TextPatternRange.Move(TextUnit, Int32) Method
Definition
Important
Some information relates to prerelease product that may be substantially modified before it’s released. Microsoft makes no warranties, express or implied, with respect to the information provided here.
Moves the text range the specified number of text units.
public:
int Move(System::Windows::Automation::Text::TextUnit unit, int count);public int Move (System.Windows.Automation.Text.TextUnit unit, int count);member this.Move : System.Windows.Automation.Text.TextUnit * int -> intPublic Function Move (unit As TextUnit, count As Integer) As IntegerParameters
- unit
- TextUnit
The text unit boundary.
- count
- Int32
The number of text units to move. A positive value moves the text range forward, a negative value moves the text range backward, and 0 has no effect.
Returns
The number of units actually moved. This can be less than the number requested if either of the new text range endpoints is greater than or less than the DocumentRange endpoints.
Examples
/// -------------------------------------------------------------------
/// <summary>
/// Starts the target application and returns the AutomationElement
/// obtained from the targets window handle.
/// </summary>
/// <param name="exe">
/// The target application.
/// </param>
/// <param name="filename">
/// The text file to be opened in the target application
/// </param>
/// <returns>
/// An AutomationElement representing the target application.
/// </returns>
/// -------------------------------------------------------------------
private AutomationElement StartTarget(string exe, string filename)
{
// Start text editor and load with a text file.
Process p = Process.Start(exe, filename);
// targetApp --> the root AutomationElement.
AutomationElement targetApp =
AutomationElement.FromHandle(p.MainWindowHandle);
return targetApp;
}
''' -------------------------------------------------------------------
''' <summary>
''' Starts the target application and returns the AutomationElement
''' obtained from the targets window handle.
''' </summary>
''' <param name="exe">
''' The target application.
''' </param>
''' <param name="filename">
''' The text file to be opened in the target application
''' </param>
''' <returns>
''' An AutomationElement representing the target application.
''' </returns>
''' -------------------------------------------------------------------
Private Function StartTarget( _
ByVal exe As String, ByVal filename As String) As AutomationElement
' Start text editor and load with a text file.
Dim p As Process = Process.Start(exe, filename)
' targetApp --> the root AutomationElement.
Dim targetApp As AutomationElement
targetApp = AutomationElement.FromHandle(p.MainWindowHandle)
Return targetApp
End Function
/// -------------------------------------------------------------------
/// <summary>
/// Obtain the text control of interest from the target application.
/// </summary>
/// <param name="targetApp">
/// The target application.
/// </param>
/// <returns>
/// An AutomationElement that represents a text provider..
/// </returns>
/// -------------------------------------------------------------------
private AutomationElement GetTextElement(AutomationElement targetApp)
{
// The control type we're looking for; in this case 'Document'
PropertyCondition cond1 =
new PropertyCondition(
AutomationElement.ControlTypeProperty,
ControlType.Document);
// The control pattern of interest; in this case 'TextPattern'.
PropertyCondition cond2 =
new PropertyCondition(
AutomationElement.IsTextPatternAvailableProperty,
true);
AndCondition textCondition = new AndCondition(cond1, cond2);
AutomationElement targetTextElement =
targetApp.FindFirst(TreeScope.Descendants, textCondition);
// If targetText is null then a suitable text control was not found.
return targetTextElement;
}
''' -------------------------------------------------------------------
''' <summary>
''' Obtain the text control of interest from the target application.
''' </summary>
''' <param name="targetApp">
''' The target application.
''' </param>
''' <returns>
''' An AutomationElement. representing a text control.
''' </returns>
''' -------------------------------------------------------------------
Private Function GetTextElement(ByVal targetApp As AutomationElement) As AutomationElement
' The control type we're looking for; in this case 'Document'
Dim cond1 As PropertyCondition = _
New PropertyCondition( _
AutomationElement.ControlTypeProperty, _
ControlType.Document)
' The control pattern of interest; in this case 'TextPattern'.
Dim cond2 As PropertyCondition = _
New PropertyCondition( _
AutomationElement.IsTextPatternAvailableProperty, _
True)
Dim textCondition As AndCondition = New AndCondition(cond1, cond2)
Dim targetTextElement As AutomationElement = _
targetApp.FindFirst(TreeScope.Descendants, textCondition)
' If targetText is null then a suitable text control was not found.
Return targetTextElement
End Function
/// -------------------------------------------------------------------
/// <summary>
/// Moves a text range a specified number of text units. The text range
/// is the current selection.
/// </summary>
/// <param name="targetTextElement">
/// The AutomationElment that represents a text control.
/// </param>
/// <param name="textUnit">
/// The text unit value.
/// </param>
/// <param name="units">
/// The number of text units to move.
/// </param>
/// <param name="direction">
/// Direction to move the text range. Valid values are -1, 0, 1.
