Tutorial: Copy data to Azure Data Box Heavy via SMB
Copy data to Azure Data Box Heavy
Important
Azure Data Box now supports access tier assignment at the blob level. The steps contained within this tutorial reflect the updated data copy process and are specific to block blobs.
The information contained within this section applies to orders placed after April 1, 2024.
This tutorial describes how to connect to and copy data from your host computer using the local web UI.
In this tutorial, you learn how to:
- Connect to Data Box Heavy
- Copy data to Data Box Heavy
You can copy data from your source server to your Data Box via SMB, NFS, REST, data copy service or to managed disks.
In each case, make sure that the share names, folder names, and data size follow guidelines described in the Azure Storage and Data Box Heavy service limits.
Prerequisites
Before you begin, make sure that:
- You complete the Tutorial: Set up Azure Data Box Heavy.
- You receive your Data Box Heavy and that the order status in the portal is Delivered.
- You have a host computer that has the data that you want to copy over to Data Box Heavy. Your host computer must:
- Run a Supported operating system.
- Be connected to a high-speed network. For fastest copy speeds, two 40-GbE connections (one per node) can be utilized in parallel. If you do not have 40-GbE connection available, we recommend that you have at least two 10-GbE connections (one per node).
Connect to Data Box Heavy shares
Based on the storage account selected, Data Box Heavy creates up to:
- Three shares for each associated storage account for GPv1 and GPv2.
- One share for premium storage.
- One share for a blob storage account, containing one folder for each of the four access tiers.
The following table identifies the names of the Data Box shares to which you can connect, and the type of data uploaded to your target storage account. It also identifies the hierarchy of shares and directories into which you copy your source data.
| Storage type | Share name | First-level entity | Second-level entity | Third-level entity |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Block blob | <storageAccountName>_BlockBlob | <\accessTier> | <\containerName> | <\blockBlob> |
| Page blob | <\storageAccountName>_PageBlob | <\containerName> | <\pageBlob> | |
| File storage | <\storageAccountName>_AzFile | <\fileShareName> | <\file> |
You can't copy files directly to the root folder of any Data Box share. Instead, create folders within the Data Box share depending on your use case.
Block blobs support the assignment of access tiers at the file level. When copying files to the block blob share, the recommended best-practice is to add new subfolders within the appropriate access tier. After creating new subfolders, continue adding files to each subfolder as appropriate.
A new container is created for any folder residing at the root of the block blob share. Any file within that folder is copied to the storage account's default access tier as a block blob.
For more information about blob access tiers, see Access tiers for blob data. For more detailed information about access tier best practices, see Best practices for using blob access tiers.
The following table shows the UNC path to the shares on your Data Box and the corresponding Azure Storage path URL to which data is uploaded. The final Azure Storage path URL can be derived from the UNC share path.
| Azure Storage types | Data Box shares |
|---|---|
| Azure Block blobs | \\<DeviceIPAddress>\<storageaccountname_BlockBlob>\<accessTier>\<ContainerName>\myBlob.txthttps://<storageaccountname>.blob.core.windows.net/<ContainerName>/myBlob.txt |
| Azure Page blobs | \\<DeviceIPAddress>\<storageaccountname_PageBlob>\<ContainerName>\myBlob.vhdhttps://<storageaccountname>.blob.core.windows.net/<ContainerName>/myBlob.vhd |
| Azure Files | \\<DeviceIPAddress>\<storageaccountname_AzFile>\<ShareName>\myFile.txthttps://<storageaccountname>.file.core.windows.net/<ShareName>/myFile.txt |
For more information about blob access tiers, see Access tiers for blob data. For more detailed information about access tier best practices, see Best practices for using blob access tiers.
The steps to connect using a Windows or a Linux client are different.
Note
Follow the same steps to connect to both the nodes of the device in parallel.
Connect on a Windows system
If using a Windows Server host computer, follow these steps to connect to the Data Box Heavy.
The first step is to authenticate and start a session. Go to Connect and copy. Click Get credentials to get the access credentials for the shares associated with your storage account.
