Tutorial: Control traffic routing with weighted endpoints by using Traffic Manager
This tutorial describes how to use Azure Traffic Manager to control routing of user traffic between endpoints by using the weighted routing method. In this routing method, you assign weights to each endpoint in the Traffic Manager profile configuration. User traffic is then routed based on the weight assigned to each endpoint. The weight is an integer from 1 to 1,000. The higher the weight value assigned to an endpoint, the higher its priority.
In this tutorial, you learn how to:
- Create two VMs running a basic website on IIS.
- Create two test VMs to view Traffic Manager in action.
- Configure a DNS name for the VMs running IIS.
- Create a Traffic Manager profile.
- Add VM endpoints to the Traffic Manager profile.
- View Traffic Manager in action.
If you don't have an Azure subscription, create a free account before you begin.
Prerequisites
To see Traffic Manager in action, deploy the following for this tutorial:
- Two instances of basic websites running in different Azure regions: East US and West Europe.
- Two test VMs for testing Traffic Manager: one in East US and the other in West Europe. The test VMs are used to illustrate how Traffic Manager routes user traffic to a website that has higher weight assigned to its endpoint.
Sign in to Azure
Sign in to the Azure portal.
Create websites
In this section, you create two website instances that provide the two service endpoints for the Traffic Manager profile in two Azure regions. To create the two websites, complete the following steps:
- Create two VMs for running a basic website: one in East US, and the other in West Europe.
- Install an IIS server on each VM. Update the default webpage that describes the VM name that a user is connected to when visiting the website.
Create VMs for running websites
In this section, you create two VMs (myIISVMEastUS and myIISVMWestEurope) in the East US and West Europe Azure regions.
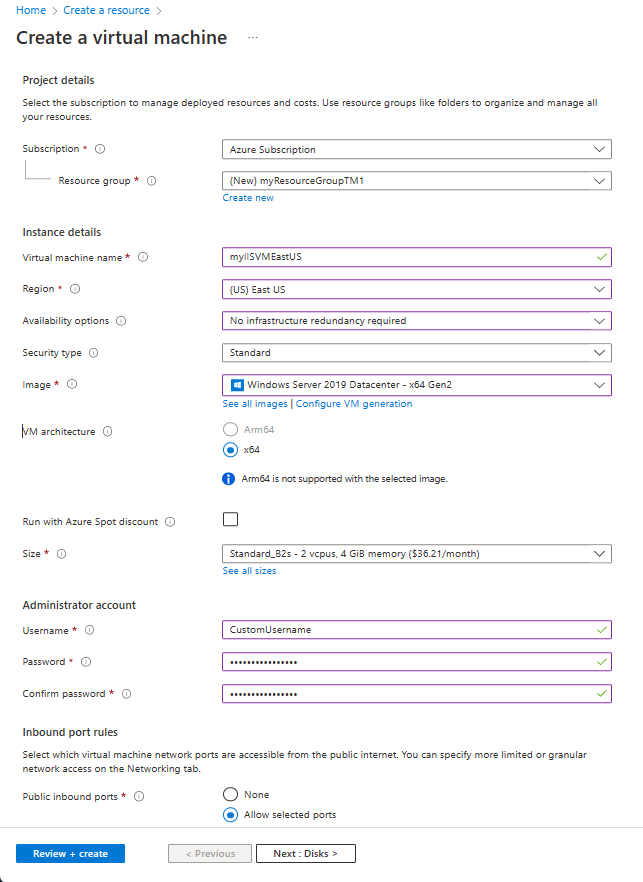
On the upper, left corner of the Azure portal, select Create a resource > Compute > Windows Server 2019 Datacenter.
In Create a virtual machine, type or select the following values in the Basics tab:
- Subscription > Resource Group: Select Create new and then type myResourceGroupTM1.
- Instance Details > Virtual machine name: Type myIISVMEastUS.
- Instance Details > Region: Select East US.
- Administrator Account > Username: Enter a user name of your choosing.
