Migrate Azure Kubernetes Service (AKS) and MySQL Flexible Server workloads to availability zone support
This guide describes how to migrate an Azure Kubernetes Service and MySQL Flexible Server workload to complete availability zone support across all dependent services. For complete list of all workload dependencies, see Workload service dependencies.
Availability zone support for this workload must be enabled during the creation of your AKS cluster or MySQL Flexible Server. If you want availability zone support for an existing AKS cluster and MySQL Flexible Server, you'll need to redeploy those resources.
This migration guidance focuses mainly on the infrastructure and availability considerations of running the following architecture on Azure:

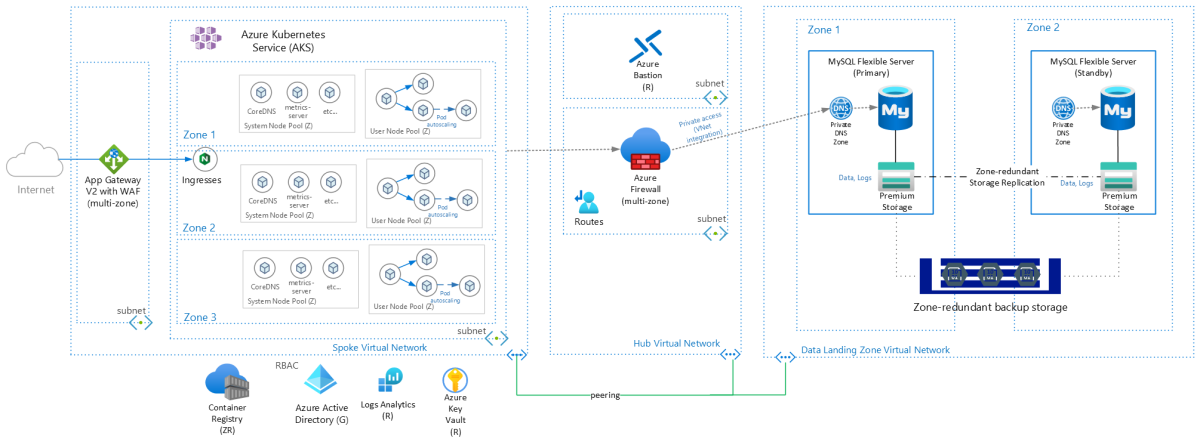
Workload service dependencies
To provide full workload support for availability zones, each service dependency in the workload must support availability zones.
There are two approaches types of availability zone supported services: zonal or zone-redundant. Most services support one or the other. However, in some cases, there are options for choosing either a zonal or zone-redundant resource for that service. We indicate which services support zonal and zone-redundant resources in the following recommendations. We also indicate which services are global and regional.
The AKS and MySQL workload architecture consists of the following component dependencies:
Azure Kubernetes Service (AKS)
Zonal : The system node pool and user node pools are zonal when you pre-select the zones in which the node pools are deployed during creation time. We recommend that you pre-select all three zones for better resiliency. More user node pools that support availability zones can be added to an existing AKS cluster and by supplying a value for the
zonesparameter.Zone-redundant: Kubernetes control plane components such as etcd, API server, Scheduler, and Controller Manager are automatically replicated or distributed across zones.
Note
To enable zone-redundancy of the AKS cluster control plane components, you must define your default system node pool with zones when you create an AKS cluster. Adding more zonal node pools to an existing non-zonal AKS cluster won't make the AKS cluster zone-redundant, because that action doesn't distribute the control plane components across zones after-the-fact.
Azure Database for MySQL Flexible Server
Zonal: The zonal availability mode means that a standby server is always available within the same zone as the primary server. While this option reduces failover time and network latency, it's less resilient due to a single zone outage impacting both the primary and standby servers.
Zone-redundant: The zone-redundant availability mode means that a standby server is always available within another zone in the same region as the primary server. Two zones will be enabled for zone redundancy for the primary and standby servers. We recommend this configuration for better resiliency.
Azure Standard Load Balancer or Azure Application Gateway
Standard Load Balancer
To understand considerations related to Standard Load Balancer resources, see Load Balancer and Availability Zones.
Zone-redundant: Choosing zone-redundancy is the recommended way to configure your Frontend IP with your existing Load Balancer. The zone-redundant front-end corresponds with the AKS cluster back-end pool, which is distributed across multiple zones.
Zonal: If you're pinning your node pools to specific zones such as zone 1 and 2, you can pre-select zone 1 and 2 for your Frontend IP in the existing Load Balancer. The reason why you may want to pin your node pools to specific zones could be due to the availability of specialized VM SKU series such as M-series.
Azure Application Gateway
Using the Application Gateway Ingress Controller add-on with your AKS cluster is supported only on Application Gateway v2 SKUs (Standard and WAF). To understand further considerations related to Azure Application Gateway, see Scaling Application Gateway v2 and WAF v2.
Zonal: To use the benefits of availability zones, we recommend that the Application Gateway resource be created in multiple zones, such as zone 1, 2, and 3. Select all three zones for best intra-region resiliency strategy. However, to correspond to your backend node pools, you may pin your node pools to specific zones by pre-selecting zone 1 and 2 during the creation of your App Gateway resource. The reason why you may want to pin your node pools to specific zones could be due to the availability of specialized VM SKU series such as M-series.
Zone Redundant Storage (ZRS)
We recommend that your AKS cluster is configured with managed ZRS disks because they're zone-redundant resources. Volumes can be scheduled on all zones.
Kubernetes is aware of Azure availability zones since version 1.12. You can deploy a
PersistentVolumeClaimobject referencing an Azure Managed Disk in a multi-zone AKS cluster. Kubernetes will take care of scheduling any pod that claims this PVC in the correct availability zone.For Azure Database for SQL, we recommend that the data and log files are hosted in zone-redundant storage (ZRS). These files are replicated to the standby server via the storage-level replication available with ZRS.
Azure Firewall
Zonal: To use the benefits of availability zones, we recommend that the Azure Firewall resource be created in multiple zones, such as zone 1, 2, and 3. We recommend that you select all three zones for the best intra-region resiliency strategy.
Azure Bastion
Regional: Azure Bastion is deployed within VNets or peered VNets and is associated to an Azure region. For more information, se Bastion FAQ.
Azure Container Registry (ACR)
Zone-redundant: We recommend that you create a zone-redundant registry in the Premium service tier. You can also create a zone-redundant registry replica by setting the zoneRedundancy property for the replica. To learn how to enable zone redundancy for your ACR, see Enable zone redundancy in Azure Container Registry for resiliency and high availability.
Azure Cache for Redis
Zone-redundant: Azure Cache for Redis supports zone-redundant configurations in the Premium and Enterprise tiers. A zone-redundant cache places its nodes across different availability zones in the same region.
Microsoft Entra ID
Global: Microsoft Entra ID is a global service with multiple levels of internal redundancy and automatic recoverability. Microsoft Entra ID is deployed in over 30 datacenters around the world that provide availability zones where present. This number is growing rapidly as more regions are deployed.
Azure Key Vault
Regional: Azure Key Vault is deployed in a region. To maintain high durability of your keys and secrets, the contents of your key vault are replicated within the region and to a secondary region within the same geography.
Zone-redundant: For Azure regions with availability zones and no region pair, Key Vault uses zone-redundant storage (ZRS) to replicate the contents of your key vault three times within the single location/region.
Workload considerations
Azure Kubernetes Service (AKS)
Pods can communicate with other pods, regardless of which node or the availability zone in which the pod lands on the node. Your application may experience higher response time if the pods are located in different availability zones. While the extra round-trip latencies between pods are expected to fall within an acceptable range for most applications, there are application scenarios which require low latency, especially for a chatty communication pattern between pods.
We recommend that you test your application to ensure it performs well across availability zones.
For performance reasons such low latency, pods can be co-located in the same data center within the same availability zone. To co-locate pods in the same data center within the same availability zone, you can create user node pools with a unique zone and proximity placement group. You can add a proximity placement group (PPG) to an existing AKS cluster by creating a new agent node pool and specifying the PPG. Use Pod Topology Spread Constraints to control how pods are spread in your AKS cluster across availability zones, nodes and regions.