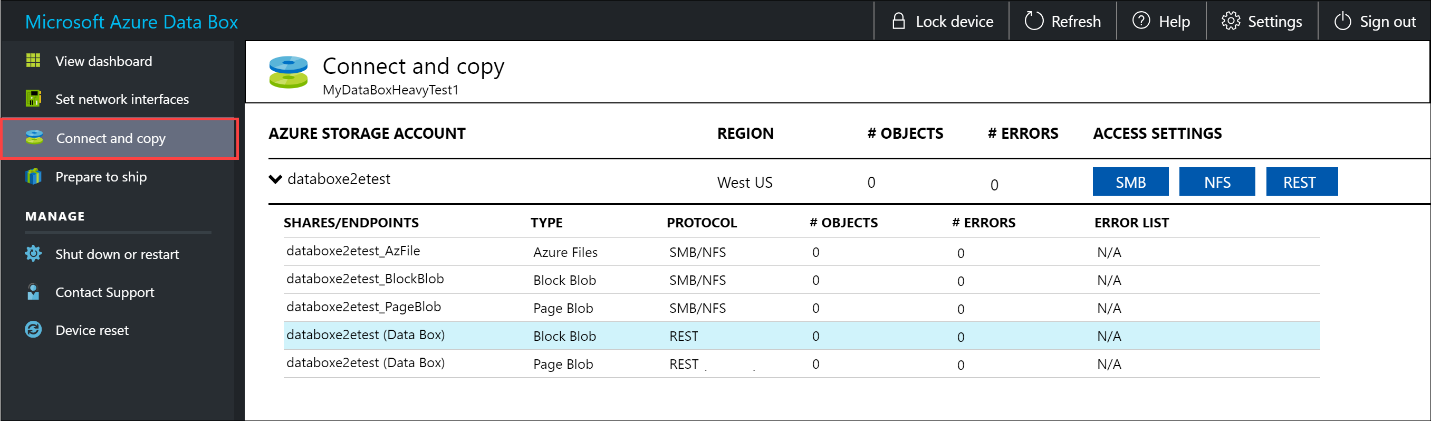
In the Access share and copy data dialog box, copy the Username and the Password corresponding to the share. Click OK.
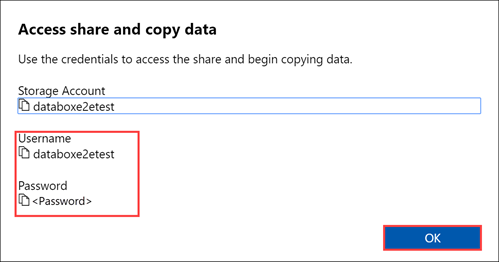
To access the shares associated with your storage account (databoxe2etest in the following example) from your host computer, open a command window. At the command prompt, type:
net use \\<IP address of the device>\<share name> /u:<user name for the share>Depending upon your data format, the share paths are as follows:
- Azure Block blob -
\\10.100.10.100\databoxe2etest_BlockBlob - Azure Page blob -
\\10.100.10.100\databoxe2etest_PageBlob - Azure Files -
\\10.100.10.100\databoxe2etest_AzFile
- Azure Block blob -
Enter the password for the share when prompted. The following sample can be used to connect to BlockBlob share on the Data Box having in IP address of 10.100.10.100.
net use \\10.100.10.100\databoxe2etest_BlockBlob /u:databoxe2etest Enter the password for 'databoxe2etest' to connect to '10.100.10.100': The command completed successfully.Press Windows + R. In the Run window, specify the
\\<device IP address>. Click OK to open File Explorer.
You should now see the shares as folders. Note that in this example the BlockBlob share is being used. Accordingly, the four folders representing the four available access tiers are present. These folders are not available in other shares.
