Zero Trust deployment plan with Microsoft 365
This article provides a deployment plan for building Zero Trust security with Microsoft 365. Zero Trust is a new security model that assumes breach and verifies each request as though it originated from an uncontrolled network. Regardless of where the request originates or what resource it accesses, the Zero Trust model teaches us to "never trust, always verify."
Use this article together with this poster.
Zero Trust security architecture
A Zero Trust approach extends throughout the entire digital estate and serves as an integrated security philosophy and end-to-end strategy.
This illustration provides a representation of the primary elements that contribute to Zero Trust.
In the illustration:
- Security policy enforcement is at the center of a Zero Trust architecture. This includes multifactor authentication with Conditional Access that takes into account user account risk, device status, and other criteria and policies that you set.
- Identities, devices, data, apps, network, and other infrastructure components are all configured with appropriate security. Policies that are configured for each of these components are coordinated with your overall Zero Trust strategy. For example, device policies determine the criteria for healthy devices and Conditional Access policies require healthy devices for access to specific apps and data.
- Threat protection and intelligence monitors the environment, surfaces current risks, and takes automated action to remediate attacks.
For more information about Zero Trust, see Microsoft's Zero Trust Guidance Center.
Deploying Zero Trust for Microsoft 365
Microsoft 365 is built intentionally with many security and information protection capabilities to help you build Zero Trust into your environment. Many of the capabilities can be extended to protect access to other SaaS apps your organization uses and the data within these apps.
This illustration represents the work of deploying Zero Trust capabilities. This work is broken into units of work that can be configured together, starting from the bottom and working to the top to ensure that prerequisite work is complete.
In this illustration:
- Zero Trust begins with a foundation of identity and device protection.
- Threat protection capabilities are built on top of this foundation to provide real-time monitoring and remediation of security threats.
- Information protection and governance provide sophisticated controls targeted at specific types of data to protect your most valuable information and to help you comply with compliance standards, including protecting personal information.
This article assumes you are using cloud identity. If you need guidance for this objective, see Deploy your identity infrastructure for Microsoft 365.
Tip
When you understand the steps and the end-to-end deployment process, you can use the Set up your Microsoft Zero Trust security model advanced deployment guide when signed in to the Microsoft 365 admin center. This guide steps you through applying Zero Trust principles for standard and advanced technology pillars. To step through the guide without signing in, go to the Microsoft 365 Setup portal.
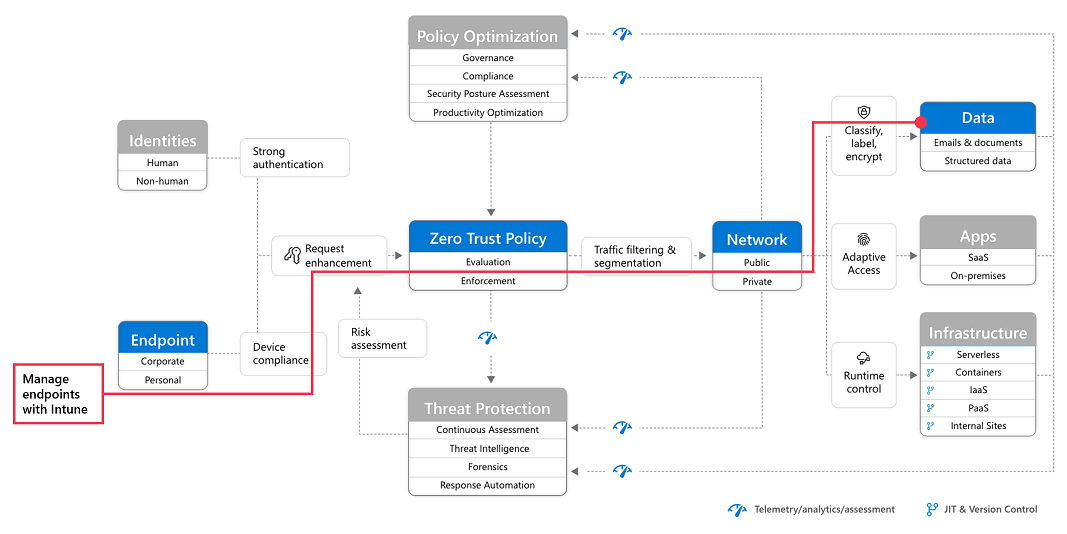
Step 1: Configure Zero Trust identity and device access protection: Starting-point policies
The first step is to build your Zero Trust foundation by configuring identity and device access protection.
Go to Zero Trust identity and device access protection for detailed prescriptive guidance. This series of articles describes a set of identity and device access prerequisite configurations and a set of Microsoft Entra Conditional Access, Microsoft Intune, and other policies to secure access to Microsoft 365 for enterprise cloud apps and services, other SaaS services, and on-premises applications published with Microsoft Entra application proxy.
| Includes | Prerequisites | Doesn't include |
|---|---|---|
Recommended identity and device access policies for three levels of protection:
Additional recommendations for:
|
Microsoft E3 or E5 Microsoft Entra ID in either of these modes:
|
Device enrollment for policies that require managed devices. See Step 2. Manage endpoints with Intune to enroll devices |
Start by implementing the starting-point tier. These policies don't require enrolling devices into management.
