Alterar a chave primária de usuários na Identidade do ASP.NET
por Tom FitzMacken
Em Visual Studio 2013, o aplicativo Web padrão usa um valor de cadeia de caracteres para a chave para contas de usuário. ASP.NET Identity permite que você altere o tipo da chave para atender aos seus requisitos de dados. Por exemplo, você pode alterar o tipo da chave de uma cadeia de caracteres para um inteiro.
Este tópico mostra como começar com o aplicativo Web padrão e alterar a chave da conta de usuário para um inteiro. Você pode usar as mesmas modificações para implementar qualquer tipo de chave em seu projeto. Ele mostra como fazer essas alterações no aplicativo Web padrão, mas você pode aplicar modificações semelhantes a um aplicativo personalizado. Ele mostra as alterações necessárias ao trabalhar com MVC ou Web Forms.
Versões de software usadas no tutorial
- Visual Studio 2013 com a Atualização 2 (ou posterior)
- ASP.NET Identity 2.1 ou posterior
Para executar as etapas neste tutorial, você deve ter Visual Studio 2013 Atualização 2 (ou posterior) e um aplicativo Web criado a partir do modelo ASP.NET Aplicativo Web. O modelo foi alterado na Atualização 3. Este tópico mostra como alterar o modelo na Atualização 2 e na Atualização 3.
Este tópico contém as seguintes seções:
- Alterar o tipo da chave na classe de usuário Identidade
- Adicionar classes de identidade personalizadas que usam o tipo de chave
- Alterar a classe de contexto e o gerenciador de usuários para usar o tipo de chave
- Alterar a configuração de inicialização para usar o tipo de chave
- Para MVC com a Atualização 2, altere o AccountController para passar o tipo de chave
- Para MVC com a Atualização 3, altere AccountController e ManageController para passar o tipo de chave
- Para Web Forms com a Atualização 2, altere páginas de conta para passar o tipo de chave
- Para Web Forms com a Atualização 3, altere páginas de conta para passar o tipo de chave
- Executar o aplicativo
- Outros recursos
Alterar o tipo da chave na classe de usuário Identidade
Em seu projeto criado a partir do modelo ASP.NET Aplicativo Web, especifique que a classe ApplicationUser usa um inteiro para a chave para contas de usuário. Em IdentityModels.cs, altere a classe ApplicationUser para herdar de IdentityUser que tenha um tipo de int para o parâmetro genérico TKey. Você também passa os nomes de três classes personalizadas que ainda não implementou.
public class ApplicationUser : IdentityUser<int, CustomUserLogin, CustomUserRole,
CustomUserClaim>
{
...
Você alterou o tipo da chave, mas, por padrão, o restante do aplicativo ainda pressupõe que a chave seja uma cadeia de caracteres. Você deve indicar explicitamente o tipo da chave no código que pressupõe uma cadeia de caracteres.
Na classe ApplicationUser , altere o método GenerateUserIdentityAsync para incluir int, conforme mostrado no código realçado abaixo. Essa alteração não é necessária para projetos Web Forms com o modelo de Atualização 3.
public async Task<ClaimsIdentity> GenerateUserIdentityAsync(
UserManager<ApplicationUser, int> manager)
{
// Note the authenticationType must match the one defined in
// CookieAuthenticationOptions.AuthenticationType
var userIdentity = await manager.CreateIdentityAsync(
this, DefaultAuthenticationTypes.ApplicationCookie);
// Add custom user claims here
return userIdentity;
}
Adicionar classes de identidade personalizadas que usam o tipo de chave
As outras classes de identidade, como IdentityUserRole, IdentityUserClaim, IdentityUserLogin, IdentityRole, UserStore, RoleStore, ainda estão configuradas para usar uma chave de cadeia de caracteres. Crie novas versões dessas classes que especificam um inteiro para a chave. Você não precisa fornecer muito código de implementação nessas classes, você está apenas definindo int como a chave.
Adicione as seguintes classes ao arquivo IdentityModels.cs.
public class CustomUserRole : IdentityUserRole<int> { }
public class CustomUserClaim : IdentityUserClaim<int> { }
public class CustomUserLogin : IdentityUserLogin<int> { }
public class CustomRole : IdentityRole<int, CustomUserRole>
{
public CustomRole() { }
public CustomRole(string name) { Name = name; }
}
public class CustomUserStore : UserStore<ApplicationUser, CustomRole, int,
CustomUserLogin, CustomUserRole, CustomUserClaim>
{
public CustomUserStore(ApplicationDbContext context)
: base(context)
{
}
}
public class CustomRoleStore : RoleStore<CustomRole, int, CustomUserRole>
{
public CustomRoleStore(ApplicationDbContext context)
: base(context)
{
}
}
Alterar a classe de contexto e o gerenciador de usuários para usar o tipo de chave
Em IdentityModels.cs, altere a definição da classe ApplicationDbContext para usar suas novas classes personalizadas e um int para a chave, conforme mostrado no código realçado.
public class ApplicationDbContext : IdentityDbContext<ApplicationUser, CustomRole,
int, CustomUserLogin, CustomUserRole, CustomUserClaim>
{
...
