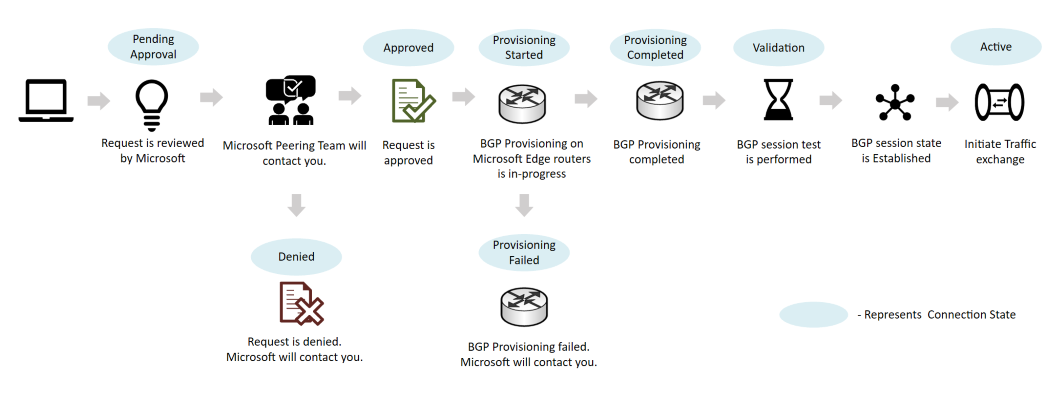
Direct peering walkthrough
In this article, you learn how to set up and manage a Direct peering.
Create a Direct peering
To provision a Direct peering, complete the following steps:
- Review Microsoft peering policy to understand requirements for Direct peering.
- Follow the instructions in Create or modify a Direct peering to submit a peering request.
- After you submit a peering request, Microsoft will contact using your registered email address to provide LOA (Letter Of Authorization) or for other information.
- Once peering request is approved, connection state changes to ProvisioningStarted. Then, you need to:
- complete wiring according to the LOA.
- (optionally) perform link test using 169.254.0.0/16.
- configure BGP session and then notify Microsoft.
- Microsoft provisions BGP session with DENY ALL policy and validate end-to-end.
- If successful, you receive a notification that peering connection state is Active.
- Traffic is then allowed through the new peering.
Note
Connection states are different from standard BGP session states.
Convert a legacy Direct peering to an Azure resource
To convert a legacy Direct peering to an Azure resource, complete the following steps:
- Follow the instructions in Convert a legacy Direct peering to Azure resource
- After you submit the conversion request, Microsoft reviews the request and contacts you if necessary.
- Once approved, you see your Direct peering with a connection state as Active.
Deprovision Direct peering
Contact Microsoft peering team to deprovision a Direct peering.
When a Direct peering is set for deprovision, the connection state changes to PendingRemove.
Note
If you run PowerShell cmdlet to delete the Direct peering when the ConnectionState is ProvisioningStarted or ProvisioningCompleted, the operation will fail.
Related content
- Learn about the Prerequisites to set up peering with Microsoft.
- Learn about the Peering policy.
Feedback
Coming soon: Throughout 2024 we will be phasing out GitHub Issues as the feedback mechanism for content and replacing it with a new feedback system. For more information see: https://aka.ms/ContentUserFeedback.
Submit and view feedback for