- Administrator Account > Password: Enter a password of your choosing. The password must be at least 12 characters long and meet the defined complexity requirements.
- Inbound Port Rules > Public inbound ports: Select Allow selected ports.
- Inbound Port Rules > Select inbound ports: Select RDP and HTTP in the pull down box.
Select the Management tab, or select Next: Disks, then Next: Networking, then Next: Management. Under Monitoring, set Boot diagnostics to Off.
Select Review + create.
Review the settings, and then click Create.
Follow the steps to create a second VM named myIISVMWestEurope, with a Resource group name of myResourceGroupTM2, a location of West Europe, and all the other settings the same as myIISVMEastUS.
The VMs take a few minutes to create. Do not continue with the remaining steps until both VMs are created.
Install IIS and customize the default webpage
In this section, you install the IIS server on the two VMs myIISVMEastUS and myIISVMWestEurope, and then update the default webpage. The customized webpage shows the name of the VM that you're connecting to when you visit the website from a web browser.
Select All resources on the left menu. From the resource list, select myIISVMEastUS in the myResourceGroupTM1 resource group.
On the Overview page, select Connect. In Connect to virtual machine, select Download RDP file.
Open the downloaded .rdp file. If you're prompted, select Connect. Enter the user name and password that you specified when you created the VM. You might need to select More choices > Use a different account, to specify the credentials that you entered when you created the VM.
Select OK.
You might receive a certificate warning during the sign-in process. If you receive the warning, select Yes or Continue to proceed with the connection.
On the server desktop, browse to Windows Administrative Tools > Server Manager.
Open Windows PowerShell on VM1. Use the following commands to install the IIS server and update the default .htm file.
# Install IIS Install-WindowsFeature -name Web-Server -IncludeManagementTools # Remove default .htm file remove-item C:\inetpub\wwwroot\iisstart.htm #Add custom .htm file Add-Content -Path "C:\inetpub\wwwroot\iisstart.htm" -Value $("Hello World from " + $env:computername)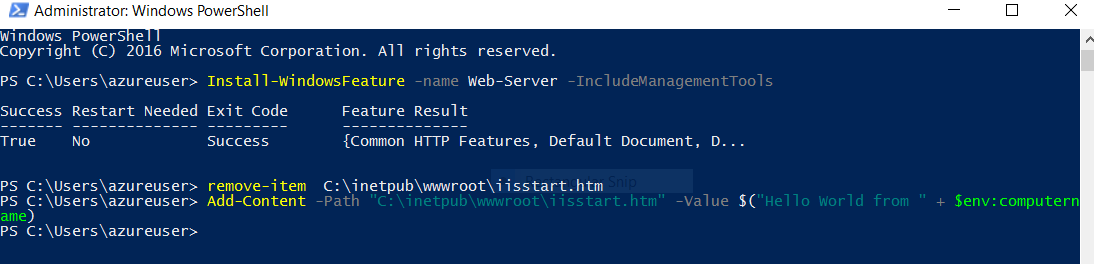
Close the RDP connection with myIISVMEastUS.
Repeat steps 1-8. Create an RDP connection with the VM myIISVMWestEurope within the myResourceGroupTM2 resource group, to install IIS and customize its default webpage.
Configure DNS names for the VMs running IIS
Traffic Manager routes user traffic based on the DNS name of the service endpoints. In this section, you configure the DNS names for the IIS servers myIISVMEastUS and myIISVMWestEurope.
- Select All resources on the left menu. From the resource list, select myIISVMEastUS in the myResourceGroupTM1 resource group.
- On the Overview page, under DNS name, select Configure.
- On the Configuration page, under the DNS name label, add a unique name. Then select Save.
- Repeat steps 1-3 for the VM named myIISVMWestEurope in the myResourceGroupTM2 resource group.
Create a test VM
In this section, you create a VM (myVMEastUS and myVMWestEurope) in each Azure region (East US and West Europe). You will use these VMs to test how Traffic Manager routes traffic to the website endpoint that has the higher weight value.
On the upper, left corner of the Azure portal, select Create a resource > Compute > Windows Server 2019 Datacenter.
