Performance issue when querying views across linked servers
Applies to: SQL Server
Symptoms
Executing a query against views on a linked server remotely takes more time than executing the same query directly against a base table on the linked server.
Cause
Executing a query against a view and a base table results in a different behavior because of the data cardinality estimation, which is used for calculating the expected number of rows returned. The number for querying views is set to a constant value of 10,000 while the number for querying base tables is derived from statistical information.
Cardinality estimation on a base table queried by linked servers
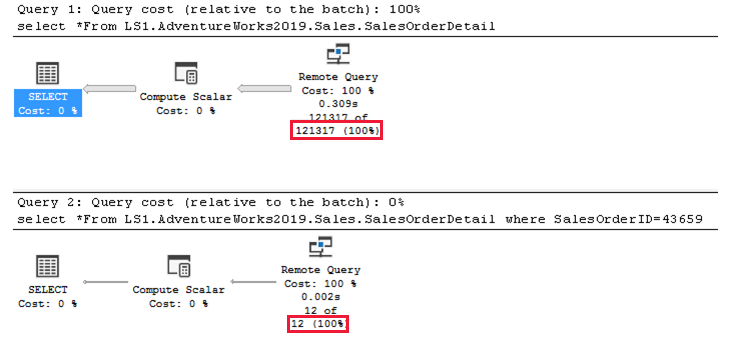
The Microsoft OLE DB Provider (SQLOLEDB) (no longer maintained) or Microsoft® OLE DB Driver 18 for SQL Server® (MSOLEDBSQL) both support distribution statistics on base tables. SQL Server can utilize the statistics and histogram over linked servers in the same way as any regular query does. For example, if you create a linked server called LS1 that has the AdventureWorks2019 database with the Sales.SalesOrderDetail table, the following queries can utilize the statistical histogram:
SELECT * FROM LS1.AdventureWorks2019.Sales.SalesOrderDetail;
SELECT * FROM LS1.AdventureWorks2019.Sales.SalesOrderDetail WHERE SalesOrderID=43659;
The following graphical query plans show the estimated number of rows returned on each remote query.
Cardinality estimation on views queried by linked servers
Linked server queries against views don't utilize statistics-based cardinality estimation. The cardinality estimation against a view is a constant value of 10,000. The following test illustrates this:
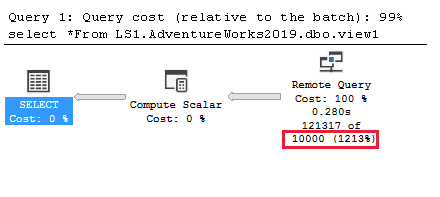
Create a view named
dbo.View1that references theSales.SalesOrderDetailtable from theAdventureWorks2019database of the linked server LS1.USE AdventureWorks2019; GO CREATE VIEW [dbo].[view1] AS SELECT * FROM Sales.SalesOrderDetail;Query the view remotely.
SELECT * FROM LS1.AdventureWorks2019.dbo.view1;The cardinality estimation of the query shows exactly 10,000 rows.
Cardinality estimation on a view queried by linked servers with WHERE clause
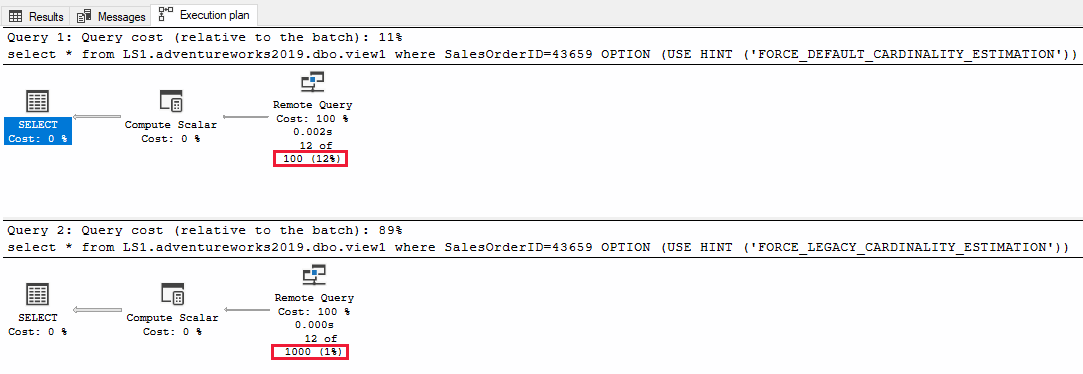
If you execute a query with the WHERE clause against views on a linked server, the cardinality estimation against views is also a constant value. However, the value varies depending on the compatibility level of the database.
