Quickstart: Create Apache Spark cluster in Azure HDInsight using Azure portal
In this quickstart, you use the Azure portal to create an Apache Spark cluster in Azure HDInsight. You then create a Jupyter Notebook, and use it to run Spark SQL queries against Apache Hive tables. Azure HDInsight is a managed, full-spectrum, open-source analytics service for enterprises. The Apache Spark framework for HDInsight enables fast data analytics and cluster computing using in-memory processing. Jupyter Notebook lets you interact with your data, combine code with markdown text, and do simple visualizations.
For in-depth explanations of available configurations, see Set up clusters in HDInsight. For more information regarding the use of the portal to create clusters, see Create clusters in the portal.
If you're using multiple clusters together, you may want to create a virtual network; if you're using a Spark cluster may also want to use the Hive Warehouse Connector. For more information, see Plan a virtual network for Azure HDInsight and Integrate Apache Spark and Apache Hive with the Hive Warehouse Connector.
Important
Billing for HDInsight clusters is prorated per minute, whether you are using them or not. Be sure to delete your cluster after you have finished using it. For more information, see the Clean up resources section of this article.
Prerequisites
An Azure account with an active subscription. Create an account for free.
Create an Apache Spark cluster in HDInsight
You use the Azure portal to create an HDInsight cluster that uses Azure Storage Blobs as the cluster storage. For more information on using Data Lake Storage Gen2, see Quickstart: Set up clusters in HDInsight.
Sign in to the Azure portal.
From the top menu, select + Create a resource.
Select Analytics > Azure HDInsight to go to the Create HDInsight cluster page.
From the Basics tab, provide the following information:
Property Description Subscription From the drop-down list, select the Azure subscription that's used for the cluster. Resource group From the drop-down list, select your existing resource group, or select Create new. Cluster name Enter a globally unique name. Region From the drop-down list, select a region where the cluster is created. Availability zone Optional - specify an availability zone in which to deploy your cluster Cluster type Select cluster type to open a list. From the list, select Spark. Cluster version This field will auto-populate with the default version once the cluster type has been selected. Cluster login username Enter the cluster login username. The default name is admin. You use this account to log in to the Jupyter Notebook later in the quickstart. Cluster login password Enter the cluster login password. Secure Shell (SSH) username Enter the SSH username. The SSH username used for this quickstart is sshuser. By default, this account shares the same password as the Cluster Login username account. 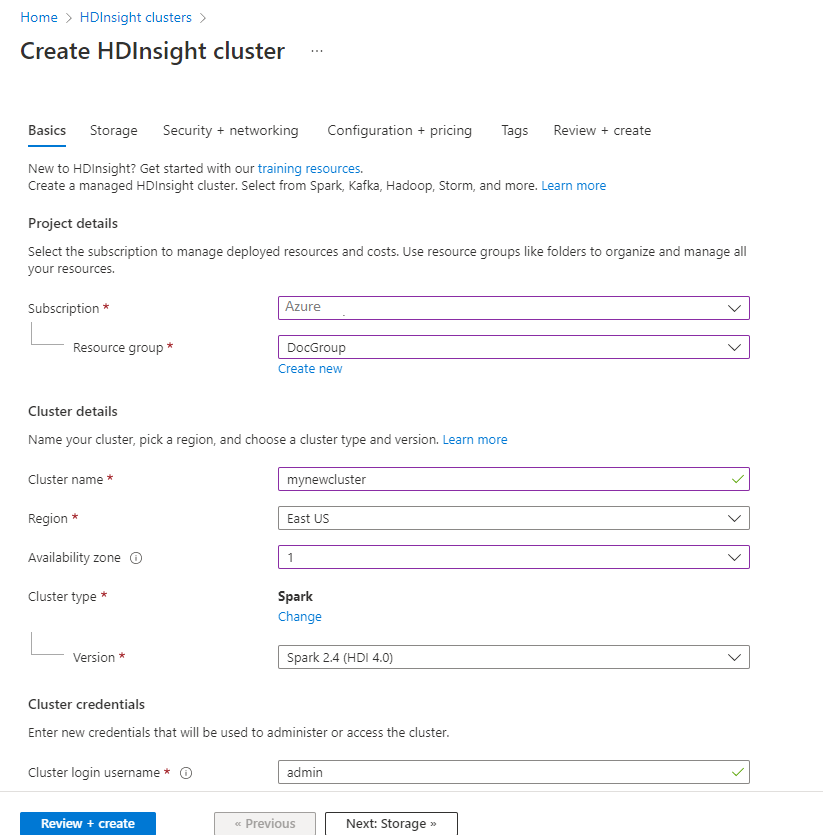
Select Next: Storage >> to continue to the Storage page.