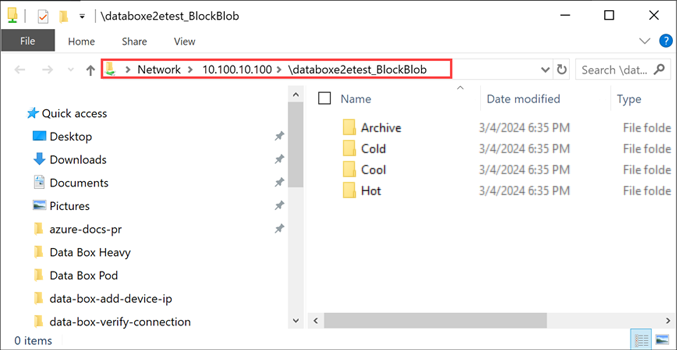
Always create a folder for the files that you intend to copy under the share and then copy the files to that folder. You cannot copy files directly to the root folder in the storage account. Any folders created under the PageBlob share represents containers into which data is uploaded as blobs. Similarly, any sub-folders created within the folders representing access tiers in the BlockBlob share also represents a blob storage container. Folders created within the AzFile share represent file shares.
Folders created at the root of the BlockBlob share will be created as blob containers. The access tier of these container will be inherited from the storage account.
Connect on a Linux system
If using a Linux client, use the following command to mount the SMB share.
sudo mount -t nfs -o vers=2.1 10.126.76.172:/databoxe2etest_BlockBlob /home/databoxubuntuhost/databox
The vers parameter is the version of SMB that your Linux host supports. Plug in the appropriate version in the above command.
For versions of SMB that the Data Box Heavy supports, see Supported file systems for Linux clients.
Copy data to Data Box Heavy
Once you're connected to the Data Box Heavy shares, the next step is to copy data.
Copy considerations
Before you begin the data copy, review the following considerations:
Make sure that you copy the data to shares that correspond to the appropriate data format. For instance, copy the block blob data to the share for block blobs. Copy the VHDs to page blob.
If the data format doesn't match the appropriate share type, then at a later step, the data upload to Azure will fail.
While copying data, make sure that the data size conforms to the size limits described in the Azure storage and Data Box Heavy limits.
If data, which is being uploaded by Data Box Heavy, is concurrently uploaded by other applications outside of Data Box Heavy, then this could result in upload job failures and data corruption.
We recommend that:
- You don't use both SMB and NFS at the same time.
- Copy the same data to same end destination on Azure.
In these cases, the final outcome can't be determined.
Always create a folder for the files that you intend to copy under the share and then copy the files to that folder. The folder created under block blob and page blob shares represents a container to which the data is uploaded as blobs. You cannot copy files directly to root folder in the storage account.
After you've connected to the SMB share, begin data copy.
You can use any SMB compatible file copy tool such as Robocopy to copy your data. Multiple copy jobs can be initiated using Robocopy. Use the following command:
robocopy <Source> <Target> * /e /r:3 /w:60 /is /nfl /ndl /np /MT:32 or 64 /fft /Log+:<LogFile>The attributes are described in the following table.
Attribute Description /e Copies subdirectories including empty directories. /r: Specifies the number of retries on failed copies. /w: Specifies the wait time between retries, in seconds. /is Includes the same files. /nfl Specifies that file names aren't logged. /ndl Specifies that directory names aren't logged. /np Specifies that the progress of the copying operation (the number of files or directories copied so far) will not be displayed. Displaying the progress significantly lowers the performance. /MT Use multithreading, recommended 32 or 64 threads. This option not used with encrypted files. You may need to separate encrypted and unencrypted files. However, single threaded copy significantly lowers the performance. /fft Use to reduce the time stamp granularity for any file system. /b Copies files in Backup mode. /z Copies files in Restart mode, use this if the environment is unstable. This option reduces throughput due to additional logging. /zb Uses Restart mode. If access is denied, this option uses Backup mode. This option reduces throughput due to checkpointing. /efsraw Copies all encrypted files in EFS raw mode. Use only with encrypted files. log+:<LogFile> Appends the output to the existing log file. The following sample shows the output of the robocopy command to copy files to the Data Box Heavy.