In Create a virtual machine, type or select the following values in the Basics tab:
- Subscription > Resource Group: Select myResourceGroupTM1.
- Instance Details > Virtual machine name: Type myVMEastUS.
- Instance Details > Region: Select East US.
- Administrator Account > Username: Enter a user name of your choosing.
- Administrator Account > Password: Enter a password of your choosing. The password must be at least 12 characters long and meet the defined complexity requirements.
- Inbound Port Rules > Public inbound ports: Select Allow selected ports.
- Inbound Port Rules > Select inbound ports: Select RDP in the pull down box.
Select the Management tab, or select Next: Disks, then Next: Networking, then Next: Management. Under Monitoring, set Boot diagnostics to Off.
Select Review + create.
Review the settings, and then click Create.
Follow the steps to create a second VM named myVMWestEurope, with a Resource group name of myResourceGroupTM2, a location of West Europe, and all the other settings the same as myVMEastUS.
The VMs take a few minutes to create. Do not continue with the remaining steps until both VMs are created.
Create a Traffic Manager profile
Create a Traffic Manager profile based on the Weighted routing method.
On the upper-left side of the screen, select Create a resource > Networking > Traffic Manager profile > Create.
In Create Traffic Manager profile, enter or select the following information. Accept the defaults for the other settings, and then select Create.
Setting Value Name Enter a unique name within the trafficmanager.net zone. It results in the DNS name trafficmanager.net, which is used to access your Traffic Manager profile. Routing method Select the Weighted routing method. Subscription Select your subscription. Resource group Select Use existing and then select myResourceGroupTM1. 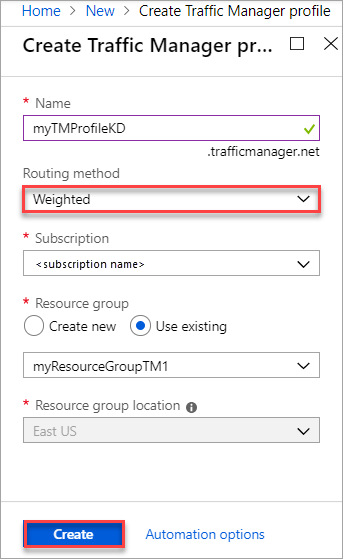
Add Traffic Manager endpoints
Add the two VMs running the IIS servers myIISVMEastUS and myIISVMWestEurope, to route user traffic to them.
In the portal’s search bar, search for the Traffic Manager profile name that you created in the preceding section. Select the profile in the results that are displayed.
In Traffic Manager profile, in the Settings section, select Endpoints > Add.
Enter or select the following information. Accept the defaults for the other settings, and then select OK.
Setting Value Type Enter the Azure endpoint. Name Enter myEastUSEndpoint. Target resource type Select Public IP address. Target resource Choose a public IP address to show the listing of resources with public IP addresses under the same subscription. In Resource, select the public IP address named myIISVMEastUS-ip. This is the public IP address of the IIS server VM in East US. Weight Enter 100. Repeat steps 2 and 3 to add another endpoint named myWestEuropeEndpoint for the public IP address myIISVMWestEurope-ip. This address is associated with the IIS server VM named myIISVMWestEurope. For Weight, enter 25.
When the addition of both endpoints is complete, they're displayed in the Traffic Manager profile along with their monitoring status as Online.
Test the Traffic Manager profile
To view Traffic Manager in action, complete the following steps:
- Determine the DNS name of your Traffic Manager profile.
- View Traffic Manager in action.
Determine DNS name of Traffic Manager profile
In this tutorial, for simplicity, you use the DNS name of the Traffic Manager profile to visit the websites.
You can determine the DNS name of the Traffic Manager profile as follows:
In the portal’s search bar, search for the Traffic Manager profile name that you created in the preceding section. In the results that are displayed, select the Traffic Manager profile.