Under Storage, provide the following values:
Property Description Primary storage type Use the default value Azure Storage. Selection method Use the default value Select from list. Primary storage account Use the auto-populated value. Container Use the auto-populated value. 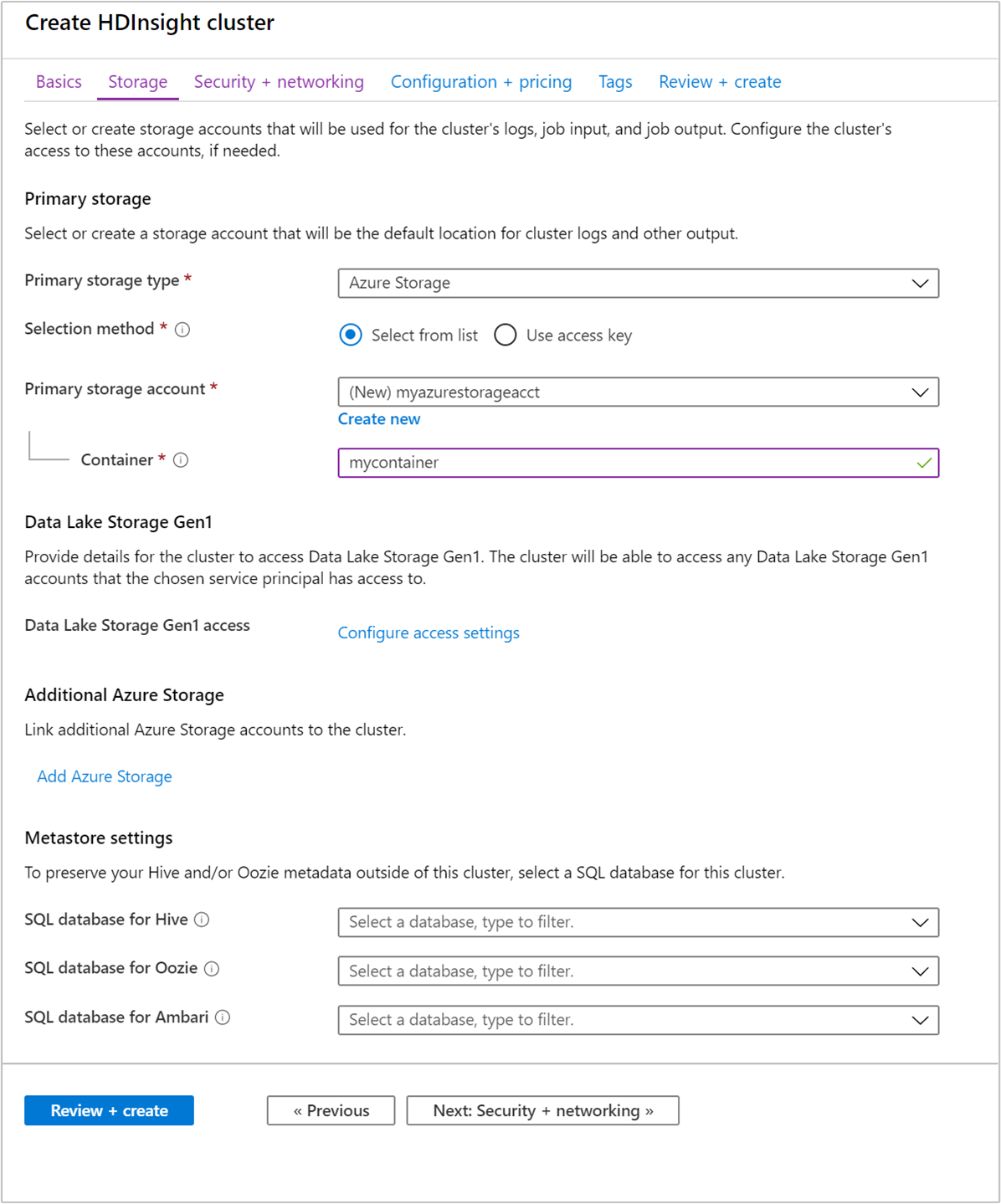
Select Review + create to continue.
Under Review + create, select Create. It takes about 20 minutes to create the cluster. The cluster must be created before you can proceed to the next session.
If you run into an issue with creating HDInsight clusters, it could be that you don't have the right permissions to do so. For more information, see Access control requirements.
Create a Jupyter Notebook
Jupyter Notebook is an interactive notebook environment that supports various programming languages. The notebook allows you to interact with your data, combine code with markdown text and perform simple visualizations.
From a web browser, navigate to
https://CLUSTERNAME.azurehdinsight.net/jupyter, whereCLUSTERNAMEis the name of your cluster. If prompted, enter the cluster login credentials for the cluster.Select New > PySpark to create a notebook.

A new notebook is created and opened with the name Untitled(Untitled.pynb).
Run Apache Spark SQL statements
SQL (Structured Query Language) is the most common and widely used language for querying and defining data. Spark SQL functions as an extension to Apache Spark for processing structured data, using the familiar SQL syntax.
