Create an FCI with a premium file share (SQL Server on Azure VMs)
Applies to:
SQL Server on Azure VM
Tip
There are many methods to deploy an availability group. Simplify your deployment and eliminate the need for an Azure Load Balancer or distributed network name (DNN) for your Always On availability group by creating your SQL Server virtual machines (VMs) in multiple subnets within the same Azure virtual network. If you've already created your availability group in a single subnet, you can migrate it to a multi-subnet environment.
This article explains how to create a failover cluster instance (FCI) with SQL Server on Azure Virtual Machines (VMs) by using a premium file share.
Premium file shares are SSD backed and provide consistently low-latency file shares that are fully supported for use with failover cluster instances for SQL Server 2012 or later on Windows Server 2012 or later. Premium file shares give you greater flexibility, allowing you to resize and scale a file share without any downtime.
To learn more, see an overview of FCI with SQL Server on Azure VMs and cluster best practices.
Note
It's now possible to lift and shift your failover cluster instance solution to SQL Server on Azure VMs using Azure Migrate. See Migrate failover cluster instance to learn more.
Prerequisites
Before you complete the instructions in this article, you should already have:
- An Azure subscription.
- An account that has permissions to create objects on both Azure virtual machines and in Active Directory.
- Two or more Azure VMs for an FCI in an availability set or different availability zones.
- A premium file share to be used as the clustered drive, based on the storage quota of your database for your data files.
- The latest version of PowerShell.
Mount premium file share
To mount your premium file share, follow these steps:
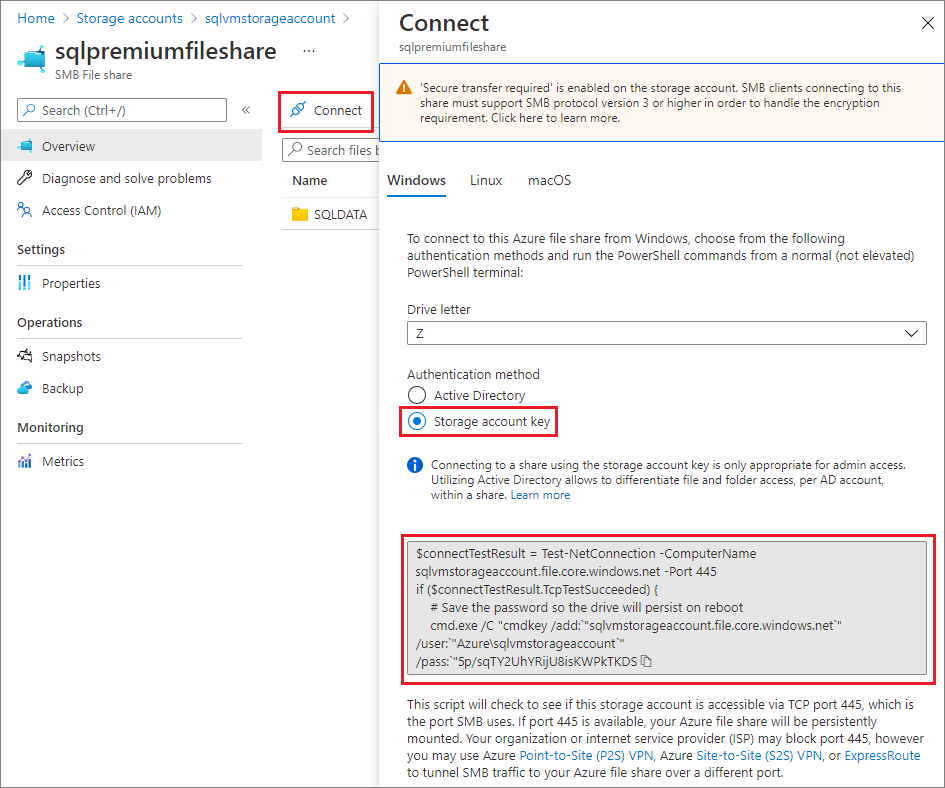
Sign in to the Azure portal, and go to your storage account.
Go to File shares under Data storage, and then select the premium file share you want to use for your SQL storage.
Select Connect to bring up the connection string for your file share.
In the dropdown list, select the drive letter you want to use, choose Storage account key as the authentication method, and then copy the code block to a text editor, such as Notepad.
