How to create a command-line predictor
PSReadLine 2.1.0 introduced the concept of a smart command-line predictor by implementing the Predictive IntelliSense feature. PSReadLine 2.2.2 expanded on that feature by adding a plugin model that allows you create your own command-line predictors.
Predictive IntelliSense enhances tab completion by providing suggestions, on the command line, as you type. The prediction suggestion appears as colored text following your cursor. This enables you to discover, edit, and execute full commands based on matching predictions from your command history or additional domain-specific plugins.
System requirements
To create and use a plugin predictor, you must be using the following versions of software:
- PowerShell 7.2 (or higher) - provides the APIs necessary for creating a command predictor
- PSReadLine 2.2.2 (or higher) - allows you to configure PSReadLine to use the plugin
Overview of a predictor
A predictor is a PowerShell binary module. The module must implement the
System.Management.Automation.Subsystem.Prediction.ICommandPredictor interface. This interface
declares the methods used to query for prediction results and provide feedback.
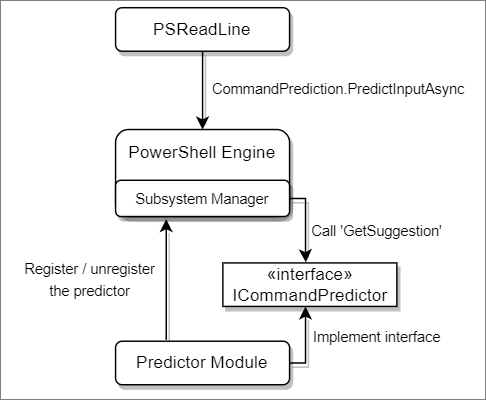
A predictor module must register a CommandPredictor subsystem with PowerShell's SubsystemManager
when loaded and unregister itself when unloaded.
The following diagram shows the architecture of a predictor in PowerShell.
Creating the code
To create a predictor, you must have the .NET 6 SDK installed for your platform. For more information on the SDK, see Download .NET 6.0.
Create a new PowerShell module project by following these steps:
Use the
dotnetcommand-line tool to create a starter classlib project.dotnet new classlib --name SamplePredictorEdit the
SamplePredictor.csprojto contain the following information:<Project Sdk="Microsoft.NET.Sdk"> <PropertyGroup> <TargetFramework>net6.0</TargetFramework> </PropertyGroup> <ItemGroup> <PackageReference Include="Microsoft.PowerShell.SDK" Version="7.2.0" /> </ItemGroup> </Project>Delete the default
Class1.csfile created bydotnetand copy the following code to aSamplePredictorClass.csfile in your project folder.using System; using System.Collections.Generic; using System.Threading; using System.Management.Automation; using System.Management.Automation.Subsystem; using System.Management.Automation.Subsystem.Prediction; namespace PowerShell.Sample { public class SamplePredictor : ICommandPredictor { private readonly Guid _guid; internal SamplePredictor(string guid) { _guid = new Guid(guid); } /// <summary> /// Gets the unique identifier for a subsystem implementation. /// </summary> public Guid Id => _guid; /// <summary> /// Gets the name of a subsystem implementation. /// </summary> public string Name => "SamplePredictor"; /// <summary> /// Gets the description of a subsystem implementation. /// </summary> public string Description => "A sample predictor"; /// <summary> /// Get the predictive suggestions. It indicates the start of a suggestion rendering session. /// </summary> /// <param name="client">Represents the client that initiates the call.</param> /// <param name="context">The <see cref="PredictionContext"/> object to be used for prediction.</param> /// <param name="cancellationToken">The cancellation token to cancel the prediction.</param> /// <returns>An instance of <see cref="SuggestionPackage"/>.</returns> public SuggestionPackage GetSuggestion(PredictionClient client, PredictionContext context, CancellationToken cancellationToken) { string input = context.InputAst.Extent.Text; if (string.IsNullOrWhiteSpace(input)) { return default; } return new SuggestionPackage(new List<PredictiveSuggestion>{ new PredictiveSuggestion(string.Concat(input, " HELLO WORLD")) }); } #region "interface methods for processing feedback" /// <summary> /// Gets a value indicating whether the predictor accepts a specific kind of feedback. /// </summary> /// <param name="client">Represents the client that initiates the call.</param> /// <param name="feedback">A specific type of feedback.</param> /// <returns>True or false, to indicate whether the specific feedback is accepted.</returns> public bool CanAcceptFeedback(PredictionClient client, PredictorFeedbackKind feedback) => false; /// <summary> /// One or more suggestions provided by the predictor were displayed to the user. /// </summary> /// <param name="client">Represents the client that initiates the call.</param> /// <param name="session">The mini-session where the displayed suggestions came from.