Compilar una aplicación de LUIS mediante programación con Node.js
Importante
LUIS se retirará el 1 de octubre de 2025. Además, a partir del 1 de abril de 2023, ya no se podrán crear recursos de este servicio. Se recomienda migrar las aplicaciones de LUIS al reconocimiento del lenguaje conversacional para aprovechar el soporte continuo del producto y las capacidades multilingües.
LUIS proporciona una API de programación que hace lo mismo que el sitio web de LUIS. Esto puede ahorrarle tiempo si tiene datos preexistentes. Además, resultaría más rápido crear una aplicación de LUIS mediante programación que si especifica la información manualmente.
Precaución
Este documento no se ha actualizado con el texto y las capturas de pantallas del portal de LUIS más reciente.
Requisitos previos
- Inicie sesión en el sitio web de LUIS y busque la clave de creación en la configuración de la cuenta. Esta clave se usa para llamar a las API de creación.
- Si no tiene una suscripción a Azure, cree una cuenta gratuita antes de empezar.
- Este artículo empieza con un archivo CSV para los archivos de registro de solicitudes de usuario de una empresa hipotética. Descárguela aquí.
- Instale la versión de Node.js más reciente. Puede descargarlo aquí.
- [Recomendado] Visual Studio Code para IntelliSense y depuración. Descárguelo gratis aquí.
Todo el código de este artículo está disponible en el repositorio Azure-Samples de Language Understanding en GitHub.
Asignación de datos preexistentes a intenciones y entidades
Aunque tenga en mente un sistema que no se ha creado con LUIS, si contiene datos textuales que se asignan a cosas diferentes que quieren hacer los usuarios, podría crear en LUIS una asignación de las categorías existentes de entradas de usuario a las intenciones. Si puede identificar palabras o frases importantes en lo que han dicho los usuarios, se pueden asignar a entidades.
Abra el archivo IoT.csv . Contiene un registro de consultas de usuario a un servicio hipotético de domótica, así como su clasificación, lo que ha dicho el usuario y algunas columnas con información útil que se ha extraído de estas.
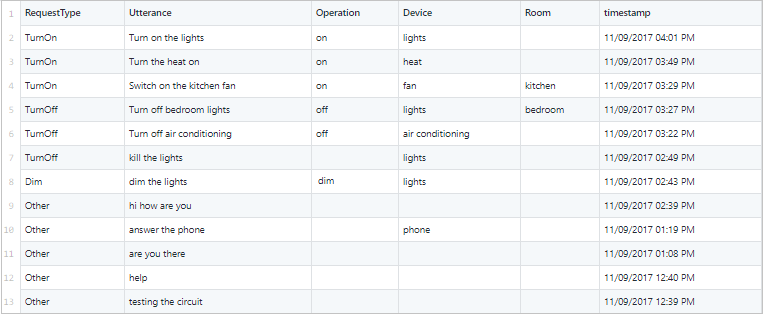
Verá que la columna RequestType podrían ser intenciones. En la columna Request (Solicitud) se muestra una expresión de ejemplo. Los demás campos podrían ser entidades si aparecen en la expresión. Dado que hay intenciones, entidades y expresiones de ejemplo, tiene los requisitos de una aplicación de ejemplo sencilla.
Pasos para generar una aplicación de LUIS a partir de datos que no son de LUIS
Para generar una nueva aplicación de LUIS desde el archivo CSV:
- Analice los datos del archivo CSV:
- Convierta a un formato que pueda cargar en LUIS mediante la API de creación.
- De los datos analizados, recopile información sobre las intenciones y entidades.
- Cree llamadas API de creación para:
- Crear la aplicación.
- Agregue las intenciones y entidades que se recopilaron a partir de los datos analizados.
- Una vez que haya creado la aplicación de LUIS, puede agregar las expresiones de ejemplo a partir de los datos analizados.
Puede ver el flujo de este programa en la última parte del archivo index.js. Copie o descargue este código y guárdelo en index.js.
