High availability of SAP HANA scale-out system on Red Hat Enterprise Linux
This article describes how to deploy a highly available SAP HANA system in a scale-out configuration. Specifically, the configuration uses HANA system replication (HSR) and Pacemaker on Azure Red Hat Enterprise Linux virtual machines (VMs). The shared file systems in the presented architecture are NFS mounted and are provided by Azure NetApp Files or NFS share on Azure Files.
In the example configurations and installation commands, the HANA instance is 03 and the HANA system ID is HN1.
Prerequisites
Some readers will benefit from consulting a variety of SAP notes and resources before proceeding further with the topics in this article:
- SAP note 1928533 includes:
- A list of Azure VM sizes that are supported for the deployment of SAP software.
- Important capacity information for Azure VM sizes.
- Supported SAP software, and operating system and database combinations.
- The required SAP kernel version for Windows and Linux on Microsoft Azure.
- SAP note 2015553: Lists prerequisites for SAP-supported SAP software deployments in Azure.
- SAP note [2002167]: Has recommended operating system settings for RHEL.
- SAP note 2009879: Has SAP HANA guidelines for RHEL.
- SAP Note 3108302 has SAP HANA Guidelines for Red Hat Enterprise Linux 9.x.
- SAP note 2178632: Contains detailed information about all monitoring metrics reported for SAP in Azure.
- SAP note 2191498: Contains the required SAP host agent version for Linux in Azure.
- SAP note 2243692: Contains information about SAP licensing on Linux in Azure.
- SAP note 1999351: Contains additional troubleshooting information for the Azure enhanced monitoring extension for SAP.
- SAP note 1900823: Contains information about SAP HANA storage requirements.
- SAP community wiki: Contains all required SAP notes for Linux.
- Azure Virtual Machines planning and implementation for SAP on Linux.
- Azure Virtual Machines deployment for SAP on Linux.
- Azure Virtual Machines DBMS deployment for SAP on Linux.
- SAP HANA network requirements.
- General RHEL documentation:
- High availability add-on overview.
- High availability add-on administration.
- High availability add-on reference.
- Red Hat Enterprise Linux networking guide.
- How do I configure SAP HANA scale-out system replication in a Pacemaker cluster with HANA file systems on NFS shares.
- Active/Active (read-enabled): RHEL HA solution for SAP HANA scale out and system replication.
- Azure-specific RHEL documentation:
- Azure NetApp Files documentation.
- NFS v4.1 volumes on Azure NetApp Files for SAP HANA.
- Azure Files documentation
Overview
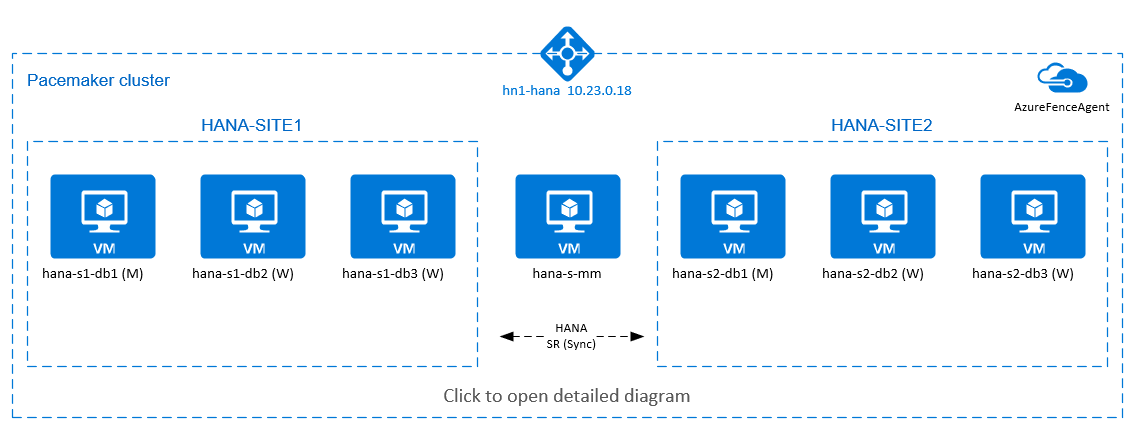
To achieve HANA high availability for HANA scale-out installations, you can configure HANA system replication, and protect the solution with a Pacemaker cluster to allow automatic failover. When an active node fails, the cluster fails over the HANA resources to the other site.
In the following diagram, there are three HANA nodes on each site, and a majority maker node to prevent a "split-brain" scenario. The instructions can be adapted to include more VMs as HANA DB nodes.
The HANA shared file system /hana/shared in the presented architecture can be provided by Azure NetApp Files or NFS share on Azure Files. The HANA shared file system is NFS mounted on each HANA node in the same HANA system replication site. File systems /hana/data and /hana/log are local file systems and aren't shared between the HANA DB nodes. SAP HANA will be installed in non-shared mode.
For recommended SAP HANA storage configurations, see SAP HANA Azure VMs storage configurations.
Important
If deploying all HANA file systems on Azure NetApp Files, for production systems, where performance is a key, we recommend to evaluate and consider using Azure NetApp Files application volume group for SAP HANA.
The preceding diagram shows three subnets represented within one Azure virtual network, following the SAP HANA network recommendations:
- For client communication:
client10.23.0.0/24 - For internal HANA internode communication:
inter10.23.1.128/26 - For HANA system replication:
hsr10.23.1.192/26
Because /hana/data and /hana/log are deployed on local disks, it isn't necessary to deploy separate subnet and separate virtual network cards for communication to the storage.
If you're using Azure NetApp Files, the NFS volumes for /hana/shared, are deployed in a separate subnet, delegated to Azure NetApp Files: anf 10.23.1.0/26.
Set up the infrastructure
In the instructions that follow, we assume that you've already created the resource group, the Azure virtual network with three Azure network subnets: client, inter and hsr.
Deploy Linux virtual machines via the Azure portal
Deploy the Azure VMs. For this configuration, deploy seven virtual machines:
- Three virtual machines to serve as HANA DB nodes for HANA replication site 1: hana-s1-db1, hana-s1-db2 and hana-s1-db3.
- Three virtual machines to serve as HANA DB nodes for HANA replication site 2: hana-s2-db1, hana-s2-db2 and hana-s2-db3.
- A small virtual machine to serve as majority maker: hana-s-mm.
The VMs deployed as SAP DB HANA nodes should be certified by SAP for HANA, as published in the SAP HANA hardware directory. When you're deploying the HANA DB nodes, make sure to select accelerated network.
For the majority maker node, you can deploy a small VM, because this VM doesn't run any of the SAP HANA resources. The majority maker VM is used in the cluster configuration to achieve and odd number of cluster nodes in a split-brain scenario. The majority maker VM only needs one virtual network interface in the
clientsubnet in this example.Deploy local managed disks for
/hana/dataand/hana/log. The minimum recommended storage configuration for/hana/dataand/hana/logis described in SAP HANA Azure VMs storage configurations.Deploy the primary network interface for each VM in the
clientvirtual network subnet. When the VM is deployed via Azure portal, the network interface name is automatically generated. In this article, we'll refer to the automatically generated, primary network interfaces as hana-s1-db1-client, hana-s1-db2-client, hana-s1-db3-client, and so on. These network interfaces are attached to theclientAzure virtual network subnet.Important
Make sure that the operating system you select is SAP-certified for SAP HANA on the specific VM types that you're using. For a list of SAP HANA certified VM types and operating system releases for those types, see SAP HANA certified IaaS platforms. Drill into the details of the listed VM type to get the complete list of SAP HANA-supported operating system releases for that type.
Create six network interfaces, one for each HANA DB virtual machine, in the
intervirtual network subnet (in this example, hana-s1-db1-inter, hana-s1-db2-inter, hana-s1-db3-inter, hana-s2-db1-inter, hana-s2-db2-inter, and hana-s2-db3-inter).Create six network interfaces, one for each HANA DB virtual machine, in the
hsrvirtual network subnet (in this example, hana-s1-db1-hsr, hana-s1-db2-hsr, hana-s1-db3-hsr, hana-s2-db1-hsr, hana-s2-db2-hsr, and hana-s2-db3-hsr).Attach the newly created virtual network interfaces to the corresponding virtual machines:
- Go to the virtual machine in the Azure portal.
- On the left pane, select Virtual Machines. Filter on the virtual machine name (for example, hana-s1-db1), and then select the virtual machine.
- On the Overview pane, select Stop to deallocate the virtual machine.
- Select Networking, and then attach the network interface. In the Attach network interface dropdown list, select the already created network interfaces for the
interandhsrsubnets. - Select Save.
- Repeat steps b through e for the remaining virtual machines (in our example, hana-s1-db2, hana-s1-db3, hana-s2-db1, hana-s2-db2 and hana-s2-db3)
- Leave the virtual machines in the stopped state for now.
Enable accelerated networking for the additional network interfaces for the
interandhsrsubnets by doing the following:Open Azure Cloud Shell in the Azure portal.
Run the following commands to enable accelerated networking for the additional network interfaces, which are attached to the
interandhsrsubnets.az network nic update --id /subscriptions/your subscription/resourceGroups/your resource group/providers/Microsoft.Network/networkInterfaces/hana-s1-db1-inter --accelerated-networking true az network nic update --id /subscriptions/your subscription/resourceGroups/your resource group/providers/Microsoft.Network/networkInterfaces/hana-s1-db2-inter --accelerated-networking true az network nic update --id /subscriptions/your subscription/resourceGroups/your resource group/providers/Microsoft.Network/networkInterfaces/hana-s1-db3-inter --accelerated-networking true az network nic update --id /subscriptions/your subscription/resourceGroups/your resource group/providers/Microsoft.Network/networkInterfaces/hana-s2-db1-inter --accelerated-networking true az network nic update --id /subscriptions/your subscription/resourceGroups/your resource group/providers/Microsoft.Network/networkInterfaces/hana-s2-db2-inter --accelerated-networking true az network nic update --id /subscriptions/your subscription/resourceGroups/your resource group/providers/Microsoft.Network/networkInterfaces/hana-s2-db3-inter --accelerated-networking true az network nic update --id /subscriptions/your subscription/resourceGroups/your resource group/providers/Microsoft.Network/networkInterfaces/hana-s1-db1-hsr --accelerated-networking true az network nic update --id /subscriptions/your subscription/resourceGroups/your resource group/providers/Microsoft.Network/networkInterfaces/hana-s1-db2-hsr --accelerated-networking true az network nic update --id /subscriptions/your subscription/resourceGroups/your resource group/providers/Microsoft.Network/networkInterfaces/hana-s1-db3-hsr --accelerated-networking true az network nic update --id /subscriptions/your subscription/resourceGroups/your resource group/providers/Microsoft.Network/networkInterfaces/hana-s2-db1-hsr --accelerated-networking true az network nic update --id /subscriptions/your subscription/resourceGroups/your resource group/providers/Microsoft.Network/networkInterfaces/hana-s2-db2-hsr --accelerated-networking true az network nic update --id /subscriptions/your subscription/resourceGroups/your resource group/providers/Microsoft.Network/networkInterfaces/hana-s2-db3-hsr --accelerated-networking true
Start the HANA DB virtual machines.
Configure Azure load balancer
During VM configuration, you have an option to create or select exiting load balancer in networking section. Follow below steps, to setup standard load balancer for high availability setup of HANA database.
Note
- For HANA scale out, select the NIC for the
clientsubnet when adding the virtual machines in the backend pool. - The full set of command in Azure CLI and PowerShell adds the VMs with primary NIC in the backend pool.
Follow the steps in Create load balancer to set up a standard load balancer for a high-availability SAP system by using the Azure portal. During the setup of the load balancer, consider the following points:
- Frontend IP Configuration: Create a front-end IP. Select the same virtual network and subnet name as your database virtual machines.
- Backend Pool: Create a back-end pool and add database VMs.
- Inbound rules: Create a load-balancing rule. Follow the same steps for both load-balancing rules.
- Frontend IP address: Select a front-end IP.
- Backend pool: Select a back-end pool.
- High-availability ports: Select this option.
- Protocol: Select TCP.
- Health Probe: Create a health probe with the following details:
- Protocol: Select TCP.
- Port: For example, 625<instance-no.>.
- Interval: Enter 5.
- Probe Threshold: Enter 2.
- Idle timeout (minutes): Enter 30.
- Enable Floating IP: Select this option.
Note
The health probe configuration property numberOfProbes, otherwise known as Unhealthy threshold in the portal, isn't respected. To control the number of successful or failed consecutive probes, set the property probeThreshold to 2. It's currently not possible to set this property by using the Azure portal, so use either the Azure CLI or the PowerShell command.
Important
Floating IP isn't supported on a NIC secondary IP configuration in load-balancing scenarios. For details, see Azure Load Balancer limitations. If you need an additional IP address for the VM, deploy a second NIC.
Note
When you're using the standard load balancer, you should be aware of the following limitation. When you place VMs without public IP addresses in the back-end pool of an internal load balancer, there's no outbound internet connectivity. To allow routing to public end points, you need to perform additional configuration. For more information, see Public endpoint connectivity for Virtual Machines using Azure Standard Load Balancer in SAP high-availability scenarios.
Important
Don't enable TCP timestamps on Azure VMs placed behind Azure Load Balancer. Enabling TCP timestamps causes the health probes to fail. Set the parameter net.ipv4.tcp_timestamps to 0. For details, see Load Balancer health probes and SAP note 2382421.
Deploy NFS
There are two options for deploying Azure native NFS for /hana/shared. You can deploy NFS volume on Azure NetApp Files or NFS share on Azure Files. Azure files support NFSv4.1 protocol, NFS on Azure NetApp files supports both NFSv4.1 and NFSv3.
The next sections describe the steps to deploy NFS - you'll need to select only one of the options.
Tip
You chose to deploy /hana/shared on NFS share on Azure Files or NFS volume on Azure NetApp Files.
Deploy the Azure NetApp Files infrastructure
Deploy the Azure NetApp Files volumes for the /hana/shared file system. You need a separate /hana/shared volume for each HANA system replication site. For more information, see Set up the Azure NetApp Files infrastructure.
In this example, you use the following Azure NetApp Files volumes:
- volume HN1-shared-s1 (nfs://10.23.1.7/HN1-shared-s1)
- volume HN1-shared-s2 (nfs://10.23.1.7/HN1-shared-s2)
Deploy the NFS on Azure Files infrastructure
Deploy Azure Files NFS shares for the /hana/shared file system. You'll need a separate /hana/shared Azure Files NFS share for each HANA system replication site. For more information, see How to create an NFS share.
In this example, the following Azure Files NFS shares were used:
- share hn1-shared-s1 (sapnfsafs.file.core.windows.net:/sapnfsafs/hn1-shared-s1)
- share hn1-shared-s2 (sapnfsafs.file.core.windows.net:/sapnfsafs/hn1-shared-s2)
Operating system configuration and preparation
The instructions in the next sections are prefixed with one of the following abbreviations:
- [A]: Applicable to all nodes
- [AH]: Applicable to all HANA DB nodes
- [M]: Applicable to the majority maker node
- [AH1]: Applicable to all HANA DB nodes on SITE 1
- [AH2]: Applicable to all HANA DB nodes on SITE 2
- [1]: Applicable only to HANA DB node 1, SITE 1
- [2]: Applicable only to HANA DB node 1, SITE 2
Configure and prepare your operating system by doing the following:
[A] Maintain the host files on the virtual machines. Include entries for all subnets. The following entries are added to
/etc/hostsfor this example.# Client subnet 10.23.0.11 hana-s1-db1 10.23.0.12 hana-s1-db1 10.23.0.13 hana-s1-db2 10.23.0.14 hana-s2-db1 10.23.0.15 hana-s2-db2 10.23.0.16 hana-s2-db3 10.23.0.17 hana-s-mm # Internode subnet 10.23.1.138 hana-s1-db1-inter 10.23.1.139 hana-s1-db2-inter 10.23.1.140 hana-s1-db3-inter 10.23.1.141 hana-s2-db1-inter 10.23.1.142 hana-s2-db2-inter 10.23.1.143 hana-s2-db3-inter # HSR subnet 10.23.1.202 hana-s1-db1-hsr 10.23.1.203 hana-s1-db2-hsr 10.23.1.204 hana-s1-db3-hsr 10.23.1.205 hana-s2-db1-hsr 10.23.1.206 hana-s2-db2-hsr 10.23.1.207 hana-s2-db3-hsr[A] Create configuration file /etc/sysctl.d/ms-az.conf with Microsoft for Azure configuration settings.
vi /etc/sysctl.d/ms-az.conf # Add the following entries in the configuration file net.ipv6.conf.all.disable_ipv6 = 1 net.ipv4.tcp_max_syn_backlog = 16348 net.ipv4.conf.all.rp_filter = 0 sunrpc.tcp_slot_table_entries = 128 vm.swappiness=10Tip
Avoid setting
net.ipv4.ip_local_port_rangeandnet.ipv4.ip_local_reserved_portsexplicitly in thesysctlconfiguration files, to allow the SAP host agent to manage the port ranges. For more details, see SAP note 2382421.[A] Install the NFS client package.
yum install nfs-utils[AH] Red Hat for HANA configuration.
Configure RHEL, as described in the Red Hat customer portal and in the following SAP notes:
- 2292690 - SAP HANA DB: Recommended OS settings for RHEL 7
- 2777782 - SAP HANA DB: Recommended OS settings for RHEL 8
- 2455582 - Linux: Running SAP applications compiled with GCC 6.x
- 2593824 - Linux: Running SAP applications compiled with GCC 7.x
- 2886607 - Linux: Running SAP applications compiled with GCC 9.x
Prepare the file systems
The following sections provide steps for the preparation of your file systems. You chose to deploy /hana/shared' on NFS share on Azure Files or NFS volume on Azure NetApp Files.
Mount the shared file systems (Azure NetApp Files NFS)
In this example, the shared HANA file systems are deployed on Azure NetApp Files and mounted over NFSv4.1. Follow the steps in this section, only if you're using NFS on Azure NetApp Files.
[AH] Prepare the OS for running SAP HANA on NetApp Systems with NFS, as described in SAP note 3024346 - Linux Kernel Settings for NetApp NFS. Create configuration file /etc/sysctl.d/91-NetApp-HANA.conf for the NetApp configuration settings.
vi /etc/sysctl.d/91-NetApp-HANA.conf # Add the following entries in the configuration file net.core.rmem_max = 16777216 net.core.wmem_max = 16777216 net.ipv4.tcp_rmem = 4096 131072 16777216 net.ipv4.tcp_wmem = 4096 16384 16777216 net.core.netdev_max_backlog = 300000 net.ipv4.tcp_slow_start_after_idle=0 net.ipv4.tcp_no_metrics_save = 1 net.ipv4.tcp_moderate_rcvbuf = 1 net.ipv4.tcp_window_scaling = 1 net.ipv4.tcp_sack = 1[AH] Adjust the sunrpc settings, as recommended in SAP note 3024346 - Linux Kernel Settings for NetApp NFS.
vi /etc/modprobe.d/sunrpc.conf # Insert the following line options sunrpc tcp_max_slot_table_entries=128[AH] Create mount points for the HANA database volumes.
mkdir -p /hana/shared[AH] Verify the NFS domain setting. Make sure that the domain is configured as the default Azure NetApp Files domain:
defaultv4iddomain.com. Make sure the mapping is set tonobody.
(This step is only needed if you're using Azure NetAppFiles NFS v4.1.)Important
Make sure to set the NFS domain in
/etc/idmapd.confon the VM to match the default domain configuration on Azure NetApp Files:defaultv4iddomain.com. If there's a mismatch between the domain configuration on the NFS client and the NFS server, the permissions for files on Azure NetApp volumes that are mounted on the VMs will be displayed asnobody.sudo cat /etc/idmapd.conf # Example [General] Domain = defaultv4iddomain.com [Mapping] Nobody-User = nobody Nobody-Group = nobody[AH] Verify
nfs4_disable_idmapping. It should be set toY. To create the directory structure wherenfs4_disable_idmappingis located, run the mount command. You won't be able to manually create the directory under /sys/modules, because access is reserved for the kernel or drivers.
This step is only needed, if using Azure NetAppFiles NFSv4.1.# Check nfs4_disable_idmapping cat /sys/module/nfs/parameters/nfs4_disable_idmapping # If you need to set nfs4_disable_idmapping to Y mkdir /mnt/tmp mount 10.9.0.4:/HN1-shared /mnt/tmp umount /mnt/tmp echo "Y" > /sys/module/nfs/parameters/nfs4_disable_idmapping # Make the configuration permanent echo "options nfs nfs4_disable_idmapping=Y" >> /etc/modprobe.d/nfs.confFor more information on how to change the
nfs4_disable_idmappingparameter, see the Red Hat customer portal.[AH1] Mount the shared Azure NetApp Files volumes on the SITE1 HANA DB VMs.
sudo mount -o rw,nfsvers=4.1,hard,timeo=600,rsize=262144,wsize=262144,noatime,lock,_netdev,sec=sys 10.23.1.7:/HN1-shared-s1 /hana/shared[AH2] Mount the shared Azure NetApp Files volumes on the SITE2 HANA DB VMs.
sudo mount -o rw,nfsvers=4.1,hard,timeo=600,rsize=262144,wsize=262144,noatime,lock,_netdev,sec=sys 10.23.1.7:/HN1-shared-s2 /hana/shared[AH] Verify that the corresponding
/hana/shared/file systems are mounted on all HANA DB VMs, with NFS protocol version NFSv4.sudo nfsstat -m # Verify that flag vers is set to 4.1 # Example from SITE 1, hana-s1-db1 /hana/shared from 10.23.1.7:/HN1-shared-s1 Flags: rw,noatime,vers=4.1,rsize=262144,wsize=262144,namlen=255,hard,proto=tcp,timeo=600,retrans=2,sec=sys,clientaddr=10.23.0.11,local_lock=none,addr=10.23.1.7 # Example from SITE 2, hana-s2-db1 /hana/shared from 10.23.1.7:/HN1-shared-s2 Flags: rw,noatime,vers=4.1,rsize=262144,wsize=262144,namlen=255,hard,proto=tcp,timeo=600,retrans=2,sec=sys,clientaddr=10.23.0.14,local_lock=none,addr=10.23.1.7
Mount the shared file systems (Azure Files NFS)
In this example, the shared HANA file systems are deployed on NFS on Azure Files. Follow the steps in this section, only if you're using NFS on Azure Files.
[AH] Create mount points for the HANA database volumes.
mkdir -p /hana/shared[AH1] Mount the shared Azure NetApp Files volumes on the SITE1 HANA DB VMs.
sudo vi /etc/fstab # Add the following entry sapnfsafs.file.core.windows.net:/sapnfsafs/hn1-shared-s1 /hana/shared nfs nfsvers=4.1,sec=sys 0 0 # Mount all volumes sudo mount -a[AH2] Mount the shared Azure NetApp Files volumes on the SITE2 HANA DB VMs.
sudo vi /etc/fstab # Add the following entries sapnfsafs.file.core.windows.net:/sapnfsafs/hn1-shared-s2 /hana/shared nfs nfsvers=4.1,sec=sys 0 0 # Mount the volume sudo mount -a[AH] Verify that the corresponding
/hana/shared/file systems are mounted on all HANA DB VMs with NFS protocol version NFSv4.1.sudo nfsstat -m # Example from SITE 1, hana-s1-db1 sapnfsafs.file.core.windows.net:/sapnfsafs/hn1-shared-s1 Flags: rw,relatime,vers=4.1,rsize=1048576,wsize=1048576,namlen=255,hard,proto=tcp,timeo=600,retrans=2,sec=sys,clientaddr=10.23.0.19,local_lock=none,addr=10.23.0.35 # Example from SITE 2, hana-s2-db1 sapnfsafs.file.core.windows.net:/sapnfsafs/hn1-shared-s2 Flags: rw,relatime,vers=4.1,rsize=1048576,wsize=1048576,namlen=255,hard,proto=tcp,timeo=600,retrans=2,sec=sys,clientaddr=10.23.0.22,local_lock=none,addr=10.23.0.35
Prepare the data and log local file systems
In the presented configuration, you deploy file systems /hana/data and /hana/log on a managed disk, and you attach these file systems locally to each HANA DB VM. Run the following steps to create the local data and log volumes on each HANA DB virtual machine.
Set up the disk layout with Logical Volume Manager (LVM). The following example assumes that each HANA virtual machine has three data disks attached, and that these disks are used to create two volumes.
[AH] List all of the available disks:
ls /dev/disk/azure/scsi1/lun*Example output:
/dev/disk/azure/scsi1/lun0 /dev/disk/azure/scsi1/lun1 /dev/disk/azure/scsi1/lun2[AH] Create physical volumes for all of the disks that you want to use:
sudo pvcreate /dev/disk/azure/scsi1/lun0 sudo pvcreate /dev/disk/azure/scsi1/lun1 sudo pvcreate /dev/disk/azure/scsi1/lun2[AH] Create a volume group for the data files. Use one volume group for the log files and one for the shared directory of SAP HANA:
sudo vgcreate vg_hana_data_HN1 /dev/disk/azure/scsi1/lun0 /dev/disk/azure/scsi1/lun1 sudo vgcreate vg_hana_log_HN1 /dev/disk/azure/scsi1/lun2[AH] Create the logical volumes. A linear volume is created when you use
lvcreatewithout the-iswitch. We suggest that you create a striped volume for better I/O performance. Align the stripe sizes to the values documented in SAP HANA VM storage configurations. The-iargument should be the number of the underlying physical volumes and the-Iargument is the stripe size. In this article, two physical volumes are used for the data volume, so the-iswitch argument is set to2. The stripe size for the data volume is256 KiB. One physical volume is used for the log volume, so you don't need to use explicit-ior-Iswitches for the log volume commands.Important
Use the
-iswitch, and set it to the number of the underlying physical volume, when you use more than one physical volume for each data or log volume. Use the-Iswitch to specify the stripe size when you're creating a striped volume. See SAP HANA VM storage configurations for recommended storage configurations, including stripe sizes and number of disks.sudo lvcreate -i 2 -I 256 -l 100%FREE -n hana_data vg_hana_data_HN1 sudo lvcreate -l 100%FREE -n hana_log vg_hana_log_HN1 sudo mkfs.xfs /dev/vg_hana_data_HN1/hana_data sudo mkfs.xfs /dev/vg_hana_log_HN1/hana_log[AH] Create the mount directories and copy the UUID of all of the logical volumes:
sudo mkdir -p /hana/data/HN1 sudo mkdir -p /hana/log/HN1 # Write down the ID of /dev/vg_hana_data_HN1/hana_data and /dev/vg_hana_log_HN1/hana_log sudo blkid[AH] Create
fstabentries for the logical volumes and mount:sudo vi /etc/fstabInsert the following line in the
/etc/fstabfile:/dev/disk/by-uuid/UUID of /dev/mapper/vg_hana_data_HN1-hana_data /hana/data/HN1 xfs defaults,nofail 0 2 /dev/disk/by-uuid/UUID of /dev/mapper/vg_hana_log_HN1-hana_log /hana/log/HN1 xfs defaults,nofail 0 2Mount the new volumes:
sudo mount -a
Installation
In this example for deploying SAP HANA in a scale-out configuration with HSR on Azure VMs, you're using HANA 2.0 SP4.
Prepare for HANA installation
[AH] Before the HANA installation, set the root password. You can disable the root password after the installation has been completed. Run as
rootcommandpasswdto set the password.[1,2] Change the permissions on
/hana/shared.chmod 775 /hana/shared[1] Verify that you can sign in hana-s1-db2 and hana-s1-db3 via secure shell (SSH), without being prompted for a password. If that isn't the case, exchange
sshkeys, as documented in Using key-based authentication.ssh root@hana-s1-db2 ssh root@hana-s1-db3[2] Verify that you can sign in hana-s2-db2 and hana-s2-db3 via SSH, without being prompted for a password. If that isn't the case, exchange
sshkeys, as documented in Using key-based authentication.ssh root@hana-s2-db2 ssh root@hana-s2-db3[AH] Install additional packages, which are required for HANA 2.0 SP4. For more information, see SAP Note 2593824 for RHEL 7.
# If using RHEL 7 yum install libgcc_s1 libstdc++6 compat-sap-c++-7 libatomic1 # If using RHEL 8 yum install libatomic libtool-ltdl.x86_64[A] Disable the firewall temporarily, so that it doesn't interfere with the HANA installation. You can re-enable it after the HANA installation is done.
# Execute as root systemctl stop firewalld systemctl disable firewalld
HANA installation on the first node on each site
[1] Install SAP HANA by following the instructions in the SAP HANA 2.0 installation and update guide. The following instructions show the SAP HANA installation on the first node on SITE 1.
Start the
hdblcmprogram asrootfrom the HANA installation software directory. Use theinternal_networkparameter and pass the address space for subnet, which is used for the internal HANA internode communication../hdblcm --internal_network=10.23.1.128/26At the prompt, enter the following values:
- For Choose an action, enter 1 (for install).
- For Additional components for installation, enter 2, 3.
- For the installation path, press Enter (defaults to /hana/shared).
- For Local Host Name, press Enter to accept the default.
- For Do you want to add hosts to the system?, enter n.
- For SAP HANA System ID, enter HN1.
- For Instance number [00], enter 03.
- For Local Host Worker Group [default], press Enter to accept the default.
- For Select System Usage / Enter index [4], enter 4 (for custom).
- For Location of Data Volumes [/hana/data/HN1], press Enter to accept the default.
- For Location of Log Volumes [/hana/log/HN1], press Enter to accept the default.
- For Restrict maximum memory allocation? [n], enter n.
- For Certificate Host Name For Host hana-s1-db1 [hana-s1-db1], press Enter to accept the default.
- For SAP Host Agent User (sapadm) Password, enter the password.
- For Confirm SAP Host Agent User (sapadm) Password, enter the password.
- For System Administrator (hn1adm) Password, enter the password.
- For System Administrator Home Directory [/usr/sap/HN1/home], press Enter to accept the default.
- For System Administrator Login Shell [/bin/sh], press Enter to accept the default.
- For System Administrator User ID [1001], press Enter to accept the default.
- For Enter ID of User Group (sapsys) [79], press Enter to accept the default.
- For System Database User (system) Password, enter the system's password.
- For Confirm System Database User (system) Password, enter system's password.
- For Restart system after machine reboot? [n], enter n.
- For Do you want to continue (y/n), validate the summary and if everything looks good, enter y.
[2] Repeat the preceding step to install SAP HANA on the first node on SITE 2.
[1,2] Verify global.ini.
Display global.ini, and ensure that the configuration for the internal SAP HANA internode communication is in place. Verify the
communicationsection. It should have the address space for theintersubnet, andlisteninterfaceshould be set to.internal. Verify theinternal_hostname_resolutionsection. It should have the IP addresses for the HANA virtual machines that belong to theintersubnet.sudo cat /usr/sap/HN1/SYS/global/hdb/custom/config/global.ini # Example from SITE1 [communication] internal_network = 10.23.1.128/26 listeninterface = .internal [internal_hostname_resolution] 10.23.1.138 = hana-s1-db1 10.23.1.139 = hana-s1-db2 10.23.1.140 = hana-s1-db3[1,2] Prepare global.ini for installation in non-shared environment, as described in SAP note 2080991.
sudo vi /usr/sap/HN1/SYS/global/hdb/custom/config/global.ini [persistence] basepath_shared = no[1,2] Restart SAP HANA to activate the changes.
sudo -u hn1adm /usr/sap/hostctrl/exe/sapcontrol -nr 03 -function StopSystem sudo -u hn1adm /usr/sap/hostctrl/exe/sapcontrol -nr 03 -function StartSystem[1,2] Verify that the client interface uses the IP addresses from the
clientsubnet for communication.# Execute as hn1adm /usr/sap/HN1/HDB03/exe/hdbsql -u SYSTEM -p "password" -i 03 -d SYSTEMDB 'select * from SYS.M_HOST_INFORMATION'|grep net_publicname # Expected result - example from SITE 2 "hana-s2-db1","net_publicname","10.23.0.14"For information about how to verify the configuration, see SAP note 2183363 - Configuration of SAP HANA internal network.
[AH] Change permissions on the data and log directories to avoid a HANA installation error.
sudo chmod o+w -R /hana/data /hana/log[1] Install the secondary HANA nodes. The example instructions in this step are for SITE 1.
Start the resident
hdblcmprogram asroot.cd /hana/shared/HN1/hdblcm ./hdblcmAt the prompt, enter the following values:
- For Choose an action, enter 2 (for add hosts).
- For Enter comma separated host names to add, enter hana-s1-db2, hana-s1-db3.
- For Additional components for installation, enter 2, 3.
- For Enter Root User Name [root], press Enter to accept the default.
- For Select roles for host 'hana-s1-db2' [1], select 1 (for worker).
- For Enter Host Failover Group for host 'hana-s1-db2' [default], press Enter to accept the default.
- For Enter Storage Partition Number for host 'hana-s1-db2' [<<assign automatically>>], press Enter to accept the default.
- For Enter Worker Group for host 'hana-s1-db2' [default], press Enter to accept the default.
- For Select roles for host 'hana-s1-db3' [1], select 1 (for worker).
- For Enter Host Failover Group for host 'hana-s1-db3' [default], press Enter to accept the default.
- For Enter Storage Partition Number for host 'hana-s1-db3' [<<assign automatically>>], press Enter to accept the default.
- For Enter Worker Group for host 'hana-s1-db3' [default], press Enter to accept the default.
- For System Administrator (hn1adm) Password, enter the password.
- For Enter SAP Host Agent User (sapadm) Password, enter the password.
- For Confirm SAP Host Agent User (sapadm) Password, enter the password.
- For Certificate Host Name For Host hana-s1-db2 [hana-s1-db2], press Enter to accept the default.
- For Certificate Host Name For Host hana-s1-db3 [hana-s1-db3], press Enter to accept the default.
- For Do you want to continue (y/n), validate the summary and if everything looks good, enter y.
[2] Repeat the preceding step to install the secondary SAP HANA nodes on SITE 2.
Configure SAP HANA 2.0 system replication
The following steps get you set up for system replication:
[1] Configure system replication on SITE 1:
Back up the databases as hn1adm:
hdbsql -d SYSTEMDB -u SYSTEM -p "passwd" -i 03 "BACKUP DATA USING FILE ('initialbackupSYS')" hdbsql -d HN1 -u SYSTEM -p "passwd" -i 03 "BACKUP DATA USING FILE ('initialbackupHN1')"Copy the system PKI files to the secondary site:
scp /usr/sap/HN1/SYS/global/security/rsecssfs/data/SSFS_HN1.DAT hana-s2-db1:/usr/sap/HN1/SYS/global/security/rsecssfs/data/ scp /usr/sap/HN1/SYS/global/security/rsecssfs/key/SSFS_HN1.KEY hana-s2-db1:/usr/sap/HN1/SYS/global/security/rsecssfs/key/Create the primary site:
hdbnsutil -sr_enable --name=HANA_S1[2] Configure system replication on SITE 2:
Register the second site to start the system replication. Run the following command as <hanasid>adm:
sapcontrol -nr 03 -function StopWait 600 10 hdbnsutil -sr_register --remoteHost=hana-s1-db1 --remoteInstance=03 --replicationMode=sync --name=HANA_S2 sapcontrol -nr 03 -function StartSystem[1] Check the replication status and wait until all databases are in sync.
sudo su - hn1adm -c "python /usr/sap/HN1/HDB03/exe/python_support/systemReplicationStatus.py" # | Database | Host | Port | Service Name | Volume ID | Site ID | Site Name | Secondary | Secondary | Secondary | Secondary | Secondary | Replication | Replication | Replication | # | | | | | | | | Host | Port | Site ID | Site Name | Active Status | Mode | Status | Status Details | # | -------- | ------------- | ----- | ------------ | --------- | ------- | --------- | ------------- | --------- | --------- | --------- | ------------- | ----------- | ----------- | -------------- | # | HN1 | hana-s1-db3 | 30303 | indexserver | 5 | 1 | HANA_S1 | hana-s2-db3 | 30303 | 2 | HANA_S2 | YES | SYNC | ACTIVE | | # | SYSTEMDB | hana-s1-db1 | 30301 | nameserver | 1 | 1 | HANA_S1 | hana-s2-db1 | 30301 | 2 | HANA_S2 | YES | SYNC | ACTIVE | | # | HN1 | hana-s1-db1 | 30307 | xsengine | 2 | 1 | HANA_S1 | hana-s2-db1 | 30307 | 2 | HANA_S2 | YES | SYNC | ACTIVE | | # | HN1 | hana-s1-db1 | 30303 | indexserver | 3 | 1 | HANA_S1 | hana-s2-db1 | 30303 | 2 | HANA_S2 | YES | SYNC | ACTIVE | | # | HN1 | hana-s1-db2 | 30303 | indexserver | 4 | 1 | HANA_S1 | hana-s2-db2 | 30303 | 2 | HANA_S2 | YES | SYNC | ACTIVE | | # # status system replication site "2": ACTIVE # overall system replication status: ACTIVE # # Local System Replication State # # mode: PRIMARY # site id: 1 # site name: HANA_S1[1,2] Change the HANA configuration so that communication for HANA system replication is directed though the HANA system replication virtual network interfaces.
Stop HANA on both sites.
sudo -u hn1adm /usr/sap/hostctrl/exe/sapcontrol -nr 03 -function StopSystem HDBEdit global.ini to add the host mapping for HANA system replication. Use the IP addresses from the
hsrsubnet.sudo vi /usr/sap/HN1/SYS/global/hdb/custom/config/global.ini #Add the section [system_replication_hostname_resolution] 10.23.1.202 = hana-s1-db1 10.23.1.203 = hana-s1-db2 10.23.1.204 = hana-s1-db3 10.23.1.205 = hana-s2-db1 10.23.1.206 = hana-s2-db2 10.23.1.207 = hana-s2-db3Start HANA on both sites.
sudo -u hn1adm /usr/sap/hostctrl/exe/sapcontrol -nr 03 -function StartSystem HDB
For more information, see Host name resolution for system replication.
[AH] Re-enable the firewall and open the necessary ports.
Re-enable the firewall.
# Execute as root systemctl start firewalld systemctl enable firewalldOpen the necessary firewall ports. You will need to adjust the ports for your HANA instance number.
Important
Create firewall rules to allow HANA internode communication and client traffic. The required ports are listed on TCP/IP ports of all SAP products. The following commands are just an example. In this scenario, you use system number 03.
# Execute as root sudo firewall-cmd --zone=public --add-port={30301,30303,30306,30307,30313,30315,30317,30340,30341,30342,1128,1129,40302,40301,40307,40303,40340,50313,50314,30310,30302}/tcp --permanent sudo firewall-cmd --zone=public --add-port={30301,30303,30306,30307,30313,30315,30317,30340,30341,30342,1128,1129,40302,40301,40307,40303,40340,50313,50314,30310,30302}/tcp
Create a Pacemaker cluster
To create a basic Pacemaker cluster, follow the steps in Setting up Pacemaker on Red Hat Enterprise Linux in Azure. Include all virtual machines, including the majority maker in the cluster.
Important
Don't set quorum expected-votes to 2. This isn't a two-node cluster. Make sure that the cluster property concurrent-fencing is enabled, so that node fencing is deserialized.
Create file system resources
For the next part of this process, you need to create file system resources. Here's how:
[1,2] Stop SAP HANA on both replication sites. Run as <sid>adm.
sapcontrol -nr 03 -function StopSystem[AH] Unmount file system
/hana/shared, which was temporarily mounted for the installation on all HANA DB VMs. Before you can unmount it, you need to stop any processes and sessions that are using the file system.umount /hana/shared[1] Create the file system cluster resources for
/hana/sharedin the disabled state. You use--disabledbecause you have to define the location constraints before the mounts are enabled.
You chose to deploy /hana/shared' on NFS share on Azure Files or NFS volume on Azure NetApp Files.In this example, the '/hana/shared' file system is deployed on Azure NetApp Files and mounted over NFSv4.1. Follow the steps in this section, only if you're using NFS on Azure NetApp Files.
# /hana/shared file system for site 1 pcs resource create fs_hana_shared_s1 --disabled ocf:heartbeat:Filesystem device=10.23.1.7:/HN1-shared-s1 directory=/hana/shared \ fstype=nfs options='defaults,rw,hard,timeo=600,rsize=262144,wsize=262144,proto=tcp,noatime,sec=sys,nfsvers=4.1,lock,_netdev' op monitor interval=20s on-fail=fence timeout=120s OCF_CHECK_LEVEL=20 \ op start interval=0 timeout=120 op stop interval=0 timeout=120 # /hana/shared file system for site 2 pcs resource create fs_hana_shared_s2 --disabled ocf:heartbeat:Filesystem device=10.23.1.7:/HN1-shared-s1 directory=/hana/shared \ fstype=nfs options='defaults,rw,hard,timeo=600,rsize=262144,wsize=262144,proto=tcp,noatime,sec=sys,nfsvers=4.1,lock,_netdev' op monitor interval=20s on-fail=fence timeout=120s OCF_CHECK_LEVEL=20 \ op start interval=0 timeout=120 op stop interval=0 timeout=120 # clone the /hana/shared file system resources for both site1 and site2 pcs resource clone fs_hana_shared_s1 meta clone-node-max=1 interleave=true pcs resource clone fs_hana_shared_s2 meta clone-node-max=1 interleave=true
The suggested timeouts values allow the cluster resources to withstand protocol-specific pause, related to NFSv4.1 lease renewals on Azure NetApp Files. For more information see NFS in NetApp Best practice.
In this example, the '/hana/shared' file system is deployed on NFS on Azure Files. Follow the steps in this section, only if you're using NFS on Azure Files.
# /hana/shared file system for site 1 pcs resource create fs_hana_shared_s1 --disabled ocf:heartbeat:Filesystem device=sapnfsafs.file.core.windows.net:/sapnfsafs/hn1-shared-s1 directory=/hana/shared \ fstype=nfs options='defaults,rw,hard,proto=tcp,noatime,nfsvers=4.1,lock' op monitor interval=20s on-fail=fence timeout=120s OCF_CHECK_LEVEL=20 \ op start interval=0 timeout=120 op stop interval=0 timeout=120 # /hana/shared file system for site 2 pcs resource create fs_hana_shared_s2 --disabled ocf:heartbeat:Filesystem device=sapnfsafs.file.core.windows.net:/sapnfsafs/hn1-shared-s2 directory=/hana/shared \ fstype=nfs options='defaults,rw,hard,proto=tcp,noatime,nfsvers=4.1,lock' op monitor interval=20s on-fail=fence timeout=120s OCF_CHECK_LEVEL=20 \ op start interval=0 timeout=120 op stop interval=0 timeout=120 # clone the /hana/shared file system resources for both site1 and site2 pcs resource clone fs_hana_shared_s1 meta clone-node-max=1 interleave=true pcs resource clone fs_hana_shared_s2 meta clone-node-max=1 interleave=trueThe
OCF_CHECK_LEVEL=20attribute is added to the monitor operation, so that monitor operations perform a read/write test on the file system. Without this attribute, the monitor operation only verifies that the file system is mounted. This can be a problem because when connectivity is lost, the file system might remain mounted, despite being inaccessible.The
on-fail=fenceattribute is also added to the monitor operation. With this option, if the monitor operation fails on a node, that node is immediately fenced. Without this option, the default behavior is to stop all resources that depend on the failed resource, then restart the failed resource, and then start all the resources that depend on the failed resource. Not only can this behavior take a long time when an SAP HANA resource depends on the failed resource, but it also can fail altogether. The SAP HANA resource can't stop successfully, if the NFS share holding the HANA binaries is inaccessible.The timeouts in the above configurations may need to be adapted to the specific SAP setup.
[1] Configure and verify the node attributes. All SAP HANA DB nodes on replication site 1 are assigned attribute
S1, and all SAP HANA DB nodes on replication site 2 are assigned attributeS2.# HANA replication site 1 pcs node attribute hana-s1-db1 NFS_SID_SITE=S1 pcs node attribute hana-s1-db2 NFS_SID_SITE=S1 pcs node attribute hana-s1-db3 NFS_SID_SITE=S1 # HANA replication site 2 pcs node attribute hana-s2-db1 NFS_SID_SITE=S2 pcs node attribute hana-s2-db2 NFS_SID_SITE=S2 pcs node attribute hana-s2-db3 NFS_SID_SITE=S2 # To verify the attribute assignment to nodes execute pcs node attribute[1] Configure the constraints that determine where the NFS file systems will be mounted, and enable the file system resources.
# Configure the constraints pcs constraint location fs_hana_shared_s1-clone rule resource-discovery=never score=-INFINITY NFS_SID_SITE ne S1 pcs constraint location fs_hana_shared_s2-clone rule resource-discovery=never score=-INFINITY NFS_SID_SITE ne S2 # Enable the file system resources pcs resource enable fs_hana_shared_s1 pcs resource enable fs_hana_shared_s2When you enable the file system resources, the cluster will mount the
/hana/sharedfile systems.[AH] Verify that the Azure NetApp Files volumes are mounted under
/hana/shared, on all HANA DB VMs on both sites.Example, if using Azure NetApp Files:
sudo nfsstat -m # Verify that flag vers is set to 4.1 # Example from SITE 1, hana-s1-db1 /hana/shared from 10.23.1.7:/HN1-shared-s1 Flags: rw,noatime,vers=4.1,rsize=262144,wsize=262144,namlen=255,hard,proto=tcp,timeo=600,retrans=2,sec=sys,clientaddr=10.23.0.11,local_lock=none,addr=10.23.1.7 # Example from SITE 2, hana-s2-db1 /hana/shared from 10.23.1.7:/HN1-shared-s2 Flags: rw,noatime,vers=4.1,rsize=262144,wsize=262144,namlen=255,hard,proto=tcp,timeo=600,retrans=2,sec=sys,clientaddr=10.23.0.14,local_lock=none,addr=10.23.1.7Example, if using Azure Files NFS:
sudo nfsstat -m # Example from SITE 1, hana-s1-db1 sapnfsafs.file.core.windows.net:/sapnfsafs/hn1-shared-s1 Flags: rw,relatime,vers=4.1,rsize=1048576,wsize=1048576,namlen=255,hard,proto=tcp,timeo=600,retrans=2,sec=sys,clientaddr=10.23.0.19,local_lock=none,addr=10.23.0.35 # Example from SITE 2, hana-s2-db1 sapnfsafs.file.core.windows.net:/sapnfsafs/hn1-shared-s2 Flags: rw,relatime,vers=4.1,rsize=1048576,wsize=1048576,namlen=255,hard,proto=tcp,timeo=600,retrans=2,sec=sys,clientaddr=10.23.0.22,local_lock=none,addr=10.23.0.35
[1] Configure and clone the attribute resources, and configure the constraints, as follows:
# Configure the attribute resources pcs resource create hana_nfs_s1_active ocf:pacemaker:attribute active_value=true inactive_value=false name=hana_nfs_s1_active pcs resource create hana_nfs_s2_active ocf:pacemaker:attribute active_value=true inactive_value=false name=hana_nfs_s2_active # Clone the attribute resources pcs resource clone hana_nfs_s1_active meta clone-node-max=1 interleave=true pcs resource clone hana_nfs_s2_active meta clone-node-max=1 interleave=true # Configure the constraints, which will set the attribute values pcs constraint order fs_hana_shared_s1-clone then hana_nfs_s1_active-clone pcs constraint order fs_hana_shared_s2-clone then hana_nfs_s2_active-cloneTip
If your configuration includes file systems other than /
hana/shared, and these file systems are NFS mounted, then include thesequential=falseoption. This option ensures that there are no ordering dependencies among the file systems. All NFS mounted file systems must start before the corresponding attribute resource, but they don't need to start in any order relative to each other. For more information, see How do I configure SAP HANA scale-out HSR in a Pacemaker cluster when the HANA file systems are NFS shares.[1] Place Pacemaker in maintenance mode, in preparation for the creation of the HANA cluster resources.
pcs property set maintenance-mode=true
Create SAP HANA cluster resources
Now you're ready to create the cluster resources:
[A] Install the HANA scale-out resource agent on all cluster nodes, including the majority maker.
yum install -y resource-agents-sap-hana-scaleoutNote
For the minimum supported version of package
resource-agents-sap-hana-scaleoutfor your operating system release, see Support policies for RHEL HA clusters - Management of SAP HANA in a cluster .[1,2] Install the HANA system replication hook on one HANA DB node on each system replication site. SAP HANA should still be down.
Prepare the hook as
root.mkdir -p /hana/shared/myHooks cp /usr/share/SAPHanaSR-ScaleOut/SAPHanaSR.py /hana/shared/myHooks chown -R hn1adm:sapsys /hana/shared/myHooksAdjust
global.ini.# add to global.ini [ha_dr_provider_SAPHanaSR] provider = SAPHanaSR path = /hana/shared/myHooks execution_order = 1 [trace] ha_dr_saphanasr = info
[AH] The cluster requires sudoers configuration on the cluster node for <sid>adm. In this example, you achieve this by creating a new file. Run the commands as
root.sudo visudo -f /etc/sudoers.d/20-saphana # Insert the following lines and then save Cmnd_Alias SOK = /usr/sbin/crm_attribute -n hana_hn1_glob_srHook -v SOK -t crm_config -s SAPHanaSR Cmnd_Alias SFAIL = /usr/sbin/crm_attribute -n hana_hn1_glob_srHook -v SFAIL -t crm_config -s SAPHanaSR hn1adm ALL=(ALL) NOPASSWD: SOK, SFAIL Defaults!SOK, SFAIL !requiretty[1,2] Start SAP HANA on both replication sites. Run as <sid>adm.
sapcontrol -nr 03 -function StartSystem[1] Verify the hook installation. Run as <sid>adm on the active HANA system replication site.
cdtrace awk '/ha_dr_SAPHanaSR.*crm_attribute/ \ { printf "%s %s %s %s\n",$2,$3,$5,$16 }' nameserver_* # Example entries # 2020-07-21 22:04:32.364379 ha_dr_SAPHanaSR SFAIL # 2020-07-21 22:04:46.905661 ha_dr_SAPHanaSR SFAIL # 2020-07-21 22:04:52.092016 ha_dr_SAPHanaSR SFAIL # 2020-07-21 22:04:52.782774 ha_dr_SAPHanaSR SFAIL # 2020-07-21 22:04:53.117492 ha_dr_SAPHanaSR SFAIL # 2020-07-21 22:06:35.599324 ha_dr_SAPHanaSR SOK[1] Create the HANA cluster resources. Run the following commands as
root.Make sure the cluster is already in maintenance mode.
Next, create the HANA topology resource.
If you're building a RHEL 7.x cluster, use the following commands:pcs resource create SAPHanaTopology_HN1_HDB03 SAPHanaTopologyScaleOut \ SID=HN1 InstanceNumber=03 \ op start timeout=600 op stop timeout=300 op monitor interval=10 timeout=600 pcs resource clone SAPHanaTopology_HN1_HDB03 meta clone-node-max=1 interleave=trueIf you're building a RHEL >= 8.x cluster, use the following commands:
pcs resource create SAPHanaTopology_HN1_HDB03 SAPHanaTopology \ SID=HN1 InstanceNumber=03 meta clone-node-max=1 interleave=true \ op methods interval=0s timeout=5 \ op start timeout=600 op stop timeout=300 op monitor interval=10 timeout=600 pcs resource clone SAPHanaTopology_HN1_HDB03 meta clone-node-max=1 interleave=trueCreate the HANA instance resource.
Note
This article contains references to a term that Microsoft no longer uses. When the term is removed from the software, we’ll remove it from this article.
If you're building a RHEL 7.x cluster, use the following commands:
pcs resource create SAPHana_HN1_HDB03 SAPHanaController \ SID=HN1 InstanceNumber=03 PREFER_SITE_TAKEOVER=true DUPLICATE_PRIMARY_TIMEOUT=7200 AUTOMATED_REGISTER=false \ op start interval=0 timeout=3600 op stop interval=0 timeout=3600 op promote interval=0 timeout=3600 \ op monitor interval=60 role="Master" timeout=700 op monitor interval=61 role="Slave" timeout=700 pcs resource master msl_SAPHana_HN1_HDB03 SAPHana_HN1_HDB03 \ meta master-max="1" clone-node-max=1 interleave=trueIf you're building a RHEL >= 8.x cluster, use the following commands:
pcs resource create SAPHana_HN1_HDB03 SAPHanaController \ SID=HN1 InstanceNumber=03 PREFER_SITE_TAKEOVER=true DUPLICATE_PRIMARY_TIMEOUT=7200 AUTOMATED_REGISTER=false \ op demote interval=0s timeout=320 op methods interval=0s timeout=5 \ op start interval=0 timeout=3600 op stop interval=0 timeout=3600 op promote interval=0 timeout=3600 \ op monitor interval=60 role="Master" timeout=700 op monitor interval=61 role="Slave" timeout=700 pcs resource promotable SAPHana_HN1_HDB03 \ meta master-max="1" clone-node-max=1 interleave=trueImportant
It's a good idea to set
AUTOMATED_REGISTERtofalse, while you're performing failover tests, to prevent a failed primary instance to automatically register as secondary. After testing, as a best practice, setAUTOMATED_REGISTERtotrue, so that after takeover, system replication can resume automatically.Create the virtual IP and associated resources.
pcs resource create vip_HN1_03 ocf:heartbeat:IPaddr2 ip=10.23.0.18 op monitor interval="10s" timeout="20s" sudo pcs resource create nc_HN1_03 azure-lb port=62503 sudo pcs resource group add g_ip_HN1_03 nc_HN1_03 vip_HN1_03Create the cluster constraints.
If you're building a RHEL 7.x cluster, use the following commands:
#Start HANA topology, before the HANA instance pcs constraint order SAPHanaTopology_HN1_HDB03-clone then msl_SAPHana_HN1_HDB03 pcs constraint colocation add g_ip_HN1_03 with master msl_SAPHana_HN1_HDB03 4000 #HANA resources are only allowed to run on a node, if the node's NFS file systems are mounted. The constraint also avoids the majority maker node pcs constraint location SAPHanaTopology_HN1_HDB03-clone rule resource-discovery=never score=-INFINITY hana_nfs_s1_active ne true and hana_nfs_s2_active ne trueIf you're building a RHEL >= 8.x cluster, use the following commands:
#Start HANA topology, before the HANA instance pcs constraint order SAPHanaTopology_HN1_HDB03-clone then SAPHana_HN1_HDB03-clone pcs constraint colocation add g_ip_HN1_03 with master SAPHana_HN1_HDB03-clone 4000 #HANA resources are only allowed to run on a node, if the node's NFS file systems are mounted. The constraint also avoids the majority maker node pcs constraint location SAPHanaTopology_HN1_HDB03-clone rule resource-discovery=never score=-INFINITY hana_nfs_s1_active ne true and hana_nfs_s2_active ne true
[1] Place the cluster out of maintenance mode. Make sure that the cluster status is
ok, and that all of the resources are started.sudo pcs property set maintenance-mode=false #If there are failed cluster resources, you may need to run the next command pcs resource cleanupNote
The timeouts in the preceding configuration are just examples, and might need to be adapted to the specific HANA setup. For instance, you might need to increase the start timeout, if it takes longer to start the SAP HANA database.
Configure HANA active/read-enabled system replication
Starting with SAP HANA 2.0 SPS 01, SAP allows active/read-enabled setups for SAP HANA system replication. With this capability, you can use the secondary systems of SAP HANA system replication actively for read-intensive workloads. To support such a setup in a cluster, you need a second virtual IP address, which allows clients to access the secondary read-enabled SAP HANA database. To ensure that the secondary replication site can still be accessed after a takeover has occurred, the cluster needs to move the virtual IP address around with the secondary of the SAP HANA resource.
This section describes the additional steps you must take to manage this type of system replication in a Red Hat high availability cluster, with a second virtual IP address.
Before proceeding further, make sure you have fully configured a Red Hat high availability cluster, managing an SAP HANA database, as described earlier in this article.
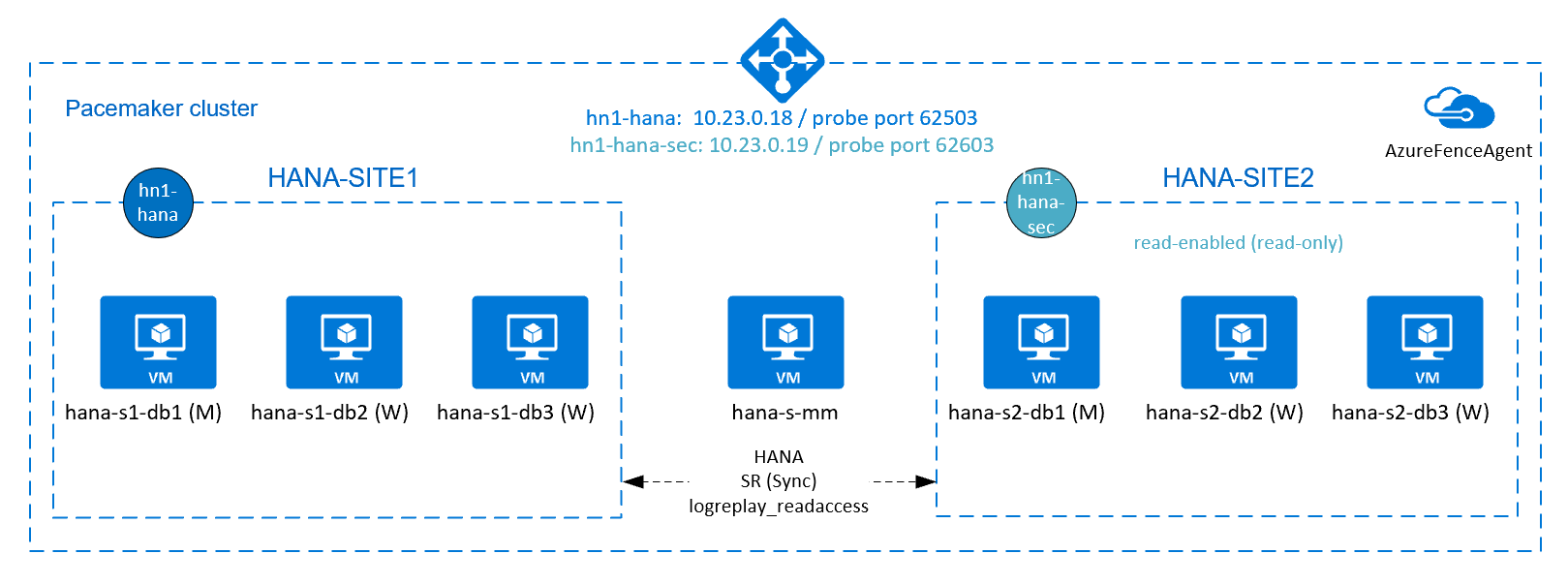
Additional setup in Azure Load Balancer for active/read-enabled setup
To proceed with provisioning your second virtual IP, make sure you have configured Azure Load Balancer as described in Configure Azure Load Balancer.
For the standard load balancer, follow these additional steps on the same load balancer that you created in the earlier section.
Create a second front-end IP pool:
- Open the load balancer, select frontend IP pool, and select Add.
- Enter the name of the second front-end IP pool (for example, hana-secondaryIP).
- Set the Assignment to Static, and enter the IP address (for example, 10.23.0.19).
- Select OK.
- After the new front-end IP pool is created, note the pool IP address.
Next, create a health probe:
- Open the load balancer, select health probes, and select Add.
- Enter the name of the new health probe (for example, hana-secondaryhp).
- Select TCP as the protocol and port 62603. Keep the Interval value set to 5, and the Unhealthy threshold value set to 2.
- Select OK.
Next, create the load-balancing rules:
- Open the load balancer, select load balancing rules, and select Add.
- Enter the name of the new load balancer rule (for example, hana-secondarylb).
- Select the front-end IP address, the back-end pool, and the health probe that you created earlier (for example, hana-secondaryIP, hana-backend, and hana-secondaryhp).
- Select HA Ports.
- Make sure to enable Floating IP.
- Select OK.
Configure HANA active/read-enabled system replication
The steps to configure HANA system replication are described in the Configure SAP HANA 2.0 system replication section. If you are deploying a read-enabled secondary scenario, while you're configuring system replication on the second node, run following command as hanasidadm:
sapcontrol -nr 03 -function StopWait 600 10
hdbnsutil -sr_register --remoteHost=hana-s1-db1 --remoteInstance=03 --replicationMode=sync --name=HANA_S2 --operationMode=logreplay_readaccess
Add a secondary virtual IP address resource for an active/read-enabled setup
You can configure the second virtual IP and the additional constraints with the following commands. If the secondary instance is down, the secondary virtual IP will be switched to the primary.
pcs property set maintenance-mode=true
pcs resource create secvip_HN1_03 ocf:heartbeat:IPaddr2 ip="10.23.0.19"
pcs resource create secnc_HN1_03 ocf:heartbeat:azure-lb port=62603
pcs resource group add g_secip_HN1_03 secnc_HN1_03 secvip_HN1_03
# RHEL 8.x:
pcs constraint location g_ip_HN1_03 rule score=500 role=master hana_hn1_roles eq "master1:master:worker:master" and hana_hn1_clone_state eq PROMOTED
pcs constraint location g_secip_HN1_03 rule score=50 hana_hn1_roles eq 'master1:master:worker:master'
pcs constraint order promote SAPHana_HN1_HDB03-clone then start g_ip_HN1_03
pcs constraint order start g_ip_HN1_03 then start g_secip_HN1_03
pcs constraint colocation add g_secip_HN1_03 with Slave SAPHana_HN1_HDB03-clone 5
# RHEL 7.x:
pcs constraint location g_ip_HN1_03 rule score=500 role=master hana_hn1_roles eq "master1:master:worker:master" and hana_hn1_clone_state eq PROMOTED
pcs constraint location g_secip_HN1_03 rule score=50 hana_hn1_roles eq 'master1:master:worker:master'
pcs constraint order promote msl_SAPHana_HN1_HDB03 then start g_ip_HN1_03
pcs constraint order start g_ip_HN1_03 then start g_secip_HN1_03
pcs constraint colocation add g_secip_HN1_03 with Slave msl_SAPHana_HN1_HDB03 5
pcs property set maintenance-mode=false
Make sure that the cluster status is ok, and that all of the resources are started. The second virtual IP will run on the secondary site along with SAP HANA secondary resource.
# Example output from crm_mon
#Online: [ hana-s-mm hana-s1-db1 hana-s1-db2 hana-s1-db3 hana-s2-db1 hana-s2-db2 hana-s2-db3 ]
#
#Active resources:
#
#rsc_st_azure (stonith:fence_azure_arm): Started hana-s-mm
#Clone Set: fs_hana_shared_s1-clone [fs_hana_shared_s1]
# Started: [ hana--s1-db1 hana-s1-db2 hana-s1-db3 ]
#Clone Set: fs_hana_shared_s2-clone [fs_hana_shared_s2]
# Started: [ hana-s2-db1 hana-s2-db2 hana-s2-db3 ]
#Clone Set: hana_nfs_s1_active-clone [hana_nfs_s1_active]
# Started: [ hana-s1-db1 hana-s1-db2 hana-s1-db3 ]
#Clone Set: hana_nfs_s2_active-clone [hana_nfs_s2_active]
# Started: [ hana-s2-db1 hana-s2-db2 hana-s2-db3 ]
#Clone Set: SAPHanaTopology_HN1_HDB03-clone [SAPHanaTopology_HN1_HDB03]
# Started: [ hana-s1-db1 hana-s1-db2 hana-s1-db3 hana-s2-db1 hana-s2-db2 hana-s2-db3 ]
#Master/Slave Set: msl_SAPHana_HN1_HDB03 [SAPHana_HN1_HDB03]
# Masters: [ hana-s1-db1 ]
# Slaves: [ hana-s1-db2 hana-s1-db3 hana-s2-db1 hana-s2-db2 hana-s2-db3 ]
#Resource Group: g_ip_HN1_03
# nc_HN1_03 (ocf::heartbeat:azure-lb): Started hana-s1-db1
# vip_HN1_03 (ocf::heartbeat:IPaddr2): Started hana-s1-db1
#Resource Group: g_secip_HN1_03
# secnc_HN1_03 (ocf::heartbeat:azure-lb): Started hana-s2-db1
# secvip_HN1_03 (ocf::heartbeat:IPaddr2): Started hana-s2-db1
In the next section, you can find the typical set of failover tests to run.
When you're testing a HANA cluster configured with a read-enabled secondary, be aware of the following behavior of the second virtual IP:
When cluster resource SAPHana_HN1_HDB03 moves to the secondary site (S2), the second virtual IP will move to the other site, hana-s1-db1. If you have configured
AUTOMATED_REGISTER="false", and HANA system replication isn't registered automatically, then the second virtual IP will run on hana-s2-db1.When you're testing server crash, the second virtual IP resources (secvip_HN1_03) and the Azure Load Balancer port resource (secnc_HN1_03) run on the primary server, alongside the primary virtual IP resources. While the secondary server is down, the applications that are connected to the read-enabled HANA database will connect to the primary HANA database. This behavior is expected. It allows applications that are connected to the read-enabled HANA database to operate while a secondary server is unavailable.
During failover and fallback, the existing connections for applications that are using the second virtual IP to connect to the HANA database might be interrupted.
Test SAP HANA failover
Before you start a test, check the cluster and SAP HANA system replication status.
Verify that there are no failed cluster actions.
#Verify that there are no failed cluster actions pcs status # Example #Stack: corosync #Current DC: hana-s-mm (version 1.1.19-8.el7_6.5-c3c624ea3d) - partition with quorum #Last updated: Thu Sep 24 06:00:20 2020 #Last change: Thu Sep 24 05:59:17 2020 by root via crm_attribute on hana-s1-db1 # #7 nodes configured #45 resources configured # #Online: [ hana-s-mm hana-s1-db1 hana-s1-db2 hana-s1-db3 hana-s2-db1 hana-s2-db2 hana-s2-db3 ] # #Active resources: # #rsc_st_azure (stonith:fence_azure_arm): Started hana-s-mm #Clone Set: fs_hana_shared_s1-clone [fs_hana_shared_s1] # Started: [ hana--s1-db1 hana-s1-db2 hana-s1-db3 ] #Clone Set: fs_hana_shared_s2-clone [fs_hana_shared_s2] # Started: [ hana-s2-db1 hana-s2-db2 hana-s2-db3 ] #Clone Set: hana_nfs_s1_active-clone [hana_nfs_s1_active] # Started: [ hana-s1-db1 hana-s1-db2 hana-s1-db3 ] #Clone Set: hana_nfs_s2_active-clone [hana_nfs_s2_active] # Started: [ hana-s2-db1 hana-s2-db2 hana-s2-db3 ] #Clone Set: SAPHanaTopology_HN1_HDB03-clone [SAPHanaTopology_HN1_HDB03] # Started: [ hana-s1-db1 hana-s1-db2 hana-s1-db3 hana-s2-db1 hana-s2-db2 hana-s2-db3 ] #Master/Slave Set: msl_SAPHana_HN1_HDB03 [SAPHana_HN1_HDB03] # Masters: [ hana-s1-db1 ] # Slaves: [ hana-s1-db2 hana-s1-db3 hana-s2-db1 hana-s2-db2 hana-s2-db3 ] #Resource Group: g_ip_HN1_03 # nc_HN1_03 (ocf::heartbeat:azure-lb): Started hana-s1-db1 # vip_HN1_03 (ocf::heartbeat:IPaddr2): Started hana-s1-db1Verify that SAP HANA system replication is in sync.
# Verify HANA HSR is in sync sudo su - hn1adm -c "python /usr/sap/HN1/HDB03/exe/python_support/systemReplicationStatus.py" #| Database | Host | Port | Service Name | Volume ID | Site ID | Site Name | Secondary | Secondary| Secondary | Secondary | Secondary | Replication | Replication | Replication | #| | | | | | | | Host | Port | Site ID | Site Name | Active Status | Mode | Status | Status Details | #| -------- | ----------- | ----- | ------------ | --------- | ------- | --------- | ------------- | -------- | --------- | --------- | ------------- | ----------- | ----------- | -------------- | #| HN1 | hana-s1-db3 | 30303 | indexserver | 5 | 2 | HANA_S1 | hana-s2-db3 | 30303 | 1 | HANA_S2 | YES | SYNC | ACTIVE | | #| HN1 | hana-s1-db2 | 30303 | indexserver | 4 | 2 | HANA_S1 | hana-s2-db2 | 30303 | 1 | HANA_S2 | YES | SYNC | ACTIVE | | #| SYSTEMDB | hana-s1-db1 | 30301 | nameserver | 1 | 2 | HANA_S1 | hana-s2-db1 | 30301 | 1 | HANA_S2 | YES | SYNC | ACTIVE | | #| HN1 | hana-s1-db1 | 30307 | xsengine | 2 | 2 | HANA_S1 | hana-s2-db1 | 30307 | 1 | HANA_S2 | YES | SYNC | ACTIVE | | #| HN1 | hana-s1-db1 | 30303 | indexserver | 3 | 2 | HANA_S1 | hana-s2-db1 | 30303 | 1 | HANA_S2 | YES | SYNC | ACTIVE | | #status system replication site "1": ACTIVE #overall system replication status: ACTIVE #Local System Replication State #~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~ #mode: PRIMARY #site id: 1 #site name: HANA_S1
Verify the cluster configuration for a failure scenario, when a node loses access to the NFS share (
/hana/shared).The SAP HANA resource agents depend on binaries, stored on
/hana/shared, to perform operations during failover. File system/hana/sharedis mounted over NFS in the presented configuration. A test that can be performed, is to create a temporary firewall rule to block access to the/hana/sharedNFS mounted file system on one of the primary site VMs. This approach validates that the cluster will fail over, if access to/hana/sharedis lost on the active system replication site.Expected result: When you block the access to the
/hana/sharedNFS mounted file system on one of the primary site VMs, the monitoring operation that performs read/write operation on file system, will fail, as it is not able to access the file system and will trigger HANA resource failover. The same result is expected when your HANA node loses access to the NFS share.You can check the state of the cluster resources by running
crm_monorpcs status. Resource state before starting the test:# Output of crm_mon #7 nodes configured #45 resources configured #Online: [ hana-s-mm hana-s1-db1 hana-s1-db2 hana-s1-db3 hana-s2-db1 hana-s2-db2 hana-s2-db3 ] # #Active resources: #rsc_st_azure (stonith:fence_azure_arm): Started hana-s-mm # Clone Set: fs_hana_shared_s1-clone [fs_hana_shared_s1] # Started: [ hana-s1-db1 hana-s1-db2 hana-s1-db3 ] # Clone Set: fs_hana_shared_s2-clone [fs_hana_shared_s2] # Started: [ hana-s2-db1 hana-s2-db2 hana-s2-db3 ] # Clone Set: hana_nfs_s1_active-clone [hana_nfs_s1_active] # Started: [ hana-s1-db1 hana-s1-db2 hana-s1-db3 ] # Clone Set: hana_nfs_s2_active-clone [hana_nfs_s2_active] # Started: [ hana-s2-db1 hana-s2-db2 hana-s2-db3 ] # Clone Set: SAPHanaTopology_HN1_HDB03-clone [SAPHanaTopology_HN1_HDB03] # Started: [ hana-s1-db1 hana-s1-db2 hana-s1-db3 hana-s2-db1 hana-s2-db2 hana-s2-db3 ] # Master/Slave Set: msl_SAPHana_HN1_HDB03 [SAPHana_HN1_HDB03] # Masters: [ hana-s1-db1 ] # Slaves: [ hana-s1-db2 hana-s1-db3 hana-s2-db1 hana-s2-db2 hana-s2-db3 ] # Resource Group: g_ip_HN1_03 # nc_HN1_03 (ocf::heartbeat:azure-lb): Started hana-s1-db1 # vip_HN1_03 (ocf::heartbeat:IPaddr2): Started hana-s1-db1To simulate failure for
/hana/shared:- If using NFS on ANF, first confirm the IP address for the
/hana/sharedANF volume on the primary site. You can do that by runningdf -kh|grep /hana/shared. - If using NFS on Azure Files, first determine the IP address of the private end point for your storage account.
Then, set up a temporary firewall rule to block access to the IP address of the
/hana/sharedNFS file system by executing the following command on one of the primary HANA system replication site VMs.In this example, the command was executed on hana-s1-db1 for ANF volume
/hana/shared.iptables -A INPUT -s 10.23.1.7 -j DROP; iptables -A OUTPUT -d 10.23.1.7 -j DROPThe HANA VM that lost access to
/hana/sharedshould restart or stop, depending on the cluster configuration. The cluster resources are migrated to the other HANA system replication site.If the cluster hasn't started on the VM that was restarted, start the cluster by running the following:
# Start the cluster pcs cluster startWhen the cluster starts, file system
/hana/sharedis automatically mounted. If you setAUTOMATED_REGISTER="false", you will need to configure SAP HANA system replication on the secondary site. In this case, you can run these commands to reconfigure SAP HANA as secondary.# Execute on the secondary su - hn1adm # Make sure HANA is not running on the secondary site. If it is started, stop HANA sapcontrol -nr 03 -function StopWait 600 10 # Register the HANA secondary site hdbnsutil -sr_register --name=HANA_S1 --remoteHost=hana-s2-db1 --remoteInstance=03 --replicationMode=sync # Switch back to root and clean up failed resources pcs resource cleanup SAPHana_HN1_HDB03The state of the resources, after the test:
# Output of crm_mon #7 nodes configured #45 resources configured #Online: [ hana-s-mm hana-s1-db1 hana-s1-db2 hana-s1-db3 hana-s2-db1 hana-s2-db2 hana-s2-db3 ] #Active resources: #rsc_st_azure (stonith:fence_azure_arm): Started hana-s-mm # Clone Set: fs_hana_shared_s1-clone [fs_hana_shared_s1] # Started: [ hana-s1-db1 hana-s1-db2 hana-s1-db3 ] # Clone Set: fs_hana_shared_s2-clone [fs_hana_shared_s2] # Started: [ hana-s2-db1 hana-s2-db2 hana-s2-db3 ] # Clone Set: hana_nfs_s1_active-clone [hana_nfs_s1_active] # Started: [ hana-s1-db1 hana-s1-db2 hana-s1-db3 ] # Clone Set: hana_nfs_s2_active-clone [hana_nfs_s2_active] # Started: [ hana-s2-db1 hana-s2-db2 hana-s2-db3 ] # Clone Set: SAPHanaTopology_HN1_HDB03-clone [SAPHanaTopology_HN1_HDB03] # Started: [ hana-s1-db1 hana-s1-db2 hana-s1-db3 hana-s2-db1 hana-s2-db2 hana-s2-db3 ] # Master/Slave Set: msl_SAPHana_HN1_HDB03 [SAPHana_HN1_HDB03] # Masters: [ hana-s2-db1 ] # Slaves: [ hana-s1-db1 hana-s1-db2 hana-s1-db3 hana-s2-db2 hana-s2-db3 ] # Resource Group: g_ip_HN1_03 # nc_HN1_03 (ocf::heartbeat:azure-lb): Started hana-s2-db1 # vip_HN1_03 (ocf::heartbeat:IPaddr2): Started hana-s2-db1- If using NFS on ANF, first confirm the IP address for the
It's a good idea to test the SAP HANA cluster configuration thoroughly, by also performing the tests documented in HA for SAP HANA on Azure VMs on RHEL.
Next steps
- Azure Virtual Machines planning and implementation for SAP
- Azure Virtual Machines deployment for SAP
- Azure Virtual Machines DBMS deployment for SAP
- NFS v4.1 volumes on Azure NetApp Files for SAP HANA
- To learn how to establish high availability and plan for disaster recovery of SAP HANA on Azure VMs, see High Availability of SAP HANA on Azure VMs.
Feedback
Coming soon: Throughout 2024 we will be phasing out GitHub Issues as the feedback mechanism for content and replacing it with a new feedback system. For more information see: https://aka.ms/ContentUserFeedback.
Submit and view feedback for