O parâmetro ThrowIfV1Schema não é mais válido no construtor. Altere o construtor para que ele não passe um valor ThrowIfV1Schema.
public ApplicationDbContext()
: base("DefaultConnection")
{
}
Abra IdentityConfig.cs e altere a classe ApplicationUserManger para usar sua nova classe de repositório de usuários para manter dados e um int para a chave.
public class ApplicationUserManager : UserManager<ApplicationUser, int>
{
public ApplicationUserManager(IUserStore<ApplicationUser, int> store)
: base(store)
{
}
public static ApplicationUserManager Create(
IdentityFactoryOptions<ApplicationUserManager> options, IOwinContext context)
{
var manager = new ApplicationUserManager(
new CustomUserStore(context.Get<ApplicationDbContext>()));
// Configure validation logic for usernames
manager.UserValidator = new UserValidator<ApplicationUser, int>(manager)
{
AllowOnlyAlphanumericUserNames = false,
RequireUniqueEmail = true
};
// Configure validation logic for passwords
manager.PasswordValidator = new PasswordValidator
{
RequiredLength = 6,
RequireNonLetterOrDigit = true,
RequireDigit = true,
RequireLowercase = true,
RequireUppercase = true,
};
// Register two factor authentication providers. This application uses Phone
// and Emails as a step of receiving a code for verifying the user
// You can write your own provider and plug in here.
manager.RegisterTwoFactorProvider("PhoneCode",
new PhoneNumberTokenProvider<ApplicationUser, int>
{
MessageFormat = "Your security code is: {0}"
});
manager.RegisterTwoFactorProvider("EmailCode",
new EmailTokenProvider<ApplicationUser, int>
{
Subject = "Security Code",
BodyFormat = "Your security code is: {0}"
});
manager.EmailService = new EmailService();
manager.SmsService = new SmsService();
var dataProtectionProvider = options.DataProtectionProvider;
if (dataProtectionProvider != null)
{
manager.UserTokenProvider =
new DataProtectorTokenProvider<ApplicationUser, int>(
dataProtectionProvider.Create("ASP.NET Identity"));
}
return manager;
}
}
No modelo Atualização 3, você deve alterar a classe ApplicationSignInManager.
public class ApplicationSignInManager : SignInManager<ApplicationUser, int>
{ ... }
Alterar a configuração de inicialização para usar o tipo de chave
Em Startup.Auth.cs, substitua o código OnValidateIdentity, conforme realçado abaixo. Observe que a definição getUserIdCallback analisa o valor da cadeia de caracteres em um inteiro.
app.UseCookieAuthentication(new CookieAuthenticationOptions
{
AuthenticationType = DefaultAuthenticationTypes.ApplicationCookie,
LoginPath = new PathString("/Account/Login"),
Provider = new CookieAuthenticationProvider
{
OnValidateIdentity = SecurityStampValidator
.OnValidateIdentity<ApplicationUserManager, ApplicationUser, int>(
validateInterval: TimeSpan.FromMinutes(30),
regenerateIdentityCallback: (manager, user) =>
user.GenerateUserIdentityAsync(manager),
getUserIdCallback:(id)=>(id.GetUserId<int>()))
}
});
Se o projeto não reconhecer a implementação genérica do método GetUserId , talvez seja necessário atualizar o pacote NuGet de identidade ASP.NET para a versão 2.1
Você fez muitas alterações nas classes de infraestrutura usadas pelo ASP.NET Identity. Se você tentar compilar o projeto, observará muitos erros. Felizmente, os erros restantes são todos semelhantes. A classe Identity espera um inteiro para a chave, mas o controlador (ou Formulário da Web) está passando um valor de cadeia de caracteres. Em cada caso, você precisa converter de uma cadeia de caracteres para e inteiro chamando GetUserId<int>. Você pode trabalhar na lista de erros da compilação ou seguir as alterações abaixo.
As alterações restantes dependem do tipo de projeto que você está criando e qual atualização você instalou no Visual Studio. Você pode ir diretamente para a seção relevante por meio dos links a seguir
- Para MVC com a Atualização 2, altere o AccountController para passar o tipo de chave
- Para MVC com a Atualização 3, altere AccountController e ManageController para passar o tipo de chave
- Para Web Forms com a Atualização 2, altere páginas de conta para passar o tipo de chave
- Para Web Forms com a Atualização 3, altere páginas de conta para passar o tipo de chave
Para MVC com a Atualização 2, altere o AccountController para passar o tipo de chave
Abra o arquivo AccountController.cs. Você precisa alterar os métodos a seguir.