After pods that require low latency communication are co-located in the same availability zone, communications between the pods aren't direct. Instead, pod communications are channeled through a service that defines a logical set of pods in your AKS cluster. Pods can be configured to talk to AKS and the communication to the service will be automatically load-balanced to all the pods that are members of the service.
To take advantage of availability zones, node pools contain underlying VMs that are zonal resources. To support applications that have different compute or storage demands, you can create user node pools with specific VM sizes when you create the user node pool.
For example, you may decide to use the
Standard_M32msunder theM-seriesfor your user nodes because the microservices in your application require high throughput, low latency, and memory optimized VM sizes that provide high vCPU counts and large amounts of memory. Depending on the deployment region, when you select the VM size in the Azure portal, you may see that this VM size is supported only in zone 1 and 2. You can accept this resiliency configuration as a trade-off for high performance.You can't change the VM size of a node pool after you create it. For more information on node pool limitations, see Limitations.
Azure Database for MySQL Flexible Server
The implication of deploying your node pools in specific zones, such as zone 1 and 2, is that all service dependencies of your AKS cluster must also support zone 1 and 2. In this workload architecture, your AKS cluster has a service dependency on Azure Database for MySQL Flexible Servers with zone resiliency. You would select zone 1 for your primary server and zone 2 for your standby server to be co-located with your AKS user node pools.
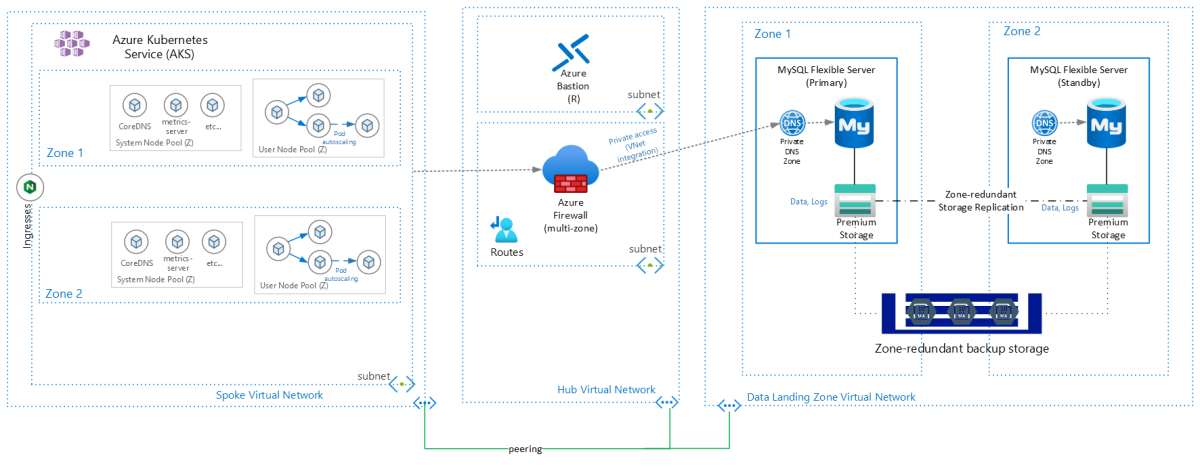
Azure Cache for Redis
Azure Cache for Redis distributes nodes in a zone-redundant cache in a round-robin manner over the availability zones that you've selected.
You can't update an existing Premium cache to use zone redundancy. To use zone redundancy, you must recreate the Azure Cache for Redis.
To achieve optimal resiliency, we recommend that you create your Azure Cache for Redis with three, or more replicas so that you can distribute the replicas across three availability zones.
Disaster recovery considerations
Availability zones are used for better resiliency to achieve high availability of your workload within the primary region of your deployment.
Disaster Recovery consists of recovery operations and practices defined in your business continuity plan. Your business continuity plan addresses both how your workload recovers during a disruptive event and how it fully recovers after the event. Consider extending your deployment to an alternative region.
