Niveles de zoom y cuadrícula de mosaico
Azure Maps usa el sistema de coordenadas de la proyección de Mercator esférica (EPSG:3857). Una proyección es el modelo matemático que se usa para transformar el globo terráqueo en un mapa plano. La proyección de Mercator esférica estira el mapa en los polos para crear un mapa cuadrado. Esta proyección distorsiona mucho la escala y el área del mapa, pero tiene dos propiedades importantes que compensan esta distorsión:
- Se trata de una proyección conforme, lo que significa que conserva la forma de los objetos relativamente pequeños. Conservar la forma de los objetos pequeños es especialmente importante cuando se muestra una imagen aérea. Por ejemplo, queremos evitar la distorsión de la forma de los edificios. Los edificios cuadrados deben aparecer cuadrados, no rectangulares.
- Se trata de una proyección cilíndrica. El norte y el sur siempre están activados, y oeste y este siempre están a la izquierda y a la derecha.
Para optimizar el rendimiento de la recuperación y visualización del mapa, este se divide en mosaicos cuadrados. Los SDK de Azure Maps usan mosaicos con un tamaño de 512×512 píxeles para los mapas de carreteras, y más pequeños, 256×256 píxeles, para las imágenes satelitales. Azure Maps proporciona mosaicos de trama y vectoriales para 23 niveles de zoom, numerados de 0 a 22. En el nivel de zoom 0, todo el mundo cabe en un solo mosaico:
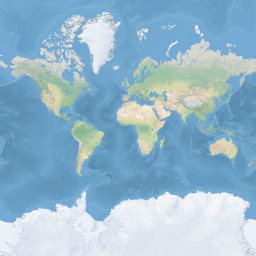
El nivel de zoom 1 utiliza cuatro mosaicos para representar el mundo: un cuadrado de 2 x 2

Cada nivel de zoom adicional divide por cuatro los mosaicos del anterior, de forma que se crea una cuadrícula de 2zoom x 2zoom. El nivel de zoom 22 es una cuadrícula de 222 x 222 o 4 194 304 x 4 194 304 mosaicos (17 592 186 044 416 mosaicos en total).
Los controles de mapa interactivo de Azure Maps para web y Android admiten 25 niveles de zoom, numerados de 0 a 24. Aunque los datos de carretera solo están disponibles en los niveles de zoom cuando los mosaicos estén disponibles.
En la tabla siguiente se proporciona la lista completa de valores para los niveles de zoom en los que el tamaño del mosaico es un cuadrado de 256 píxeles:
| Nivel de zoom | Metros/píxel | Metros/lado de mosaico |
|---|---|---|
| 0 | 156543 | 40075017 |
| 1 | 78271,5 | 20037508 |
| 2 | 39135,8 | 10018754 |
| 3 | 19567.88 | 5009377.1 |
| 4 | 9783.94 | 2504688.5 |
| 5 | 4891.97 | 1252344.3 |
| 6 | 2445.98 | 626172.1 |
| 7 | 1222.99 | 313086.1 |
| 8 | 611,5 | 156543 |
| 9 | 305.75 | 78271,5 |
| 10 | 152.87 | 39135,8 |
| 11 | 76.44 | 19567,9 |
| 12 | 38.219 | 9783.94 |
| 13 | 19.109 | 4891.97 |
| 14 | 9.555 | 2445.98 |
| 15 | 4.777 | 1222.99 |
| 16 | 2.3887 | 611.496 |
| 17 | 1.1943 | 305.748 |
| 18 | 0.5972 | 152.874 |
| 19 | 0.2986 | 76.437 |
| 20 | 0.14929 | 38.2185 |
| 21 | 0.074646 | 19.10926 |
| 22 | 0.037323 | 9.55463 |
| 23 | 0.0186615 | 4.777315 |
| 24 | 0.00933075 | 2.3886575 |
Coordenadas de píxeles
Tras elegir la proyección y la escala que se usarán en cada nivel de zoom, se pueden convertir las coordenadas geográficas en coordenadas de píxeles. El ancho y la altura de píxel completos de una imagen de mapa del mundo para un nivel de zoom determinado se calcula como:
var mapWidth = tileSize * Math.pow(2, zoom);