C:\Users>Robocopy C:\Git\azure-docs-pr\contributor-guide \\10.100.10.100\devicemanagertest1_AzFile\templates /MT:24 ------------------------------------------------------------------------------- ROBOCOPY :: Robust File Copy for Windows ------------------------------------------------------------------------------- Started : Thursday, April 4, 2019 2:34:58 PM Source : C:\Git\azure-docs-pr\contributor-guide\ Dest : \\10.100.10.100\devicemanagertest1_AzFile\templates\ Files : *.* Options : *.* /DCOPY:DA /COPY:DAT /MT:24 /R:5 /W:60 ------------------------------------------------------------------------------ 100% New File 206 C:\Git\azure-docs-pr\contributor-guide\article-metadata.md 100% New File 209 C:\Git\azure-docs-pr\contributor-guide\content-channel-guidance.md 100% New File 732 C:\Git\azure-docs-pr\contributor-guide\contributor-guide-index.md 100% New File 199 C:\Git\azure-docs-pr\contributor-guide\contributor-guide-pr-criteria.md New File 178 C:\Git\azure-docs-pr\contributor-guide\contributor-guide-pull-request-co100% .md New File 250 C:\Git\azure-docs-pr\contributor-guide\contributor-guide-pull-request-et100% e.md 100% New File 174 C:\Git\azure-docs-pr\contributor-guide\create-images-markdown.md 100% New File 197 C:\Git\azure-docs-pr\contributor-guide\create-links-markdown.md 100% New File 184 C:\Git\azure-docs-pr\contributor-guide\create-tables-markdown.md 100% New File 208 C:\Git\azure-docs-pr\contributor-guide\custom-markdown-extensions.md 100% New File 210 C:\Git\azure-docs-pr\contributor-guide\file-names-and-locations.md 100% New File 234 C:\Git\azure-docs-pr\contributor-guide\git-commands-for-master.md 100% New File 186 C:\Git\azure-docs-pr\contributor-guide\release-branches.md 100% New File 240 C:\Git\azure-docs-pr\contributor-guide\retire-or-rename-an-article.md 100% New File 215 C:\Git\azure-docs-pr\contributor-guide\style-and-voice.md 100% New File 212 C:\Git\azure-docs-pr\contributor-guide\syntax-highlighting-markdown.md 100% New File 207 C:\Git\azure-docs-pr\contributor-guide\tools-and-setup.md ------------------------------------------------------------------------------ Total Copied Skipped Mismatch FAILED Extras Dirs : 1 1 1 0 0 0 Files : 17 17 0 0 0 0 Bytes : 3.9 k 3.9 k 0 0 0 0 C:\Users>To optimize the performance, use the following robocopy parameters when copying the data. (The numbers below represent the best case scenarios.)
Platform Mostly small files < 512 KB Mostly medium files 512 KB-1 MB Mostly large files > 1 MB Data Box Heavy 6 Robocopy sessions
24 threads per sessions6 Robocopy sessions
16 threads per sessions6 Robocopy sessions
16 threads per sessionsFor more information on Robocopy command, go to Robocopy and a few examples.
Open the target folder to view and verify the copied files.
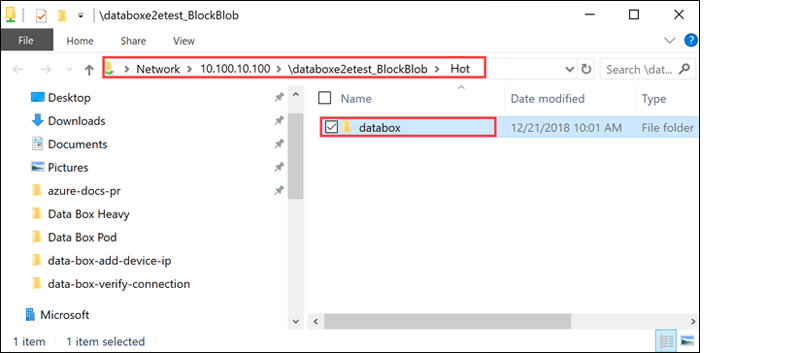
As the data is copied:
- The file names, sizes, and format are validated to ensure those meet the Azure object and storage limits as well as Azure file and container naming conventions.
- To ensure data integrity, checksum is also computed inline.
If you have any errors during the copy process, download the error files for troubleshooting. Select the arrow icon to download the error files.
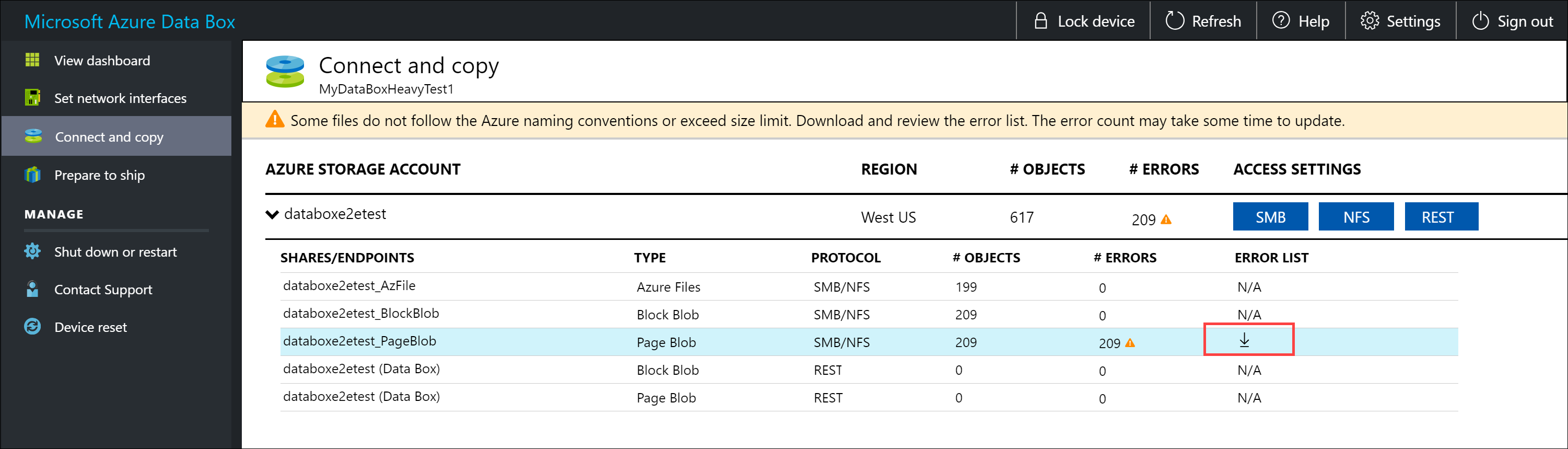
For more information, see View error logs during data copy to Data Box Heavy. For a detailed list of errors during data copy, see Troubleshoot Data Box Heavy issues.