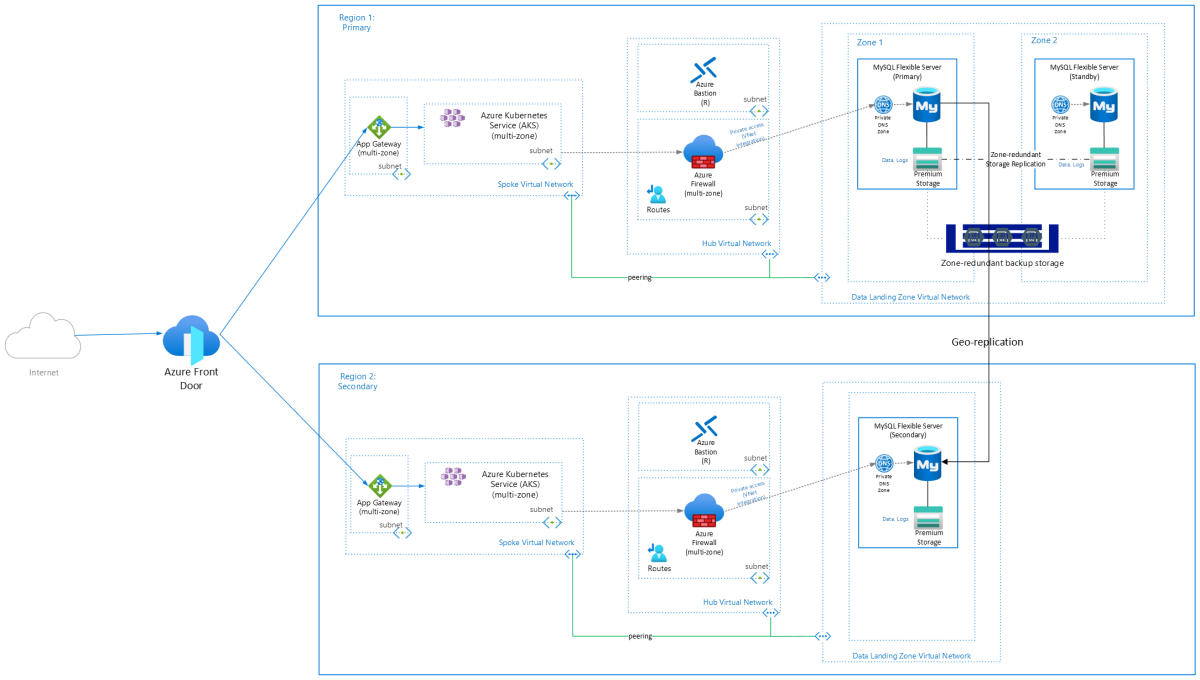
For your application tier, please review the business continuity and disaster recovery considerations for AKS in this article.
Consider running multiple AKS clusters in alternative regions. The alternative region can use a secondary paired region. Or, where there's no region pairing for your primary region, you can select an alternative region based on your consideration for available services, capacity, geographical proximity, and data sovereignty. Please review the Azure regions decision guide. Also review the deployment stamp pattern.
You have the option of configuring active-active, active-standby, active-passive for your AKS clusters.
For your database tier, disaster recovery features include geo-redundant backups with the ability to initiate geo-restore and deploying read replicas in a different region.
During an outage, you'll need to decide whether to initiate a recovery. You'll need to initiate recovery operations only when the outage is likely to last longer than your workload’s recovery time objective (RTO). Otherwise, you'll wait for service recovery by checking the service status on the Azure Service Health Dashboard. On the Service Health blade of the Azure portal, you can view any notifications associated with your subscription.
When you do initiate recovery with the geo-restore feature in Azure Database for MySQL, a new database server is created using backup data that is replicated from another region.
Next Steps
Learn more about:
Feedback
Coming soon: Throughout 2024 we will be phasing out GitHub Issues as the feedback mechanism for content and replacing it with a new feedback system. For more information see: https://aka.ms/ContentUserFeedback.
Submit and view feedback for