Use deployment scripts in Bicep
By using the deploymentScripts resource, you can run scripts in Bicep deployments and review execution results. You can use these scripts to perform custom steps such as:
- Add users to a directory.
- Perform data plane operations; for example, copy blobs or seed a database.
- Look up and validate a license key.
- Create a self-signed certificate.
- Create an object in Microsoft Entra ID.
- Look up IP address blocks from a custom system.
The benefits of deployment scripts include:
- They're easy to code, use, and debug. You can develop deployment scripts in your favorite development environments. The scripts can be embedded in Bicep files or in external script files.
- You can specify the script language and platform. Currently, Azure PowerShell and Azure CLI deployment scripts in the Linux environment are supported.
- You can allow passing command-line arguments to the script.
- You can specify script outputs and pass them back to the deployment.
The deployment script resource is available only in the regions where Azure Container Instances is available. For more information, see Resource availability for Azure Container Instances in Azure regions.
Warning
The deployment script service requires two extra resources to run and troubleshoot scripts: a storage account and a container instance. Generally, the service cleans up these resources after the deployment script finishes. You incur charges for these resources until they're removed.
For pricing information, see Container Instances pricing and Azure Storage pricing. To learn more, see Clean up deployment script resources.
Training resources
If you prefer to learn about deployment scripts through step-by-step guidance, see Extend Bicep and ARM templates by using deployment scripts.
Configure the minimum permissions
For deployment script API version 2020-10-01 or later, two principals are involved in deployment script execution:
Deployment principal: This principal is used to deploy the Bicep file. It creates underlying resources that are required for the deployment script resource to run—a storage account and an Azure container instance. To configure the least-privilege permissions, assign a custom role with the following properties to the deployment principal:
{ "roleName": "deployment-script-minimum-privilege-for-deployment-principal", "description": "Configure least privilege for the deployment principal in deployment script", "type": "customRole", "IsCustom": true, "permissions": [ { "actions": [ "Microsoft.Storage/storageAccounts/*", "Microsoft.ContainerInstance/containerGroups/*", "Microsoft.Resources/deployments/*", "Microsoft.Resources/deploymentScripts/*" ], } ], "assignableScopes": [ "[subscription().id]" ] }If the Azure Storage and Azure Container Instances resource providers weren't registered, be sure to add
Microsoft.Storage/register/actionandMicrosoft.ContainerInstance/register/action.Deployment script principal: This principal is required only if the deployment script needs to authenticate to Azure and call the Azure CLI or PowerShell. There are two ways to specify the deployment script principal:
- Specify a user-assigned managed identity in the
identityproperty. (See the deployment script resource syntax.) When you specify a user-assigned managed identity, the script service callsConnect-AzAccount -Identitybefore invoking the deployment script. The managed identity must have the required access to complete the operation in the script. Currently, only a user-assigned managed identity is supported for theidentityproperty. To log in with a different identity, use the second method in this list. - Pass the service principal credentials as secure environment variables, and then call Connect-AzAccount or az login in the deployment script.
If you use a managed identity, the deployment principal needs the built-in Managed Identity Operator role assigned to the managed identity resource.
- Specify a user-assigned managed identity in the
Currently, no built-in role is tailored for configuring deployment script permissions.
Create deployment scripts
The following example demonstrates a simple Bicep file with a deployment script resource. The script takes one string parameter and creates another string.
param name string = 'John Dole'
param location string = resourceGroup().location
resource deploymentScript 'Microsoft.Resources/deploymentScripts@2023-08-01' = {
name: 'inlineCLI'
location: location
kind: 'AzureCLI'
properties: {
azCliVersion: '2.52.0'
arguments: name
scriptContent: 'echo "The argument is ${name}."; jq -n -c --arg st "Hello ${name}" \'{"text": $st}\' > $AZ_SCRIPTS_OUTPUT_PATH'
retentionInterval: 'PT1H'
}
}
output text string = deploymentScript.properties.outputs.text
For more information about creating deployment script resources, see Create deployment scripts. For the creation of scripts for the deployment script resource, we advise you to establish a dedicated script development environment, such as an Azure container instance or a Docker image. After you develop and thoroughly test the scripts, you can integrate or invoke the script files from the deployment script resource. For more information, see Configure script development environments.