Use Remote Desktop Protocol (RDP) to connect to the SQL Server VM with the account that your SQL Server FCI will use for the service account.
Open an administrative PowerShell command console.
Run the command that you copied earlier to your text editor from the File share portal.
Go to the share by using either File Explorer or the Run dialog box (Windows + R on your keyboard). Use the network path
\\storageaccountname.file.core.windows.net\filesharename. For example,\\sqlvmstorageaccount.file.core.windows.net\sqlpremiumfileshareCreate at least one folder on the newly connected file share to place your SQL data files into.
Repeat these steps on each SQL Server VM that will participate in the cluster.
Important
Consider using a separate file share for backup files to save the input/output operations per second (IOPS) and space capacity of this share for data and log files. You can use either a Premium or Standard File Share for backup files.
Create Windows Failover Cluster
The steps to create your Windows Server Failover cluster vary depending on if you deployed your SQL Server VMs to a single subnet, or multiple subnets. To create your cluster, follow the steps in the tutorial for either a multi-subnet scenario or a single subnet scenario. Though these tutorials are for creating an availability group, the steps to create the cluster are the same.
Configure quorum
The cloud witness is the recommended quorum solution for this type of cluster configuration for SQL Server on Azure VMs.
If you have an even number of votes in the cluster, configure the quorum solution that best suits your business needs. For more information, see Quorum with SQL Server VMs.
Validate cluster
Validate the cluster on one of the virtual machines by using the Failover Cluster Manager UI or PowerShell.
To validate the cluster by using the UI, do the following on one of the virtual machines:
Under Server Manager, select Tools, and then select Failover Cluster Manager.
Under Failover Cluster Manager, select Action, and then select Validate Configuration.
Select Next.
Under Select Servers or a Cluster, enter the names of both virtual machines.
Under Testing options, select Run only tests I select.
Select Next.
Under Test Selection, select all tests except for Storage and Storage Spaces Direct, as shown here:
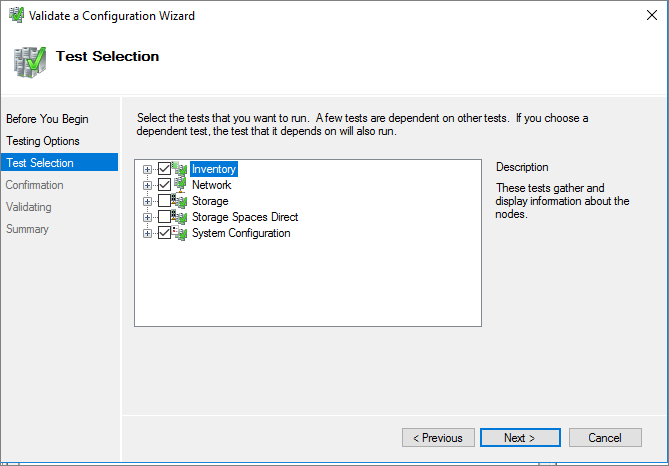
Select Next.
Under Confirmation, select Next. The Validate a Configuration wizard runs the validation tests.
To validate the cluster by using PowerShell, run the following script from an administrator PowerShell session on one of the virtual machines:
Test-Cluster –Node ("<node1>","<node2>") –Include "Inventory", "Network", "System Configuration"
Test cluster failover
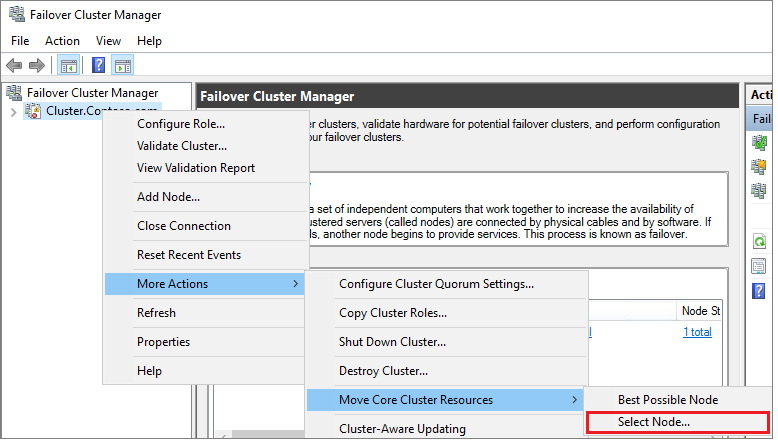
Test the failover of your cluster. In Failover Cluster Manager, right-click your cluster, select More Actions > Move Core Cluster Resource > Select node, and then select the other node of the cluster. Move the core cluster resource to every node of the cluster, and then move it back to the primary node. If you can successfully move the cluster to each node, you're ready to install SQL Server.