Importante
Recuerde quitar la clave del código cuando haya terminado y no hacerla nunca pública. En el caso de producción, use una forma segura de almacenar sus credenciales y acceder a ellas, como Azure Key Vault. Consulte el artículo Seguridad de servicios de Azure AI para más información.
var path = require('path');
const parse = require('./_parse');
const createApp = require('./_create');
const addEntities = require('./_entities');
const addIntents = require('./_intents');
const upload = require('./_upload');
// Change these values
const LUIS_authoringKey = "YOUR_AUTHORING_KEY";
const LUIS_appName = "Sample App - build from IoT csv file";
const LUIS_appCulture = "en-us";
const LUIS_versionId = "0.1";
// NOTE: final output of add-utterances api named utterances.upload.json
const downloadFile = "./IoT.csv";
const uploadFile = "./utterances.json"
// The app ID is returned from LUIS when your app is created
var LUIS_appId = ""; // default app ID
var intents = [];
var entities = [];
/* add utterances parameters */
var configAddUtterances = {
LUIS_subscriptionKey: LUIS_authoringKey,
LUIS_appId: LUIS_appId,
LUIS_versionId: LUIS_versionId,
inFile: path.join(__dirname, uploadFile),
batchSize: 100,
uri: "https://westus.api.cognitive.microsoft.com/luis/api/v2.0/apps/{appId}/versions/{versionId}/examples"
};
/* create app parameters */
var configCreateApp = {
LUIS_subscriptionKey: LUIS_authoringKey,
LUIS_versionId: LUIS_versionId,
appName: LUIS_appName,
culture: LUIS_appCulture,
uri: "https://westus.api.cognitive.microsoft.com/luis/api/v2.0/apps/"
};
/* add intents parameters */
var configAddIntents = {
LUIS_subscriptionKey: LUIS_authoringKey,
LUIS_appId: LUIS_appId,
LUIS_versionId: LUIS_versionId,
intentList: intents,
uri: "https://westus.api.cognitive.microsoft.com/luis/api/v2.0/apps/{appId}/versions/{versionId}/intents"
};
/* add entities parameters */
var configAddEntities = {
LUIS_subscriptionKey: LUIS_authoringKey,
LUIS_appId: LUIS_appId,
LUIS_versionId: LUIS_versionId,
entityList: entities,
uri: "https://westus.api.cognitive.microsoft.com/luis/api/v2.0/apps/{appId}/versions/{versionId}/entities"
};
/* input and output files for parsing CSV */
var configParse = {
inFile: path.join(__dirname, downloadFile),
outFile: path.join(__dirname, uploadFile)
};
// Parse CSV
parse(configParse)
.then((model) => {
// Save intent and entity names from parse
intents = model.intents;
entities = model.entities;
// Create the LUIS app
return createApp(configCreateApp);
}).then((appId) => {
// Add intents
LUIS_appId = appId;
configAddIntents.LUIS_appId = appId;
configAddIntents.intentList = intents;
return addIntents(configAddIntents);
}).then(() => {
// Add entities
configAddEntities.LUIS_appId = LUIS_appId;
configAddEntities.entityList = entities;
return addEntities(configAddEntities);
}).then(() => {
// Add example utterances to the intents in the app
configAddUtterances.LUIS_appId = LUIS_appId;
return upload(configAddUtterances);
}).catch(err => {
console.log(err.message);
});
Analizar el archivo CSV
Las entradas de columna que contienen las expresiones en el archivo CSV deben analizarse en un formato JSON que LUIS reconoce. Este formato JSON debe contener un campo intentName que identifique la intención de la expresión. También debe contener un campo entityLabels, que puede estar vacío si no hay ninguna entidad en la expresión.
Por ejemplo, la entrada de "Turn on the lights" (Encender las luces) se asigna a este archivo JSON:
{
"text": "Turn on the lights",
"intentName": "TurnOn",
"entityLabels": [
{
"entityName": "Operation",
"startCharIndex": 5,
"endCharIndex": 6
},
{
"entityName": "Device",
"startCharIndex": 12,
"endCharIndex": 17
}
]
}
En este ejemplo, intentName procede de la solicitud de usuario del encabezado de columna Request (Solicitud) del archivo CSV, mientras que entityName procede de las demás columnas con información clave. Por ejemplo, si hay una entrada para Operation (Operación) o Device (Dispositivo) y esa cadena también aparece en la solicitud real, se puede etiquetar como entidad. En el código siguiente se muestra este proceso de análisis. Puede copiarlo o descargarlo y guardarlo en _parse.js.
