Usar o módulo de serviços do Azure Maps
O SDK da Web do Azure Maps fornece um módulo de serviços. Este módulo é uma biblioteca auxiliar que facilita o uso dos serviços REST do Azure Maps em aplicativos Web ou Node.js usando JavaScript ou TypeScript.
Nota
Desativação do Módulo de Serviço SDK da Web do Azure Maps
O Módulo de Serviço SDK da Web do Azure Maps foi preterido e será desativado em 30/09/26. Para evitar interrupções de serviço, recomendamos migrar para o SDK REST JavaScript do Azure Maps até 30/09/26. Para obter mais informações, consulte JavaScript/TypeScript REST SDK Developers Guide (visualização).
Usar o módulo de serviços em uma página da Web
Crie um novo arquivo HTML.
Carregue o módulo de serviços do Azure Maps. Você pode carregá-lo de duas maneiras:
- Use a versão da Rede de Entrega de Conteúdo do Azure hospedada globalmente do módulo de serviços do Azure Maps. Adicione uma referência de script ao
<head>elemento do arquivo:
<script src="https://atlas.microsoft.com/sdk/javascript/service/2/atlas-service.min.js"></script>Como alternativa, carregue o módulo de serviços para o código-fonte do SDK da Web do Azure Maps localmente usando o pacote azure-maps-rest npm e hospede-o com seu aplicativo. Este pacote também inclui definições TypeScript. Utilize este comando:
npm install azure-maps-restEm seguida, use uma declaração de importação para adicionar o módulo a um arquivo de origem:
import * as service from "azure-maps-rest";
- Use a versão da Rede de Entrega de Conteúdo do Azure hospedada globalmente do módulo de serviços do Azure Maps. Adicione uma referência de script ao
Crie um pipeline de autenticação. O pipeline deve ser criado antes que você possa inicializar um ponto de extremidade do cliente de URL de serviço. Use sua própria chave de conta do Azure Maps ou credenciais do Microsoft Entra para autenticar um cliente de serviço do Azure Maps Search. Neste exemplo, o cliente de URL do serviço de Pesquisa é criado.
Se você usar uma chave de assinatura para autenticação:
// Get an Azure Maps key at https://azure.com/maps. var subscriptionKey = '<Your Azure Maps Key>'; // Use SubscriptionKeyCredential with a subscription key. var subscriptionKeyCredential = new atlas.service.SubscriptionKeyCredential(subscriptionKey); // Use subscriptionKeyCredential to create a pipeline. var pipeline = atlas.service.MapsURL.newPipeline(subscriptionKeyCredential, { retryOptions: { maxTries: 4 } // Retry options }); // Create an instance of the SearchURL client. var searchURL = new atlas.service.SearchURL(pipeline);Se você usar o Microsoft Entra ID para autenticação:
// Enter your Azure AD client ID. var clientId = "<Your Azure Active Directory Client Id>"; // Use TokenCredential with OAuth token (Azure AD or Anonymous). var aadToken = await getAadToken(); var tokenCredential = new atlas.service.TokenCredential(clientId, aadToken); // Create a repeating time-out that will renew the Azure AD token. // This time-out must be cleared when the TokenCredential object is no longer needed. // If the time-out is not cleared, the memory used by the TokenCredential will never be reclaimed. var renewToken = async () => { try { console.log("Renewing token"); var token = await getAadToken(); tokenCredential.token = token; tokenRenewalTimer = setTimeout(renewToken, getExpiration(token)); } catch (error) { console.log("Caught error when renewing token"); clearTimeout(tokenRenewalTimer); throw error; } } tokenRenewalTimer = setTimeout(renewToken, getExpiration(aadToken)); // Use tokenCredential to create a pipeline. var pipeline = atlas.service.MapsURL.newPipeline(tokenCredential, { retryOptions: { maxTries: 4 } // Retry options }); // Create an instance of the SearchURL client. var searchURL = new atlas.service.SearchURL(pipeline); function getAadToken() { // Use the signed-in auth context to get a token. return new Promise((resolve, reject) => { // The resource should always be https://atlas.microsoft.com/. const resource = "https://atlas.microsoft.com/"; authContext.acquireToken(resource, (error, token) => { if (error) { reject(error); } else { resolve(token); } }); }) } function getExpiration(jwtToken) { // Decode the JSON Web Token (JWT) to get the expiration time stamp. const json = atob(jwtToken.split(".")[1]); const decode = JSON.parse(json); // Return the milliseconds remaining until the token must be renewed. // Reduce the time until renewal by 5 minutes to avoid using an expired token. // The exp property is the time stamp of the expiration, in seconds. const renewSkew = 300000; return (1000 * decode.exp) - Date.now() - renewSkew; }Para obter mais informações, consulte Autenticação com mapas do Azure.
O código a seguir usa o cliente de URL do serviço Azure Maps Search recém-criado para geocodificar um endereço: "1 Microsoft Way, Redmond, WA". O código usa a
searchAddressfunção e exibe os resultados como uma tabela no corpo da página.// Search for "1 microsoft way, redmond, wa". searchURL.searchAddress(atlas.service.Aborter.timeout(10000), '1 microsoft way, redmond, wa') .then(response => { var html = []; // Display the total results. html.push('Total results: ', response.summary.numResults, '<br/><br/>'); // Create a table of the results. html.push('<table><tr><td></td><td>Result</td><td>Latitude</td><td>Longitude</td></tr>'); for(var i=0;i<response.results.length;i++){ html.push('<tr><td>', (i+1), '.</td><td>', response.results[i].address.freeformAddress, '</td><td>', response.results[i].position.lat, '</td><td>', response.results[i].position.lon, '</td></tr>'); } html.push('</table>'); // Add the resulting HTML to the body of the page. document.body.innerHTML = html.join(''); });
Aqui está o exemplo de código completo em execução:
<html>
<head>
<script src="https://atlas.microsoft.com/sdk/javascript/service/2/atlas-service.min.js"></script>
<script type="text/javascript">
// Get an Azure Maps key at https://azure.com/maps.
var subscriptionKey = '{Your-Azure-Maps-Subscription-key}';
// Use SubscriptionKeyCredential with a subscription key.
var subscriptionKeyCredential = new atlas.service.SubscriptionKeyCredential(subscriptionKey);
// Use subscriptionKeyCredential to create a pipeline.
var pipeline = atlas.service.MapsURL.newPipeline(subscriptionKeyCredential, {
retryOptions: { maxTries: 4 } // Retry options
});
// Create an instance of the SearchURL client.
var searchURL = new atlas.service.SearchURL(pipeline);
// Search for "1 microsoft way, redmond, wa".
searchURL.searchAddress(atlas.service.Aborter.timeout(10000), '1 microsoft way, redmond, wa')
.then(response => {
var html = [];
// Display the total results.
html.push('Total results: ', response.summary.numResults, '<br/><br/>');
// Create a table of the results.
html.push('<table><tr><td></td><td>Result</td><td>Latitude</td><td>Longitude</td></tr>');
for(var i=0;i<response.results.length;i++){
html.push('<tr><td>', (i+1), '.</td><td>',
response.results[i].address.freeformAddress,
'</td><td>',
response.results[i].position.lat,
'</td><td>',
response.results[i].position.lon,
'</td></tr>');
}
html.push('</table>');
// Add the resulting HTML to the body of the page.
document.body.innerHTML = html.join('');
});
</script>
</head>
<style>
table {
border: 1px solid black;
border-collapse: collapse;
}
td, th {
border: 1px solid black;
padding: 5px;
}
</style>
<body> </body>
</html>
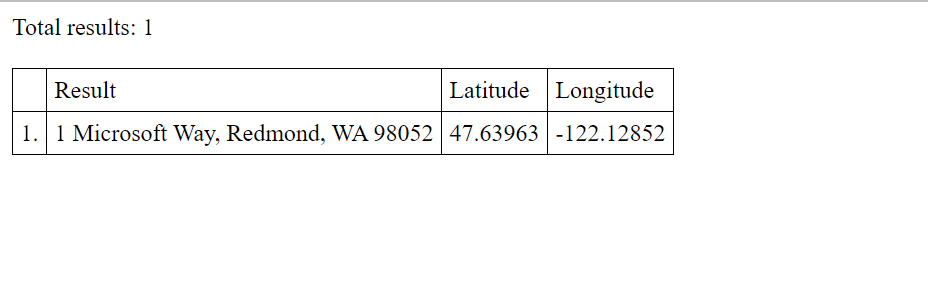
A imagem a seguir é uma captura de tela mostrando os resultados desse código de exemplo, uma tabela com o endereço pesquisado, juntamente com as coordenadas resultantes.
Suporte na nuvem do Azure Government
O SDK da Web do Azure Maps dá suporte à nuvem do Azure Government. Todas as URLs JavaScript e CSS usadas para acessar o SDK da Web do Azure Maps permanecem as mesmas, no entanto, as tarefas a seguir precisam ser feitas para se conectar à versão de nuvem do Azure Government da plataforma Azure Maps.
Ao usar o controle de mapa interativo, adicione a seguinte linha de código antes de criar uma instância da Map classe.
atlas.setDomain('atlas.azure.us');
Certifique-se de usar os detalhes de autenticação do Azure Maps da plataforma de nuvem do Azure Government ao autenticar o mapa e os serviços.
O domínio para os serviços precisa ser definido ao criar uma instância de um ponto de extremidade de URL de API. Por exemplo, o código a seguir cria uma instância da SearchURL classe e aponta o domínio para a nuvem do Azure Government.
var searchURL = new atlas.service.SearchURL(pipeline, 'atlas.azure.us');
Se acessar diretamente os serviços REST do Azure Maps, altere o domínio da URL para atlas.azure.us. Por exemplo, se estiver usando o serviço de API de pesquisa, altere o domínio da URL de https://atlas.microsoft.com/search/ para https://atlas.azure.us/search/.
Próximos passos
Saiba mais sobre as classes e métodos usados neste artigo:
Para obter mais exemplos de código que usam o módulo de serviços, consulte estes artigos: