Save costs for resources with reserved capacity - Azure SQL Database & SQL Managed Instance
Applies to:
Azure SQL Database
Azure SQL Managed Instance
Save money with Azure SQL Database or SQL Managed Instance by committing to a reservation for compute resources compared to pay-as-you-go prices. With reserved capacity, you make a commitment for SQL Database and/or SQL Managed Instance use for a period of one or three years to get a significant discount on the compute costs. To purchase reserved capacity, you need to specify the Azure region, deployment type, performance tier, and term.
You do not need to assign the reservation to a specific database or managed instance. Matching existing deployments that are already running, or ones that are newly deployed automatically, get the benefit. Hence, by purchasing a reserved capacity, existing resources infrastructure would not be modified and thus no failover/downtime is triggered on existing resources. By purchasing a reservation, you commit to usage for the compute costs for a period of one or three years. As soon as you buy a reservation, the compute charges that match the reservation attributes are no longer charged at the pay-as-you-go rates.
A reservation applies to both primary and billable secondary compute replicas, but does not cover software, networking, or storage charges associated with the service. At the end of the reservation term, the billing benefit expires and the database or managed instance is billed at the pay-as-you-go price. Reservations do not automatically renew. For pricing information, see the reserved capacity offering.
You can buy reserved capacity in the Azure portal. Pay for the reservation up front or with monthly payments. To buy reserved capacity:
- To buy a reservation, you must have the Owner role or Reservation Purchaser role on an Azure subscription.
- For Enterprise subscriptions, Add Reserved Instances must be enabled in the EA portal. Or, if that setting is disabled, you must be an EA Admin on the subscription. Reserved capacity.
For more information about how enterprise customers and pay-as-you-go customers are charged for reservation purchases, see Understand Azure reservation usage for your Enterprise enrollment and Understand Azure reservation usage for your pay-as-you-go subscription.
Note
Purchasing reserved capacity does not pre-allocate or reserve specific infrastructure resources (virtual machines or nodes) for your use.
Determine the correct size before purchase
The size of reservation should be based on the total amount of compute used by the existing or soon-to-be-deployed database or managed instance within a specific region and using the same performance tier and hardware configuration.
For example, let's suppose that you are running:
- 1 General Purpose, standard-series (Gen5) – 16 vCore elastic pool and
- 2 Business Critical standard-series (Gen5) – 4 vCore single databases.
Further, let's suppose that you plan to deploy the following within the next month:
- 1 additional General Purpose standard-series (Gen5) – 16 vCore elastic pool and
- 1 business critical standard-series (Gen5) – 32 vCore elastic pool.
Also, let's suppose that you know that you will need these resources for at least 1 year. In this case, you should purchase a 32 (2x16) vCores 1-year reservation for single database/elastic pool General Purpose - standard-series (Gen5) and a 40 (2x4 + 32) vCore 1-year reservation for single database/elastic pool Business Critical - standard-series (Gen5).
Buy reserved capacity
Sign in to the Azure portal.
Select All services > Reservations.
Select Add and then in the Purchase Reservations pane,
- Select SQL Database to purchase a new reservation for Azure SQL Database.
- Select SQL Managed Instance to purchase a new reservation for Azure SQL Managed Instance.
Fill in the required fields. Existing databases in SQL Database and SQL Managed Instance that match the attributes you select qualify to get the reserved capacity discount. The actual number of databases or managed instances that get the discount depends on the scope and quantity selected.
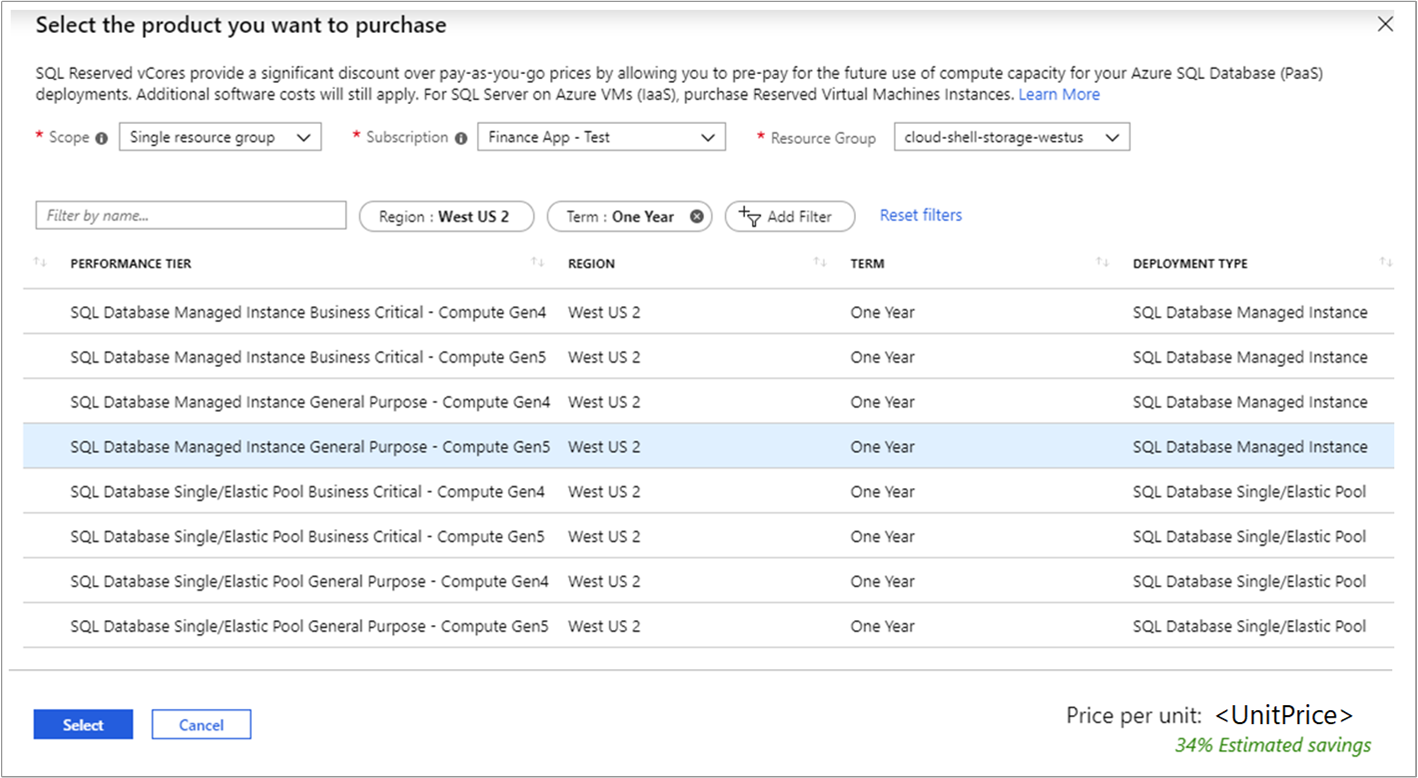
The following table describes the required fields.
