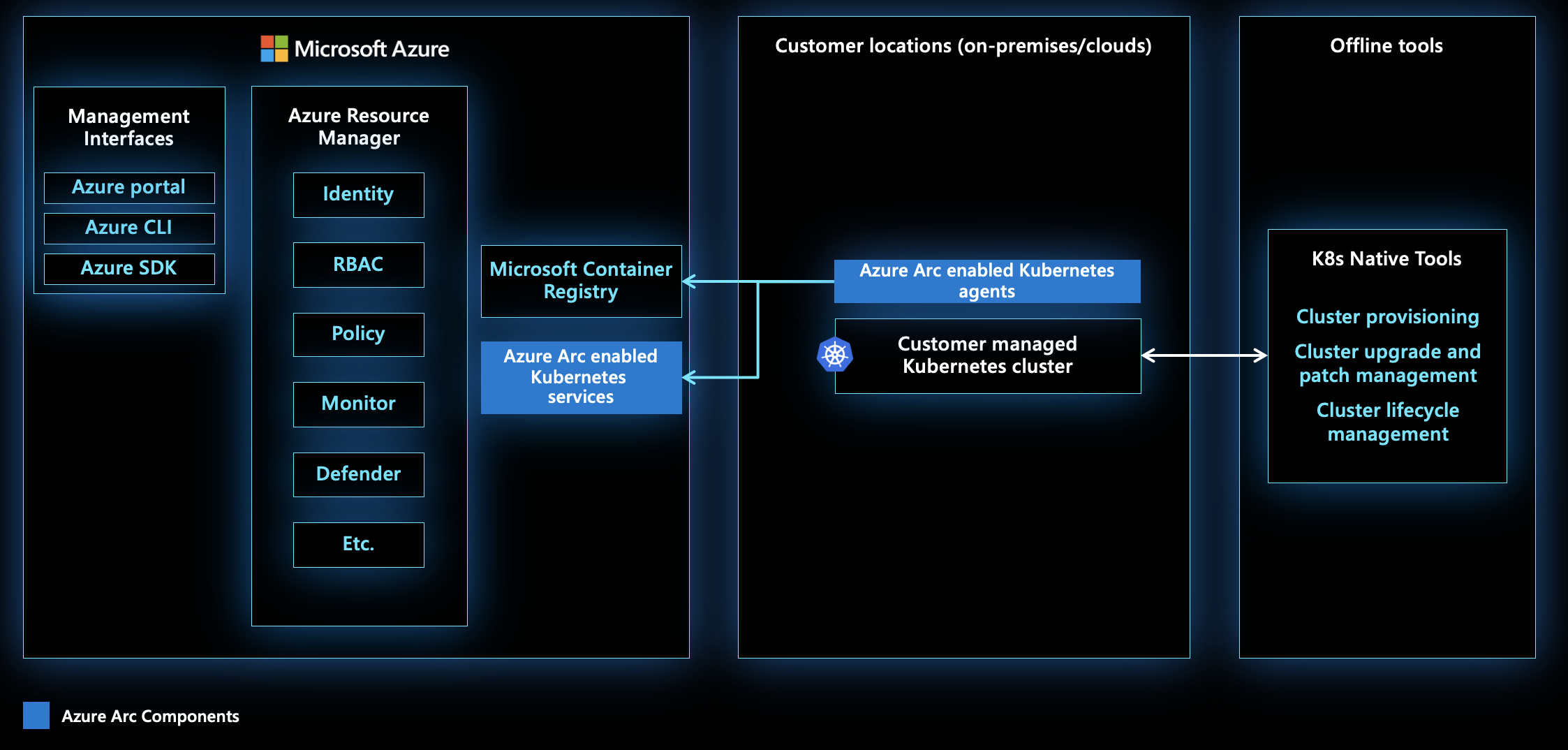
This diagram provides a high-level view of Azure Arc components. Kubernetes clusters in on-premises datacenters or different clouds are connected to Azure through the Azure Arc agents. This allows the clusters to be managed in Azure using management tools and Azure services. The clusters can also be accessed through offline management tools.
The following high-level steps are involved in connecting a Kubernetes cluster to Azure Arc:
Create a Kubernetes cluster on your choice of infrastructure (VMware vSphere, Amazon Web Services, Google Cloud Platform, etc.). The cluster must already exist before you connect it to Azure Arc.
Start the Azure Arc registration for your cluster.
The agent Helm chart is deployed on the cluster.
The cluster nodes initiate an outbound communication to the Microsoft Container Registry, pulling the images needed to create the following agents in the
azure-arcnamespace:Agent Description deployment.apps/clusteridentityoperatorAzure Arc-enabled Kubernetes currently supports only system assigned identities. clusteridentityoperatorinitiates the first outbound communication. This first communication fetches the Managed Service Identity (MSI) certificate used by other agents for communication with Azure.deployment.apps/config-agentWatches the connected cluster for source control configuration resources applied on the cluster. Updates the compliance state. deployment.apps/controller-managerAn operator of operators that orchestrates interactions between Azure Arc components. deployment.apps/metrics-agentCollects metrics of other Arc agents to verify optimal performance. deployment.apps/cluster-metadata-operatorGathers cluster metadata, including cluster version, node count, and Azure Arc agent version. deployment.apps/resource-sync-agentSyncs the above-mentioned cluster metadata to Azure. deployment.apps/flux-logs-agentCollects logs from the Flux operators deployed as a part of source control configuration. deployment.apps/extension-managerInstalls and manages lifecycle of extension Helm charts. deployment.apps/kube-aad-proxyUsed for authentication of requests sent to the cluster using cluster connect. deployment.apps/clusterconnect-agentReverse proxy agent that enables the cluster connect feature to provide access to apiserverof the cluster. Optional component deployed only if the cluster connect feature is enabled.deployment.apps/guardAuthentication and authorization webhook server used for Microsoft Entra RBAC. Optional component deployed only if Azure RBAC is enabled on the cluster.
Once all the Azure Arc-enabled Kubernetes agent pods are in
Runningstate, verify that your cluster is connected to Azure Arc. You should see:- An Azure Arc-enabled Kubernetes resource in Azure Resource Manager. Azure tracks this resource as a projection of the customer-managed Kubernetes cluster, not the actual Kubernetes cluster itself.
- Cluster metadata (such as Kubernetes version, agent version, and number of nodes) appearing on the Azure Arc-enabled Kubernetes resource as metadata.
Next steps
- Walk through our quickstart to connect a Kubernetes cluster to Azure Arc.
- View release notes to see details about the latest agent versions.
- Learn about upgrading Azure Arc-enabled Kubernetes agents.
- Learn more about the creating connections between your cluster and a Git repository as a configuration resource with Azure Arc-enabled Kubernetes.
Feedback
Coming soon: Throughout 2024 we will be phasing out GitHub Issues as the feedback mechanism for content and replacing it with a new feedback system. For more information see: https://aka.ms/ContentUserFeedback.
Submit and view feedback for