Open the error file in Notepad. The following error file indicates that the data is not aligned correctly.
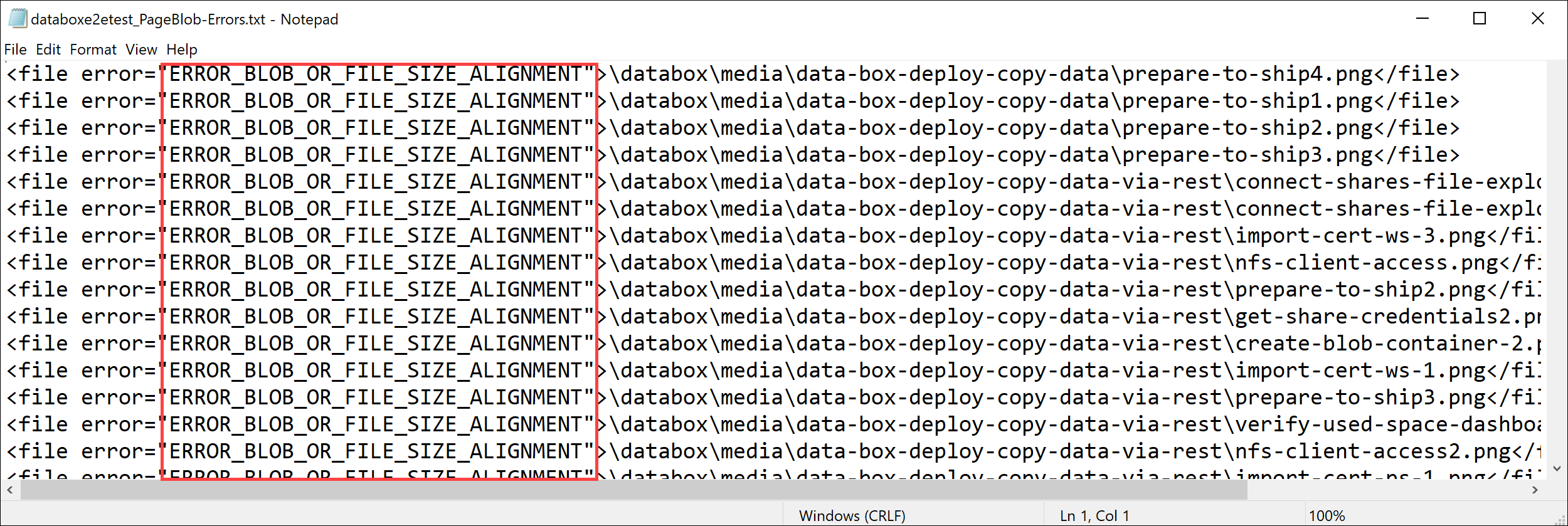
For a page blob, the data needs to be 512 bytes aligned. After this data is removed, the error resolves as shown in the following screenshot.
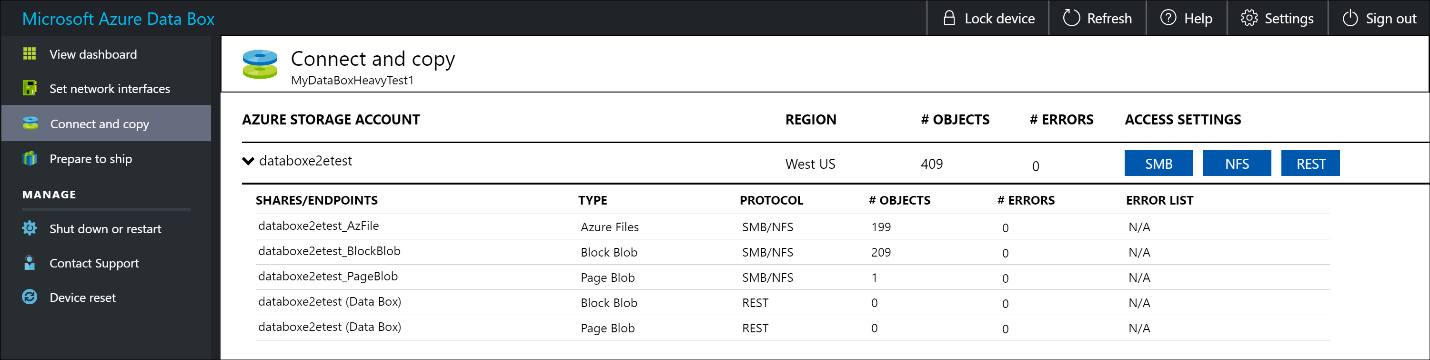
After the copy is complete, go to View Dashboard page. Verify the used space and the free space on your device.
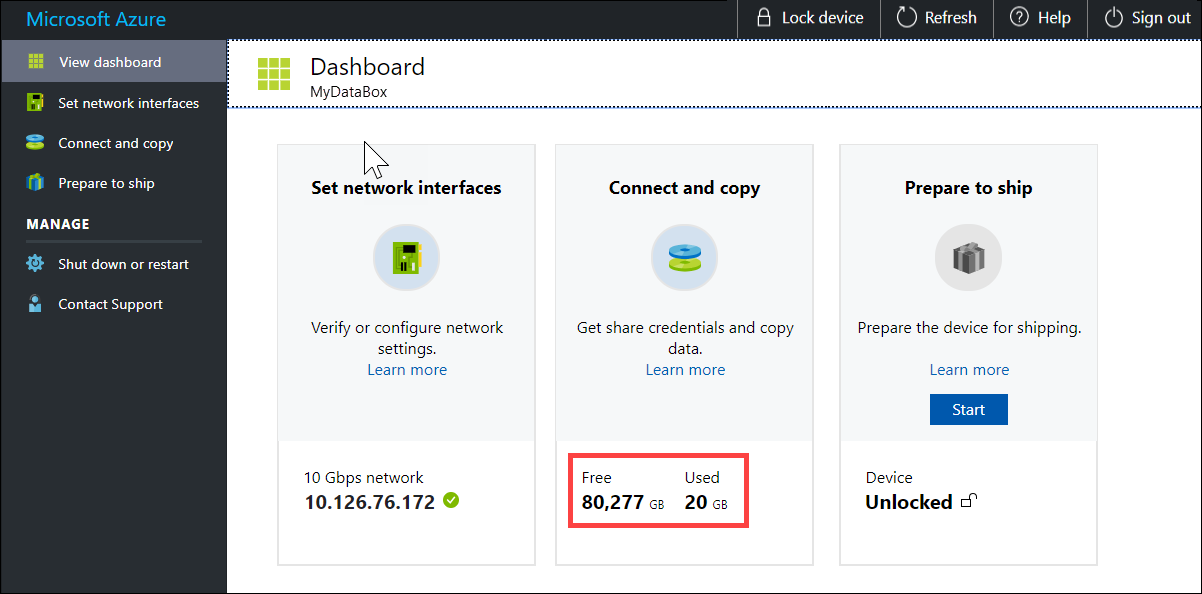
Repeat the above steps to copy data on to the second node of the device.
Next steps
In this tutorial, you learned about Azure Data Box Heavy topics such as:
- Connect to Data Box Heavy
- Copy data to Data Box Heavy
Advance to the next tutorial to learn how to ship your Data Box Heavy back to Microsoft.
Copy data via SMB
If using a Windows host, use the following command to connect to the SMB shares:
\\<IP address of your device>\ShareNameTo get the share access credentials, go to the Connect & copy page in the local web UI of the Data Box.
Use an SMB compatible file copy tool such as Robocopy to copy data to shares.
For step-by-step instructions, go to Tutorial: Copy data to Azure Data Box via SMB.
Copy data via NFS
If using an NFS host, use the following command to mount the NFS shares:
sudo mount <Data Box device IP>:/<NFS share on Data Box device> <Path to the folder on local Linux computer>To get the share access credentials, go to the Connect & copy page in the local web UI of the Data Box Heavy.
Use
cporrsynccommand to copy your data.Repeat these steps to connect and copy data to the second node of your Data Box Heavy.
For step-by-step instructions, go to Tutorial: Copy data to Azure Data Box via NFS.
Copy data via REST
- To copy data using Data Box Blob storage via REST APIs, you can connect over http or https.
- To copy data to Data Box Blob storage, you can use AzCopy.
- Repeat these steps to connect and copy data to the second node of your Data Box Heavy.
For step-by-step instructions, go to Tutorial: Copy data to Azure Data Box Blob storage via REST APIs.
Copy data via data copy service
- To copy data by using the data copy service, you need to create a job. In the local web UI of your Data Box Heavy, go to Manage > Copy data > Create.
- Fill out the parameters and create a job.
- Repeat these steps to connect and copy data to the second node of your Data Box Heavy.
For step-by-step instructions, go to Tutorial: Use the data copy service to copy data into Azure Data Box Heavy.
Copy data to managed disks
- When ordering the Data Box Heavy device, you should have selected managed disks as your storage destination.
- You can connect to Data Box Heavy via SMB or NFS shares.
- You can then copy data via SMB or NFS tools.
- Repeat these steps to connect and copy data to the second node of your Data Box Heavy.
For step-by-step instructions, go to Tutorial: Use Data Box Heavy to import data as managed disks in Azure.
Feedback
Coming soon: Throughout 2024 we will be phasing out GitHub Issues as the feedback mechanism for content and replacing it with a new feedback system. For more information see: https://aka.ms/ContentUserFeedback.
Submit and view feedback for