Método ConfirmEmail
public async Task<ActionResult> ConfirmEmail(int userId, string code)
{
if (userId == default(int) || code == null)
{
return View("Error");
}
IdentityResult result = await UserManager.ConfirmEmailAsync(userId, code);
if (result.Succeeded)
{
return View("ConfirmEmail");
}
else
{
AddErrors(result);
return View();
}
}
Método disassociate
public async Task<ActionResult> Disassociate(string loginProvider, string providerKey)
{
ManageMessageId? message = null;
IdentityResult result = await UserManager.RemoveLoginAsync(
User.Identity.GetUserId<int>(),
new UserLoginInfo(loginProvider, providerKey));
if (result.Succeeded)
{
var user = await UserManager.FindByIdAsync(User.Identity.GetUserId<int>());
await SignInAsync(user, isPersistent: false);
message = ManageMessageId.RemoveLoginSuccess;
}
else
{
message = ManageMessageId.Error;
}
return RedirectToAction("Manage", new { Message = message });
}
Método Manage(ManageUserViewModel)
public async Task<ActionResult> Manage(ManageUserViewModel model)
{
bool hasPassword = HasPassword();
ViewBag.HasLocalPassword = hasPassword;
ViewBag.ReturnUrl = Url.Action("Manage");
if (hasPassword)
{
if (ModelState.IsValid)
{
IdentityResult result = await UserManager.ChangePasswordAsync(
User.Identity.GetUserId<int>(),
model.OldPassword,
model.NewPassword);
if (result.Succeeded)
{
var user = await UserManager.FindByIdAsync(
User.Identity.GetUserId<int>());
await SignInAsync(user, isPersistent: false);
return RedirectToAction("Manage", new {
Message = ManageMessageId.ChangePasswordSuccess });
}
else
{
AddErrors(result);
}
}
}
else
{
// User does not have a password so remove any validation errors caused
// by a missing OldPassword field
ModelState state = ModelState["OldPassword"];
if (state != null)
{
state.Errors.Clear();
}
if (ModelState.IsValid)
{
IdentityResult result = await UserManager.AddPasswordAsync(
User.Identity.GetUserId<int>(), model.NewPassword);
if (result.Succeeded)
{
return RedirectToAction("Manage", new {
Message = ManageMessageId.SetPasswordSuccess });
}
else
{
AddErrors(result);
}
}
}
// If we got this far, something failed, redisplay form
return View(model);
}
Método LinkLoginCallback
public async Task<ActionResult> LinkLoginCallback()
{
var loginInfo = await AuthenticationManager.GetExternalLoginInfoAsync(XsrfKey,
User.Identity.GetUserId());
if (loginInfo == null)
{
return RedirectToAction("Manage", new { Message = ManageMessageId.Error });
}
IdentityResult result = await UserManager.AddLoginAsync(
User.Identity.GetUserId<int>(), loginInfo.Login);
if (result.Succeeded)
{
return RedirectToAction("Manage");
}
return RedirectToAction("Manage", new { Message = ManageMessageId.Error });
}
Método RemoveAccountList
public ActionResult RemoveAccountList()
{
var linkedAccounts = UserManager.GetLogins(User.Identity.GetUserId<int>());
ViewBag.ShowRemoveButton = HasPassword() || linkedAccounts.Count > 1;
return (ActionResult)PartialView("_RemoveAccountPartial", linkedAccounts);
}
Método HasPassword
private bool HasPassword()
{
var user = UserManager.FindById(User.Identity.GetUserId<int>());
if (user != null)
{
return user.PasswordHash != null;
}
return false;
}
Agora você pode executar o aplicativo e registrar um novo usuário.
Para MVC com a Atualização 3, altere AccountController e ManageController para passar o tipo de chave
Abra o arquivo AccountController.cs. Você precisa alterar o método a seguir.
Método ConfirmEmail
public async Task<ActionResult> ConfirmEmail(int userId, string code)
{
if (userId == default(int) || code == null)
{
return View("Error");
}
IdentityResult result = await UserManager.ConfirmEmailAsync(userId, code);
return View(result.Succeeded ? "ConfirmEmail" : "Error");
}
Método SendCode
public async Task<ActionResult> SendCode(string returnUrl, bool rememberMe)
{
var userId = await SignInManager.GetVerifiedUserIdAsync();
if (userId == default(int))
{
return View("Error");
}
var userFactors = await UserManager.GetValidTwoFactorProvidersAsync(userId);
var factorOptions = userFactors.Select(purpose => new SelectListItem { Text = purpose, Value = purpose }).ToList();
return View(new SendCodeViewModel { Providers = factorOptions, ReturnUrl = returnUrl, RememberMe = rememberMe });
}
Abra o arquivo ManageController.cs. Você precisa alterar os métodos a seguir.
Método Index
public async Task<ActionResult> Index(ManageMessageId? message)
{
ViewBag.StatusMessage =
message == ManageMessageId.ChangePasswordSuccess ? "Your password has been changed."
: message == ManageMessageId.SetPasswordSuccess ? "Your password has been set."
: message == ManageMessageId.SetTwoFactorSuccess ? "Your two-factor authentication provider has been set."
: message == ManageMessageId.Error ? "An error has occurred."
: message == ManageMessageId.AddPhoneSuccess ? "Your phone number was added."
: message == ManageMessageId.RemovePhoneSuccess ? "Your phone number was removed."
: "";
var model = new IndexViewModel
{
HasPassword = HasPassword(),
PhoneNumber = await UserManager.GetPhoneNumberAsync(User.Identity.GetUserId<int>()),
TwoFactor = await UserManager.GetTwoFactorEnabledAsync(User.Identity.GetUserId<int>()),
Logins = await UserManager.GetLoginsAsync(User.Identity.GetUserId<int>()),
BrowserRemembered = await AuthenticationManager.TwoFactorBrowserRememberedAsync(
User.Identity.GetUserId())
};
return View(model);
}
Métodos RemoveLogin
public ActionResult RemoveLogin()
{
var linkedAccounts = UserManager.GetLogins((User.Identity.GetUserId<int>()));
ViewBag.ShowRemoveButton = HasPassword() || linkedAccounts.Count > 1;
return View(linkedAccounts);
}
[HttpPost]
[ValidateAntiForgeryToken]
public async Task<ActionResult> RemoveLogin(string loginProvider, string providerKey)
{
ManageMessageId? message;
var result = await UserManager.RemoveLoginAsync(User.Identity.GetUserId<int>(),
new UserLoginInfo(loginProvider, providerKey));
if (result.Succeeded)
{
var user = await UserManager.FindByIdAsync(User.Identity.GetUserId<int>());
if (user != null)
{
await SignInAsync(user, isPersistent: false);
}
message = ManageMessageId.RemoveLoginSuccess;
}
else
{
message = ManageMessageId.Error;
}
return RedirectToAction("ManageLogins", new { Message = message });
}
Método AddPhoneNumber
public async Task<ActionResult> AddPhoneNumber(AddPhoneNumberViewModel model)
{
if (!ModelState.IsValid)
{
return View(model);
}
// Generate the token and send it
var code = await UserManager.GenerateChangePhoneNumberTokenAsync(
User.Identity.GetUserId<int>(), model.Number);
if (UserManager.SmsService != null)
{
var message = new IdentityMessage
{
Destination = model.Number,
Body = "Your security code is: " + code
};
await UserManager.SmsService.SendAsync(message);
}
return RedirectToAction("VerifyPhoneNumber", new { PhoneNumber = model.Number });
}
Método EnableTwoFactorAuthentication
public async Task<ActionResult> EnableTwoFactorAuthentication()
{
await UserManager.SetTwoFactorEnabledAsync(User.Identity.GetUserId<int>(), true);
var user = await UserManager.FindByIdAsync(User.Identity.GetUserId<int>());
if (user != null)
{
await SignInAsync(user, isPersistent: false);
}
return RedirectToAction("Index", "Manage");
}
Método DisableTwoFactorAuthentication
public async Task<ActionResult> DisableTwoFactorAuthentication()
{
await UserManager.SetTwoFactorEnabledAsync(User.Identity.GetUserId<int>(), false);
var user = await UserManager.FindByIdAsync(User.Identity.GetUserId<int>());
if (user != null)
{
await SignInAsync(user, isPersistent: false);
}
return RedirectToAction("Index", "Manage");
}
Métodos VerifyPhoneNumber
public async Task<ActionResult> VerifyPhoneNumber(string phoneNumber)
{
var code = await UserManager.GenerateChangePhoneNumberTokenAsync(
User.Identity.GetUserId<int>(), phoneNumber);
// Send an SMS through the SMS provider to verify the phone number
return phoneNumber == null ? View("Error") : View(new VerifyPhoneNumberViewModel { PhoneNumber = phoneNumber });
}
[HttpPost]
[ValidateAntiForgeryToken]
public async Task<ActionResult> VerifyPhoneNumber(VerifyPhoneNumberViewModel model)
{
if (!ModelState.IsValid)
{
return View(model);
}
var result = await UserManager.ChangePhoneNumberAsync(
User.Identity.GetUserId<int>(), model.PhoneNumber, model.Code);
if (result.Succeeded)
{
var user = await UserManager.FindByIdAsync(User.Identity.GetUserId<int>());
if (user != null)
{
await SignInAsync(user, isPersistent: false);
}
return RedirectToAction("Index", new { Message = ManageMessageId.AddPhoneSuccess });
}
// If we got this far, something failed, redisplay form
ModelState.AddModelError("", "Failed to verify phone");
return View(model);
}
Método RemovePhoneNumber
public async Task<ActionResult> RemovePhoneNumber()
{
var result = await UserManager.SetPhoneNumberAsync(User.Identity.GetUserId<int>(), null);
if (!result.Succeeded)
{
return RedirectToAction("Index", new { Message = ManageMessageId.Error });
}
var user = await UserManager.FindByIdAsync(User.Identity.GetUserId<int>());
if (user != null)
{
await SignInAsync(user, isPersistent: false);
}
return RedirectToAction("Index", new { Message = ManageMessageId.RemovePhoneSuccess });
}
Método ChangePassword
[HttpPost]
[ValidateAntiForgeryToken]
public async Task<ActionResult> ChangePassword(ChangePasswordViewModel model)
{
if (!ModelState.IsValid)
{
return View(model);
}
var result = await UserManager.ChangePasswordAsync(
User.Identity.GetUserId<int>(), model.OldPassword, model.NewPassword);
if (result.Succeeded)
{
var user = await UserManager.FindByIdAsync(User.Identity.GetUserId<int>());
if (user != null)
{
await SignInAsync(user, isPersistent: false);
}
return RedirectToAction("Index", new { Message = ManageMessageId.ChangePasswordSuccess });
}
AddErrors(result);
return View(model);
}
Método SetPassword
public async Task<ActionResult> SetPassword(SetPasswordViewModel model)
{
if (ModelState.IsValid)
{
var result = await UserManager.AddPasswordAsync(User.Identity.GetUserId<int>(), model.NewPassword);
if (result.Succeeded)
{
var user = await UserManager.FindByIdAsync(User.Identity.GetUserId<int>());
if (user != null)
{
await SignInAsync(user, isPersistent: false);
}
return RedirectToAction("Index", new { Message = ManageMessageId.SetPasswordSuccess });
}
AddErrors(result);
}
// If we got this far, something failed, redisplay form
return View(model);
}
Método ManageLogins
public async Task<ActionResult> ManageLogins(ManageMessageId? message)
{
ViewBag.StatusMessage =
message == ManageMessageId.RemoveLoginSuccess ? "The external login was removed."
: message == ManageMessageId.Error ? "An error has occurred."
: "";
var user = await UserManager.FindByIdAsync(User.Identity.GetUserId<int>());
if (user == null)
{
return View("Error");
}
var userLogins = await UserManager.GetLoginsAsync(User.Identity.GetUserId<int>());
var otherLogins = AuthenticationManager.GetExternalAuthenticationTypes().Where(auth => userLogins.All(ul => auth.AuthenticationType != ul.LoginProvider)).ToList();
ViewBag.ShowRemoveButton = user.PasswordHash != null || userLogins.Count > 1;
return View(new ManageLoginsViewModel
{
CurrentLogins = userLogins,
OtherLogins = otherLogins
});
}
Método LinkLoginCallback
public async Task<ActionResult> LinkLoginCallback()
{
var loginInfo = await AuthenticationManager.GetExternalLoginInfoAsync(XsrfKey, User.Identity.GetUserId());
if (loginInfo == null)
{
return RedirectToAction("ManageLogins", new { Message = ManageMessageId.Error });
}
var result = await UserManager.AddLoginAsync(User.Identity.GetUserId<int>(),
loginInfo.Login);
return result.Succeeded ? RedirectToAction("ManageLogins") :
RedirectToAction("ManageLogins", new { Message = ManageMessageId.Error });
}
Método HasPassword
private bool HasPassword()
{
var user = UserManager.FindById(User.Identity.GetUserId<int>());
if (user != null)
{
return user.PasswordHash != null;
}
return false;
}
Método HasPhoneNumber
private bool HasPhoneNumber()
{
var user = UserManager.FindById(User.Identity.GetUserId<int>());
if (user != null)
{
return user.PhoneNumber != null;
}
return false;
}
Agora você pode executar o aplicativo e registrar um novo usuário.
Para Web Forms com a Atualização 2, altere páginas de conta para passar o tipo de chave
Para Web Forms com a Atualização 2, você precisa alterar as páginas a seguir.
Confirm.aspx.cx
protected void Page_Load(object sender, EventArgs e)
{
string code = IdentityHelper.GetCodeFromRequest(Request);
string userId = IdentityHelper.GetUserIdFromRequest(Request);
if (code != null && userId != null)
{
var manager = Context.GetOwinContext().GetUserManager<ApplicationUserManager>();
var result = manager.ConfirmEmail(Int32.Parse(userId), code);
if (result.Succeeded)
{
StatusMessage = "Thank you for confirming your account.";
return;
}
}
StatusMessage = "An error has occurred";
}
RegisterExternalLogin.aspx.cs
protected void Page_Load()
{
// Process the result from an auth provider in the request
ProviderName = IdentityHelper.GetProviderNameFromRequest(Request);
if (String.IsNullOrEmpty(ProviderName))
{
RedirectOnFail();
return;
}
if (!IsPostBack)
{
var manager = Context.GetOwinContext().GetUserManager<ApplicationUserManager>();
var loginInfo = Context.GetOwinContext().Authentication.GetExternalLoginInfo();
if (loginInfo == null)
{
RedirectOnFail();
return;
}
var user = manager.Find(loginInfo.Login);
if (user != null)
{
IdentityHelper.SignIn(manager, user, isPersistent: false);
IdentityHelper.RedirectToReturnUrl(Request.QueryString["ReturnUrl"], Response);
}
else if (User.Identity.IsAuthenticated)
{
// Apply Xsrf check when linking
var verifiedloginInfo = Context.GetOwinContext().Authentication
.GetExternalLoginInfo(IdentityHelper.XsrfKey, User.Identity.GetUserId());
if (verifiedloginInfo == null)
{
RedirectOnFail();
return;
}
var result = manager.AddLogin(User.Identity.GetUserId<int>(),
verifiedloginInfo.Login);
if (result.Succeeded)
{
IdentityHelper.RedirectToReturnUrl(Request.QueryString["ReturnUrl"],
Response);
}
else
{
AddErrors(result);
return;
}
}
else
{
email.Text = loginInfo.Email;
}
}
}
Manage.aspx.cs
private bool HasPassword(ApplicationUserManager manager)
{
return manager.HasPassword(User.Identity.GetUserId<int>());
}
protected void Page_Load()
{
if (!IsPostBack)
{
// Determine the sections to render
var manager = Context.GetOwinContext().GetUserManager<ApplicationUserManager>();
if (HasPassword(manager))
{
changePasswordHolder.Visible = true;
}
else
{
setPassword.Visible = true;
changePasswordHolder.Visible = false;
}
CanRemoveExternalLogins = manager.GetLogins(
User.Identity.GetUserId<int>()).Count() > 1;
// Render success message
var message = Request.QueryString["m"];
if (message != null)
{
// Strip the query string from action
Form.Action = ResolveUrl("~/Account/Manage");
SuccessMessage =
message == "ChangePwdSuccess" ? "Your password has been changed."
: message == "SetPwdSuccess" ? "Your password has been set."
: message == "RemoveLoginSuccess" ? "The account was removed."