Save the script in an inlineScript.bicep file, and then deploy the resource by using the following script:
$resourceGroupName = Read-Host -Prompt "Enter the name of the resource group to be created"
$location = Read-Host -Prompt "Enter the location (i.e. centralus)"
New-AzResourceGroup -Name $resourceGroupName -Location $location
New-AzResourceGroupDeployment -ResourceGroupName $resourceGroupName -TemplateFile "inlineScript.bicep"
Write-Host "Press [ENTER] to continue ..."
Monitor and troubleshoot a deployment script
When you deploy a deployment script resource, you need a storage account to store the user script, the execution results, and the stdout file. You can specify your own storage account. For more information, see Use an existing storage account.
An alternative to specifying your own storage account involves setting cleanupPreference to OnExpiration. You then configure retentionInterval for a duration that allows ample time for reviewing the outputs before the storage account is removed. For more information, see Clean up deployment script resources.
Add the cleanupPreference property to the preceding Bicep file, and set the value to OnExpiration. The default value is Always. Also, set rentalInterval to PT1H (one hour) or shorter.
param name string = 'John Dole'
param location string = resourceGroup().location
resource deploymentScript 'Microsoft.Resources/deploymentScripts@2023-08-01' = {
name: 'inlineCLI'
location: location
kind: 'AzureCLI'
properties: {
azCliVersion: '2.52.0'
arguments: name
scriptContent: 'echo "The argument is ${name}."; jq -n -c --arg st "Hello ${name}" \'{"text": $st}\' > $AZ_SCRIPTS_OUTPUT_PATH'
cleanupPreference: 'OnExpiration'
retentionInterval: 'PT1H'
}
}
output text string = deploymentScript.properties.outputs.text
After you deploy the Bicep file successfully, use the Azure portal, the Azure CLI, Azure PowerShell, or the REST API to check the results.
Azure portal
After you deploy a deployment script resource, the resource is listed under the resource group in the Azure portal. The Overview page lists the two supporting resources in addition to the deployment script resource. The supporting resources will be deleted after the retention interval expires.
Notice that both supporting resources have the azscripts suffix in their names because these resources are created automatically. The other way to identify the supporting resources is by using tags.
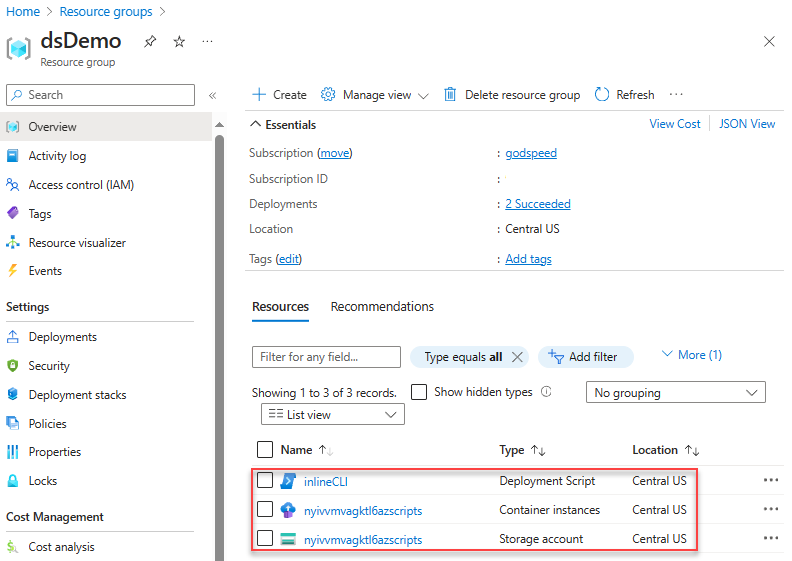
Select the deployment script resource from the list. The Overview page of a deployment script resource displays important information about the resource, such as Provisioning state and the two supporting resources (Storage account and Container instance). The Logs area shows the print text from the script.
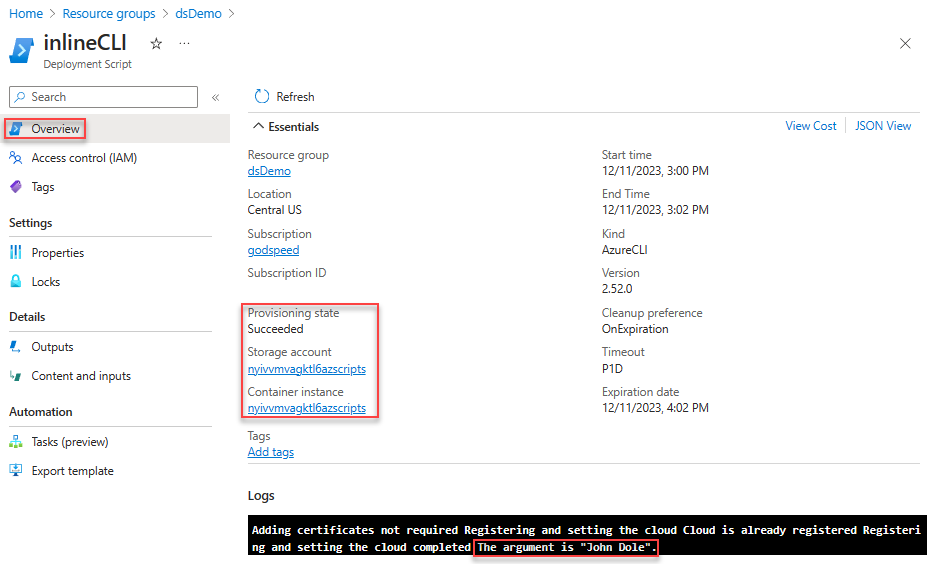
Select Outputs to display outputs of the script.
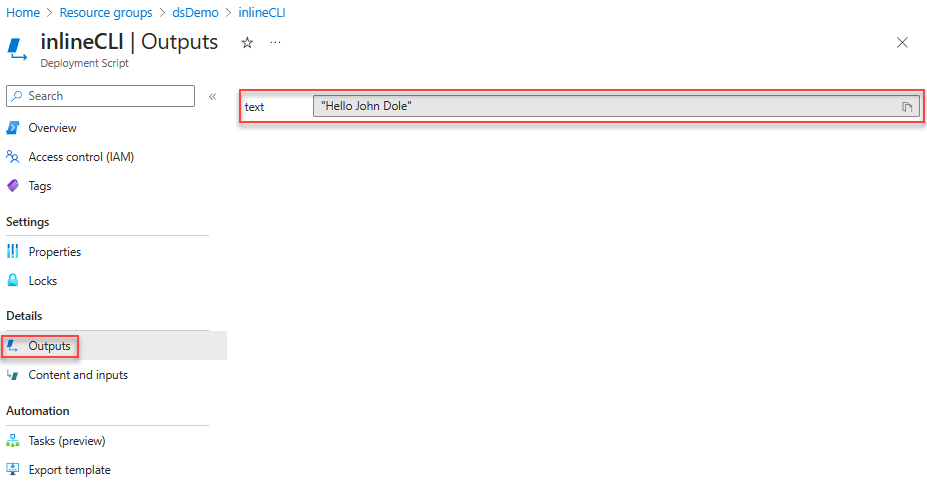
Go back to the resource group, select the storage account, select File shares, and then select the file share with azscripts appended to the share name. Two folders appear in the list: azscriptinput and azscriptoutput. The output folder contains an executionresult.json file and the script output file. The executionresult.json file contains the script execution error message. The output file is created only when you run the script successfully.