Note
The cardinality estimation value won't be impacted by the compatibility level of database where the view is defined.
- For a database compatibility level of 120 or higher (new version of cardinality estimator), the cardinality estimation is 100.
- For a database compatibility level of 110 or lower (legacy cardinality estimator), the cardinality estimation is 1,000.
See the following queries for an example:
SELECT * FROM LS1.AdventureWorks2019.dbo.view1
WHERE SalesOrderID=43659
OPTION (USE HINT ('FORCE_DEFAULT_CARDINALITY_ESTIMATION'));
GO
SELECT * FROM LS1.AdventureWorks2019.dbo.view1
WHERE SalesOrderID=43659
OPTION (USE HINT ('FORCE_LEGACY_CARDINALITY_ESTIMATION'));
See the following cardinality estimation of the queries for an example.
Resolution
In most cases, no action is needed because most application workloads won't be impacted by the cardinality estimation on views when queried from linked servers. If the workload is impacted, use one of the following methods:
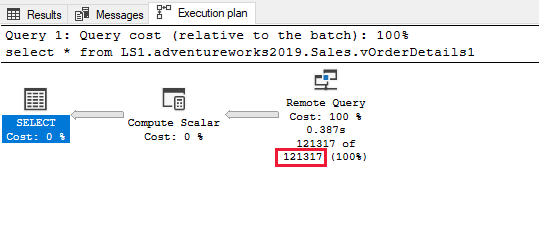
Update and change the view as an indexed view. The indexed view has at least one index with corresponding statistics. See the following queries to create and query an indexed view.
Note
This method will expose actual statistics that represent the underlying data.
--Set the options to support indexed views. SET NUMERIC_ROUNDABORT OFF; SET ANSI_PADDING, ANSI_WARNINGS, CONCAT_NULL_YIELDS_NULL, ARITHABORT, QUOTED_IDENTIFIER, ANSI_NULLS ON; GO IF OBJECT_ID ('Sales.vOrderDetails1', 'view') IS NOT NULL DROP VIEW Sales.vOrderDetails1; GO --Create view with schemabinding CREATE VIEW Sales.vOrderDetails1 WITH SCHEMABINDING AS SELECT SalesOrderID, SalesOrderDetailID, CarrierTrackingNumber, OrderQty, ProductID, UnitPrice, UnitPriceDiscount, LineTotal, ModifiedDate FROM Sales.SalesOrderDetail GO --Create an index on the view CREATE UNIQUE CLUSTERED INDEX IDX_V1 ON Sales.vOrderDetails1 (SalesOrderID, ProductID); --Select from the materialized view SELECT * FROM LS1.adventureworks2019.Sales.vOrderDetails1;See the following cardinality estimation of the query for an example.
If you execute a query with the
WHEREclause, you can increase the cardinality estimation by using theQuery Hint OPTION(USE HINT ('FORCE_LEGACY_CARDINALITY_ESTIMATION')). This approach may help in some cases especially when joining with large tables.Note
This method is appropriate for cases where the view exposes many rows.
Execute the query directly against the base tables instead of views on the linked server if appropriate.
See also
Feedback
Coming soon: Throughout 2024 we will be phasing out GitHub Issues as the feedback mechanism for content and replacing it with a new feedback system. For more information see: https://aka.ms/ContentUserFeedback.
Submit and view feedback for