Consolidated Currency Translation with Management Reporter GP Legacy Provider
This document covers creating a consolidated currency translation report that uses Microsoft Dynamics GP and Management Reporter Dynamics GP Legacy provider.
Applies to: Microsoft Dynamics GP
Original KB number: 2575539
Symptoms
There are many ways of setting up currency translation and reports in Microsoft Dynamics GP and Management Reporter, but for the purposes of this document, we'll make the following assumptions.
Note
The information described below doesn't pertain to the Management Reporter Dynamics GP Data Mart provider.
You have two companies set up in Dynamics GP. One is set with a functional currency of USD, and the other is set to a functional currency of CAD.
You want to create a consolidated report in Management Reporter where the CAD company is converted to USD.
Your two companies are using the same chart of accounts.
You're using the Management Reporter Dynamics GP Legacy provider.
To create and use currency translation, you must be using the following software.
Microsoft Dynamics GP 2010 SP1 or a later version
Management Reporter V2 FP1 or a later version
More information
Section 1: Dynamics GP and Currency Translation Setup
Functional Currency
Create Exchange Tables and Enter Rates
Multicurrency Access
Multicurrency Setup
Rate Types
Translation Type for Accounts
Section 2: Management Reporter Consolidated Report
Create Report
Translation Types
Section 1: Dynamics GP and Currency Translation Setup
Functional Currency
Confirm the functional currency in both companies.
Microsoft Dynamics GP menu >> Tools >> Setup >> Financial >> Multicurrency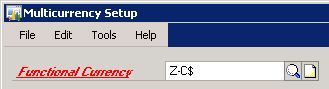
Note
All remaining steps in this section must be done in the company where the conversion will happen. In this example, the CAD company will be used.
Create Exchange Tables and Enter Rates
Create three Exchange Tables to demonstrate the different translation types. Enter rates for each.
Microsoft Dynamics GP menu >> Tools >> Setup >> System >> Exchange Table
Create an Average Table:
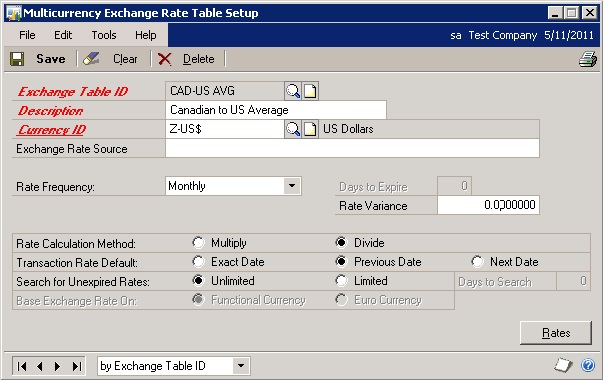
Exchange Table ID: CAD-US AVG
Description: Canadian to US Average
Currency ID: Z-US$
Rate Frequency: Monthly
Rate Calculation Method: Divide
Transaction Rate Default: Previous Date (See notes on the Transaction Rate Default in this section.)
Search for Unexpired Rates: UnlimitedSelect Rates:
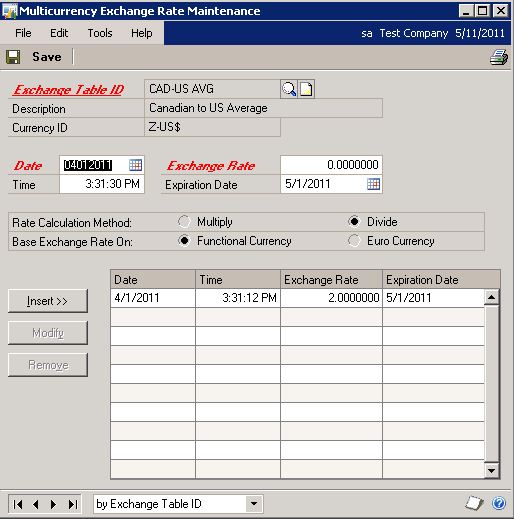
For this example, we have entered rates and dates where it will be easy to see the translation. Rates and dates will vary in your system. You must enter valid date ranges for Management Reporter to notice the rates for a given period.
Also be aware that Dynamics GP assumes that you're entering rates to go from your reporting or originating currency back to your functional currency. In this example, the rate is from CAD back to US. In Management Reporter, the rate will seem like it's multiplying because it's going from US to CAD.
Create a Current Table:
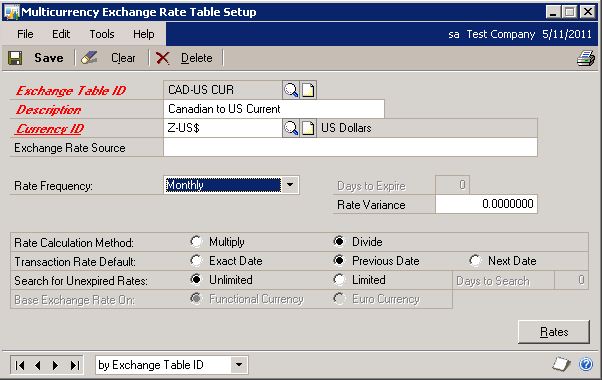
Exchange Table ID: CAD-US CUR
Description: Canadian to US Current
Currency ID: Z-US$
Rate Frequency: Monthly
Rate Calculation Method: Divide
Transaction Rate Default: Previous Date
Search for Unexpired Rates: UnlimitedSelect Rates:
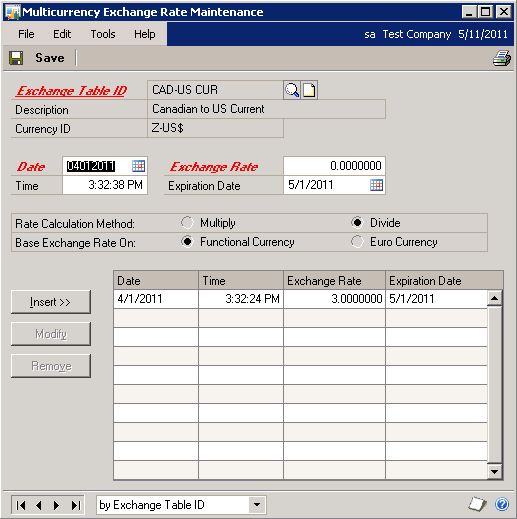
Create a Historical Table:
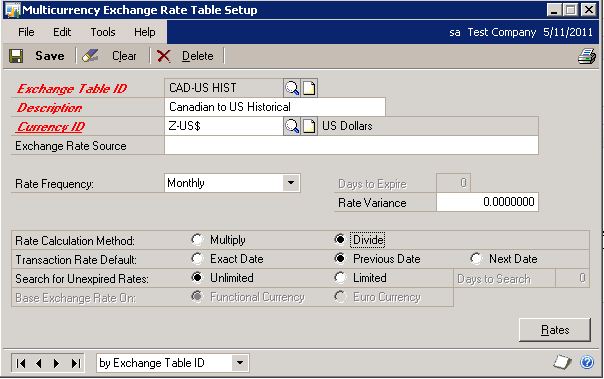
Exchange Table ID: CAD-US HIST
Description: Canadian to US Historical
Currency ID: Z-US$
Rate Frequency: Monthly
Rate Calculation Method: Divide
Transaction Rate Default: Previous Date
Search for Unexpired Rates: UnlimitedSelect Rates:
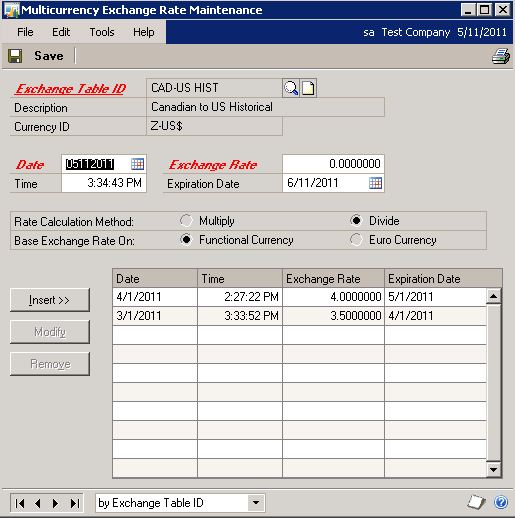
Transaction Rate Default notes:
Select a Transaction Rate Default option to determine the exchange rate that will be used when multicurrency transactions are entered. Every time that you enter a transaction, a currency must be selected. If there isn't an exchange rate for the transaction date, the option selected here will be used to select the exchange rate.
Exact Date Select if you want the default exchange rate only to be an exchange rate with the same date as the transaction date. If there's no exchange rate for the transaction date, there will be no default exchange rate.
Previous Date Select if you want the default exchange rate to be the rate for the closest previous date, if no rate exists for the transaction date. If an exchange rate exists for the transaction date, that rate will be used as the default exchange rate. You'll also have to enter the number of previous days that you want to search for an unexpired exchange rate.
If you've selected to use a previous date as the transaction rate default and there are no unexpired rates for a previous date within the number of days that you've specified as a search limit, the closest future date will appear as the default exchange rate.
Next Date Select if you want the default exchange rate to be the rate for the closest date after the transaction date, if no rate exists for the transaction date. If an exchange rate exists for the transaction date, that rate will be used as the default exchange rate. You'll also have to enter the number of previous days that you want to search for an unexpired exchange rate.
If you've selected to use the next date as the transaction rate default and there isn't one, then the closest unexpired rate before the transaction date will appear as the default exchange rate. Only the number of days that you've specified to search will be used to determine an unexpired previous rate.
Note
The Previous Date setting is recommended as that is how FRx Currency Translator functions.
Multicurrency Access
Grant the company access to the exchange tables for each currency.
Microsoft Dynamics GP menu >> Tools >> Setup >> System >> Multicurrency Access
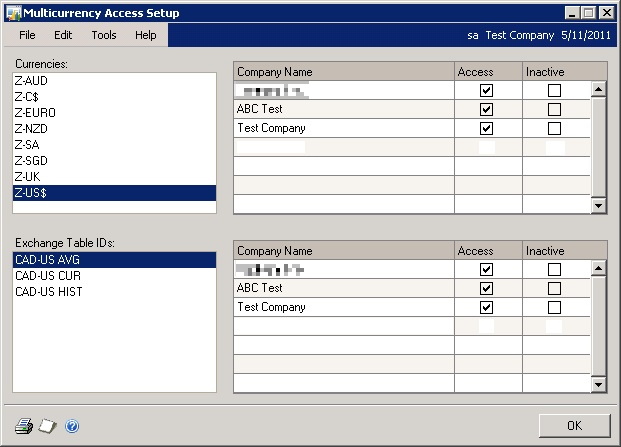
Multicurrency Setup
Set up the Multicurrency Setup window.
Microsoft Dynamics GP menu >> Tools >> Setup >> Financial >> Multicurrency
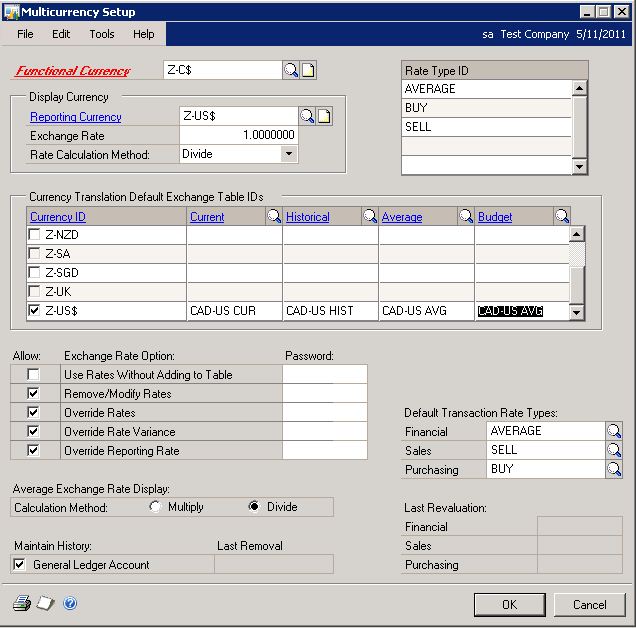
Reporting Currency: Z-US$ Exchange Rate: 1.0000000 Rate Calculation Method: Divide Currency ID Z-US$: Default Transaction Rate Types: Financial: AVERAGE Sales: SELL Purchasing: BUY
Rate Types
Configure the rate types for the exchange tables.
Microsoft Dynamics GP menu >> Tools >> Setup >> Financial >> Rate Types
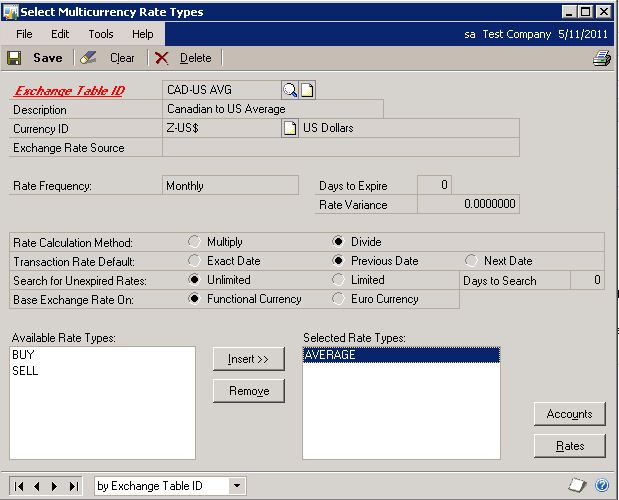
If the AVERAGE, BUY, or SELL rate types aren't in the Available Rate Types list, then they're assigned to other exchange tables. Unassigning them from those tables will let you assign them to the new tables.
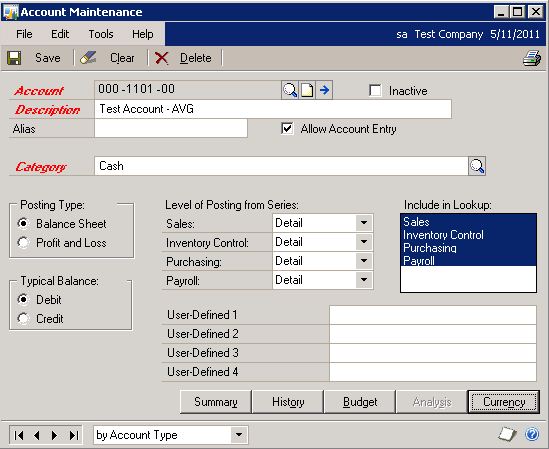
Translation Type for Accounts
Set the Currency Translation Type for the accounts that you want to translate. This setting controls whether an account will use an Average, Current, or Historical translation. The setting works with the Multicurrency Setup window (from step D) to determine which exchange table to use.
Cards >> Financial >> Account
Section 2: Management Reporter Consolidated Report
Create Report
This section assumes that both companies have the same chart of accounts. This section also assumes that the segment descriptions are the same for both companies. It's okay if the accounts and descriptions are different; it just requires more design work and isn't covered in this document.
Create a row that pulls in the wanted accounts.
File >> New >> Row

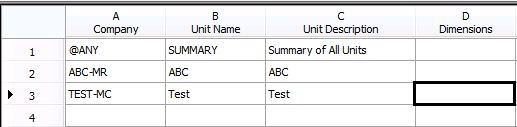
Create a tree that links to both companies. Dimensions aren't required unless you want to break out the data.
File >> New >> Tree
Create a column that handles the translation and breaks each company into its own column. In this example, there's a CAD Translated and a CAD Non-Translated column to show the translation in action. The only cell that tells Management Reporter to translate is the Currency Source cell.
File >> New >> Column
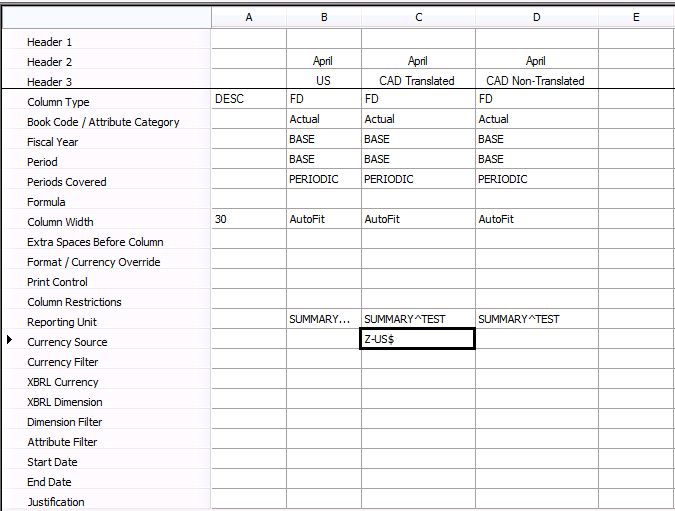
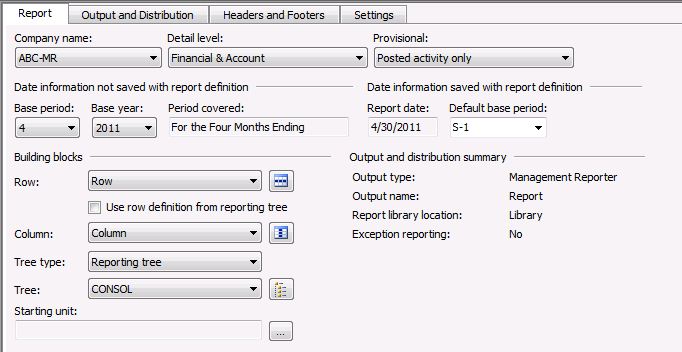
Create a report definition.
File >> New >> Report Definition
Generate the report and note the translated results.
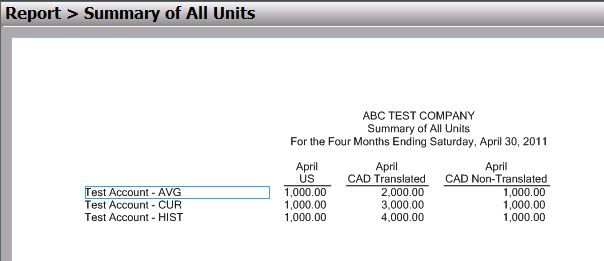
Note
- The first column is $1,000 posted in USD and is a non-translated amount.
- The second column is the translated amounts for the CAD company.
- The third column is $1,000 posted in CAD in the CAD company and is a non-translated amount.
Translation Types
Here's how each translation type works with Dynamics GP and Management Reporter.
Current - Current is an exchange rate based on each column date, which comes from the Report Date, and the column or row modifiers. Each column will use an individual rate. This translation type is typically used with balance sheet accounts and a YTD column.
Average - Average is a single exchange rate for each period. Management Reporter doesn't actually calculate an average rate as it is expected that people will enter the average for the period into the exchange table. Each period is calculated at the average rate for that period and any YTD results are summed from the period totals. This translation type is typically used with income statement accounts.
Historical - Historical is an exchange rate based on the transaction date. The transaction date is used to find the rate for that time period and that is the rate used for the translation. This translation type is typically used with non-monetary assets, such as inventory, fixed assets, long-term liabilities, or equity / kept earnings.
Entering translated beginning balance information
You can use the Currency Translation window to translate beginning balance information for average and historical currency translation types. You also can enter translated beginning balance amounts for a new translation currency or correct translated beginning balance amounts. You don't translate beginning balances for the current translation type because the current translation type uses the report date for the exchange rate.
After you set up a translation, beginning balances along with translated beginning balances for the translation currencies are created by closing a year.
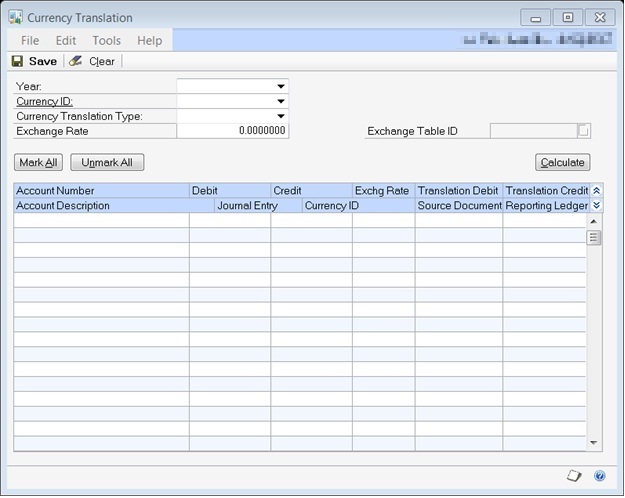
To enter translated beginning balance information:
Open the Currency Translation window. (Microsoft Dynamics GP menu >> Tools >> Routines >> Financial >> Currency Translation)
Select the Year. Only the available open and historical years are available.
Select the Currency ID. Only the currencies that you selected as translation currencies in the Multicurrency Setup window are available for the company you're using.
Select the Currency Translation Type.
Accounts with beginning balances that match the currency translation type display in the scrolling window along with any previously entered translated amounts. If you're using International Financial Reporting Standards (IFRS) ledgers, each account/reporting ledger combination displays as a separate row in the scrolling window.
To update multiple accounts with a single exchange rate, enter the exchange rate that will be used when calculating the translated debit or credit amount.
Mark the check box by the account numbers in the scrolling window that you want to translate beginning balances for.
Select Calculate to calculate the translated amounts for the selected accounts using the exchange rate.
You can enter a different exchange rate for an account in the scrolling window to translate amounts. The exchange rates entered in the scrolling window won't be used if you choose Calculate. You also can enter translated amounts.
Select Save to the translated balances.
Palaute
Tulossa pian: Vuoden 2024 aikana poistamme asteittain GitHub Issuesin käytöstä sisällön palautemekanismina ja korvaamme sen uudella palautejärjestelmällä. Lisätietoja on täällä: https://aka.ms/ContentUserFeedback.
Lähetä ja näytä palaute kohteelle