Create SQL Server FCI
After you've configured the failover cluster, you can create the SQL Server FCI.
Connect to the first virtual machine by using RDP.
In Failover Cluster Manager, make sure that all the core cluster resources are on the first virtual machine. If necessary, move all resources to this virtual machine.
If the version of the operating system is Windows Server 2019 and the Windows Cluster was created using the default Distributed Network Name (DNN), then the FCI installation for SQL Server 2017 and below fails with the error
The given key was not present in the dictionary.During installation, SQL Server setup queries for the existing Virtual Network Name (VNN) and doesn't recognize the Windows Cluster DNN. The issue has been fixed in SQL Server 2019 setup. For SQL Server 2017 and below, follow these steps to avoid the installation error:
- In Failover Cluster Manager, connect to the cluster, right-click Roles and select Create Empty Role.
- Right-click the newly created empty role, select Add Resource, and select Client Access Point.
- Enter any name and complete the wizard to create the Client Access Point.
- After the SQL Server FCI installation completes, the role containing the temporary Client Access Point can be deleted.
Locate the installation media. If the virtual machine uses one of the Azure Marketplace images, the media is located at
C:\SQLServer_<version number>_Full.Select Setup.
In the SQL Server Installation Center, select Installation.
Select New SQL Server failover cluster installation, and then follow the instructions in the wizard to install the SQL Server FCI.
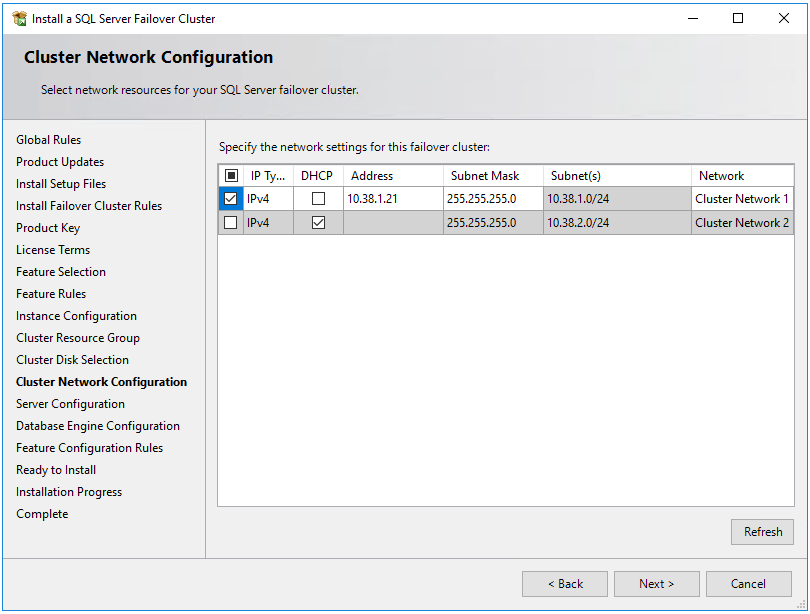
On the Cluster Network Configuration page, the IP you provide varies depending on if your SQL Server VMs were deployed to a single subnet, or multiple subnets.
- For a single subnet environment, provide the IP address that you plan to add to the Azure Load Balancer
- For a multi-subnet environment, provide the secondary IP address in the subnet of the first SQL Server VM that you previously designated as the IP address of the failover cluster instance network name:
In Database Engine Configuration, the data directories need to be on the premium file share. Enter the full path of the share, in this format:
\\storageaccountname.file.core.windows.net\filesharename\foldername. A warning appears, telling you that you've specified a file server as the data directory. This warning is expected. Ensure that the user account you used to access the VM via RDP when you persisted the file share is the same account that the SQL Server service uses to avoid possible failures.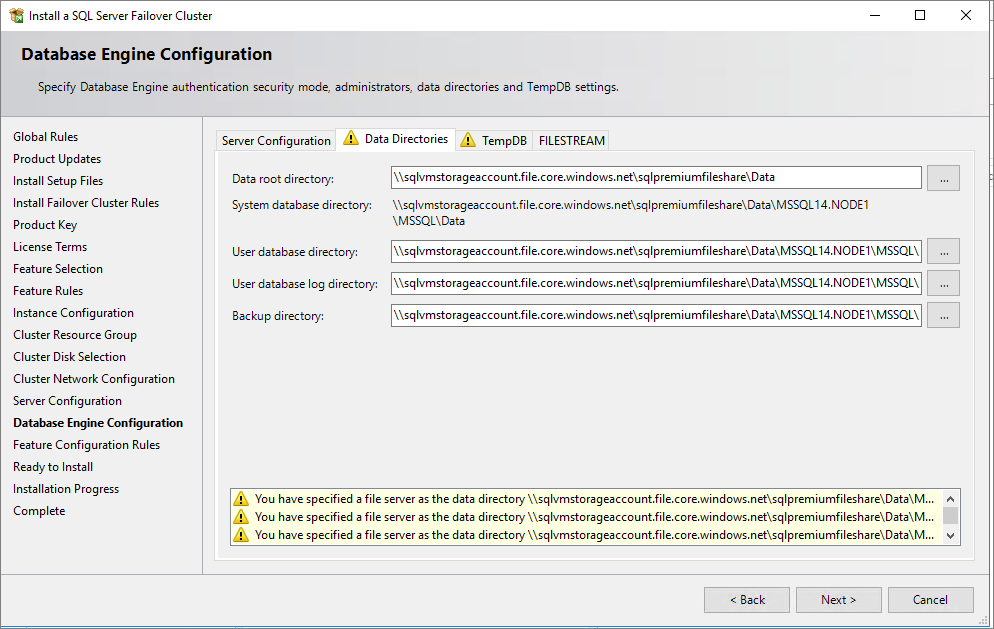
After you complete the steps in the wizard, Setup installs a SQL Server FCI on the first node.
After FCI installation succeeds on the first node, connect to the second node by using RDP.
Open the SQL Server Installation Center, and then select Installation.
Select Add node to a SQL Server failover cluster. Follow the instructions in the wizard to install SQL Server and add the node to the FCI.
For a multi-subnet scenario, in Cluster Network Configuration, enter the secondary IP address in the subnet of the second SQL Server VM that you previously designated as the IP address of the failover cluster instance network name
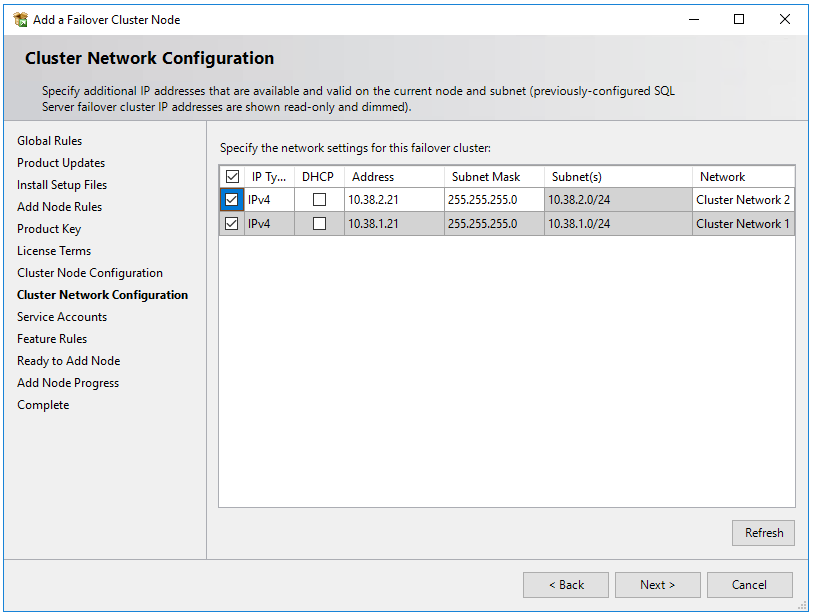
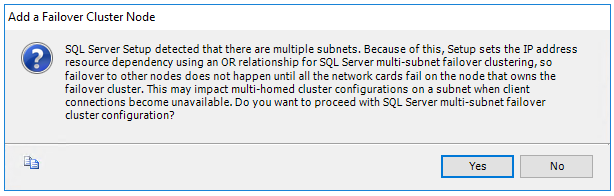
After selecting Next in Cluster Network Configuration, setup shows a dialog box indicating that SQL Server Setup detected multiple subnets as in the example image. Select Yes to confirm.