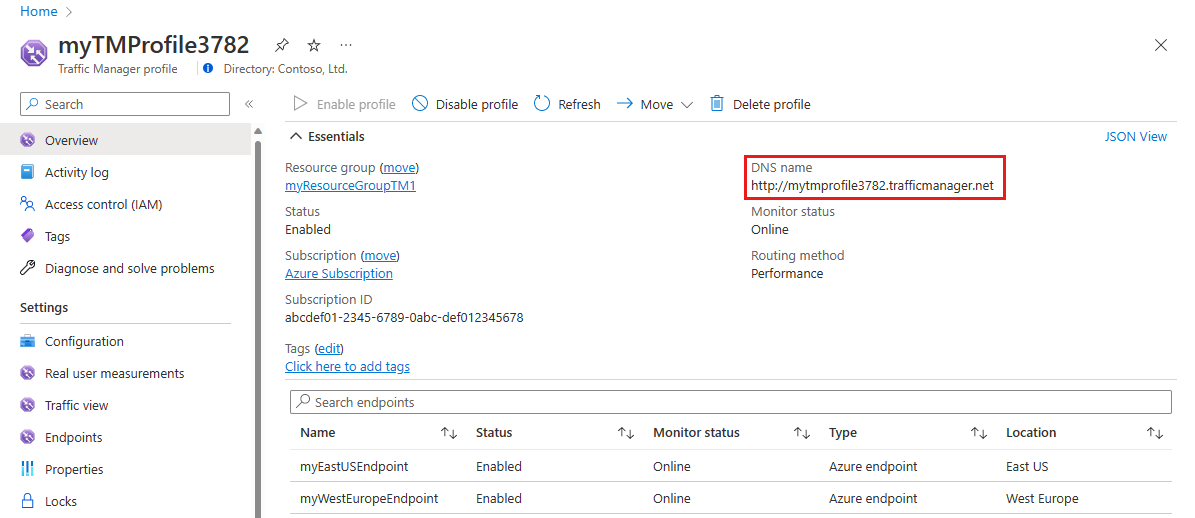
Select Overview.
The Traffic Manager profile displays its DNS name. In production deployments, you configure a vanity domain name to point to the Traffic Manager domain name, by using a DNS CNAME record.
View Traffic Manager in action
In this section, you can see Traffic Manager in action.
Select All resources on the left menu. From the resource list, select myVMEastUS in the myResourceGroupTM1 resource group.
On the Overview page, select Connect. In Connect to virtual machine, select Download RDP file.
Open the downloaded .rdp file. If you're prompted, select Connect. Enter the user name and password that you specified when creating the VM. You might need to select More choices > Use a different account, to specify the credentials that you entered when you created the VM.
Select OK.
You might receive a certificate warning during the sign-in process. If you receive the warning, select Yes or Continue to proceed with the connection.
In a web browser on the VM myVMEastUS, enter the DNS name of your Traffic Manager profile to view your website. You're routed to website hosted on the IIS server myIISVMEastUS because it's assigned a higher weight of 100. The IIS server myIISVMWestEurope is assigned a lower endpoint weight value of 25.
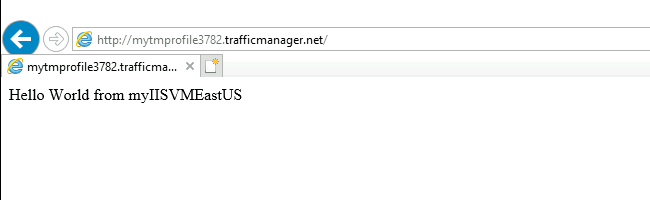
Repeat steps 1-6 on the VM myVMWestEurope to see the weighted website response.
Clean up resources
When you no longer need the resource groups that you created in this tutorial, you can delete them. To do so, select the resource group (ResourceGroupTM1 or ResourceGroupTM2), and then select Delete.
Next steps
To learn more about routing methods, see:
Feedback
Coming soon: Throughout 2024 we will be phasing out GitHub Issues as the feedback mechanism for content and replacing it with a new feedback system. For more information see: https://aka.ms/ContentUserFeedback.
Submit and view feedback for