// node 7.x
// built with streams for larger files
const fse = require('fs-extra');
const path = require('path');
const lineReader = require('line-reader');
const babyparse = require('babyparse');
const Promise = require('bluebird');
const intent_column = 0;
const utterance_column = 1;
var entityNames = [];
var eachLine = Promise.promisify(lineReader.eachLine);
function listOfIntents(intents) {
return intents.reduce(function (a, d) {
if (a.indexOf(d.intentName) === -1) {
a.push(d.intentName);
}
return a;
}, []);
}
function listOfEntities(utterances) {
return utterances.reduce(function (a, d) {
d.entityLabels.forEach(function(entityLabel) {
if (a.indexOf(entityLabel.entityName) === -1) {
a.push(entityLabel.entityName);
}
}, this);
return a;
}, []);
}
var utterance = function (rowAsString) {
let json = {
"text": "",
"intentName": "",
"entityLabels": [],
};
if (!rowAsString) return json;
let dataRow = babyparse.parse(rowAsString);
// Get intent name and utterance text
json.intentName = dataRow.data[0][intent_column];
json.text = dataRow.data[0][utterance_column];
// For each column heading that may be an entity, search for the element in this column in the utterance.
entityNames.forEach(function (entityName) {
entityToFind = dataRow.data[0][entityName.column];
if (entityToFind != "") {
strInd = json.text.indexOf(entityToFind);
if (strInd > -1) {
let entityLabel = {
"entityName": entityName.name,
"startCharIndex": strInd,
"endCharIndex": strInd + entityToFind.length - 1
}
json.entityLabels.push(entityLabel);
}
}
}, this);
return json;
};
const convert = async (config) => {
try {
var i = 0;
// get inFile stream
inFileStream = await fse.createReadStream(config.inFile, 'utf-8')
// create out file
var myOutFile = await fse.createWriteStream(config.outFile, 'utf-8');
var utterances = [];
// read 1 line at a time
return eachLine(inFileStream, (line) => {
// skip first line with headers
if (i++ == 0) {
// csv to baby parser object
let dataRow = babyparse.parse(line);
// populate entityType list
var index = 0;
dataRow.data[0].forEach(function (element) {
if ((index != intent_column) && (index != utterance_column)) {
entityNames.push({ name: element, column: index });
}
index++;
}, this);
return;
}
// transform utterance from csv to json
utterances.push(utterance(line));
}).then(() => {
console.log("intents: " + JSON.stringify(listOfIntents(utterances)));
console.log("entities: " + JSON.stringify(listOfEntities(utterances)));
myOutFile.write(JSON.stringify({ "converted_date": new Date().toLocaleString(), "utterances": utterances }));
myOutFile.end();
console.log("parse done");
console.log("JSON file should contain utterances. Next step is to create an app with the intents and entities it found.");
var model =
{
intents: listOfIntents(utterances),
entities: listOfEntities(utterances)
}
return model;
});
} catch (err) {
throw err;
}
}
module.exports = convert;
Crear la aplicación de LUIS
Una vez analizados los datos en JSON, agréguelos a una aplicación de LUIS. El siguiente código crea la aplicación de LUIS. Cópielo o descárguelo y guárdelo en _create.js.
// node 7.x
// uses async/await - promises
var rp = require('request-promise');
var fse = require('fs-extra');
var path = require('path');
// main function to call
// Call Apps_Create
var createApp = async (config) => {
try {
// JSON for the request body
// { "name": MyAppName, "culture": "en-us"}
var jsonBody = {
"name": config.appName,
"culture": config.culture
};
// Create a LUIS app
var createAppPromise = callCreateApp({
uri: config.uri,
method: 'POST',
headers: {
'Ocp-Apim-Subscription-Key': config.LUIS_subscriptionKey
},
json: true,
body: jsonBody
});
let results = await createAppPromise;
// Create app returns an app ID
let appId = results.response;
console.log(`Called createApp, created app with ID ${appId}`);
return appId;
} catch (err) {
console.log(`Error creating app: ${err.message} `);
throw err;
}
}
// Send JSON as the body of the POST request to the API
var callCreateApp = async (options) => {
try {
var response;
if (options.method === 'POST') {
response = await rp.post(options);
} else if (options.method === 'GET') { // TODO: There's no GET for create app
response = await rp.get(options);
}
// response from successful create should be the new app ID
return { response };
} catch (err) {
throw err;
}
}
module.exports = createApp;
Adición de intenciones
Cuando tenga una aplicación, debe incorporarle intenciones. El siguiente código crea la aplicación de LUIS. Cópielo o descárguelo y guárdelo en _intents.js.