Step 2: Manage endpoints with Intune
Next, enroll your devices into management and begin protecting them with more sophisticated controls.
See Manage devices with Intune for detailed prescriptive guidance.
| Includes | Prerequisites | Doesn't include |
|---|---|---|
Enroll devices with Intune:
Configure policies:
|
Register endpoints with Microsoft Entra ID | Configuring information protection capabilities, including:
For these capabilities, see Step 5. Protect and govern sensitive data (later in this article). |
For more information, see Zero Trust for Microsoft Intune.
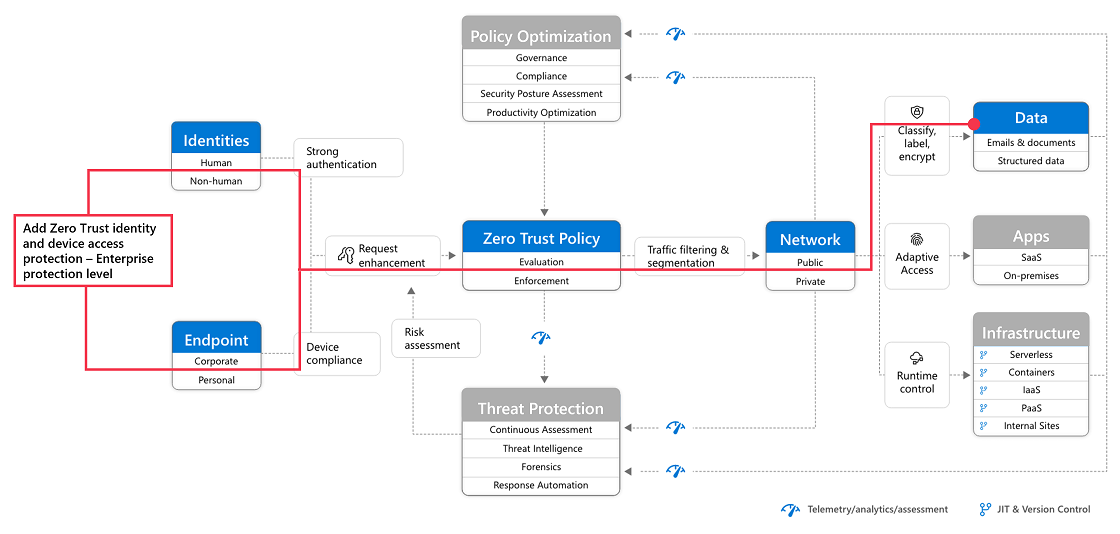
Step 3: Add Zero Trust identity and device access protection: Enterprise policies
With devices enrolled into management, you can now implement the full set of recommended Zero Trust identity and device access policies, requiring compliant devices.
Return to Common identity and device access policies and add the policies in the Enterprise tier.
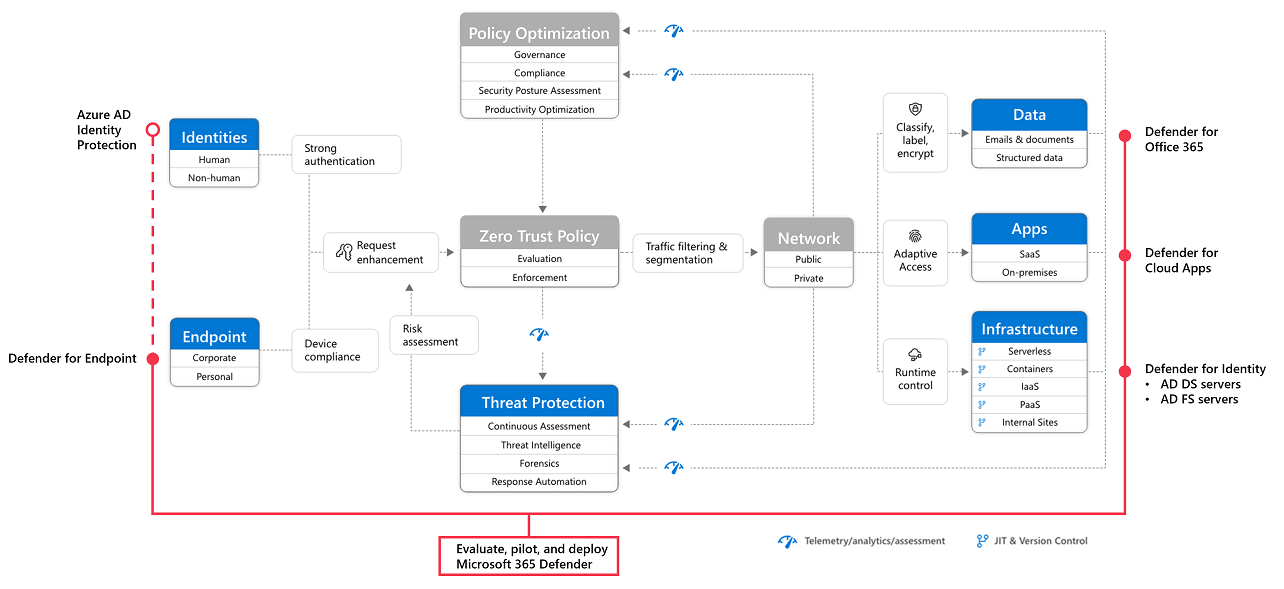
Step 4: Evaluate, pilot, and deploy Microsoft Defender XDR
Microsoft Defender XDR is an extended detection and response (XDR) solution that automatically collects, correlates, and analyzes signal, threat, and alert data from across your Microsoft 365 environment, including endpoint, email, applications, and identities.
Go to Evaluate and pilot Microsoft Defender XDR for a methodical guide to piloting and deploying Microsoft Defender XDR components.
| Includes | Prerequisites | Doesn't include |
|---|---|---|
Set up the evaluation and pilot environment for all components:
Protect against threats Investigate and respond to threats |
See the guidance to read about the architecture requirements for each component of Microsoft Defender XDR. | Microsoft Entra ID Protection isn't included in this solution guide. It's included in Step 1. Configure Zero Trust identity and device access protection. |
For more information, see these additional Zero Trust articles:
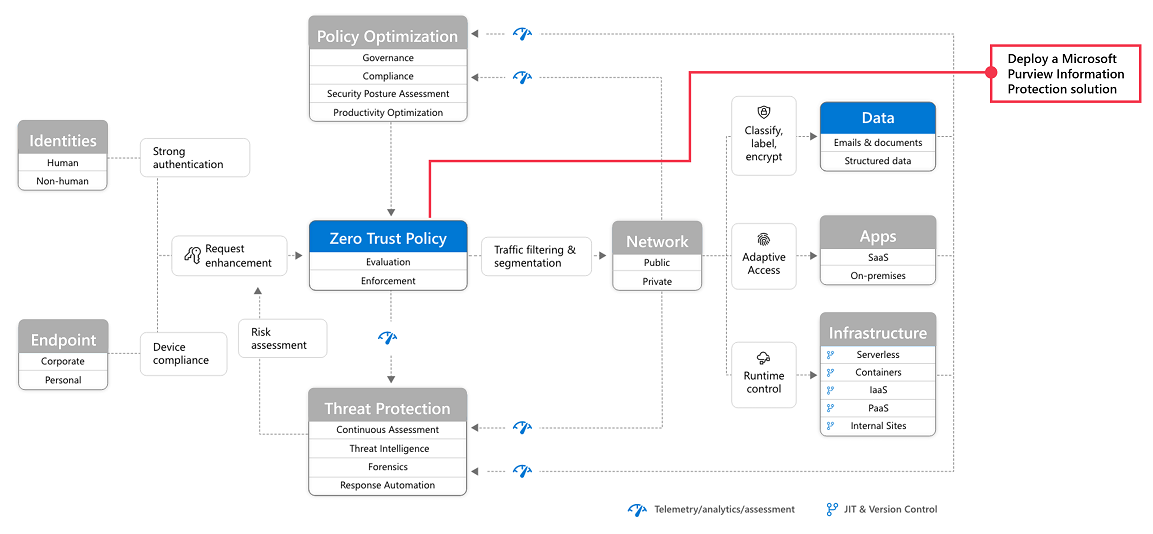
Step 5: Protect and govern sensitive data
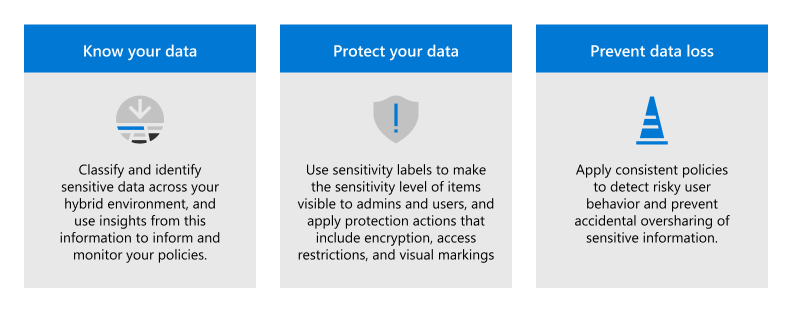
Implement Microsoft Purview Information Protection to help you discover, classify, and protect sensitive information wherever it lives or travels.
Microsoft Purview Information Protection capabilities are included with Microsoft Purview and give you the tools to know your data, protect your data, and prevent data loss.
While this work is represented at the top of the deployment stack illustrated earlier in this article, you can begin this work anytime.
Microsoft Purview Information Protection provides a framework, process, and capabilities you can use to accomplish your specific business objectives.
For more information on how to plan and deploy information protection, see Deploy a Microsoft Purview Information Protection solution.
If you're deploying information protection for data privacy regulations, this solution guide provides a recommended framework for the entire process: Deploy information protection for data privacy regulations with Microsoft 365.
Feedback
Coming soon: Throughout 2024 we will be phasing out GitHub Issues as the feedback mechanism for content and replacing it with a new feedback system. For more information see: https://aka.ms/ContentUserFeedback.
Submit and view feedback for