音声認識
音声認識を使って、入力を行ったり、操作やコマンドを指定したり、タスクを実行したりできます。
重要な API: Windows.Media.SpeechRecognition
音声認識機能は、音声認識ランタイム、ランタイムをプログラミングするための認識 API、ディクテーションと Web 検索のための定義済みの文法、ユーザーが音声認識機能を見つけて使うときに役立つ既定のシステム UI で構成されています。
音声認識を構成する
アプリで音声認識をサポートするには、ユーザーがデバイスでマイクに接続して有効にし、アプリに使用権限を付与する Microsoft プライバシー ポリシーに同意する必要があります。
マイクのオーディオ フィードにアクセスして使用するためのアクセス許可を求めるシステム ダイアログをユーザーに自動的に表示するには (次に示されているのは、音声認識と音声合成のサンプルの例)、アプリ パッケージ マニフェストでマイクデバイス機能を設定します。 詳細については、「アプリ機能の宣言」を参照してください。

ユーザーが [はい] をクリックしてマイクへのアクセスを許可すると、[設定] -> [プライバシー] -> [マイク] ページの承認済みアプリケーションの一覧にアプリが追加されます。 ただし、ユーザーはいつでもこの設定をオフにできるため、使用を試みる前に、アプリでマイクにアクセスできることを確認する必要があります。
ディクテーション、Cortana、または他の音声認識サービス (トピック制約で定義されている定義済みの文法など) もサポートする場合は、オンライン音声認識 ([設定] -> [プライバシー] -> [音声]) が有効になっていることも確認する必要があります。
次のスニペットは、マイクがあるかどうかと、マイクを使用するアクセス許可があるかどうかをアプリで確認する方法を示しています。
public class AudioCapturePermissions
{
// If no microphone is present, an exception is thrown with the following HResult value.
private static int NoCaptureDevicesHResult = -1072845856;
/// <summary>
/// Note that this method only checks the Settings->Privacy->Microphone setting, it does not handle
/// the Cortana/Dictation privacy check.
///
/// You should perform this check every time the app gets focus, in case the user has changed
/// the setting while the app was suspended or not in focus.
/// </summary>
/// <returns>True, if the microphone is available.</returns>
public async static Task<bool> RequestMicrophonePermission()
{
try
{
// Request access to the audio capture device.
MediaCaptureInitializationSettings settings = new MediaCaptureInitializationSettings();
settings.StreamingCaptureMode = StreamingCaptureMode.Audio;
settings.MediaCategory = MediaCategory.Speech;
MediaCapture capture = new MediaCapture();
await capture.InitializeAsync(settings);
}
catch (TypeLoadException)
{
// Thrown when a media player is not available.
var messageDialog = new Windows.UI.Popups.MessageDialog("Media player components are unavailable.");
await messageDialog.ShowAsync();
return false;
}
catch (UnauthorizedAccessException)
{
// Thrown when permission to use the audio capture device is denied.
// If this occurs, show an error or disable recognition functionality.
return false;
}
catch (Exception exception)
{
// Thrown when an audio capture device is not present.
if (exception.HResult == NoCaptureDevicesHResult)
{
var messageDialog = new Windows.UI.Popups.MessageDialog("No Audio Capture devices are present on this system.");
await messageDialog.ShowAsync();
return false;
}
else
{
throw;
}
}
return true;
}
}
/// <summary>
/// Note that this method only checks the Settings->Privacy->Microphone setting, it does not handle
/// the Cortana/Dictation privacy check.
///
/// You should perform this check every time the app gets focus, in case the user has changed
/// the setting while the app was suspended or not in focus.
/// </summary>
/// <returns>True, if the microphone is available.</returns>
IAsyncOperation<bool>^ AudioCapturePermissions::RequestMicrophonePermissionAsync()
{
return create_async([]()
{
try
{
// Request access to the audio capture device.
MediaCaptureInitializationSettings^ settings = ref new MediaCaptureInitializationSettings();
settings->StreamingCaptureMode = StreamingCaptureMode::Audio;
settings->MediaCategory = MediaCategory::Speech;
MediaCapture^ capture = ref new MediaCapture();
return create_task(capture->InitializeAsync(settings))
.then([](task<void> previousTask) -> bool
{
try
{
previousTask.get();
}
catch (AccessDeniedException^)
{
// Thrown when permission to use the audio capture device is denied.
// If this occurs, show an error or disable recognition functionality.
return false;
}
catch (Exception^ exception)
{
// Thrown when an audio capture device is not present.
if (exception->HResult == AudioCapturePermissions::NoCaptureDevicesHResult)
{
auto messageDialog = ref new Windows::UI::Popups::MessageDialog("No Audio Capture devices are present on this system.");
create_task(messageDialog->ShowAsync());
return false;
}
throw;
}
return true;
});
}
catch (Platform::ClassNotRegisteredException^ ex)
{
// Thrown when a media player is not available.
auto messageDialog = ref new Windows::UI::Popups::MessageDialog("Media Player Components unavailable.");
create_task(messageDialog->ShowAsync());
return create_task([] {return false; });
}
});
}
var AudioCapturePermissions = WinJS.Class.define(
function () { }, {},
{
requestMicrophonePermission: function () {
/// <summary>
/// Note that this method only checks the Settings->Privacy->Microphone setting, it does not handle
/// the Cortana/Dictation privacy check.
///
/// You should perform this check every time the app gets focus, in case the user has changed
/// the setting while the app was suspended or not in focus.
/// </summary>
/// <returns>True, if the microphone is available.</returns>
return new WinJS.Promise(function (completed, error) {
try {
// Request access to the audio capture device.
var captureSettings = new Windows.Media.Capture.MediaCaptureInitializationSettings();
captureSettings.streamingCaptureMode = Windows.Media.Capture.StreamingCaptureMode.audio;
captureSettings.mediaCategory = Windows.Media.Capture.MediaCategory.speech;
var capture = new Windows.Media.Capture.MediaCapture();
capture.initializeAsync(captureSettings).then(function () {
completed(true);
},
function (error) {
// Audio Capture can fail to initialize if there's no audio devices on the system, or if
// the user has disabled permission to access the microphone in the Privacy settings.
if (error.number == -2147024891) { // Access denied (microphone disabled in settings)
completed(false);
} else if (error.number == -1072845856) { // No recording device present.
var messageDialog = new Windows.UI.Popups.MessageDialog("No Audio Capture devices are present on this system.");
messageDialog.showAsync();
completed(false);
} else {
error(error);
}
});
} catch (exception) {
if (exception.number == -2147221164) { // REGDB_E_CLASSNOTREG
var messageDialog = new Windows.UI.Popups.MessageDialog("Media Player components not available on this system.");
messageDialog.showAsync();
return false;
}
}
});
}
})
音声入力の認識
制約は、音声入力でアプリが認識する単語と語句 (ボキャブラリ) を定義します。 制約は音声認識の中心であり、アプリで音声認識の精度をより細かく制御できるようになります。
音声入力の認識では、次の種類の制約を使用できます。
定義済みの文法
定義済みのディクテーション文法と Web 検索文法を使うと、文法を作らずにアプリに音声認識を実装できます。 これらの文法を使った場合、音声認識がリモート Web サービスで実行され、結果がデバイスに返されます。
既定のフリーテキストのディクテーション文法では、ユーザーが特定の言語で話すほとんどの単語と語句を認識できます。これは短い語句の認識に最適化されています。 SpeechRecognizer オブジェクトに制約を指定しなかった場合は、定義済みのディクテーション文法が使われます。 フリーテキストのディクテーションは、ユーザーが話す内容を限定しない場合に便利です。 一般的な用途としては、メモの作成やメッセージ内容の口述などがあります。
Web 検索文法は、ユーザーが話す可能性のある多数の単語と語句を含んでいる点でディクテーション文法と似ています ただし、ユーザーが Web 検索で一般的に使う用語の認識に最適化されています。
注意
定義済みのディクテーション文法と Web 検索文法は容量が大きく、(デバイス上ではなく) オンライン上に存在するため、カスタム文法をデバイスにインストールした場合に比べるとパフォーマンスが劣る可能性があります。
このような定義済みの文法は、10 秒までの長さの音声入力を認識でき、開発者による作成作業は必要ありません。 ただし、ネットワークへの接続が必要になります。
Web サービスの制約を使用するには、[設定] -> [プライバシー] -> [音声認識、手描き入力、入力の設定] で [自分を知ってもらう] オプションをオンにして、[設定] で音声入力とディクテーションのサポートを有効にする必要があります。
ここでは、音声入力が有効になっているかどうかをテストし、有効になっていない場合は [設定] -> [プライバシー] -> [音声認識、手描き入力、入力の設定] ページを開く方法を示します。
まず、グローバル変数 (HResultPrivacyStatementDeclined) を HResult 値 0x80045509 に初期化します。 C# または Visual Basic での例外処理に関する記事を参照してください。
private static uint HResultPrivacyStatementDeclined = 0x80045509;
認識中に標準例外をキャッチし、HResult 値が HResultPrivacyStatementDeclined 変数の値以下であるかどうかをテストします。 該当する場合は、警告を表示し、await Windows.System.Launcher.LaunchUriAsync(new Uri("ms-settings:privacy-accounts")); を呼び出して [設定] ページを開きます。
catch (Exception exception)
{
// Handle the speech privacy policy error.
if ((uint)exception.HResult == HResultPrivacyStatementDeclined)
{
resultTextBlock.Visibility = Visibility.Visible;
resultTextBlock.Text = "The privacy statement was declined." +
"Go to Settings -> Privacy -> Speech, inking and typing, and ensure you" +
"have viewed the privacy policy, and 'Get To Know You' is enabled.";
// Open the privacy/speech, inking, and typing settings page.
await Windows.System.Launcher.LaunchUriAsync(new Uri("ms-settings:privacy-accounts"));
}
else
{
var messageDialog = new Windows.UI.Popups.MessageDialog(exception.Message, "Exception");
await messageDialog.ShowAsync();
}
}
SpeechRecognitionTopicConstraint を参照してください。
プログラムによる一覧の制約
プログラムによる一覧の制約は、単語や語句の一覧を使って単純な文法を作成する手法で、軽量です。 個別の短い語句を認識するには、一覧の制約が適しています。 文法にすべての単語を明示的に指定すると、音声認識エンジンは音声と単語の一致を確認する際に音声だけを処理すればよいので、認識の精度が向上します。 また、一覧はプログラムで更新することもできます。
一覧の制約は、アプリで認識操作に利用できる音声入力を表した文字列の配列で構成されます。 アプリで一覧の制約を作成するには、音声認識の一覧の制約オブジェクトを作って、文字列の配列を渡します。 次に、そのオブジェクトを認識エンジンの制約コレクションに追加します。 音声認識エンジンが配列内の文字列のどれかを認識したら、認識は成功です。
SpeechRecognitionListConstraint を参照してください。
SRGS 文法
Speech Recognition Grammar Specification (SRGS) 文法は静的ドキュメントで、プログラムによる一覧の制約とは異なり、SRGS Version 1.0 で定義された XML 形式を使います。 SRGS 文法では、1 回の認識で複数の意味をキャプチャすることができるため、音声認識エクスペリエンスを最大限に制御することができます。
SpeechRecognitionGrammarFileConstraint を参照してください。
音声コマンドの制約
音声コマンド定義 (VCD) XML ファイルを使って、アプリをアクティブ化して操作を開始するためにユーザーが発声できる音声コマンドを定義します。 詳細については、Cortana の音声コマンドを使ったフォアグラウンド アプリのアクティブ化に関する記事を参照してください。
SpeechRecognitionVoiceCommandDefinitionConstraint/ を参照してください
注: どの種類の制約を使用するかは、作成する認識エクスペリエンスの複雑さによって異なります。 どの種類の制約も特定の認識タスクに最適な選択肢となる可能性があり、アプリですべての種類の制約を使う場合もあります。 制約を使う場合は、「カスタム認識の制約の定義」をご覧ください。
ユニバーサル Windows アプリで定義済みのディクテーション文法によって、言語のほとんどの単語と短い語句が認識されます。 これは、カスタム制約なしで音声認識エンジン オブジェクトをインスタンス化すると既定で有効になります。
この例では、以下の操作を行う方法を示します。
- 音声認識エンジンを作成します。
- 既定のユニバーサル Windows アプリ制約をコンパイルします (音声認識エンジンの文法セットには文法が追加されていません)。
- RecognizeWithUIAsync メソッドに用意された基本的な認識 UI と TTS フィードバックを使って音声の聞き取りを開始します。 既定の UI が必要でない場合は、RecognizeAsync メソッドを使います。
private async void StartRecognizing_Click(object sender, RoutedEventArgs e)
{
// Create an instance of SpeechRecognizer.
var speechRecognizer = new Windows.Media.SpeechRecognition.SpeechRecognizer();
// Compile the dictation grammar by default.
await speechRecognizer.CompileConstraintsAsync();
// Start recognition.
