语音识别
使用语音识别提供输入内容、指定操作或命令并完成任务。
语音识别由以下部分构成:语音运行时、用于为运行时编程的识别 API、用于听写和 Web 搜索的现成语法,以及帮助用户发现和使用语音识别功能的默认系统 UI。
配置语音识别
若要支持应用的语音识别,用户必须在其设备上连接并启用麦克风,并接受向应用授予相应使用权限的 Microsoft 隐私策略。
若要使用系统对话框自动提示用户,向其请求访问和使用麦克风音频馈送的权限(示例来自语音识别和语音合成示例,如下所示),只需在应用程序包清单中设置麦克风设备功能即可。 有关更多详细信息,请参阅应用功能声明。

如果用户单击“是”授予对麦克风的访问权限,你的应用会添加到“设置”->“隐私”->麦克风”页上的批准的应用程序列表中。 但是,由于用户可以随时选择关闭此设置,因此在尝试使用麦克风之前,应确认应用有权访问麦克风。
如果还希望支持听写、Cortana 或其他语音识别服务(如主题约束中定义的预定义语法),还需要确认启用了“在线语音识别”(“设置”->“隐私”->“语音”)。
此代码段显示你的应用如何检查麦克风是否存在以及应用是否有权使用它。
public class AudioCapturePermissions
{
// If no microphone is present, an exception is thrown with the following HResult value.
private static int NoCaptureDevicesHResult = -1072845856;
/// <summary>
/// Note that this method only checks the Settings->Privacy->Microphone setting, it does not handle
/// the Cortana/Dictation privacy check.
///
/// You should perform this check every time the app gets focus, in case the user has changed
/// the setting while the app was suspended or not in focus.
/// </summary>
/// <returns>True, if the microphone is available.</returns>
public async static Task<bool> RequestMicrophonePermission()
{
try
{
// Request access to the audio capture device.
MediaCaptureInitializationSettings settings = new MediaCaptureInitializationSettings();
settings.StreamingCaptureMode = StreamingCaptureMode.Audio;
settings.MediaCategory = MediaCategory.Speech;
MediaCapture capture = new MediaCapture();
await capture.InitializeAsync(settings);
}
catch (TypeLoadException)
{
// Thrown when a media player is not available.
var messageDialog = new Windows.UI.Popups.MessageDialog("Media player components are unavailable.");
await messageDialog.ShowAsync();
return false;
}
catch (UnauthorizedAccessException)
{
// Thrown when permission to use the audio capture device is denied.
// If this occurs, show an error or disable recognition functionality.
return false;
}
catch (Exception exception)
{
// Thrown when an audio capture device is not present.
if (exception.HResult == NoCaptureDevicesHResult)
{
var messageDialog = new Windows.UI.Popups.MessageDialog("No Audio Capture devices are present on this system.");
await messageDialog.ShowAsync();
return false;
}
else
{
throw;
}
}
return true;
}
}
/// <summary>
/// Note that this method only checks the Settings->Privacy->Microphone setting, it does not handle
/// the Cortana/Dictation privacy check.
///
/// You should perform this check every time the app gets focus, in case the user has changed
/// the setting while the app was suspended or not in focus.
/// </summary>
/// <returns>True, if the microphone is available.</returns>
IAsyncOperation<bool>^ AudioCapturePermissions::RequestMicrophonePermissionAsync()
{
return create_async([]()
{
try
{
// Request access to the audio capture device.
MediaCaptureInitializationSettings^ settings = ref new MediaCaptureInitializationSettings();
settings->StreamingCaptureMode = StreamingCaptureMode::Audio;
settings->MediaCategory = MediaCategory::Speech;
MediaCapture^ capture = ref new MediaCapture();
return create_task(capture->InitializeAsync(settings))
.then([](task<void> previousTask) -> bool
{
try
{
previousTask.get();
}
catch (AccessDeniedException^)
{
// Thrown when permission to use the audio capture device is denied.
// If this occurs, show an error or disable recognition functionality.
return false;
}
catch (Exception^ exception)
{
// Thrown when an audio capture device is not present.
if (exception->HResult == AudioCapturePermissions::NoCaptureDevicesHResult)
{
auto messageDialog = ref new Windows::UI::Popups::MessageDialog("No Audio Capture devices are present on this system.");
create_task(messageDialog->ShowAsync());
return false;
}
throw;
}
return true;
});
}
catch (Platform::ClassNotRegisteredException^ ex)
{
// Thrown when a media player is not available.
auto messageDialog = ref new Windows::UI::Popups::MessageDialog("Media Player Components unavailable.");
create_task(messageDialog->ShowAsync());
return create_task([] {return false; });
}
});
}
var AudioCapturePermissions = WinJS.Class.define(
function () { }, {},
{
requestMicrophonePermission: function () {
/// <summary>
/// Note that this method only checks the Settings->Privacy->Microphone setting, it does not handle
/// the Cortana/Dictation privacy check.
///
/// You should perform this check every time the app gets focus, in case the user has changed
/// the setting while the app was suspended or not in focus.