/// </param>
/// <returns>
/// The number of text units actually moved. This can be less than the
/// number requested if either of the new text range endpoints is
/// greater than or less than the DocumentRange endpoints.
/// </returns>
/// <remarks>
/// Moving the text range does not modify the text source in any way.
/// Only the text range starting and ending endpoints are modified.
/// </remarks>
/// -------------------------------------------------------------------
private Int32 MoveSelection(
AutomationElement targetTextElement,
TextUnit textUnit,
int units,
int direction)
{
TextPattern textPattern =
targetTextElement.GetCurrentPattern(TextPattern.Pattern)
as TextPattern;
if (textPattern == null)
{
// Target control doesn't support TextPattern.
return -1;
}
TextPatternRange[] currentSelection = textPattern.GetSelection();
if (currentSelection.Length > 1)
{
// For this example, we cannot move more than one text range.
return -1;
}
return currentSelection[0].Move(textUnit, Math.Sign(direction) * units);
}
''' -------------------------------------------------------------------
''' <summary>
''' Moves a text range a specified number of text units.
''' </summary>
''' <param name="targetTextElement">
''' The AutomationElement that represents a text control.
''' </param>
''' <param name="textUnit">
''' The text unit value.
''' </param>
''' <param name="units">
''' The number of text units to move.
''' </param>
''' <param name="direction">
''' Direction to move the text range. Valid values are -1, 0, 1.
''' </param>
''' <returns>
''' The number of text units actually moved. This can be less than the
''' number requested if either of the new text range endpoints is
''' greater than or less than the DocumentRange endpoints.
''' </returns>
''' <remarks>
''' Moving the text range does not modify the text source in any way.
''' Only the text range starting and ending endpoints are modified.
''' </remarks>
''' -------------------------------------------------------------------
Private Function MoveSelection( _
ByVal targetTextElement As AutomationElement, _
ByVal textUnit As TextUnit, _
ByVal units As Integer, _
ByVal direction As Integer) As Integer
Dim textPattern As TextPattern = _
DirectCast( _
targetTextElement.GetCurrentPattern(textPattern.Pattern), _
TextPattern)
If (textPattern Is Nothing) Then
' Target control doesn't support TextPattern.
Return -1
End If
Dim currentSelection As TextPatternRange() = _
textPattern.GetSelection()
If (currentSelection.Length > 1) Then
' For this example, we cannot move more than one text range.
Return -1
End If
Return currentSelection(0).Move(textUnit, Math.Sign(direction) * units)
End Function
Remarks
When it is necessary to traverse the content of a text range, a series of steps are involved behind the scenes in order for the Move method to execute successfully.
The text range is normalized; that is, the text range is collapsed to a degenerate range at the Start endpoint, which makes the End endpoint superfluous. This step is necessary to remove ambiguity in situations where a text range spans
unitboundaries; for example, "{The U}RL https://www.microsoft.com/ is embedded in text" where "{" and "}" are the text range endpoints.The resulting range is moved backward in the DocumentRange to the beginning of the requested
unitboundary.The range is moved forward or backward in the DocumentRange by the requested number of
unitboundaries.The range is then expanded from a degenerate range state by moving the End endpoint by one requested
unitboundary.
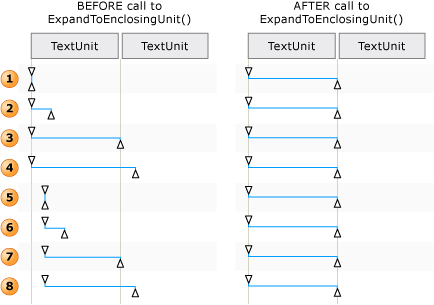
Examples of how a text range is adjusted for Move() and ExpandToEnclosingUnit()
The textual content (or inner text) of a text container and an embedded object, such as a hyperlink or table cell, is exposed as a single, continuous text stream in both the control view and the content view of the UI Automation tree; object boundaries are ignored. If a UI Automation client is retrieving the text for the purpose of reciting, interpreting, or analyzing in some manner, the text range should be checked for special cases, such as a table with textual content or other embedded objects. This can be accomplished by calling GetChildren to obtain an AutomationElement for each embedded object and then calling RangeFromChild to obtain a text range for each element; this is done recursively until all textual content has been retrieved.

Example of a text stream with embedded objects and their range spans
Move respects both hidden and visible text. The UI Automation client can check the IsHiddenAttribute for text visibility.
Move defers to the next largest TextUnit supported if the given TextUnit is not supported by the control.
The order, from smallest unit to largest, is listed below.
Note
The text is not altered in any way as the text range just spans a different part of the text.
Applies to
See also
Feedback
Coming soon: Throughout 2024 we will be phasing out GitHub Issues as the feedback mechanism for content and replacing it with a new feedback system. For more information see: https://aka.ms/ContentUserFeedback.
Submit and view feedback for