var rp = require('request-promise');
var fse = require('fs-extra');
var path = require('path');
var request = require('requestretry');
// time delay between requests
const delayMS = 1000;
// retry recount
const maxRetry = 5;
// retry request if error or 429 received
var retryStrategy = function (err, response, body) {
let shouldRetry = err || (response.statusCode === 429);
if (shouldRetry) console.log("retrying add intent...");
return shouldRetry;
}
// Call add-intents
var addIntents = async (config) => {
var intentPromises = [];
config.uri = config.uri.replace("{appId}", config.LUIS_appId).replace("{versionId}", config.LUIS_versionId);
config.intentList.forEach(function (intent) {
config.intentName = intent;
try {
// JSON for the request body
var jsonBody = {
"name": config.intentName,
};
// Create an intent
var addIntentPromise = callAddIntent({
// uri: config.uri,
url: config.uri,
fullResponse: false,
method: 'POST',
headers: {
'Ocp-Apim-Subscription-Key': config.LUIS_subscriptionKey
},
json: true,
body: jsonBody,
maxAttempts: maxRetry,
retryDelay: delayMS,
retryStrategy: retryStrategy
});
intentPromises.push(addIntentPromise);
console.log(`Called addIntents for intent named ${intent}.`);
} catch (err) {
console.log(`Error in addIntents: ${err.message} `);
}
}, this);
let results = await Promise.all(intentPromises);
console.log(`Results of all promises = ${JSON.stringify(results)}`);
let response = results;
}
// Send JSON as the body of the POST request to the API
var callAddIntent = async (options) => {
try {
var response;
response = await request(options);
return { response: response };
} catch (err) {
console.log(`Error in callAddIntent: ${err.message} `);
}
}
module.exports = addIntents;
agregar entidades
El código siguiente agrega las entidades a la aplicación de LUIS. Cópielo o descárguelo y guárdelo en _entities.js.
// node 7.x
// uses async/await - promises
const request = require("requestretry");
var rp = require('request-promise');
var fse = require('fs-extra');
var path = require('path');
// time delay between requests
const delayMS = 1000;
// retry recount
const maxRetry = 5;
// retry request if error or 429 received
var retryStrategy = function (err, response, body) {
let shouldRetry = err || (response.statusCode === 429);
if (shouldRetry) console.log("retrying add entity...");
return shouldRetry;
}
// main function to call
// Call add-entities
var addEntities = async (config) => {
var entityPromises = [];
config.uri = config.uri.replace("{appId}", config.LUIS_appId).replace("{versionId}", config.LUIS_versionId);
config.entityList.forEach(function (entity) {
try {
config.entityName = entity;
// JSON for the request body
// { "name": MyEntityName}
var jsonBody = {
"name": config.entityName,
};
// Create an app
var addEntityPromise = callAddEntity({
url: config.uri,
fullResponse: false,
method: 'POST',
headers: {
'Ocp-Apim-Subscription-Key': config.LUIS_subscriptionKey
},
json: true,
body: jsonBody,
maxAttempts: maxRetry,
retryDelay: delayMS,
retryStrategy: retryStrategy
});
entityPromises.push(addEntityPromise);
console.log(`called addEntity for entity named ${entity}.`);
} catch (err) {
console.log(`Error in addEntities: ${err.message} `);
//throw err;
}
}, this);
let results = await Promise.all(entityPromises);
console.log(`Results of all promises = ${JSON.stringify(results)}`);
let response = results;// await fse.writeJson(createResults.json, results);
}
// Send JSON as the body of the POST request to the API
var callAddEntity = async (options) => {
try {
var response;
response = await request(options);
return { response: response };
} catch (err) {
console.log(`error in callAddEntity: ${err.message}`);
}
}
module.exports = addEntities;
Adición de grabaciones de voz
Una vez que se hayan definido las entidades e intenciones en la aplicación de LUIS, puede agregar las expresiones. En el siguiente código se usa la API Utterances_AddBatch, con la que se pueden agregar hasta 100 expresiones a la vez. Cópielo o descárguelo y guárdelo en _upload.js.