</param> /// <param name="countOrIndex"> /// When the value is greater than 0, it's the number of displayed suggestions from the list /// returned in <paramref name="session"/>, starting from the index 0. When the value is /// less than or equal to 0, it means a single suggestion from the list got displayed, and /// the index is the absolute value. /// </param> public void OnSuggestionDisplayed(PredictionClient client, uint session, int countOrIndex) { } /// <summary> /// The suggestion provided by the predictor was accepted. /// </summary> /// <param name="client">Represents the client that initiates the call.</param> /// <param name="session">Represents the mini-session where the accepted suggestion came from.</param> /// <param name="acceptedSuggestion">The accepted suggestion text.</param> public void OnSuggestionAccepted(PredictionClient client, uint session, string acceptedSuggestion) { } /// <summary> /// A command line was accepted to execute. /// The predictor can start processing early as needed with the latest history. /// </summary> /// <param name="client">Represents the client that initiates the call.</param> /// <param name="history">History command lines provided as references for prediction.</param> public void OnCommandLineAccepted(PredictionClient client, IReadOnlyList<string> history) { } /// <summary> /// A command line was done execution. /// </summary> /// <param name="client">Represents the client that initiates the call.</param> /// <param name="commandLine">The last accepted command line.</param> /// <param name="success">Shows whether the execution was successful.</param> public void OnCommandLineExecuted(PredictionClient client, string commandLine, bool success) { } #endregion; } /// <summary> /// Register the predictor on module loading and unregister it on module un-loading. /// </summary> public class Init : IModuleAssemblyInitializer, IModuleAssemblyCleanup { private const string Identifier = "843b51d0-55c8-4c1a-8116-f0728d419306"; /// <summary> /// Gets called when assembly is loaded. /// </summary> public void OnImport() { var predictor = new SamplePredictor(Identifier); SubsystemManager.RegisterSubsystem(SubsystemKind.CommandPredictor, predictor); } /// <summary> /// Gets called when the binary module is unloaded. /// </summary> public void OnRemove(PSModuleInfo psModuleInfo) { SubsystemManager.UnregisterSubsystem(SubsystemKind.CommandPredictor, new Guid(Identifier)); } } }The following example code returns the string "HELLO WORLD" for the prediction result for all user input. Since the sample predictor doesn't process any feedback, the code doesn't implement the feedback methods from the interface. Change the prediction and feedback code to meet the needs of your predictor.
Note
The list view of PSReadLine doesn't support multiline suggestions. Each suggestion should be a single line. If your code has a multiline suggestion, you should split the lines into separate suggestions or join the lines with a semicolon (
;).Run
dotnet buildto produce the assembly. You can find the compiled assembly in thebin/Debug/net6.0location of your project folder.Note
To ensure a responsive user experience, the ICommandPredictor interface has a 20ms time out for responses from the Predictors. Your predictor code must return results in less than 20ms to be displayed.
Using your predictor plugin
To try out your new predictor, open a new PowerShell 7.2 session and run the following commands:
Set-PSReadLineOption -PredictionSource HistoryAndPlugin
Import-Module .\bin\Debug\net6.0\SamplePredictor.dll
With the assembly is loaded in the session, you see the text "HELLO WORLD" appear as you type in the
terminal. You can press F2 to switch between the Inline view and the List view.
For more information about PSReadLine options, see Set-PSReadLineOption.
You can get a list of installed predictors, using the following command:
Get-PSSubsystem -Kind CommandPredictor
Kind SubsystemType IsRegistered Implementations
---- ------------- ------------ ---------------
CommandPredictor ICommandPredictor True {SamplePredictor}
Note
Get-PSSubsystem is an experimental cmdlet that was introduced in PowerShell 7.1 You must enable
the PSSubsystemPluginModel experimental feature to use this cmdlet. For more information, see
Using Experimental Features.
Feedback
Coming soon: Throughout 2024 we will be phasing out GitHub Issues as the feedback mechanism for content and replacing it with a new feedback system. For more information see: https://aka.ms/ContentUserFeedback.
Submit and view feedback for
