Complex Types - EF Designer
This topic shows how to map complex types with the Entity Framework Designer (EF Designer) and how to query for entities that contain properties of complex type.
The following image shows the main windows that are used when working with the EF Designer.
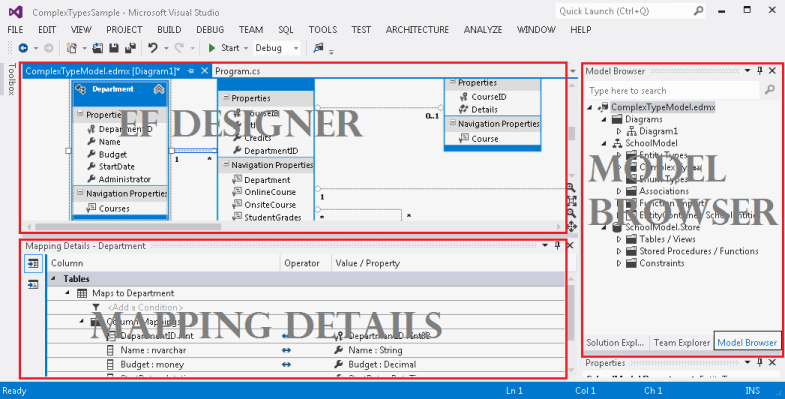
Note
When you build the conceptual model, warnings about unmapped entities and associations may appear in the Error List. You can ignore these warnings because after you choose to generate the database from the model, the errors will go away.
What is a Complex Type
Complex types are non-scalar properties of entity types that enable scalar properties to be organized within entities. Like entities, complex types consist of scalar properties or other complex type properties.
When you work with objects that represent complex types, be aware of the following:
- Complex types do not have keys and therefore cannot exist independently. Complex types can only exist as properties of entity types or other complex types.
- Complex types cannot participate in associations and cannot contain navigation properties.
- Complex type properties cannot be null. An **InvalidOperationException **occurs when DbContext.SaveChanges is called and a null complex object is encountered. Scalar properties of complex objects can be null.
- Complex types cannot inherit from other complex types.
- You must define the complex type as a class.
- EF detects changes to members on a complex type object when DbContext.DetectChanges is called. Entity Framework calls DetectChanges automatically when the following members are called: DbSet.Find, DbSet.Local, DbSet.Remove, DbSet.Add, DbSet.Attach, DbContext.SaveChanges, DbContext.GetValidationErrors, DbContext.Entry, DbChangeTracker.Entries.
Refactor an Entity’s Properties into New Complex Type
If you already have an entity in your conceptual model you may want to refactor some of the properties into a complex type property.
On the designer surface, select one or more properties (excluding navigation properties) of an entity, then right-click and select Refactor -> Move to New Complex Type.

A new complex type with the selected properties is added to the Model Browser. The complex type is given a default name.
A complex property of the newly created type replaces the selected properties. All property mappings are preserved.
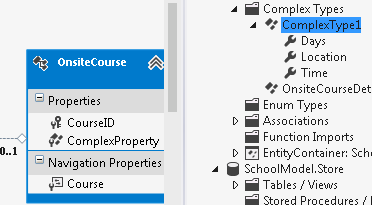
Create a New Complex Type
You can also create a new complex type that does not contain properties of an existing entity.
Right-click the Complex Types folder in the Model Browser, point to AddNew Complex Type…. Alternatively, you can select the Complex Types folder and press the Insert key on your keyboard.
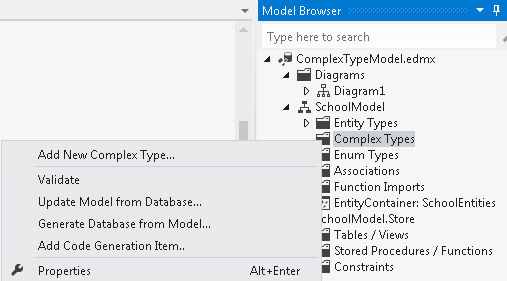
A new complex type is added to the folder with a default name. You can now add properties to the type.
Add Properties to a Complex Type
Properties of a complex type can be scalar types or existing complex types. However, complex type properties cannot have circular references. For example, a complex type OnsiteCourseDetails cannot have a property of complex type OnsiteCourseDetails.
You can add a property to a complex type in any of the ways listed below.
Right-click a complex type in the Model Browser, point to Add, then point to Scalar Property or Complex Property, then select the desired property type. Alternatively, you can select a complex type and then press the Insert key on your keyboard.
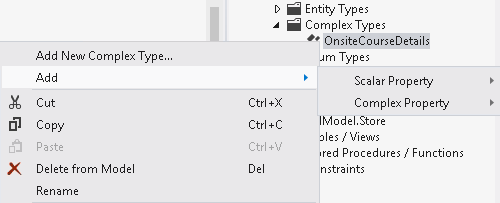
A new property is added to the complex type with a default name.
OR -
Right-click an entity property on the EF Designer surface and select Copy, then right-click the complex type in the Model Browser and select Paste.
Rename a Complex Type
When you rename a complex type, all references to the type are updated throughout the project.
Slowly double-click a complex type in the Model Browser. The name will be selected and in edit mode.
OR -
Right-click a complex type in the Model Browser and select Rename.
OR -
Select a complex type in the Model Browser and press the F2 key.
OR -
Right-click a complex type in the Model Browser and select Properties. Edit the name in the Properties window.
Add an Existing Complex Type to an Entity and Map its Properties to Table Columns
Right-click an entity, point to Add New, and select Complex Property. A complex type property with a default name is added to the entity. A default type (chosen from the existing complex types) is assigned to the property.
Assign the desired type to the property in the Properties window. After adding a complex type property to an entity, you must map its properties to table columns.
Right-click an entity type on the design surface or in the Model Browser and select Table Mappings. The table mappings are displayed in the Mapping Details window.
Expand the Maps to <Table Name> node. A Column Mappings node appears.
Expand the Column Mappings node. A list of all the columns in the table appears. The default properties (if any) to which the columns map are listed under the Value/Property heading.
Select the column you want to map, and then right-click the corresponding Value/Property field. A drop-down list of all the scalar properties is displayed.
Select the appropriate property.
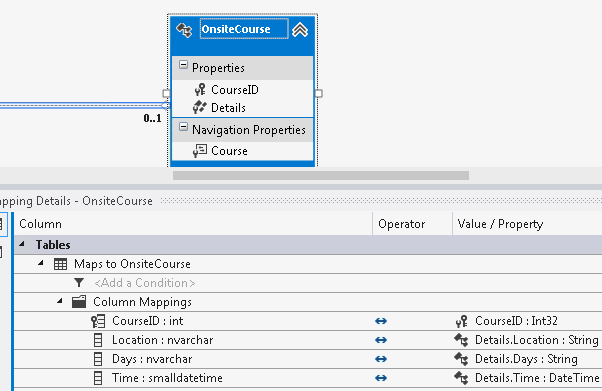
Repeat steps 6 and 7 for each table column.
Note
To delete a column mapping, select the column that you want to map, and then click the Value/Property field. Then, select Delete from the drop-down list.
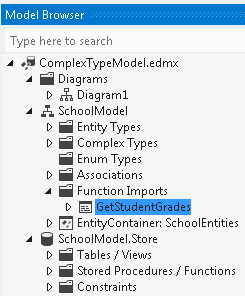
Map a Function Import to a Complex Type
Function imports are based on stored procedures. To map a function import to a complex type, the columns returned by the corresponding stored procedure must match the properties of the complex type in number and must have storage types that are compatible with the property types.
Double-click on an imported function that you want to map to a complex type.
Fill in the settings for the new function import, as follows:
Specify the stored procedure for which you are creating a function import in the Stored Procedure Name field. This field is a drop-down list that displays all the stored procedures in the storage model.
Specify the name of the function import in the Function Import Name field.
Select Complex as the return type and then specify the specific complex return type by choosing the appropriate type from the drop-down list.
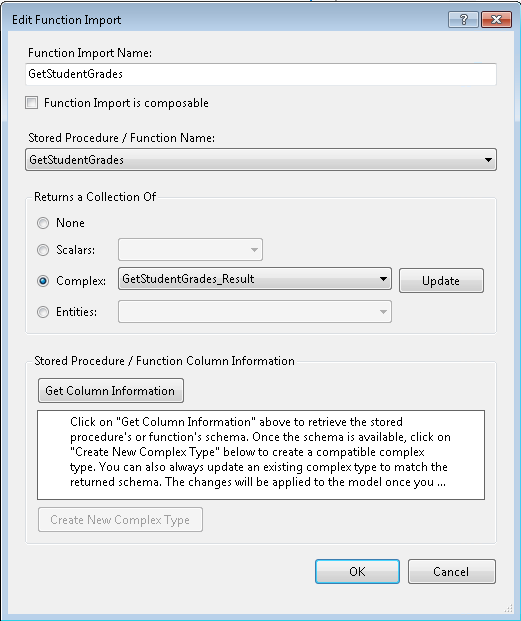
Click OK. The function import entry is created in the conceptual model.
Customize Column Mapping for Function Import
- Right-click the function import in the Model Browser and select Function Import Mapping. The Mapping Details window appears and shows the default mapping for the function import. Arrows indicate the mappings between column values and property values. By default, the column names are assumed to be the same as the complex type's property names. The default column names appear in gray text.
- If necessary, change the column names to match the column names that are returned by the stored procedure that corresponds to the function import.
Delete a Complex Type
When you delete a complex type, the type is deleted from the conceptual model and mappings for all instances of the type are deleted. However, references to the type are not updated. For example, if an entity has a complex type property of type ComplexType1 and ComplexType1 is deleted in the Model Browser, the corresponding entity property is not updated. The model will not validate because it contains an entity that references a deleted complex type. You can update or delete references to deleted complex types by using the Entity Designer.
Right-click a complex type in the Model Browser and select Delete.
OR -
Select a complex type in the Model Browser and press the Delete key on your keyboard.
Query for Entities Containing Properties of Complex Type
The following code shows how to execute a query that returns a collection of entity type objects that contain a complex type property.
using (SchoolEntities context = new SchoolEntities())
{
var courses =
from c in context.OnsiteCourses
order by c.Details.Time
select c;
foreach (var c in courses)
{
Console.WriteLine("Time: " + c.Details.Time);
Console.WriteLine("Days: " + c.Details.Days);
Console.WriteLine("Location: " + c.Details.Location);
}
}
Feedback
Coming soon: Throughout 2024 we will be phasing out GitHub Issues as the feedback mechanism for content and replacing it with a new feedback system. For more information see: https://aka.ms/ContentUserFeedback.
Submit and view feedback for