// node 7.x
// uses async/await - promises
var rp = require('request-promise');
var fse = require('fs-extra');
var path = require('path');
var request = require('requestretry');
// time delay between requests
const delayMS = 500;
// retry recount
const maxRetry = 5;
// retry request if error or 429 received
var retryStrategy = function (err, response, body) {
let shouldRetry = err || (response.statusCode === 429);
if (shouldRetry) console.log("retrying add examples...");
return shouldRetry;
}
// main function to call
var upload = async (config) => {
try{
// read in utterances
var entireBatch = await fse.readJson(config.inFile);
// break items into pages to fit max batch size
var pages = getPagesForBatch(entireBatch.utterances, config.batchSize);
var uploadPromises = [];
// load up promise array
pages.forEach(page => {
config.uri = "https://westus.api.cognitive.microsoft.com/luis/api/v2.0/apps/{appId}/versions/{versionId}/examples".replace("{appId}", config.LUIS_appId).replace("{versionId}", config.LUIS_versionId)
var pagePromise = sendBatchToApi({
url: config.uri,
fullResponse: false,
method: 'POST',
headers: {
'Ocp-Apim-Subscription-Key': config.LUIS_subscriptionKey
},
json: true,
body: page,
maxAttempts: maxRetry,
retryDelay: delayMS,
retryStrategy: retryStrategy
});
uploadPromises.push(pagePromise);
})
//execute promise array
let results = await Promise.all(uploadPromises)
console.log(`\n\nResults of all promises = ${JSON.stringify(results)}`);
let response = await fse.writeJson(config.inFile.replace('.json','.upload.json'),results);
console.log("upload done");
} catch(err){
throw err;
}
}
// turn whole batch into pages batch
// because API can only deal with N items in batch
var getPagesForBatch = (batch, maxItems) => {
try{
var pages = [];
var currentPage = 0;
var pageCount = (batch.length % maxItems == 0) ? Math.round(batch.length / maxItems) : Math.round((batch.length / maxItems) + 1);
for (let i = 0;i<pageCount;i++){
var currentStart = currentPage * maxItems;
var currentEnd = currentStart + maxItems;
var pagedBatch = batch.slice(currentStart,currentEnd);
var j = 0;
pagedBatch.forEach(item=>{
item.ExampleId = j++;
});
pages.push(pagedBatch);
currentPage++;
}
return pages;
}catch(err){
throw(err);
}
}
// send json batch as post.body to API
var sendBatchToApi = async (options) => {
try {
var response = await request(options);
//return {page: options.body, response:response};
return {response:response};
}catch(err){
throw err;
}
}
module.exports = upload;
Ejecución del código
Instalar las dependencias de Node.js
Instale las dependencias de Node.js en la línea de comandos o terminal.
> npm install
Cambiar la configuración
Para poder usar esta aplicación, debe cambiar los valores del archivo index.js por su clave de punto de conexión e indicar el nombre que quiere que tenga la aplicación. También puede establecer la referencia cultural de la aplicación o cambiar el número de versión.
Abra el archivo index.js y cambie estos valores en la parte superior del archivo.
// Change these values
const LUIS_programmaticKey = "YOUR_AUTHORING_KEY";
const LUIS_appName = "Sample App";
const LUIS_appCulture = "en-us";
const LUIS_versionId = "0.1";
Ejecute el script.
Ejecute el script desde un terminal o línea de comandos con Node.js.
> node index.js
Or
> npm start
Progreso de la aplicación
Mientras se ejecuta la aplicación, en la línea de comandos se muestra el progreso. El resultado de la línea de comandos incluye el formato de las respuestas de LUIS.
> node index.js
intents: ["TurnOn","TurnOff","Dim","Other"]
entities: ["Operation","Device","Room"]
parse done
JSON file should contain utterances. Next step is to create an app with the intents and entities it found.
Called createApp, created app with ID 314b306c-0033-4e09-92ab-94fe5ed158a2
Called addIntents for intent named TurnOn.
Called addIntents for intent named TurnOff.
Called addIntents for intent named Dim.
Called addIntents for intent named Other.
Results of all calls to addIntent = [{"response":"e7eaf224-8c61-44ed-a6b0-2ab4dc56f1d0"},{"response":"a8a17efd-f01c-488d-ad44-a31a818cf7d7"},{"response":"bc7c32fc-14a0-4b72-bad4-d345d807f965"},{"response":"727a8d73-cd3b-4096-bc8d-d7cfba12eb44"}]
called addEntity for entity named Operation.
called addEntity for entity named Device.
called addEntity for entity named Room.
Results of all calls to addEntity= [{"response":"6a7e914f-911d-4c6c-a5bc-377afdce4390"},{"response":"56c35237-593d-47f6-9d01-2912fa488760"},{"response":"f1dd440c-2ce3-4a20-a817-a57273f169f3"}]
retrying add examples...
Results of add utterances = [{"response":[{"value":{"UtteranceText":"turn on the lights","ExampleId":-67649},"hasError":false},{"value":{"UtteranceText":"turn the heat on","ExampleId":-69067},"hasError":false},{"value":{"UtteranceText":"switch on the kitchen fan","ExampleId":-3395901},"hasError":false},{"value":{"UtteranceText":"turn off bedroom lights","ExampleId":-85402},"hasError":false},{"value":{"UtteranceText":"turn off air conditioning","ExampleId":-8991572},"hasError":false},{"value":{"UtteranceText":"kill the lights","ExampleId":-70124},"hasError":false},{"value":{"UtteranceText":"dim the lights","ExampleId":-174358},"hasError":false},{"value":{"UtteranceText":"hi how are you","ExampleId":-143722},"hasError":false},{"value":{"UtteranceText":"answer the phone","ExampleId":-69939},"hasError":false},{"value":{"UtteranceText":"are you there","ExampleId":-149588},"hasError":false},{"value":{"UtteranceText":"help","ExampleId":-81949},"hasError":false},{"value":{"UtteranceText":"testing the circuit","ExampleId":-11548708},"hasError":false}]}]
upload done
Abra la aplicación de LUIS
Una vez concluido el script, puede iniciar sesión en LUIS y ver la aplicación de LUIS que ha creado en Mis aplicaciones. Debería poder ver las expresiones que ha agregado en las intenciones TurnOn, TurnOff y None.
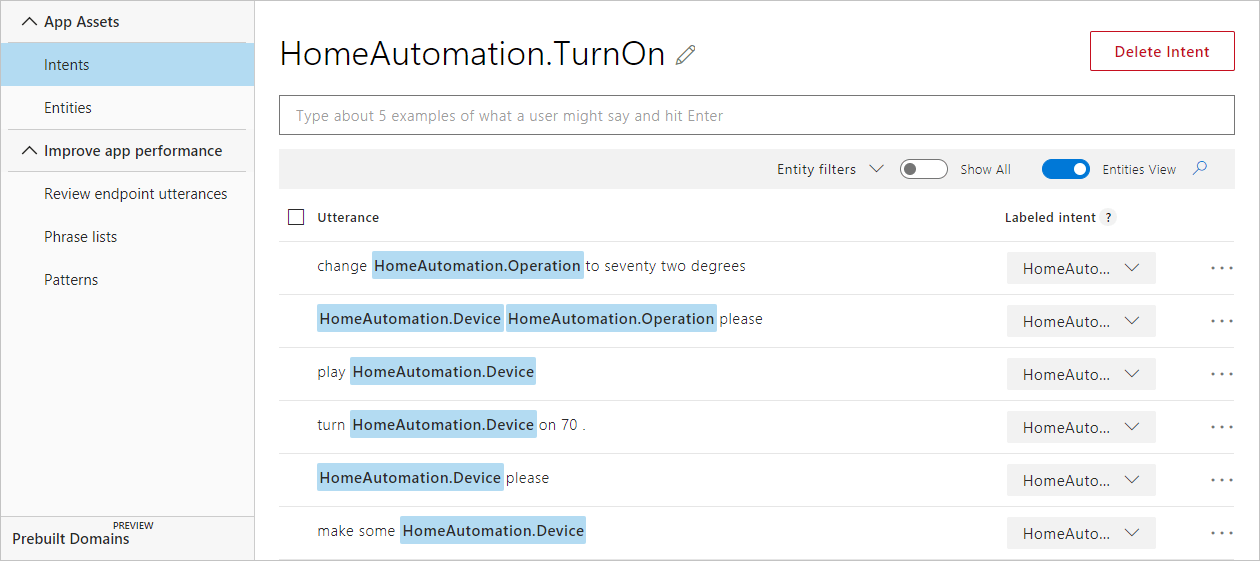
Pasos siguientes
Probar y entrenar la aplicación en el sitio web de LUIS.
Recursos adicionales
En esta aplicación de ejemplo se usan las siguientes API de LUIS: