Building a Conditional Access policy
As explained in the article What is Conditional Access, a Conditional Access policy is an if-then statement, of Assignments and Access controls. A Conditional Access policy brings signals together, to make decisions, and enforce organizational policies.
How does an organization create these policies? What is required? How are they applied?
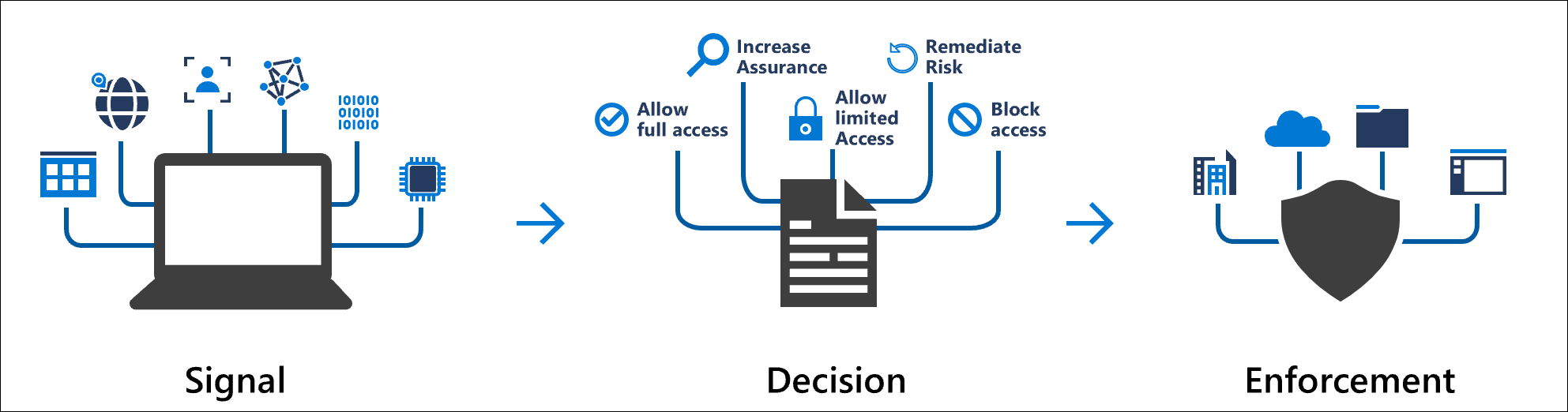
Multiple Conditional Access policies may apply to an individual user at any time. In this case, all policies that apply must be satisfied. For example, if one policy requires multifactor authentication and another requires a compliant device, you must complete MFA, and use a compliant device. All assignments are logically ANDed. If you've more than one assignment configured, all assignments must be satisfied to trigger a policy.
If a policy where "Require one of the selected controls" is selected, we prompt in the order defined, as soon as the policy requirements are satisfied, access is granted.
All policies are enforced in two phases:
- Phase 1: Collect session details
- Gather session details, like network location and device identity that will be necessary for policy evaluation.
- Phase 1 of policy evaluation occurs for enabled policies and policies in report-only mode.
- Phase 2: Enforcement
- Use the session details gathered in phase 1 to identify any requirements that haven't been met.
- If there's a policy that is configured to block access, with the block grant control, enforcement will stop here and the user will be blocked.
- The user will be prompted to complete more grant control requirements that weren't satisfied during phase 1 in the following order, until policy is satisfied:
- Once all grant controls have been satisfied, apply session controls (App Enforced, Microsoft Defender for Cloud Apps, and token Lifetime)
- Phase 2 of policy evaluation occurs for all enabled policies.
Assignments
The assignments portion controls the who, what, and where of the Conditional Access policy.
Users and groups
Users and groups assign who the policy will include or exclude. This assignment can include all users, specific groups of users, directory roles, or external guest users.
Cloud apps or actions
Cloud apps or actions can include or exclude cloud applications, user actions, or authentication contexts that will be subjected to the policy.
Conditions
A policy can contain multiple conditions.
Sign-in risk
For organizations with Microsoft Entra ID Protection, the risk detections generated there can influence your Conditional Access policies.
Device platforms
Organizations with multiple device operating system platforms may wish to enforce specific policies on different platforms.
The information used to calculate the device platform comes from unverified sources such as user agent strings that can be changed.
Locations
Locations connect IP addresses, geographies, and Global Secure Access' compliant network to Conditional Access policy decisions. Administrators can choose to define locations and mark some as trusted like those for their organization's primary network locations.
Client apps
The software the user is employing to access the cloud app. For example, 'Browser', and 'Mobile apps and desktop clients'. By default, all newly created Conditional Access policies will apply to all client app types even if the client apps condition isn't configured.
The behavior of the client apps condition was updated in August 2020. If you have existing Conditional Access policies, they'll remain unchanged. However, if you select on an existing policy, the configure toggle has been removed and the client apps the policy applies to are selected.
Filter for devices
This control allows targeting specific devices based on their attributes in a policy.
Access controls
The access controls portion of the Conditional Access policy controls how a policy is enforced.
Grant
Grant provides administrators with a means of policy enforcement where they can block or grant access.
Block access
Block access does just that, it will block access under the specified assignments. The block control is powerful and should be wielded with the appropriate knowledge.
Grant access
The grant control can trigger enforcement of one or more controls.
- Require multifactor authentication
- Require device to be marked as compliant (Intune)
- Require Microsoft Entra hybrid joined device
- Require approved client app
- Require app protection policy
- Require password change
- Require terms of use
Administrators can choose to require one of the previous controls or all selected controls using the following options. The default for multiple controls is to require all.
- Require all the selected controls (control and control)
- Require one of the selected controls (control or control)
Session
Session controls can limit the experience
- Use app enforced restrictions
- Currently works with Exchange Online and SharePoint Online only.
- Passes device information to allow control of experience granting full or limited access.
- Use Conditional Access App Control
- Uses signals from Microsoft Defender for Cloud Apps to do things like:
- Block download, cut, copy, and print of sensitive documents.
- Monitor risky session behavior.
- Require labeling of sensitive files.
- Uses signals from Microsoft Defender for Cloud Apps to do things like:
- Sign-in frequency
- Ability to change the default sign in frequency for modern authentication.
- Persistent browser session
- Allows users to remain signed in after closing and reopening their browser window.
- Customize continuous access evaluation
- Disable resilience defaults
Simple policies
A Conditional Access policy must contain at minimum the following to be enforced:
- Name of the policy.
- Assignments
- Users and/or groups to apply the policy to.
- Cloud apps or actions to apply the policy to.
- Access controls
- Grant or Block controls

The article Common Conditional Access policies includes some policies that we think would be useful to most organizations.
Next steps
Create a Conditional Access policy
Use report-only mode for Conditional Access to determine the results of new policy decisions.
Planning a cloud-based Microsoft Entra multifactor authentication deployment
Atsiliepimai
Jau greitai: 2024 m. palaipsniui atsisakysime „GitHub“ problemų, kaip turiniui taikomo atsiliepimų mechanizmo, ir pakeisime jį nauja atsiliepimų sistema. Daugiau informacijos žr. https://aka.ms/ContentUserFeedback.
Pateikti ir peržiūrėti atsiliepimą, skirtą