Troubleshoot software update synchronization in Configuration Manager
This article helps you diagnose and resolve some common issues with software update synchronization in Configuration Manager.
We'll begin by asking if the prerequisites for software update synchronization are met. If you met the prerequisites but still face the issue, we'll take you through a series of steps to resolve your issue.
Original product version: Configuration Manager (current branch), Microsoft System Center 2012 R2 Configuration Manager, Microsoft System Center 2012 Configuration Manager
Original KB number: 4505439
Verify the Prerequisites
The first step in troubleshooting synchronization issues is to verify that the following prerequisites are met:
Verify that Prerequisites for software updates in Configuration Manager are met.
When you install the software update point on a remote site system server, the WSUS Administration console must be installed on the site server.
Verify that WSUS running on a software update point isn't configured to be a replica.
To verify it, open the WSUS console on the software update point. Select Options in the console tree pane, and then select Update Source and Proxy Server in the display pane.
Verify that the Update Services service is running on the WSUS server.
Verify that the Default website or WSUS Administration website is running on the WSUS server.
Check the Update Source settings in WSUS
Check the Update Source settings in the WSUS console on the software update point site system server. These settings are set automatically by WSUS Configuration Manager (WCM). If these settings don't match, review WCM.log.
To check the update source settings in WSUS, open the WSUS console on the software update point site system server. Select Options in the console tree pane, and then select Update Source and Proxy Server in the display pane.
Verify that the following settings are configured correctly:
Synchronize from Microsoft Update
Generally, this setting should be selected when you're in the WSUS console on the software update point for the top-level site. Starting with Configuration Manager 2012 SP1, you can specify an existing WSUS server as the upstream synchronization source location for the top-level site. If you've specified an existing WSUS server as the upstream source location, then this setting shouldn't be selected.
Synchronize from another Windows Server Update Services server
Generally, this setting should be selected when you're in the WSUS console for:
- Software update points for top-level site if an upstream source location is specified instead of Microsoft Update.
- Software update points for a primary site.
- Other software update points installed in the primary site.
- Internet-based software update points.
- Software update points for a secondary site.
Server name: It should be the fully qualified domain name (FQDN) of the upstream update source.
- For the first software update point in the primary site, it should be the software update point for the parent site.
- For other software update points in the site, it should be the first software update point on the same site.
- For an Internet-based software update point, it should be the first software update point on the same site.
Port number: It should be the port number for the upstream WSUS server. To determine the port number on the upstream WSUS server, see Determine the port settings used by WSUS and the software update point.
Use SSL when synchronizing update information: When the software update point is in HTTPS mode, this setting must be selected. When using Secure Sockets Layer (SSL) for software updates, several requirements apply. For more information, see Check SSL configuration.
This server is a replica of the upstream server: Never select this setting on the software update point for the top-level site or the first software update point for the primary site. This setting should be selected on:
- Internet-based software update points
- Other software update points for the primary site.
- Software update points for a secondary site
Synchronization fails because of authentication and proxy issues
WSUS Configuration Manager configures the WSUS server once every hour. It does so to ensure that the settings configured in WSUS match the setting specified in the Configuration Manager console.
If WCM fails to configure the WSUS server properly, synchronization attempts can fail with an error similar to the following screenshot:
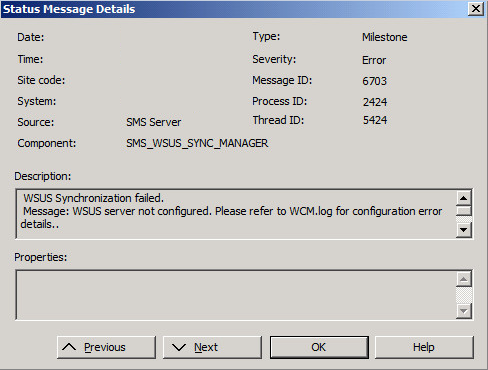
You'll also find the following error in the WsyncMgr.log file on the site server (located in \Logs):
Sync failed: WSUS server not configured. Please refer to WCM.log for configuration error details. Source: CWSyncMgr::DoSync
Sync failed. Will retry in 60 minutes
Synchronization may fail because of authentication or proxy issues. When this issue occurs, you'll see an error similar to the following error in the WCM.log file:
System.Net.WebException: The request failed with HTTP status 502
The error may not always be HTTP status 502, and may in fact be one of the following errors:
- HTTP Status 401 Unauthorized
- HTTP Status 403 Forbidden
- HTTP Status 407 Proxy Authentication Required
- HTTP Status 502 Proxy Error
- No connection could be made because the target machine actively refused it
- Authentication failed because the remote party has closed the transport stream
To troubleshoot authentication or proxy issues, follow these steps:
- Verify that the Update Services service is running on the WSUS server.
- Verify that the Default website or WSUS Administration website is running on the WSUS server.
- Verify that the fully qualified domain name (FQDN) for the software update point site system server is correct and accessible from the site server.
- If the software update point is remote from the site server, verify that you can connect to the WSUS server from the site server. For more information, see Check connectivity from the site server to the WSUS server.
- Check the port settings configured for the software update point. Verify that they're the same as the port settings configured for the website used by WSUS running on the software update point. For more information, see Determine the port settings used by WSUS and the software update point.
- Verify that the proxy and account settings are correctly configured for the software update point. For more information, see Configure proxy setting for the software update point.
- Verify that the software update point connection account is configured (if necessary). And verify that it has permissions to connect to the WSUS server. For more information, see Configure the WSUS Server Connection Account for the software update point.
- Verify that the permissions on the
ApiRemoting30virtual directory are set correctly in IIS. When WSUS Synchronization Manager starts synchronization, the computer and Administrator accounts must have access to theApiRemoting30virtual directory under the WSUS website in IIS. To check permissions on theApiRemoting30virtual directory:- On the WSUS server, open IIS Manager.
- Expand Sites, expand the website for the WSUS server, right-click the
ApiRemoting30virtual directory, and then select Edit Permissions.
- If the software update point is configured for SSL (HTTPS), verify that WSUS is correctly configured for SSL. For more information, see Check SSL configuration.
- Review WSUSCtrl.log for errors. For more information, see WSUS Control Manager reports an error.
Synchronization fails because of web service issues
Synchronization may be failing because of issues with the web service. When this issue occurs, you'll see an error similar to the following errors in the WCM.log file:
System.Net.WebException: The request failed with HTTP status 500
System.Net.WebException: The request failed with HTTP status 503
To troubleshoot web service issues, follow these steps:
- Verify that the Update Services service is running on the WSUS server.
- Verify that the Default website or WSUS Administration website is running on the WSUS server.
- Check the port settings configured for the software update point. Verify that they're the same as the port settings configured for the website used by WSUS running on the software update point. For more information, see Determine the port settings used by WSUS and the software update point.
- Review WSUSCtrl.log for errors. For more information, see WSUS Control Manager reports an error.
Synchronization fails because of SSL issues
If you're using SSL, verify the following settings:
- Verify that the certificate configured for the WSUS website is configured with the correct FQDN. If the certificate doesn't have the correct FQDN, see Add a subject alternative name to a secure LDAP certificate.
- Verify that the certificate hasn't expired.
- Verify that WSUS is correctly configured for SSL. For more information, see Check SSL configuration.
Synchronization fails because of issues with the EULA
Synchronization issues can often be traced back to issues relating to the End User Licensing Agreement (EULA). To verify whether it's your issue, follow these steps:
Review the SoftwareDistribution.log file on the WSUS server to find out why the EULAs aren't getting downloaded. Look for
.txtin the log to find relevant entries.Verify that the firewall is configured to allow communication with Microsoft Update. For more information, see Connection from the WSUS server to the Internet.
Verify the proxy server settings.
Run the following command from a Command Prompt to have WSUS download the missing content again, including EULAs:
%ProgramFiles%\Update Services\Tools\wsusutil.exe reset
Synchronization fails because of errors communicating with Microsoft Update
When this issue occurs, you usually receive the following errors:
A connection attempt failed because the connected party did not properly respond after a period of time, or established connection failed because connected host has failed to respond.
0x80072EFE - The connection with the server was terminated abnormally
To troubleshoot this issue, follow these steps:
- Verify that the WSUS server can connect to the Internet.
- Verify that the firewall is configured to allow communication with Microsoft Update. For more information, see Connection from the WSUS server to the Internet.
- Verify the proxy server settings.
WSUS Control Manager reports an error
Unlike WCM and WSyncMgr, WSUS Control Manager (WSUSCtrl) resides on the software update point (SUP) itself. If SUP is remote, WSUSCtrl.log will be present on the SUP instead of on the site server. WSUS Control Manager periodically checks WSUS to make sure WSUS components are healthy. If WSUS components are unhealthy, WCM and WSyncMgr can't communicate with WSUS. In most cases, errors in WCM.log resemble the errors in WsyncMgr.log. However, an exception could be when the SUP is remote from the site server. If WSUS components are healthy, WSUSCtrl.log on the remote SUP doesn't report any errors. However, if the site server can't connect to the WSUS server remotely, you'll see errors in WCM.log and/or WSyncMgr.log even though WSUS itself is healthy.
To check whether WSUS is functioning as expected, run the following command on the WSUS server. Then review the Application log in Event Viewer for errors:
%ProgramFiles%\Update Services\Tools\wsusutil.exe checkhealth
Check connectivity from the site server to the WSUS server
If the WSUS server is remote from the site server, the WSUS Administration console must be installed on the site server. The console installs the required APIs that are used by Configuration Manager to connect to the WSUS server. To test whether Configuration Manager can connect to the WSUS server, use the locally installed WSUS Administration console.
To connect to the remote WSUS server by using the WSUS Administration console, follow these steps:
- Start the WSUS Administration console.
- Right-click Update Services in the tree view, and select Connect to Server.
- Specify the Server Name and Port Number of the remote WSUS server, and then select Connect. Make sure that you specify the FQDN of the WSUS server and the correct port number.
WSUS connection failures
For more information, see Troubleshoot WSUS connection failures.
More information
- For more information about software update synchronization process, see Software updates synchronization.
- You can also post a question in our Configuration Manager support forum for security, updates, and compliance here.
- Visit our blog for all the latest news, information, and tech tips on Configuration Manager.
Feedback
Coming soon: Throughout 2024 we will be phasing out GitHub Issues as the feedback mechanism for content and replacing it with a new feedback system. For more information see: https://aka.ms/ContentUserFeedback.
Submit and view feedback for