Use jump servers
The security report produced for Contoso recommends implementing jump servers in addition to using PAWs. Having determined how to use PAWs, you decide to investigate jump servers further to figure out how they could benefit Contoso IT.
What are jump servers?
A jump server is a hardened server used to access and manage devices in a different security zone, such as between an internal network and a perimeter network. The jump server can function as the single point of contact and management.
For medium-sized organizations, jump servers can provide a means to help enhance security in locations where physical security is more challenging. For example, in branch offices where there is no datacenter. For large organizations, administrators can deploy datacenter-housed jump servers; these jump servers can provide highly controlled access to servers and domain controllers.
Jump servers do not typically have any sensitive data, but user credentials are stored in the memory and malicious hackers can target those credentials. For that reason, jump servers must be hardened.
Tip
You typically use a PAW to access a jump server to help to ensure secure access.
This server will run on dedicated hardware that supports both hardware and software-based security features such as:
- Windows Defender Credential Guard, to encrypt the domain credentials in memory.
- Windows Defender Remote Credential Guard, to prevent remote credentials from being sent to the jump server, instead using Kerberos version 5 single sign-on tickets.
- Windows Defender Device Guard:
- Using Hypervisor Enforced Code Integrity (HVCI) to use virtualization-based security to enforce kernel mode components to follow with the code integrity policy.
- Using Config Code Integrity to allow administrators to create a custom code integrity policy and specify trusted software.
By using jump servers, either with or without PAWs, you can create logical security zones. Within a zone, computers have similar security and connectivity configurations. You can use GPOs to configure these settings within a domain environment.
Tip
Administrative users can connect to your jump servers using Remote Desktop Protocol (RDP) and smart cards to perform administrative tasks.
Implement jump servers
The following graphic depicts a typical jump server and PAW deployment. An administrative user uses a smart card to authenticate to a standard workstation using a standard account. The user can access standard apps to perform day-to-day office productivity tasks. The administrator also has an administrative account and uses a smart card to authenticate to their administrative PAW. This in turn connects to the configured administrative jump server, which has administrative access to the appropriate object.
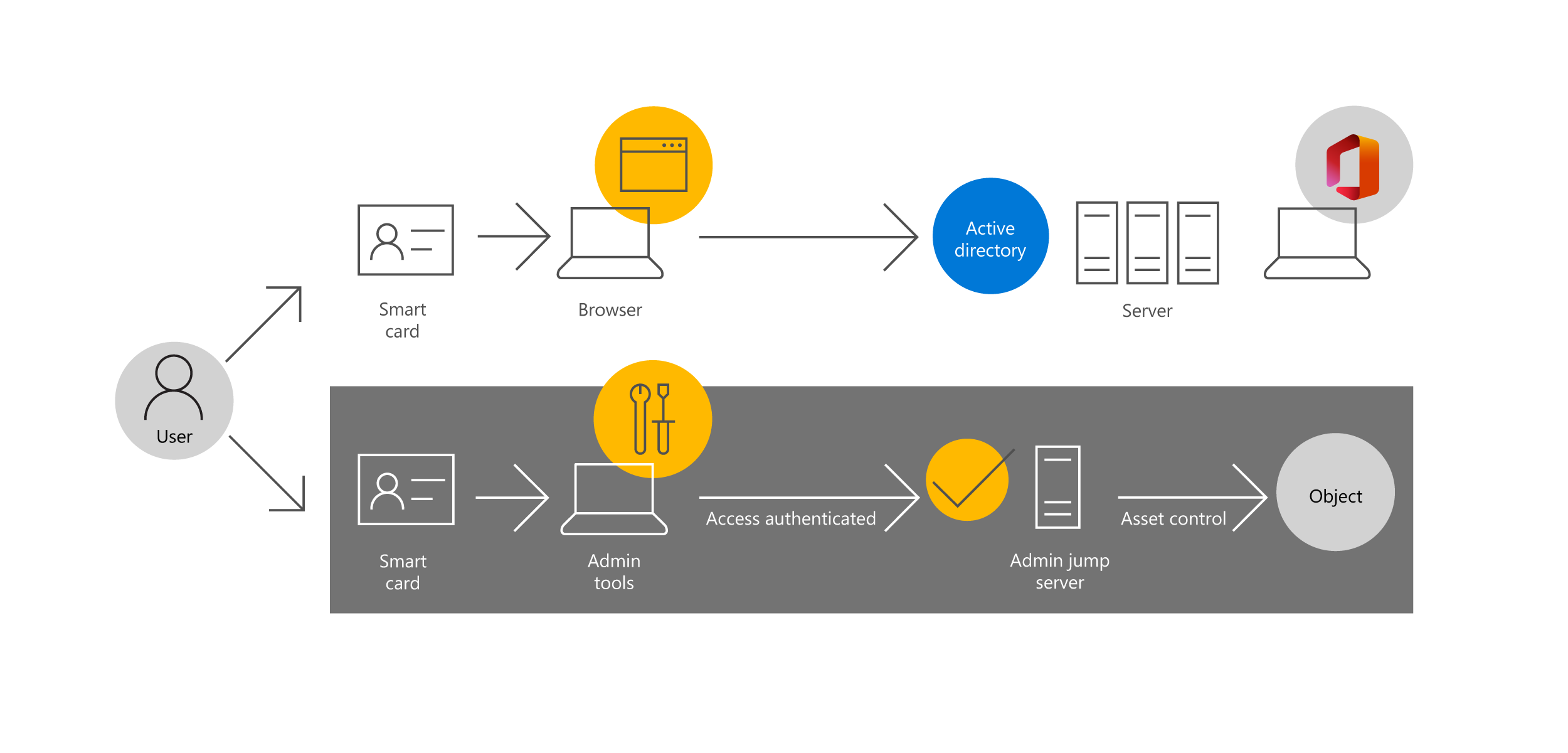
When you implement jump servers, there are a number of considerations. These include:
- Remote Desktop Gateway. If an administrator must connect directly to a target server (using RDP), implement Remote Desktop Gateway. This enables you to implement restrictions on connections to the jump server, and to destination servers that it will be used to manage.
- Hyper-V. Consider implementing VMs for each administrator on your jump servers. Each VM can be configured to allow a specific or subset of administrative tasks. Therefore, you should install Hyper-V on your jump servers.
Tip
You can enforce shutdown of these VMs after administrative tasks are completed. By shutting down VMs when not in use, you reduce your attack surface.
Server features. To implement jump servers, your server computers must support the following features:
- UEFI secure boot.
- Virtualization support.
- Signed Kernel mode drivers.
Remote administration tools. You should always use remote administration tools to manage servers. Install Windows Admin Center and the Remote Server Administration Tools (RSAT) on your administrator's VMs (or the physical jump server if you don't implement Hyper-V).
Caution
You should also prevent the use of remote administration tools on general-purpose computers.
RDP connectivity. Ensure that administrators connect using RDP to their VMs when they perform administrative tasks.