After you complete the instructions in the wizard, setup adds the second SQL Server FCI node.
Repeat these steps on any other nodes that you want to add to the SQL Server failover cluster instance.
Note
Azure Marketplace gallery images come with SQL Server Management Studio installed. If you didn't use a marketplace image Download SQL Server Management Studio (SSMS).
Register with SQL IaaS Agent extension
To manage your SQL Server VM from the portal, register it with the SQL IaaS Agent extension. Only limited functionality is available on SQL VMs that have failover clustered instances of SQL Server (FCIs).
If your SQL Server VM has already been registered with the SQL IaaS Agent extension and you've enabled any features that require the agent, you'll need to unregister the SQL Server VM from the extension and register it again after your FCI is installed.
Register a SQL Server VM with PowerShell (-LicenseType can be PAYG or AHUB):
# Get the existing compute VM
$vm = Get-AzVM -Name <vm_name> -ResourceGroupName <resource_group_name>
# Register SQL VM with SQL IaaS Agent extension
New-AzSqlVM -Name $vm.Name -ResourceGroupName $vm.ResourceGroupName -Location $vm.Location `
-LicenseType <license_type>
Configure connectivity
If you deployed your SQL Server VMs in multiple subnets, skip this step. If you deployed your SQL Server VMs to a single subnet, then you need to configure an additional component to route traffic to your FCI. You can configure a virtual network name (VNN) with an Azure Load Balancer, or a distributed network name for a failover cluster instance. Review the differences between the two and then deploy either a distributed network name or a virtual network name and Azure Load Balancer for your failover cluster instance.
Limitations
- Microsoft Distributed Transaction Coordinator (MSDTC) isn't supported on Windows Server 2016 and earlier.
- FILESTREAM isn't supported for a failover cluster with a premium file share. To use filestream, deploy your cluster by using Storage Spaces Direct or Azure shared disks instead.
- SQL Server FCIs registered with the extension don't support features that require the agent, such as automated backup, patching, and advanced portal management. See the table of benefits.
- Database Snapshots aren't currently supported with Azure Files due to sparse files limitations.
- Since database snapshots aren't supported, CHECKDB for user databases falls back to CHECKDB WITH TABLOCK. TABLOCK limits the checks that are performed - DBCC CHECKCATALOG isn't run on the database, and Service Broker data isn't validated.
- DBCC CHECKDB on
masterandmsdbdatabase isn't supported. - Databases that use the in-memory OLTP feature aren't supported on a failover cluster instance deployed with a premium file share. If your business requires in-memory OLTP, consider deploying your FCI with Azure shared disks or Storage Spaces Direct instead.
Limited extension support
At this time, SQL Server failover cluster instances on Azure virtual machines, registered with the SQL IaaS Agent extension, only support a limited number of features. See the table of benefits.
If your SQL Server VM has already been registered with the SQL IaaS Agent extension and you've enabled any features that require the agent, you need to unregister from the extension by deleting the SQL virtual machine resource for the corresponding VMs and then register it with the SQL IaaS Agent extension again. When you're deleting the SQL virtual machine resource by using the Azure portal, clear the check box next to the correct virtual machine to avoid deleting the virtual machine.
Related content
- Create an FCI with Azure shared disks (SQL Server on Azure VMs)
- Create an FCI with Storage Spaces Direct (SQL Server on Azure VMs)
- Windows Server Failover Cluster with SQL Server on Azure VMs
- Failover cluster instances with SQL Server on Azure Virtual Machines
- Failover cluster instance overview
- HADR configuration best practices (SQL Server on Azure VMs)
Feedback
Coming soon: Throughout 2024 we will be phasing out GitHub Issues as the feedback mechanism for content and replacing it with a new feedback system. For more information see: https://aka.ms/ContentUserFeedback.
Submit and view feedback for