/// </summary>
/// <returns>True, if the microphone is available.</returns>
return new WinJS.Promise(function (completed, error) {
try {
// Request access to the audio capture device.
var captureSettings = new Windows.Media.Capture.MediaCaptureInitializationSettings();
captureSettings.streamingCaptureMode = Windows.Media.Capture.StreamingCaptureMode.audio;
captureSettings.mediaCategory = Windows.Media.Capture.MediaCategory.speech;
var capture = new Windows.Media.Capture.MediaCapture();
capture.initializeAsync(captureSettings).then(function () {
completed(true);
},
function (error) {
// Audio Capture can fail to initialize if there's no audio devices on the system, or if
// the user has disabled permission to access the microphone in the Privacy settings.
if (error.number == -2147024891) { // Access denied (microphone disabled in settings)
completed(false);
} else if (error.number == -1072845856) { // No recording device present.
var messageDialog = new Windows.UI.Popups.MessageDialog("No Audio Capture devices are present on this system.");
messageDialog.showAsync();
completed(false);
} else {
error(error);
}
});
} catch (exception) {
if (exception.number == -2147221164) { // REGDB_E_CLASSNOTREG
var messageDialog = new Windows.UI.Popups.MessageDialog("Media Player components not available on this system.");
messageDialog.showAsync();
return false;
}
}
});
}
})
识别语音输入
约束可定义该应用在语音输入中识别出的字词和短语(词汇)。 约束是语音识别的核心,可让你的应用更好地控制语音识别的准确性。
可以使用以下类型的约束来识别语音输入。
预定义的语法
预定义的听写和 Web 搜索语法在无需你创作语法的情况下为你的应用提供语音识别。 使用这些语法时,语音识别由远程 Web 服务执行,并且结果将返回到设备。
默认自由文本听写语法可以识别用户以特定语言说出的大部分字词或短语,并且为识别短语进行了优化。 如果没有为 SpeechRecognizer 对象指定任何约束,将使用预定义的听写语法。 当你不希望限制用户可说内容的种类时,自由文本听写非常有用。 典型用法包括为一条消息创建笔记或听写其内容。
诸如听写语法等 Web 搜索语法包含了用户可能说出的大量字词和短语。 但是,优化它的目的是识别用户搜索 Web 时通常使用的术语。
注意
由于预定义的听写和 Web 搜索语法可能很大,而且处于联机状态(不在设备上),性能可能不如安装在设备上的自定义语法快。
可以使用这些预定义语法识别长达 10 秒的语音输入,并且不要求你进行任何创作。 然而,它们确实需要连接到网络。
若要使用 Web 服务约束,必须在设置中启用语音输入和听写支持,方法是在“设置- 隐私 ->> 语音- 语音、墨迹书写和键入”中启用“了解我”选项。
下面我们将介绍如何测试是否已启用语音输入,如果未启用,则打开“设置”->“隐私”->“语音、墨迹书写和键入”页面。
首先,我们将全局变量 (HResultPrivacyStatementDeclined) 初始化为 0x80045509 的 HResult 值。 请参阅采用 C# 或 Visual Basic 的异常处理。
private static uint HResultPrivacyStatementDeclined = 0x80045509;
如果 HResult 值等于 HResultPrivacyStatementDeclined 变量的值,则我们会在识别和测试过程中发现任何标准异常。 如果情况如此,我们将会显示一则警告并调用 await Windows.System.Launcher.LaunchUriAsync(new Uri("ms-settings:privacy-accounts")); 以打开“设置”页。
catch (Exception exception)
{
// Handle the speech privacy policy error.
if ((uint)exception.HResult == HResultPrivacyStatementDeclined)
{
resultTextBlock.Visibility = Visibility.Visible;
resultTextBlock.Text = "The privacy statement was declined." +
"Go to Settings -> Privacy -> Speech, inking and typing, and ensure you" +
"have viewed the privacy policy, and 'Get To Know You' is enabled.";
// Open the privacy/speech, inking, and typing settings page.
await Windows.System.Launcher.LaunchUriAsync(new Uri("ms-settings:privacy-accounts"));
}
else
{
var messageDialog = new Windows.UI.Popups.MessageDialog(exception.Message, "Exception");
await messageDialog.ShowAsync();
}
}
请参阅 SpeechRecognitionTopicConstraint。
编程列表约束
编程列表约束提供一种轻型方法,用于使用字词或短语的列表创建一种简单的语法。 列表约束非常适用于识别清晰的短语。 因为语音识别引擎仅须处理语音即可确认匹配,所以采用某种语法明确指定所有字词也可提高识别准确度。 也可以以编程方式更新该列表。
列表约束由字符串数组组成,此数组表示你的应用将为识别操作接受的语音输入。 你可以通过创建语音识别列表约束对象并传递字符串数组在应用中创建列表约束。 然后,将该对象添加到识别器的约束集合。 当语音识别器识别数组中的任何一个字符串时,识别成功。
请参阅 SpeechRecognitionListConstraint。
SRGS 语法
语音识别语法规范 (SRGS) 语法是一个静态文档,与编程列表约束不同,它使用由 SRGS 版本 1.0 定义的 XML 格式。 SRGS 语法提供了对语音识别体验的最大控制,方法是让你在单个识别中捕获多个语义含义。
请参阅 SpeechRecognitionGrammarFileConstraint。
语音命令约束
使用语音命令定义 (VCD) XML 文件定义用户可以在激活应用时说出以启动操作的命令。 有关更多详细信息,请参阅通过 Cortana 使用语音命令激活前台应用。
请参阅 SpeechRecognitionVoiceCommandDefinitionConstraint/
注意:使用的约束类型的类型取决于待创建识别体验的复杂程度。 对于特定识别任务,任一类型都可能是最佳选择,你也可能在应用中发现所有类型的约束的用途。 要开始使用约束,请参阅定义自定义识别约束。
预定义的通用 Windows 应用听写语法可识别使用某种语言的大部分字词和短语。 如果语音识别器对象在没有自定义约束的情况下实例化,它会自动激活。
在该示例中,我们展示如何:
- 创建语音识别器。
- 编译默认 Universal Windows App 约束(未向语音识别器的语法集添加任何语法)。
- 开始使用 RecognizeWithUIAsync 方法提供的基本识别 UI 和 TTS 反馈侦听语音。 如果不需要默认 UI,则使用 RecognizeAsync 方法。
private async void StartRecognizing_Click(object sender, RoutedEventArgs e)
{
// Create an instance of SpeechRecognizer.
var speechRecognizer = new Windows.Media.SpeechRecognition.SpeechRecognizer();
// Compile the dictation grammar by default.
await speechRecognizer.CompileConstraintsAsync();
// Start recognition.
Windows.Media.SpeechRecognition.SpeechRecognitionResult speechRecognitionResult = await speechRecognizer.RecognizeWithUIAsync();
// Do something with the recognition result.
var messageDialog = new Windows.UI.Popups.MessageDialog(speechRecognitionResult.Text, "Text spoken");
await messageDialog.ShowAsync();
}
自定义识别 UI
当你的应用通过调用 SpeechRecognizer.RecognizeWithUIAsync 来尝试进行语音识别时,多个屏幕将按以下顺序显示。
如果你使用基于预定义语法的约束(听写或 Web 搜索):
- 侦听屏幕。
- 思考屏幕。
- 听到你说屏幕或错误屏幕。
如果你使用的约束基于字词或短语列表,或者基于 SRGS 语法文件:
- 侦听屏幕。
- 你说的是屏幕,如果用户所说的内容可以解释为不止一种可能性结果。
- 听到你说屏幕或错误屏幕。
下图演示了语音识别器在不同屏幕间的流程的示例,该识别器使用基于 SRGS 语法文件的约束。 在本例中,语音识别是成功的。

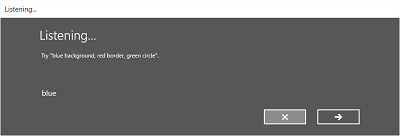
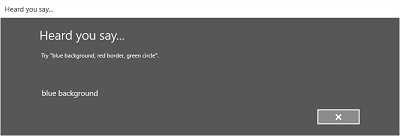
侦听屏幕可提供应用可识别的字词或短语的示例。 下面我们介绍如何使用 SpeechRecognizerUIOptions 类的属性(通过调用 SpeechRecognizer.UIOptions 属性获取)自定义侦听屏幕上的内容。
private async void WeatherSearch_Click(object sender, RoutedEventArgs e)
{
// Create an instance of SpeechRecognizer.
var speechRecognizer = new Windows.Media.SpeechRecognition.SpeechRecognizer();
// Listen for audio input issues.
speechRecognizer.RecognitionQualityDegrading += speechRecognizer_RecognitionQualityDegrading;
// Add a web search grammar to the recognizer.
var webSearchGrammar = new Windows.Media.SpeechRecognition.SpeechRecognitionTopicConstraint(Windows.Media.SpeechRecognition.SpeechRecognitionScenario.WebSearch, "webSearch");
speechRecognizer.UIOptions.AudiblePrompt = "Say what you want to search for...";
speechRecognizer.UIOptions.ExampleText = @"Ex. 'weather for London'";
speechRecognizer.Constraints.Add(webSearchGrammar);
// Compile the constraint.
await speechRecognizer.CompileConstraintsAsync();
// Start recognition.
Windows.Media.SpeechRecognition.SpeechRecognitionResult speechRecognitionResult = await speechRecognizer.RecognizeWithUIAsync();
//await speechRecognizer.RecognizeWithUIAsync();
// Do something with the recognition result.
var messageDialog = new Windows.UI.Popups.MessageDialog(speechRecognitionResult.Text, "Text spoken");
await messageDialog.ShowAsync();
}
相关文章
示例
反馈
即将发布:在整个 2024 年,我们将逐步淘汰作为内容反馈机制的“GitHub 问题”,并将其取代为新的反馈系统。 有关详细信息,请参阅:https://aka.ms/ContentUserFeedback。
提交和查看相关反馈