Windows.Media.SpeechRecognition.SpeechRecognitionResult speechRecognitionResult = await speechRecognizer.RecognizeWithUIAsync();
// Do something with the recognition result.
var messageDialog = new Windows.UI.Popups.MessageDialog(speechRecognitionResult.Text, "Text spoken");
await messageDialog.ShowAsync();
}
認識 UI をカスタマイズする
アプリが SpeechRecognizer.RecognizeWithUIAsync を呼び出して音声認識を試みると、複数の画面が次の順序で表示されます。
定義済みの文法に基づく制約を使っている場合 (ディクテーションまたは Web 検索):
- [聞き取り中] 画面。
- [認識中] 画面。
- [聞き取りの確認] 画面またはエラー画面。
単語や語句の一覧に基づく制約、または、SGRS 文法ファイルに基づく制約を使っている場合:
- [聞き取り中] 画面。
- [確認] 画面 (ユーザーの発言が複数の潜在的な結果として解釈できる場合)。
- [聞き取りの確認] 画面またはエラー画面。
次の図に、SGRS 文法ファイルに基づく制約を使う音声認識エンジンの画面間のフロー例を示します。 この例では、音声認識に成功しています。

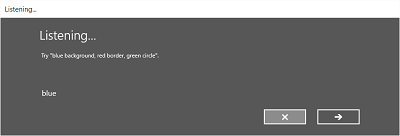
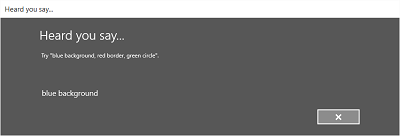
[聞き取り中] 画面では、アプリが認識できる単語または語句の例を表示できます。 ここでは、SpeechRecognizerUIOptions クラス (SpeechRecognizer.UIOptions プロパティを呼び出して取得する) のプロパティを使って [聞き取り中] 画面のコンテンツをカスタマイズする方法について説明します。
private async void WeatherSearch_Click(object sender, RoutedEventArgs e)
{
// Create an instance of SpeechRecognizer.
var speechRecognizer = new Windows.Media.SpeechRecognition.SpeechRecognizer();
// Listen for audio input issues.
speechRecognizer.RecognitionQualityDegrading += speechRecognizer_RecognitionQualityDegrading;
// Add a web search grammar to the recognizer.
var webSearchGrammar = new Windows.Media.SpeechRecognition.SpeechRecognitionTopicConstraint(Windows.Media.SpeechRecognition.SpeechRecognitionScenario.WebSearch, "webSearch");
speechRecognizer.UIOptions.AudiblePrompt = "Say what you want to search for...";
speechRecognizer.UIOptions.ExampleText = @"Ex. 'weather for London'";
speechRecognizer.Constraints.Add(webSearchGrammar);
// Compile the constraint.
await speechRecognizer.CompileConstraintsAsync();
// Start recognition.
Windows.Media.SpeechRecognition.SpeechRecognitionResult speechRecognitionResult = await speechRecognizer.RecognizeWithUIAsync();
//await speechRecognizer.RecognizeWithUIAsync();
// Do something with the recognition result.
var messageDialog = new Windows.UI.Popups.MessageDialog(speechRecognitionResult.Text, "Text spoken");
await messageDialog.ShowAsync();
}
関連記事
サンプル
Windows developer
フィードバック
以下は間もなく提供いたします。2024 年を通じて、コンテンツのフィードバック メカニズムとして GitHub の issue を段階的に廃止し、新しいフィードバック システムに置き換えます。 詳細については、「https://aka.ms/ContentUserFeedback」を参照してください。
フィードバックの送信と表示