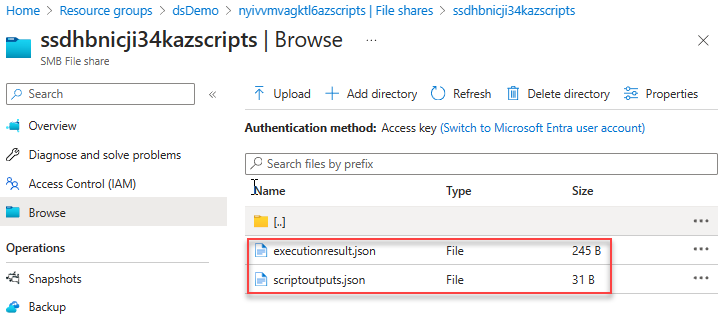
The input folder contains the system script file and the user deployment script file. You can replace the user deployment script file with a revised one and rerun the deployment script from the Azure container instance.
Azure CLI
You can use the Azure CLI to manage deployment scripts at the subscription or resource group scope:
- az deployment-scripts delete: Delete a deployment script.
- az deployment-scripts list: List all deployment scripts.
- az deployment-scripts show: Retrieve a deployment script.
- az deployment-scripts show-log: Show deployment script logs.
The output of the list command is similar to this example:
{
"arguments": "John Dole",
"azCliVersion": "2.52.0",
"cleanupPreference": "OnExpiration",
"containerSettings": {
"containerGroupName": null
},
"environmentVariables": null,
"forceUpdateTag": null,
"id": "/subscriptions/01234567-89AB-CDEF-0123-456789ABCDEF/resourceGroups/dsDemo/providers/Microsoft.Resources/deploymentScripts/inlineCLI",
"identity": null,
"kind": "AzureCLI",
"location": "centralus",
"name": "inlineCLI",
"outputs": {
"text": "Hello John Dole"
},
"primaryScriptUri": null,
"provisioningState": "Succeeded",
"resourceGroup": "dsDemo",
"retentionInterval": "1:00:00",
"scriptContent": "echo \"The argument is John Dole.\"; jq -n -c --arg st \"Hello John Dole\" '{\"text\": $st}' > $AZ_SCRIPTS_OUTPUT_PATH",
"status": {
"containerInstanceId": "/subscriptions/01234567-89AB-CDEF-0123-456789ABCDEF/resourceGroups/dsDemo/providers/Microsoft.ContainerInstance/containerGroups/jgczqtxom5oreazscripts",
"endTime": "2023-12-11T20:20:12.149468+00:00",
"error": null,
"expirationTime": "2023-12-11T21:20:12.149468+00:00",
"startTime": "2023-12-11T20:18:26.674492+00:00",
"storageAccountId": "/subscriptions/01234567-89AB-CDEF-0123-456789ABCDEF/resourceGroups/dsDemo/providers/Microsoft.Storage/storageAccounts/jgczqtxom5oreazscripts"
},
"storageAccountSettings": null,
"supportingScriptUris": null,
"systemData": {
"createdAt": "2023-12-11T19:45:32.239063+00:00",
"createdBy": "johndole@contoso.com",
"createdByType": "User",
"lastModifiedAt": "2023-12-11T20:18:26.183565+00:00",
"lastModifiedBy": "johndole@contoso.com",
"lastModifiedByType": "User"
},
"tags": null,
"timeout": "1 day, 0:00:00",
"type": "Microsoft.Resources/deploymentScripts"
}
Azure PowerShell
You can use Azure PowerShell to manage deployment scripts at the subscription or resource group scope:
- Get-AzDeploymentScript: Get or list deployment scripts.
- Get-AzDeploymentScriptLog: Get the log of a deployment script execution.
- Remove-AzDeploymentScript: Remove a deployment script and its associated resources.
- Save-AzDeploymentScriptLog: Save the log of a deployment script execution to disk.
The Get-AzDeploymentScript output is similar to this example:
Name : inlinePS
Id : /subscriptions/01234567-89AB-CDEF-0123-456789ABCDEF/resourceGroups/dsDemo/providers/Microsoft.Resources/deploymentScripts/inlinePS
ResourceGroupName : dsDemo
Location : centralus
SubscriptionId : 01234567-89AB-CDEF-0123-456789ABCDEF
ProvisioningState : Succeeded
Identity :
ScriptKind : AzurePowerShell
AzPowerShellVersion : 10.0
StartTime : 12/11/2023 9:45:50 PM
EndTime : 12/11/2023 9:46:59 PM
ExpirationDate : 12/11/2023 10:46:59 PM
CleanupPreference : OnExpiration
StorageAccountId : /subscriptions/01234567-89AB-CDEF-0123-456789ABCDEF/resourceGroups/dsDemo/providers/Microsoft.Storage/storageAccounts/ee5o4rmoo6ilmazscripts
ContainerInstanceId : /subscriptions/01234567-89AB-CDEF-0123-456789ABCDEF/resourceGroups/dsDemo/providers/Microsoft.ContainerInstance/containerGroups/ee5o4rmoo6ilmazscripts
Outputs :
Key Value
================== ==================
text Hello John Dole.
RetentionInterval : PT1H
Timeout : P1D
REST API
You can use the REST API to get information about the deployment script resource at the resource group level and the subscription level:
/subscriptions/<SubscriptionID>/resourcegroups/<ResourceGroupName>/providers/microsoft.resources/deploymentScripts/<DeploymentScriptResourceName>?api-version=2020-10-01
/subscriptions/<SubscriptionID>/providers/microsoft.resources/deploymentScripts?api-version=2020-10-01
The following example uses ARMClient. ARMClient is not a supported Microsoft tool.
armclient login
armclient get /subscriptions/01234567-89AB-CDEF-0123-456789ABCDEF/resourcegroups/myrg/providers/microsoft.resources/deploymentScripts/myDeployementScript?api-version=2020-10-01
The output is similar to this example:
{
"kind": "AzureCLI",
"identity": null,
"location": "centralus",
"systemData": {
"createdAt": "2023-12-11T19:45:32.239063+00:00",
"createdBy": "johndole@contoso.com",
"createdByType": "User",
"lastModifiedAt": "2023-12-11T20:18:26.183565+00:00",
"lastModifiedBy": "johndole@contoso.com",
"lastModifiedByType": "User"
},
"properties": {
"provisioningState": "Succeeded",
"azCliVersion": "2.52.0",
"scriptContent": "echo \"The argument is John Dole.\"; jq -n -c --arg st \"Hello John Dole\" '{\"text\": $st}' > $AZ_SCRIPTS_OUTPUT_PATH",
"arguments": "John Dole",
"retentionInterval": "1:00:00",
"timeout": "1 day, 0:00:00",
"containerSettings": {
"containerGroupName": null
},
"status": {
"containerInstanceId": "/subscriptions/01234567-89AB-CDEF-0123-456789ABCDEF/resourceGroups/dsDemo/providers/Microsoft.ContainerInstance/containerGroups/jgczqtxom5oreazscripts",
"endTime": "2023-12-11T20:20:12.149468+00:00",
"error": null,
"expirationTime": "2023-12-11T21:20:12.149468+00:00",
"startTime": "2023-12-11T20:18:26.674492+00:00",
"storageAccountId": "/subscriptions/01234567-89AB-CDEF-0123-456789ABCDEF/resourceGroups/dsDemo/providers/Microsoft.Storage/storageAccounts/jgczqtxom5oreazscripts"
},
"outputs": {
"text": "Hello John Dole"
},
"cleanupPreference": "OnSuccess"
},
"id": "/subscriptions/01234567-89AB-CDEF-0123-456789ABCDEF/resourceGroups/dsDemo/providers/Microsoft.Resources/deploymentScripts/inlineCLI",
"type": "Microsoft.Resources/deploymentScripts",
"name": "inlineCLI",
}
The following REST API returns the log:
/subscriptions/<SubscriptionID>/resourcegroups/<ResourceGroupName>/providers/microsoft.resources/deploymentScripts/<DeploymentScriptResourceName>/logs?api-version=2020-10-01
It works only before the deployment script resources are deleted.
Deployment script error codes
The following table lists the error codes for the deployment script:
| Error code | Description |
|---|---|
DeploymentScriptInvalidOperation |
The deployment script resource definition in the Bicep file contains invalid property names. |
DeploymentScriptResourceConflict |
You can't delete a deployment script resource if it's in a nonterminal state and the execution hasn't exceeded one hour. Or you can't rerun the same deployment script with the same resource identifier (same subscription, resource group name, and resource name) but different script body content at the same time. |
DeploymentScriptOperationFailed |
The deployment script operation failed internally. Contact Microsoft support. |
DeploymentScriptStorageAccountAccessKeyNotSpecified |
The access key wasn't specified for the existing storage account. |
DeploymentScriptContainerGroupContainsInvalidContainers |
A container group that the deployment script service created was externally modified, and invalid containers were added. |
DeploymentScriptContainerGroupInNonterminalState |
Two or more deployment script resources use the same Azure container instance name in the same resource group, and one of them hasn't finished its execution yet. |
DeploymentScriptExistingStorageNotInSameSubscriptionAsDeploymentScript |
The existing storage provided in deployment is not found in the subscription where the script is being deployed. |
DeploymentScriptStorageAccountInvalidKind |
The existing storage account of the BlobBlobStorage or BlobStorage type doesn't support file shares and can't be used. |
DeploymentScriptStorageAccountInvalidKindAndSku |
The existing storage account doesn't support file shares. For a list of supported types of storage accounts, see Use an existing storage account. |
DeploymentScriptStorageAccountNotFound |
The storage account doesn't exist, or an external process or tool deleted it. |
DeploymentScriptStorageAccountWithServiceEndpointEnabled |
The specified storage account has a service endpoint. A storage account with a service endpoint isn't supported. |
DeploymentScriptStorageAccountInvalidAccessKey |
An invalid access key was specified for the existing storage account. |
DeploymentScriptStorageAccountInvalidAccessKeyFormat |
The storage account key has an invalid format. See Manage storage account access keys. |
DeploymentScriptExceededMaxAllowedTime |
Deployment script execution time exceeded the timeout value specified in the deployment script resource definition. |
DeploymentScriptInvalidOutputs |
The deployment script output isn't a valid JSON object. |
DeploymentScriptContainerInstancesServiceLoginFailure |
The user-assigned managed identity couldn't sign in after 10 attempts with one-minute intervals. |
DeploymentScriptContainerGroupNotFound |
An external tool or process deleted a container group that the deployment script service created. |
DeploymentScriptDownloadFailure |
Download of a supporting script failed. See Use supporting scripts. |
DeploymentScriptError |
The user script threw an error. |
DeploymentScriptBootstrapScriptExecutionFailed |
The bootstrap script threw an error. The bootstrap script is the system script that orchestrates execution of the deployment script. |
DeploymentScriptExecutionFailed |
An unknown error occurred during execution of the deployment script. |
DeploymentScriptContainerInstancesServiceUnavailable |
During creation of a container instance, the Azure Container Instances service threw a "service unavailable" error. |
DeploymentScriptContainerGroupInNonterminalState |
During creation of a container instance, another deployment script was using the same container instance name in the same scope (same subscription, resource group name, and resource name). |
DeploymentScriptContainerGroupNameInvalid |
The specified container instance name doesn't meet the Azure Container Instances requirements. See Troubleshoot common issues in Azure Container Instances. |
Access a private virtual network
You can run deployment scripts in private networks with some additional configurations. For more information, see Access a private virtual network.
Next steps
In this article, you learned how to use deployment scripts. To learn more, see:
Feedback
Coming soon: Throughout 2024 we will be phasing out GitHub Issues as the feedback mechanism for content and replacing it with a new feedback system. For more information see: https://aka.ms/ContentUserFeedback.
Submit and view feedback for