: String.Empty;
successMessage.Visible = !String.IsNullOrEmpty(SuccessMessage);
}
}
}
protected void ChangePassword_Click(object sender, EventArgs e)
{
if (IsValid)
{
var manager = Context.GetOwinContext().GetUserManager<ApplicationUserManager>();
IdentityResult result = manager.ChangePassword(
User.Identity.GetUserId<int>(),
CurrentPassword.Text,
NewPassword.Text);
if (result.Succeeded)
{
var user = manager.FindById(User.Identity.GetUserId<int>());
IdentityHelper.SignIn(manager, user, isPersistent: false);
Response.Redirect("~/Account/Manage?m=ChangePwdSuccess");
}
else
{
AddErrors(result);
}
}
}
protected void SetPassword_Click(object sender, EventArgs e)
{
if (IsValid)
{
// Create the local login info and link the local account to the user
var manager = Context.GetOwinContext().GetUserManager<ApplicationUserManager>();
IdentityResult result = manager.AddPassword(User.Identity.GetUserId<int>(),
password.Text);
if (result.Succeeded)
{
Response.Redirect("~/Account/Manage?m=SetPwdSuccess");
}
else
{
AddErrors(result);
}
}
}
public IEnumerable<UserLoginInfo> GetLogins()
{
var manager = Context.GetOwinContext().GetUserManager<ApplicationUserManager>();
var accounts = manager.GetLogins(User.Identity.GetUserId<int>());
CanRemoveExternalLogins = accounts.Count() > 1 || HasPassword(manager);
return accounts;
}
public void RemoveLogin(string loginProvider, string providerKey)
{
var manager = Context.GetOwinContext().GetUserManager<ApplicationUserManager>();
var result = manager.RemoveLogin(User.Identity.GetUserId<int>(),
new UserLoginInfo(loginProvider, providerKey));
string msg = String.Empty;
if (result.Succeeded)
{
var user = manager.FindById(User.Identity.GetUserId<int>());
IdentityHelper.SignIn(manager, user, isPersistent: false);
msg = "?m=RemoveLoginSuccess";
}
Response.Redirect("~/Account/Manage" + msg);
}
Agora você pode executar o aplicativo e registrar um novo usuário.
Para Web Forms com a Atualização 3, altere páginas de conta para passar o tipo de chave
Para Web Forms com a Atualização 3, você precisa alterar as páginas a seguir.
Confirm.aspx.cx
protected void Page_Load(object sender, EventArgs e)
{
string code = IdentityHelper.GetCodeFromRequest(Request);
string userId = IdentityHelper.GetUserIdFromRequest(Request);
if (code != null && userId != null)
{
var manager = Context.GetOwinContext().GetUserManager<ApplicationUserManager>();
var result = manager.ConfirmEmail(Int32.Parse(userId), code);
if (result.Succeeded)
{
StatusMessage = "Thank you for confirming your account.";
return;
}
}
StatusMessage = "An error has occurred";
}
RegisterExternalLogin.aspx.cs
protected void Page_Load()
{
// Process the result from an auth provider in the request
ProviderName = IdentityHelper.GetProviderNameFromRequest(Request);
if (String.IsNullOrEmpty(ProviderName))
{
RedirectOnFail();
return;
}
if (!IsPostBack)
{
var manager = Context.GetOwinContext().GetUserManager<ApplicationUserManager>();
var loginInfo = Context.GetOwinContext().Authentication.GetExternalLoginInfo();
if (loginInfo == null)
{
RedirectOnFail();
return;
}
var user = manager.Find(loginInfo.Login);
if (user != null)
{
IdentityHelper.SignIn(manager, user, isPersistent: false);
IdentityHelper.RedirectToReturnUrl(Request.QueryString["ReturnUrl"], Response);
}
else if (User.Identity.IsAuthenticated)
{
// Apply Xsrf check when linking
var verifiedloginInfo = Context.GetOwinContext().Authentication
.GetExternalLoginInfo(IdentityHelper.XsrfKey, User.Identity.GetUserId());
if (verifiedloginInfo == null)
{
RedirectOnFail();
return;
}
var result = manager.AddLogin(User.Identity.GetUserId<int>(),
verifiedloginInfo.Login);
if (result.Succeeded)
{
IdentityHelper.RedirectToReturnUrl(Request.QueryString["ReturnUrl"],
Response);
}
else
{
AddErrors(result);
return;
}
}
else
{
email.Text = loginInfo.Email;
}
}
}
Manage.aspx.cs
public partial class Manage : System.Web.UI.Page
{
protected string SuccessMessage
{
get;
private set;
}
private bool HasPassword(ApplicationUserManager manager)
{
return manager.HasPassword(User.Identity.GetUserId<int>());
}
public bool HasPhoneNumber { get; private set; }
public bool TwoFactorEnabled { get; private set; }
public bool TwoFactorBrowserRemembered { get; private set; }
public int LoginsCount { get; set; }
protected void Page_Load()
{
var manager = Context.GetOwinContext().GetUserManager<ApplicationUserManager>();
HasPhoneNumber = String.IsNullOrEmpty(manager.GetPhoneNumber(
User.Identity.GetUserId<int>()));
// Enable this after setting up two-factor authentientication
//PhoneNumber.Text = manager.GetPhoneNumber(User.Identity.GetUserId()) ?? String.Empty;
TwoFactorEnabled = manager.GetTwoFactorEnabled(User.Identity.GetUserId<int>());
LoginsCount = manager.GetLogins(User.Identity.GetUserId<int>()).Count;
var authenticationManager = HttpContext.Current.GetOwinContext().Authentication;
if (!IsPostBack)
{
// Determine the sections to render
if (HasPassword(manager))
{
ChangePassword.Visible = true;
}
else
{
CreatePassword.Visible = true;
ChangePassword.Visible = false;
}
// Render success message
var message = Request.QueryString["m"];
if (message != null)
{
// Strip the query string from action
Form.Action = ResolveUrl("~/Account/Manage");
SuccessMessage =
message == "ChangePwdSuccess" ? "Your password has been changed."
: message == "SetPwdSuccess" ? "Your password has been set."
: message == "RemoveLoginSuccess" ? "The account was removed."
: message == "AddPhoneNumberSuccess" ? "Phone number has been added"
: message == "RemovePhoneNumberSuccess" ? "Phone number was removed"
: String.Empty;
successMessage.Visible = !String.IsNullOrEmpty(SuccessMessage);
}
}
}
private void AddErrors(IdentityResult result)
{
foreach (var error in result.Errors)
{
ModelState.AddModelError("", error);
}
}
// Remove phonenumber from user
protected void RemovePhone_Click(object sender, EventArgs e)
{
var manager = Context.GetOwinContext().GetUserManager<ApplicationUserManager>();
var result = manager.SetPhoneNumber(User.Identity.GetUserId<int>(), null);
if (!result.Succeeded)
{
return;
}
var user = manager.FindById(User.Identity.GetUserId<int>());
if (user != null)
{
IdentityHelper.SignIn(manager, user, isPersistent: false);
Response.Redirect("/Account/Manage?m=RemovePhoneNumberSuccess");
}
}
// DisableTwoFactorAuthentication
protected void TwoFactorDisable_Click(object sender, EventArgs e)
{
var manager = Context.GetOwinContext().GetUserManager<ApplicationUserManager>();
manager.SetTwoFactorEnabled(User.Identity.GetUserId<int>(), false);
Response.Redirect("/Account/Manage");
}
//EnableTwoFactorAuthentication
protected void TwoFactorEnable_Click(object sender, EventArgs e)
{
var manager = Context.GetOwinContext().GetUserManager<ApplicationUserManager>();
manager.SetTwoFactorEnabled(User.Identity.GetUserId<int>(), true);
Response.Redirect("/Account/Manage");
}
}
VerifyPhoneNumber.aspx.cs
public partial class VerifyPhoneNumber : System.Web.UI.Page
{
protected void Page_Load(object sender, EventArgs e)
{
var manager = Context.GetOwinContext().GetUserManager<ApplicationUserManager>();
var phonenumber = Request.QueryString["PhoneNumber"];
var code = manager.GenerateChangePhoneNumberToken(
User.Identity.GetUserId<int>(), phonenumber);
PhoneNumber.Value = phonenumber;
}
protected void Code_Click(object sender, EventArgs e)
{
if (!ModelState.IsValid)
{
ModelState.AddModelError("", "Invalid code");
return;
}
var manager = Context.GetOwinContext().GetUserManager<ApplicationUserManager>();
var result = manager.ChangePhoneNumber(
User.Identity.GetUserId<int>(), PhoneNumber.Value, Code.Text);
if (result.Succeeded)
{
var user = manager.FindById(User.Identity.GetUserId<int>());
if (user != null)
{
IdentityHelper.SignIn(manager, user, false);
Response.Redirect("/Account/Manage?m=AddPhoneNumberSuccess");
}
}
// If we got this far, something failed, redisplay form
ModelState.AddModelError("", "Failed to verify phone");
}
}
AddPhoneNumber.aspx.cs
public partial class AddPhoneNumber : System.Web.UI.Page
{
protected void PhoneNumber_Click(object sender, EventArgs e)
{
var manager = Context.GetOwinContext().GetUserManager<ApplicationUserManager>();
var code = manager.GenerateChangePhoneNumberToken(
User.Identity.GetUserId<int>(), PhoneNumber.Text);
if (manager.SmsService != null)
{
var message = new IdentityMessage
{
Destination = PhoneNumber.Text,
Body = "Your security code is " + code
};
manager.SmsService.Send(message);
}
Response.Redirect("/Account/VerifyPhoneNumber?PhoneNumber=" + HttpUtility.UrlEncode(PhoneNumber.Text));
}
}
ManagePassword.aspx.cs
public partial class ManagePassword : System.Web.UI.Page
{
protected string SuccessMessage
{
get;
private set;
}
private bool HasPassword(ApplicationUserManager manager)
{
return manager.HasPassword(User.Identity.GetUserId<int>());
}
protected void Page_Load(object sender, EventArgs e)
{
var manager = Context.GetOwinContext().GetUserManager<ApplicationUserManager>();
if (!IsPostBack)
{
// Determine the sections to render
if (HasPassword(manager))
{
changePasswordHolder.Visible = true;
}
else
{
setPassword.Visible = true;
changePasswordHolder.Visible = false;
}
// Render success message
var message = Request.QueryString["m"];
if (message != null)
{
// Strip the query string from action
Form.Action = ResolveUrl("~/Account/Manage");
}
}
}
protected void ChangePassword_Click(object sender, EventArgs e)
{
if (IsValid)
{
var manager = Context.GetOwinContext().GetUserManager<ApplicationUserManager>();
IdentityResult result = manager.ChangePassword(
User.Identity.GetUserId<int>(), CurrentPassword.Text, NewPassword.Text);
if (result.Succeeded)
{
var user = manager.FindById(User.Identity.GetUserId<int>());
IdentityHelper.SignIn(manager, user, isPersistent: false);
Response.Redirect("~/Account/Manage?m=ChangePwdSuccess");
}
else
{
AddErrors(result);
}
}
}
protected void SetPassword_Click(object sender, EventArgs e)
{
if (IsValid)
{
// Create the local login info and link the local account to the user
var manager = Context.GetOwinContext().GetUserManager<ApplicationUserManager>();
IdentityResult result = manager.AddPassword(
User.Identity.GetUserId<int>(), password.Text);
if (result.Succeeded)
{
Response.Redirect("~/Account/Manage?m=SetPwdSuccess");
}
else
{
AddErrors(result);
}
}
}
private void AddErrors(IdentityResult result)
{
foreach (var error in result.Errors)
{
ModelState.AddModelError("", error);
}
}
}
ManageLogins.aspx.cs
public partial class ManageLogins : System.Web.UI.Page
{
protected string SuccessMessage
{
get;
private set;
}
protected bool CanRemoveExternalLogins
{
get;
private set;
}
private bool HasPassword(ApplicationUserManager manager)
{
return manager.HasPassword(User.Identity.GetUserId<int>());
}
protected void Page_Load(object sender, EventArgs e)
{
var manager = Context.GetOwinContext().GetUserManager<ApplicationUserManager>();
CanRemoveExternalLogins = manager.GetLogins(
User.Identity.GetUserId<int>()).Count() > 1;
SuccessMessage = String.Empty;
successMessage.Visible = !String.IsNullOrEmpty(SuccessMessage);
}
public IEnumerable<UserLoginInfo> GetLogins()
{
var manager = Context.GetOwinContext().GetUserManager<ApplicationUserManager>();
var accounts = manager.GetLogins(User.Identity.GetUserId<int>());
CanRemoveExternalLogins = accounts.Count() > 1 || HasPassword(manager);
return accounts;
}
public void RemoveLogin(string loginProvider, string providerKey)
{
var manager = Context.GetOwinContext().GetUserManager<ApplicationUserManager>();
var result = manager.RemoveLogin(
User.Identity.GetUserId<int>(), new UserLoginInfo(loginProvider, providerKey));
string msg = String.Empty;
if (result.Succeeded)
{
var user = manager.FindById(User.Identity.GetUserId<int>());
IdentityHelper.SignIn(manager, user, isPersistent: false);
msg = "?m=RemoveLoginSuccess";
}
Response.Redirect("~/Account/ManageLogins" + msg);
}
}
TwoFactorAuthenticationSignIn.aspx.cs
public partial class TwoFactorAuthenticationSignIn : System.Web.UI.Page
{
private ApplicationSignInManager signinManager;
private ApplicationUserManager manager;
public TwoFactorAuthenticationSignIn()
{
manager = Context.GetOwinContext().GetUserManager<ApplicationUserManager>();
signinManager = Context.GetOwinContext().GetUserManager<ApplicationSignInManager>();
}
protected void Page_Load(object sender, EventArgs e)
{
var userId = signinManager.GetVerifiedUserId<ApplicationUser, int>();
if (userId == default(int))
{
Response.Redirect("/Account/Error", true);
}
var userFactors = manager.GetValidTwoFactorProviders(userId);
Providers.DataSource = userFactors.Select(x => x).ToList();
Providers.DataBind();
}
protected void CodeSubmit_Click(object sender, EventArgs e)
{
bool rememberMe = false;
bool.TryParse(Request.QueryString["RememberMe"], out rememberMe);
var result = signinManager.TwoFactorSignIn<ApplicationUser, int>(SelectedProvider.Value, Code.Text, isPersistent: rememberMe, rememberBrowser: RememberBrowser.Checked);
switch (result)
{
case SignInStatus.Success:
IdentityHelper.RedirectToReturnUrl(Request.QueryString["ReturnUrl"], Response);
break;
case SignInStatus.LockedOut:
Response.Redirect("/Account/Lockout");
break;
case SignInStatus.Failure:
default:
FailureText.Text = "Invalid code";
ErrorMessage.Visible = true;
break;
}
}
protected void ProviderSubmit_Click(object sender, EventArgs e)
{
if (!signinManager.SendTwoFactorCode(Providers.SelectedValue))
{
Response.Redirect("/Account/Error");
}
var user = manager.FindById(signinManager.GetVerifiedUserId<ApplicationUser, int>());
if (user != null)
{
var code = manager.GenerateTwoFactorToken(user.Id, Providers.SelectedValue);
}
SelectedProvider.Value = Providers.SelectedValue;
sendcode.Visible = false;
verifycode.Visible = true;
}
}
Executar aplicativo
Você concluiu todas as alterações necessárias para o modelo de Aplicativo Web padrão. Execute o aplicativo e registre um novo usuário. Depois de registrar o usuário, você observará que a tabela AspNetUsers tem uma coluna de Id que é um inteiro.
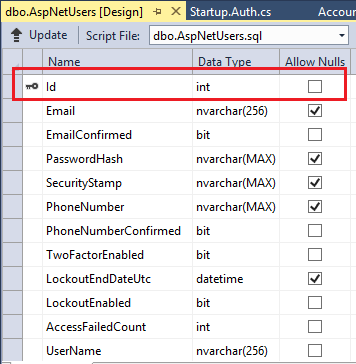
Se você já criou as tabelas ASP.NET Identity com uma chave primária diferente, precisará fazer algumas alterações adicionais. Se possível, basta excluir o banco de dados existente. O banco de dados será recriado com o design correto quando você executar o aplicativo Web e adicionar um novo usuário. Se a exclusão não for possível, execute as primeiras migrações de código para alterar as tabelas. No entanto, a nova chave primária de inteiro não será configurada como uma propriedade SQL IDENTITY no banco de dados. Você deve definir manualmente a coluna Id como uma IDENTITY.
Outros recursos
- Visão geral de provedores de armazenamento personalizados para a Identidade do ASP.NET
- Migração de um site existente da Associação do SQL para a Identidade do ASP.NET
- Migrando dados do provedor universal para associação e perfis de usuário para ASP.NET Identidade
- Aplicativo de exemplo com chave primária alterada
Comentários
Em breve: Ao longo de 2024, eliminaremos os problemas do GitHub como o mecanismo de comentários para conteúdo e o substituiremos por um novo sistema de comentários. Para obter mais informações, consulte https://aka.ms/ContentUserFeedback.
Enviar e exibir comentários de