Verify the kernel is ready. The kernel is ready when you see a hollow circle next to the kernel name in the notebook. Solid circle denotes that the kernel is busy.
When you start the notebook for the first time, the kernel performs some tasks in the background. Wait for the kernel to be ready.
Paste the following code in an empty cell, and then press SHIFT + ENTER to run the code. The command lists the Hive tables on the cluster:
%%sql SHOW TABLESWhen you use a Jupyter Notebook with your HDInsight cluster, you get a preset
sqlContextthat you can use to run Hive queries using Spark SQL.%%sqltells Jupyter Notebook to use the presetsqlContextto run the Hive query. The query retrieves the top 10 rows from a Hive table (hivesampletable) that comes with all HDInsight clusters by default. It takes about 30 seconds to get the results. The output looks like: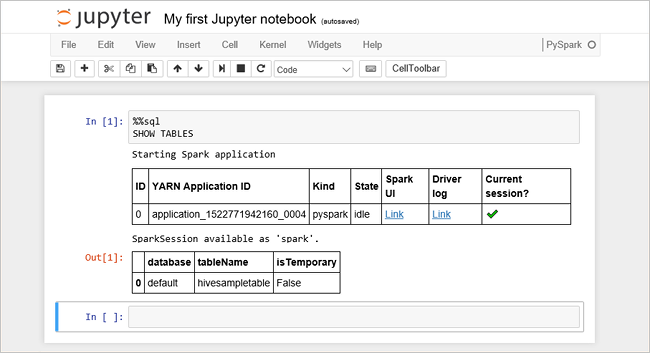 is quickstart." border="true":::
is quickstart." border="true":::Every time you run a query in Jupyter, your web browser window title shows a (Busy) status along with the notebook title. You also see a solid circle next to the PySpark text in the top-right corner.
Run another query to see the data in
hivesampletable.%%sql SELECT * FROM hivesampletable LIMIT 10The screen shall refresh to show the query output.
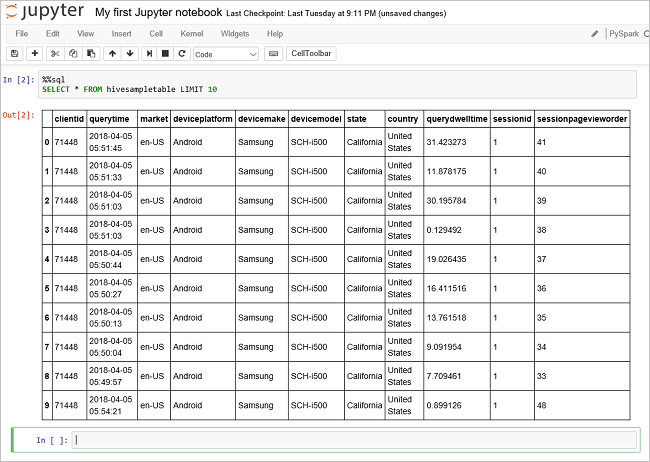 Insight" border="true":::
Insight" border="true":::From the File menu on the notebook, select Close and Halt. Shutting down the notebook releases the cluster resources.
Clean up resources
HDInsight saves your data in Azure Storage or Azure Data Lake Storage, so you can safely delete a cluster when it isn't in use. You're also charged for an HDInsight cluster, even when it isn't in use. Since the charges for the cluster are many times more than the charges for storage, it makes economic sense to delete clusters when they aren't in use. If you plan to work on the tutorial listed in Next steps immediately, you might want to keep the cluster.
Switch back to the Azure portal, and select Delete.
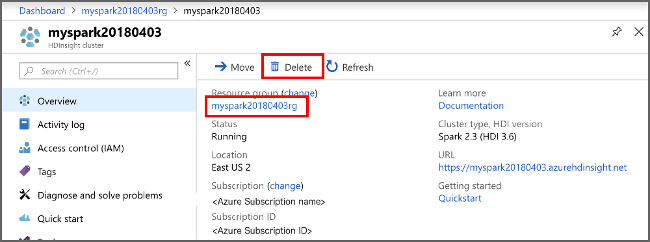 sight cluster" border="true":::
sight cluster" border="true":::
You can also select the resource group name to open the resource group page, and then select Delete resource group. By deleting the resource group, you delete both the HDInsight cluster, and the default storage account.
Next steps
In this quickstart, you learned how to create an Apache Spark cluster in HDInsight and run a basic Spark SQL query. Advance to the next tutorial to learn how to use an HDInsight cluster to run interactive queries on sample data.
Feedback
Coming soon: Throughout 2024 we will be phasing out GitHub Issues as the feedback mechanism for content and replacing it with a new feedback system. For more information see: https://aka.ms/ContentUserFeedback.
Submit and view feedback for