Field Description Subscription The subscription used to pay for the capacity reservation. The payment method on the subscription is charged the upfront costs for the reservation. The subscription type must be an enterprise agreement (offer number MS-AZR-0017P or MS-AZR-0148P) or an individual agreement with pay-as-you-go pricing (offer number MS-AZR-0003P or MS-AZR-0023P). For an enterprise subscription, the charges are deducted from the enrollment's Azure Prepayment (previously called monetary commitment) balance or charged as overage. For an individual subscription with pay-as-you-go pricing, the charges are billed to the credit card or invoice payment method on the subscription. Scope The vCore reservation's scope can cover one subscription or multiple subscriptions (shared scope). If you select
Shared, the vCore reservation discount is applied to the database or managed instance running in any subscriptions within your billing context. For enterprise customers, the shared scope is the enrollment and includes all subscriptions within the enrollment. For pay-as-you-go customers, the shared scope is all pay-as-you-go subscriptions created by the account administrator.
Single subscription, the vCore reservation discount is applied to the databases or managed instances in this subscription.
Single resource group, the reservation discount is applied to the instances of databases or managed instances in the selected subscription and the selected resource group within that subscription.
Management group, the reservation discount is applied to the matching resource in the list of subscriptions that are a part of both the management group and billing scope.Region The Azure region that's covered by the capacity reservation. Deployment Type The SQL resource type that you want to buy the reservation for. Performance Tier The service tier for the databases or managed instances. Term One year or three years. Quantity The amount of compute resources being purchased within the capacity reservation. The quantity is a number of vCores in the selected Azure region and Performance tier that are being reserved and will get the billing discount. For example, if you run or plan to run multiple databases with the total compute capacity of standard-series (Gen5) 16 vCores in the East US region, then you would specify the quantity as 16 to maximize the benefit for all the databases. Review the cost of the capacity reservation in the Costs section.
Select Purchase.
Select View this Reservation to see the status of your purchase.
Cancel, exchange, or refund reservations
You can cancel, exchange, or refund reservations with certain limitations. For more information, see Self-service exchanges and refunds for Azure Reservations.
vCore size flexibility
vCore size flexibility helps you scale up or down within a performance tier and region, without losing the reserved capacity benefit. Reserved capacity also provides you with the flexibility to temporarily move your hot databases in and out of elastic pools (within the same region and performance tier) as part of your normal operations without losing the reserved capacity benefit. By keeping an unapplied buffer in your reservation, you can effectively manage the performance spikes without exceeding your budget.
Limitation
You cannot reserve DTU-based (basic, standard, or premium) databases in SQL Database. Reserved capacity pricing is only supported for features and products that are in General Availability state.
Need help? Contact us
If you have questions or need help, create a support request.
Next steps
The vCore reservation discount is applied automatically to the number of databases or managed instances that match the capacity reservation scope and attributes. You can update the scope of the capacity reservation through the Azure portal, PowerShell, Azure CLI, or the API.
- For information on Azure SQL Database service tiers for the vCore model, see vCore model overview - Azure SQL Database.
- For information on Azure SQL Managed Instance service tiers for the vCore model, see vCore model overview - Azure SQL Managed Instance.
To learn how to manage the capacity reservation, see manage reserved capacity.
To learn more about Azure Reservations, see the following articles:
Feedback
Coming soon: Throughout 2024 we will be phasing out GitHub Issues as the feedback mechanism for content and replacing it with a new feedback system. For more information see: https://aka.ms/ContentUserFeedback.
Submit and view feedback for