var mapHeight = mapWidth;
Dado que el ancho y la altura del mapa son diferentes en cada nivel de zoom, también lo son las coordenadas de los píxeles. El píxel situado en la esquina superior izquierda del mapa siempre tiene coordenadas de píxel (0, 0). El píxel situado en la esquina inferior derecha del mapa tiene coordenadas de píxel (width-1, height-1) o, haciendo referencia a las ecuaciones de la sección anterior, (tileSize * 2zoom–1, tileSize * 2zoom–1). Por ejemplo, al usar mosaicos cuadrados de 512 en el nivel 2, las coordenadas de los píxeles van de (0, 0) a (2047, 2047), como se observa a continuación:

Dada la latitud y la longitud en grados y el nivel de detalle, las coordenadas XY de los píxeles se calcula de la manera siguiente:
var sinLatitude = Math.sin(latitude * Math.PI/180);
var pixelX = ((longitude + 180) / 360) * tileSize * Math.pow(2, zoom);
var pixelY = (0.5 – Math.log((1 + sinLatitude) / (1 – sinLatitude)) / (4 * Math.PI)) * tileSize * Math.pow(2, zoom);
Se supone que los valores de latitud y longitud se encuentran en el datum WGS 84. Aunque Azure Maps usa una proyección esférica, es importante convertir todas las coordenadas geográficas en un dato común. WGS 84 es el dato de referencia elegido. Se supone que el valor de longitud oscila entre -180 y +180 grados, y el valor de latitud debe recortarse para variar entre -85,05112878 y 85,05112878. La adhesión a estos valores evita una singularidad en los polos y garantiza que el mapa proyectado tenga una forma cuadrada.
Coordenadas de mosaicos
Para optimizar el rendimiento de la recuperación y visualización del mapa, el mapa representado se corta en mosaicos. El número de píxeles y el número de mosaicos difieren en cada nivel de zoom:
var numberOfTilesWide = Math.pow(2, zoom);
var numberOfTilesHigh = numberOfTilesWide;
Cada mosaico tiene coordenadas XY que van de (0, 0) en la esquina superior izquierda a (2zoom–1, 2zoom–1) en la esquina inferior derecha. Por ejemplo, en el nivel de zoom 3, las coordenadas del mosaico van de (0, 0) a (7, 7) de la manera siguiente:

Dado un par de coordenadas XY de píxeles, puede determinar fácilmente las coordenadas XY del mosaico que contiene ese píxel:
var tileX = Math.floor(pixelX / tileSize);
var tileY = Math.floor(pixelY / tileSize);
El nivel de zoom determina los mosaicos. Las coordenadas x e y se corresponden con la posición del mosaico en la cuadrícula para ese nivel de zoom.
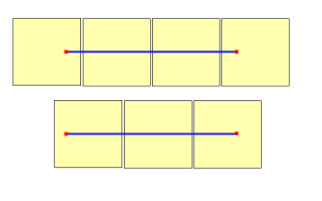
Al determinar qué nivel de zoom se usará, recuerde que cada ubicación está en una posición fija en su mosaico. Como resultado, el número de mosaicos necesarios para mostrar una extensión determinada del territorio depende de la ubicación específica de la cuadrícula de zoom en el mundo. Por ejemplo, si hay dos puntos separados 900 metros, puede que al mostrar una ruta entre ellos en el nivel de zoom 17, solo ocupen tres mosaicos. Sin embargo, si el punto occidental está a la derecha de su mosaico y el punto oriental a la izquierda, puede ocupar cuatro mosaicos:
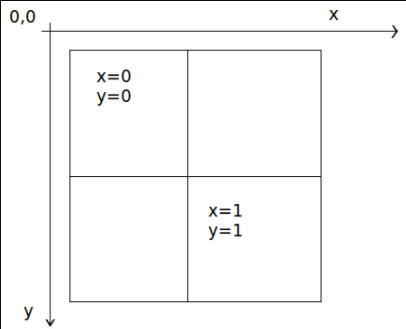
Una vez determinado el nivel de zoom, se pueden calcular los valores x e y. El mosaico superior izquierdo de cada cuadrícula de zoom es x=0, y=0; el mosaico inferior derecho está en x=2zoom-1, y=2zoom-1.
Esta es la cuadrícula de zoom para el nivel de zoom 1:
Índices de quadkeys
Algunas plataformas de mapas usan una convención de nomenclatura de indexación de quadkey que combina las coordenadas ZY de un mosaico en una cadena de una sola dimensión llamada "claves de quadtree" o simplemente "quadkeys". Cada quadkey identifica de forma inequívoca un único mosaico con un nivel de detalle determinado y se puede usar como clave en los índices comunes de árbol B de la base de datos. Los SDK de Azure Maps permiten superponer capas de mosaicos que usan la convención de nomenclatura de quadkey, además de otras convenciones de nomenclatura, tal y como se documenta en quadkey.
Nota
La convención de nomenclatura de quadkeys solo funciona con los niveles de zoom iguales o mayores que uno. Los SDK de Azure Maps admiten el nivel de zoom de 0, que es un único mosaico de mapa para todo el mundo.
Para convertir las coordenadas del mosaico en un quadkey, los bits de las coordenadas Y y X se intercalan, y el resultado se interpreta como un número en base 4 (donde se mantienen los ceros iniciales) y se convierte en una cadena. Por ejemplo, dadas las coordenadas XY (3, 5) de un mosaico de nivel 3, el valor de quadkey se calcula de la siguiente manera:
tileX = 3 = 011 (base 2)
tileY = 5 = 101 (base 2)
quadkey = 100111 (base 2) = 213 (base 4) = "213"
Los Qquadkeys tienen varias propiedades interesantes. En primer lugar, la longitud de un quadkey (el número de dígitos) es igual al nivel de zoom del mosaico correspondiente. En segundo lugar, el quadkey de cualquier mosaico comienza con el quadkey de su mosaico primario (el mosaico contenedor del nivel anterior). Como se muestra en el ejemplo siguiente, el mosaico 2 es el elemento primario de los mosaicos 20 a 23:

Por último, los quadkeys proporcionan una clave de índice unidimensional que normalmente respeta la proximidad de los mosaicos en el espacio XY. En otras palabras, normalmente, dos mosaicos que tengan coordenadas XY cercanas tendrán quadkeys que estarán relativamente cerca. Esto es importante para optimizar el rendimiento de la base de datos, porque a menudo los mosaicos vecinos se solicitan en grupos, por lo que es conveniente mantener esos mosaicos en los mismos bloques de disco, con el fin de minimizar el número de lecturas de disco.
Código fuente de la matemática de los mosaicos
En el código de ejemplo siguiente se muestra cómo implementar las funciones descritas en este documento. Estas funciones se pueden traducir fácilmente a otros lenguajes de programación según sea necesario.
using System;
using System.Text;
namespace AzureMaps
{
/// <summary>
/// Tile System math for the Spherical Mercator projection coordinate system (EPSG:3857)
/// </summary>
public static class TileMath
{
//Earth radius in meters.
private const double EarthRadius = 6378137;
private const double MinLatitude = -85.05112878;
private const double MaxLatitude = 85.05112878;
private const double MinLongitude = -180;
private const double MaxLongitude = 180;
/// <summary>
/// Clips a number to the specified minimum and maximum values.
/// </summary>
/// <param name="n">The number to clip.</param>
/// <param name="minValue">Minimum allowable value.</param>
/// <param name="maxValue">Maximum allowable value.</param>
/// <returns>The clipped value.</returns>
private static double Clip(double n, double minValue, double maxValue)
{
return Math.Min(Math.Max(n, minValue), maxValue);
}
/// <summary>
/// Calculates width and height of the map in pixels at a specific zoom level from -180 degrees to 180 degrees.
/// </summary>
/// <param name="zoom">Zoom Level to calculate width at</param>
/// <param name="tileSize">The size of the tiles in the tile pyramid.</param>
/// <returns>Width and height of the map in pixels</returns>
public static double MapSize(double zoom, int tileSize)
{
return Math.Ceiling(tileSize * Math.Pow(2, zoom));
}
/// <summary>
/// Calculates the Ground resolution at a specific degree of latitude in meters per pixel.
/// </summary>
/// <param name="latitude">Degree of latitude to calculate resolution at</param>
/// <param name="zoom">Zoom level to calculate resolution at</param>
/// <param name="tileSize">The size of the tiles in the tile pyramid.</param>
/// <returns>Ground resolution in meters per pixels</returns>
public static double GroundResolution(double latitude, double zoom, int tileSize)
{
latitude = Clip(latitude, MinLatitude, MaxLatitude);
return Math.Cos(latitude * Math.PI / 180) * 2 * Math.PI * EarthRadius / MapSize(zoom, tileSize);
}
/// <summary>
/// Determines the map scale at a specified latitude, level of detail, and screen resolution.
/// </summary>
/// <param name="latitude">Latitude (in degrees) at which to measure the map scale.</param>
/// <param name="zoom">Level of detail, from 1 (lowest detail) to 23 (highest detail).</param>
/// <param name="screenDpi">Resolution of the screen, in dots per inch.</param>
/// <param name="tileSize">The size of the tiles in the tile pyramid.</param>
/// <returns>The map scale, expressed as the denominator N of the ratio 1 : N.</returns>
public static double MapScale(double latitude, double zoom, int screenDpi, int tileSize)
{
return GroundResolution(latitude, zoom, tileSize) * screenDpi / 0.0254;
}
/// <summary>
/// Global Converts a Pixel coordinate into a geospatial coordinate at a specified zoom level.
/// Global Pixel coordinates are relative to the top left corner of the map (90, -180)
/// </summary>
/// <param name="pixel">Pixel coordinates in the format of [x, y].</param>
/// <param name="zoom">Zoom level</param>
/// <param name="tileSize">The size of the tiles in the tile pyramid.</param>
/// <returns>A position value in the format [longitude, latitude].</returns>
public static double[] GlobalPixelToPosition(double[] pixel, double zoom, int tileSize)
{
var mapSize = MapSize(zoom, tileSize);
var x = (Clip(pixel[0], 0, mapSize - 1) / mapSize) - 0.5;
var y = 0.5 - (Clip(pixel[1], 0, mapSize - 1) / mapSize);
return new double[] {
360 * x, //Longitude
90 - 360 * Math.Atan(Math.Exp(-y * 2 * Math.PI)) / Math.PI //Latitude
};
}
/// <summary>
/// Converts a point from latitude/longitude WGS-84 coordinates (in degrees) into pixel XY coordinates at a specified level of detail.
/// </summary>
/// <param name="position">Position coordinate in the format [longitude, latitude]</param>
/// <param name="zoom">Zoom level.</param>
/// <param name="tileSize">The size of the tiles in the tile pyramid.</param>
/// <returns>A global pixel coordinate.</returns>
public static double[] PositionToGlobalPixel(double[] position, int zoom, int tileSize)
{
var latitude = Clip(position[1], MinLatitude, MaxLatitude);
var longitude = Clip(position[0], MinLongitude, MaxLongitude);
var x = (longitude + 180) / 360;
var sinLatitude = Math.Sin(latitude * Math.PI / 180);
var y = 0.5 - Math.Log((1 + sinLatitude) / (1 - sinLatitude)) / (4 * Math.PI);
var mapSize = MapSize(zoom, tileSize);
return new double[] {
Clip(x * mapSize + 0.5, 0, mapSize - 1),
Clip(y * mapSize + 0.5, 0, mapSize - 1)
};
}
/// <summary>
/// Converts pixel XY coordinates into tile XY coordinates of the tile containing the specified pixel.
/// </summary>
/// <param name="pixel">Pixel coordinates in the format of [x, y].</param>
/// <param name="tileSize">The size of the tiles in the tile pyramid.</param>
/// <param name="tileX">Output parameter receiving the tile X coordinate.</param>
/// <param name="tileY">Output parameter receiving the tile Y coordinate.</param>
public static void GlobalPixelToTileXY(double[] pixel, int tileSize, out int tileX, out int tileY)
{
tileX = (int)(pixel[0] / tileSize);
tileY = (int)(pixel[1] / tileSize);
}
/// <summary>
/// Performs a scale transform on a global pixel value from one zoom level to another.
/// </summary>
/// <param name="pixel">Pixel coordinates in the format of [x, y].</param>
/// <param name="oldZoom">The zoom level in which the input global pixel value is from.</param>
/// <returns>A scale pixel coordinate.</returns>
public static double[] ScaleGlobalPixel(double[] pixel, double oldZoom, double newZoom)
{
var scale = Math.Pow(2, oldZoom - newZoom);
return new double[] { pixel[0] * scale, pixel[1] * scale };
}
/// <summary>
/// Performs a scale transform on a set of global pixel values from one zoom level to another.
/// </summary>
/// <param name="pixels">A set of global pixel value from the old zoom level. Points are in the format [x,y].</param>
/// <param name="oldZoom">The zoom level in which the input global pixel values is from.</param>
/// <param name="newZoom">The new zoom level in which the output global pixel values should be aligned with.</param>
/// <returns>A set of global pixel values that has been scaled for the new zoom level.</returns>
public static double[][] ScaleGlobalPixels(double[][] pixels, double oldZoom, double newZoom)
{
var scale = Math.Pow(2, oldZoom - newZoom);
var output = new System.Collections.Generic.List<double[]>();
foreach (var p in pixels)
{
output.Add(new double[] { p[0] * scale, p[1] * scale });
}
return output.ToArray();
}
/// <summary>
/// Converts tile XY coordinates into a global pixel XY coordinates of the upper-left pixel of the specified tile.
/// </summary>
/// <param name="tileX">Tile X coordinate.</param>
/// <param name="tileY">Tile Y coordinate.</param>
/// <param name="tileSize">The size of the tiles in the tile pyramid.</param>
/// <param name="pixelX">Output parameter receiving the X coordinate of the point, in pixels.</param>
/// <param name="pixelY">Output parameter receiving the Y coordinate of the point, in pixels.</param>
public static double[] TileXYToGlobalPixel(int tileX, int tileY, int tileSize)
{
return new double[] { tileX * tileSize, tileY * tileSize };
}
/// <summary>
/// Converts tile XY coordinates into a quadkey at a specified level of detail.
/// </summary>
/// <param name="tileX">Tile X coordinate.</param>
/// <param name="tileY">Tile Y coordinate.</param>
/// <param name="zoom">Zoom level</param>
/// <returns>A string containing the quadkey.</returns>
public static string TileXYToQuadKey(int tileX, int tileY, int zoom)
{
var quadKey = new StringBuilder();
for (int i = zoom; i > 0; i--)
{
char digit = '0';
int mask = 1 << (i - 1);
if ((tileX & mask) != 0)
{
digit++;
}
if ((tileY & mask) != 0)
{
digit++;
digit++;
}
quadKey.Append(digit);
}
return quadKey.ToString();
}
/// <summary>
/// Converts a quadkey into tile XY coordinates.
/// </summary>
/// <param name="quadKey">Quadkey of the tile.</param>
/// <param name="tileX">Output parameter receiving the tile X coordinate.</param>
/// <param name="tileY">Output parameter receiving the tile Y coordinate.</param>
/// <param name="zoom">Output parameter receiving the zoom level.</param>
public static void QuadKeyToTileXY(string quadKey, out int tileX, out int tileY, out int zoom)
{
tileX = tileY = 0;
zoom = quadKey.Length;
for (int i = zoom; i > 0; i--)
{
int mask = 1 << (i - 1);
switch (quadKey[zoom - i])
{
case '0':
break;
case '1':
tileX |= mask;
break;
case '2':
tileY |= mask;
break;
case '3':
tileX |= mask;
tileY |= mask;
break;
default:
throw new ArgumentException("Invalid QuadKey digit sequence.");
}
}
}
/// <summary>
/// Calculates the XY tile coordinates that a coordinate falls into for a specific zoom level.
/// </summary>
/// <param name="position">Position coordinate in the format [longitude, latitude]</param>
/// <param name="zoom">Zoom level</param>
/// <param name="tileSize">The size of the tiles in the tile pyramid.</param>
/// <param name="tileX">Output parameter receiving the tile X position.</param>
/// <param name="tileY">Output parameter receiving the tile Y position.</param>
public static void PositionToTileXY(double[] position, int zoom, int tileSize, out int tileX, out int tileY)
{
var latitude = Clip(position[1], MinLatitude, MaxLatitude);
var longitude = Clip(position[0], MinLongitude, MaxLongitude);
var x = (longitude + 180) / 360;
var sinLatitude = Math.Sin(latitude * Math.PI / 180);
var y = 0.5 - Math.Log((1 + sinLatitude) / (1 - sinLatitude)) / (4 * Math.PI);
//tileSize needed in calculations as in rare cases the multiplying/rounding/dividing can make the difference of a pixel which can result in a completely different tile.
var mapSize = MapSize(zoom, tileSize);
tileX = (int)Math.Floor(Clip(x * mapSize + 0.5, 0, mapSize - 1) / tileSize);
tileY = (int)Math.Floor(Clip(y * mapSize + 0.5, 0, mapSize - 1) / tileSize);
}
/// <summary>
/// Calculates the tile quadkey strings that are within a specified viewport.
/// </summary>
/// <param name="position">Position coordinate in the format [longitude, latitude]</param>
/// <param name="zoom">Zoom level</param>
/// <param name="width">The width of the map viewport in pixels.</param>
/// <param name="height">The height of the map viewport in pixels.</param>
/// <param name="tileSize">The size of the tiles in the tile pyramid.</param>
/// <returns>A list of quadkey strings that are within the specified viewport.</returns>
public static string[] GetQuadkeysInView(double[] position, int zoom, int width, int height, int tileSize)
{
var p = PositionToGlobalPixel(position, zoom, tileSize);
var top = p[1] - height * 0.5;
var left = p[0] - width * 0.5;
var bottom = p[1] + height * 0.5;
var right = p[0] + width * 0.5;
var tl = GlobalPixelToPosition(new double[] { left, top }, zoom, tileSize);
var br = GlobalPixelToPosition(new double[] { right, bottom }, zoom, tileSize);
//Boudning box in the format: [west, south, east, north];
var bounds = new double[] { tl[0], br[1], br[0], tl[1] };
return GetQuadkeysInBoundingBox(bounds, zoom, tileSize);
}
/// <summary>
/// Calculates the tile quadkey strings that are within a bounding box at a specific zoom level.
/// </summary>
/// <param name="bounds">A bounding box defined as an array of numbers in the format of [west, south, east, north].</param>
/// <param name="zoom">Zoom level to calculate tiles for.</param>
/// <param name="tileSize">The size of the tiles in the tile pyramid.</param>
/// <returns>A list of quadkey strings.</returns>
public static string[] GetQuadkeysInBoundingBox(double[] bounds, int zoom, int tileSize)
{
var keys = new System.Collections.Generic.List<string>();
if (bounds != null && bounds.Length >= 4)
{
PositionToTileXY(new double[] { bounds[3], bounds[0] }, zoom, tileSize, out int tlX, out int tlY);
PositionToTileXY(new double[] { bounds[1], bounds[2] }, zoom, tileSize, out int brX, out int brY);
for (int x = tlX; x <= brX; x++)
{
for (int y = tlY; y <= brY; y++)
{
keys.Add(TileXYToQuadKey(x, y, zoom));
}
}
}
return keys.ToArray();
}
/// <summary>
/// Calculates the bounding box of a tile.
/// </summary>
/// <param name="tileX">Tile X coordinate</param>
/// <param name="tileY">Tile Y coordinate</param>
/// <param name="zoom">Zoom level</param>
/// <param name="tileSize">The size of the tiles in the tile pyramid.</param>
/// <returns>A bounding box of the tile defined as an array of numbers in the format of [west, south, east, north].</returns>
public static double[] TileXYToBoundingBox(int tileX, int tileY, double zoom, int tileSize)
{
//Top left corner pixel coordinates
var x1 = (double)(tileX * tileSize);
var y1 = (double)(tileY * tileSize);
//Bottom right corner pixel coordinates
var x2 = (double)(x1 + tileSize);
var y2 = (double)(y1 + tileSize);
var nw = GlobalPixelToPosition(new double[] { x1, y1 }, zoom, tileSize);
var se = GlobalPixelToPosition(new double[] { x2, y2 }, zoom, tileSize);
return new double[] { nw[0], se[1], se[0], nw[1] };
}
/// <summary>
/// Calculates the best map view (center, zoom) for a bounding box on a map.
/// </summary>
/// <param name="bounds">A bounding box defined as an array of numbers in the format of [west, south, east, north].</param>
/// <param name="mapWidth">Map width in pixels.</param>
/// <param name="mapHeight">Map height in pixels.</param>
/// <param name="padding">Width in pixels to use to create a buffer around the map. This is to keep markers from being cut off on the edge</param>
/// <param name="tileSize">The size of the tiles in the tile pyramid.</param>
/// <param name="latitude">Output parameter receiving the center latitude coordinate.</param>
/// <param name="longitude">Output parameter receiving the center longitude coordinate.</param>
/// <param name="zoom">Output parameter receiving the zoom level</param>
public static void BestMapView(double[] bounds, double mapWidth, double mapHeight, int padding, int tileSize, out double centerLat, out double centerLon, out double zoom)
{
if (bounds == null || bounds.Length < 4)
{
centerLat = 0;
centerLon = 0;
zoom = 1;
return;
}
double boundsDeltaX;
//Check if east value is greater than west value which would indicate that bounding box crosses the antimeridian.
if (bounds[2] > bounds[0])
{
boundsDeltaX = bounds[2] - bounds[0];
centerLon = (bounds[2] + bounds[0]) / 2;
}
else
{
boundsDeltaX = 360 - (bounds[0] - bounds[2]);
centerLon = ((bounds[2] + bounds[0]) / 2 + 360) % 360 - 180;
}
var ry1 = Math.Log((Math.Sin(bounds[1] * Math.PI / 180) + 1) / Math.Cos(bounds[1] * Math.PI / 180));
var ry2 = Math.Log((Math.Sin(bounds[3] * Math.PI / 180) + 1) / Math.Cos(bounds[3] * Math.PI / 180));
var ryc = (ry1 + ry2) / 2;
centerLat = Math.Atan(Math.Sinh(ryc)) * 180 / Math.PI;
var resolutionHorizontal = boundsDeltaX / (mapWidth - padding * 2);
var vy0 = Math.Log(Math.Tan(Math.PI * (0.25 + centerLat / 360)));
var vy1 = Math.Log(Math.Tan(Math.PI * (0.25 + bounds[3] / 360)));
var zoomFactorPowered = (mapHeight * 0.5 - padding) / (40.7436654315252 * (vy1 - vy0));
var resolutionVertical = 360.0 / (zoomFactorPowered * tileSize);
var resolution = Math.Max(resolutionHorizontal, resolutionVertical);
zoom = Math.Log(360 / (resolution * tileSize), 2);
}
}
}
Nota
Los controles de mapa interactivos de los SDK de Azure Maps tienen funciones auxiliares para la conversión entre las posiciones geoespaciales y los píxeles de la ventanilla.
Pasos siguientes
Acceda directamente a los mosaicos de mapa desde los servicios de REST de Azure Maps:
Más información sobre los conceptos geoespaciales: