Troublshooting Autodiscover (Exchange 2007/2010)
What is Autodiscover?
Exchange Autodiscover is a service which is run on Exchange Client Access Servers. It is one of the new features it included in exchange 2007.
The Autodiscover service makes it easier to configure Outlook 2007 or Outlook 2010 and some mobile phones. Autodiscover Service cannot be used with earlier versions of Outlook, including Outlook 2003. In earlier versions of Microsoft Exchange (Exchange 2003 SP2 or earlier) and Outlook (Outlook 2003 or earlier), you had to configure all user profiles manually to access Exchange.
The Autodiscover service uses a user's e-mail address and password to automatically configure a user's profile. Using the e-mail address, the Autodiscover service provides the following information to the client:
- The user’s display name.
- Separate connection settings for internal and external connectivity.
- The location of the user’s Mailbox server.
- The URLs for various Outlook features that manage functionality such as OOF, free/busy information, Unified Messaging, and the offline address book.
- Outlook Anywhere server settings.
How the Autodiscover Service Works
When you install the Client Access server role on a computer running Exchange 2010/2007, a default virtual directory named Autodiscover is created under the default Web site in Internet Information Services (IIS). This virtual directory handles Autodiscover service requests from Outlook 2007 or Outlook 2010 clients and supported mobile phones under the following circumstances:
- When a new user account is configured or updated.
- When an Outlook client periodically checks for changes to the Exchange Web Services URLs.
- When underlying network connection changes occur in your Exchange messaging environment.
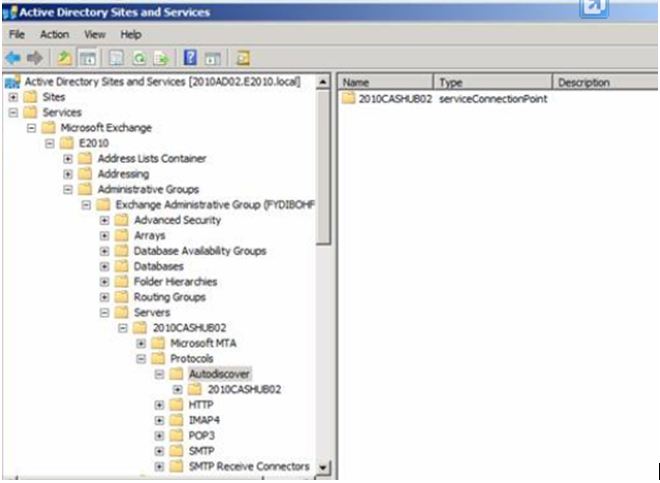
Additionally, a new Active Directory object named the service connection point (SCP) is created on the server where you install the Client Access server role. And Autodiscover information is stored in it.
You can view this SCP using Active Directory Sites and Services after you have enabled the “View Services Node” option:
- The SCP object is used by domain-connected clients to locate the Autodiscover service.
- The SCP object contains two pieces of information:
- The serviceBindingInformation attribute.
- The keywords attribute
The serviceBindingInformation attribute has the Fully Qualified Domain Name (FQDN) of the Client Access server in the form of: https://cas01.contoso.com/autodiscover/autodiscover.xml, where cas01.contoso.com is the fully qualified domain name (FQDN) for the Client Access server.
The keywords attribute specifies the Active Directory sites to which this SCP record is associated. By default, this attribute specifies the Active Directory site to which the Client Access server belongs.
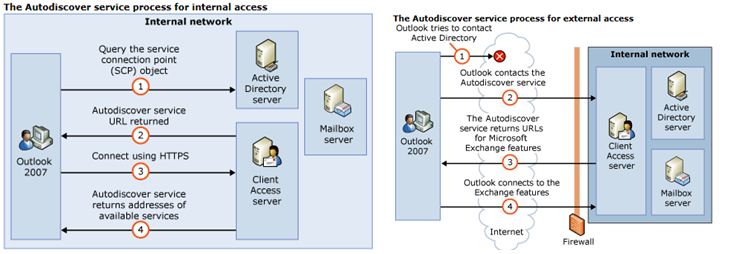
When a domain-connected client connects to the Active Directory directory service:
– The Exchange 2007 client authenticates to Active Directory and tries to locate the Autodiscover SCP objects that were created during Setup by using the user's credentials.
– In deployments that include multiple Client Access servers, an Autodiscover SCP record is created for each Client Access server. By using the user credentials, the Outlook 2007 client authenticates to Active Directory and searches for the autodiscover SCP objects.
– After the client obtains and enumerates the instances of the Autodiscover service, the client connects to the first Client Access server in the enumerated and sorted list and obtains the profile information in the form of XML data that is needed to connect to the user's mailbox and available Microsoft Exchange features.
An Outlook 2007/2010 client connects to the Autodiscover service as follows:
1- Outlook 2007/2010 sends a LDAP query to Active Directory looking for all available SCP objects.
2- Outlook 2007/2010 sorts and enumerates the returned results based on the client's Active Directory site by using the keyword attribute of the SCP record. One of two lists is created, an in-site list or an out-of-site list.
3. Outlook first tries to connect to each Autodiscover URL that it had previously generated from either an in-site list or an out-of-site list.
- If that doesn't work, Outlook will try to connect to the predefined URLs (for example, https://autodiscover.contoso.com/autodiscover/autodiscover.xml) by using DNS.
- If that fails also, Outlook will try the HTTP redirect method.
- If that fails also, Outlook will try to use the SRV record lookup method.
- If all lookup methods fail, Outlook will be unable to obtain Outlook Anywhere configuration and URL settings.
4. The Autodiscover service queries Active Directory to obtain the connection settings and URLs for the Exchange services that have been configured.
5. The Autodiscover service returns an HTTPS response with an XML file that includes the connection settings and URLs for the available Exchange services.
6. Outlook uses the appropriate configuration information and connection settings to connect to your Exchange messaging environment.
- When Outlook 2007/2010 is started on a client that is not domain-connected, it first tries to locate the Autodiscover service by looking up the SCP object in Active Directory. Because the client is unable to contact Active Directory, it tries to locate the Autodiscover service by using Domain Name System (DNS). In this scenario, the client will determine right side of the user’s e-mail address, that is, contoso.com, and check DNS by using two predefined URLs. For example, if your SMTP domain is contoso.com, Outlook will try the following two URLs to try to connect to the Autodiscover service:
https://contoso.com/autodiscover/autodiscover.xml
https://autodiscover.contoso.com/autodiscover/autodiscover.xml
- Another option related to DNS is made possible with an Outlook 2007 software update. When this software update is applied, Outlook 2007 clients will perform an additional check for a DNS SRV record to locate the Autodiscover service which does not require multiple Web sites and IP addresses.
- For more information about this software update for Outlook 2007, see Microsoft Knowledge Base article 940881, A new feature is available that enables Outlook 2007 to use DNS Service Location (SRV) records to locate the Exchange Autodiscover service.
Problems with Autodiscover service or how it’s configured can causes issues such as:
- Cannot view free/busy information.
- Cannot download Offline Address Book (OAB) / receive error code: 0x8004010F.
- The Out Of Office assistant is not working.
- Prompt for a user name and password during the Autodiscover process.
- Outlook anywhere stop working.
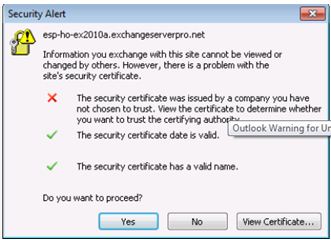
One of the most common issues I see has to do with certificates, so I will highlight few things about certificates.
Certificates are used to encrypt traffic between exchange servers and clients.
There are three things that need to be true in order for a certificate to be valid:
- The name used to access the resource needs match the certificate exactly.
- The Certificate date must be valid
- The Certificate Authority which issued the certificate must be trusted by the client. (It needs to exist in the “Trusted Root Certificate Authorities)
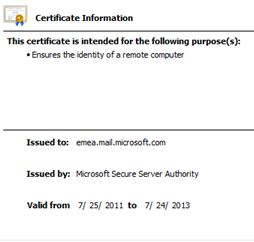
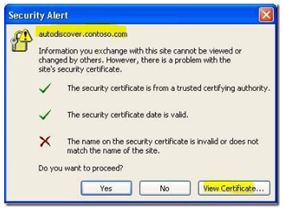
Example: If I connect to OWA with mail.mydomain.com, then the certificate also needs to have mail.mydomain.com either on the subject or the subject alternative name field.
The components that are usually affected with certificate name mismatch are Autodiscover, Out of Office, Free Busy and Outlook Anywhere.
Reasons:
1- Not using a trusted certificate
Solution : use a 3rd party cert provider
2- The certificate name does not match the DNS name\s
Solution : create a new cert request containing all the names used to access the server. Minimum of
Autodiscover.domain.com
<ExternalName>.domain.com
<InternalName>.domain.local (if using for internal systems also)
3- Can’t resolve fully qualified domain names (FQDN)
Solution : make sure that the FQDNs for your external URLs as well as autodiscover have A records registered in DNS
Verify you can access the autodiscover XML file https :// autodiscover.domain.com/autodiscover/autodiscover.xml
It should look like below
4- SCP Record does not contain the correct value.
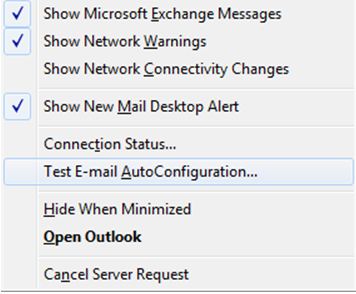
- Test from outlook:
- Hold CTRL and Click the outlook Icon in the system tray and select “Test Email Auto Configuration”
- Deselect the “Use Guessmart” and “Secure Guessmart Authentication” and click Test.
2. Check SCP value returned
- If you get info on the results tab then AutoDiscover is working
- If not, go to Log tab and look at the URL that is returned
- Test the URL (Type it into Internet explorer) if it is not working, change SCP to a valid URL, using Set-ClientAccessServer cmdlet.
- Set the SCP along with the internal URL: Set-ClientAccessServer CASServerName -AutoDiscoverServiceInternalUri https://mail.domain.local/Autodiscover/Autodiscover.xml
Troubleshooting Free/Busy Information for Outlook 2007/2010
- The Availability service for Microsoft Exchange Server 2007/2010 provides calendar information for your users, which is known as free/busy information.
- The Autodiscover service provides information for the Availability service by locating and providing the external and internal URLs for the Outlook 2007/2010 client.
- There may be problem which involves a failure in either the Autodiscover service or the Availability service.
- To determine whether the Autodiscover service is unable to provide information to clients by using Outlook 2007, you can enable outlook logging using the following steps:
- In Outlook 2007, on the Tools menu, click Options, click the Other tab, and then click Advanced Options.
- On the Advanced Options page, select Enable logging (troubleshooting), and then click OK.
- Restart Outlook 2007, and then try to view free/busy information for another user.
- In Microsoft Windows, click Start, click Run, and then type %temp%.
- In Windows Explorer, open the olkdisc.log file and locate the files in the olkas directory.
- The information that is contained in this directory can frequently provide information about which service is not functioning correctly.
If you are using outlook 2010, then do the below:
- Launch Outlook 2010, Click File, Options, then Click Advanced.
- Scroll down to Other, and check the box to enable troubleshooting logging.
- Restart Outlook.
With logging enabled, a pop up will appear in the system tray reminding you that Outlook logging is enabled, and a header on the top of the outlook window
- When Outlook launches a log file is generated and updated as the launch occurs. This file is located in your user’s TEMP folder. By default that is in the following location:
Windows XP: C:\Documents and Settings\<User Name>\Local Settings\Temp
Windows Vista and Windows 7: C:\Users\<User Name>\AppData\Local\Temp
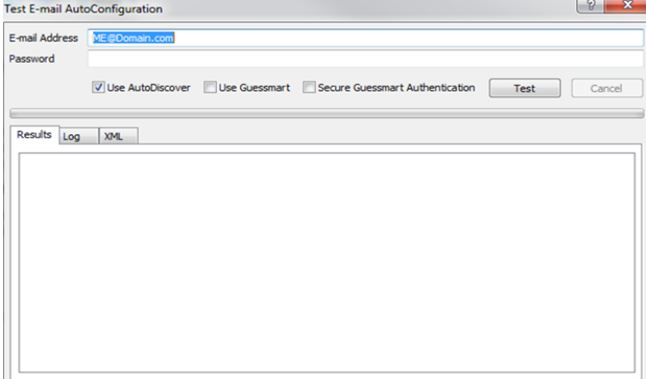
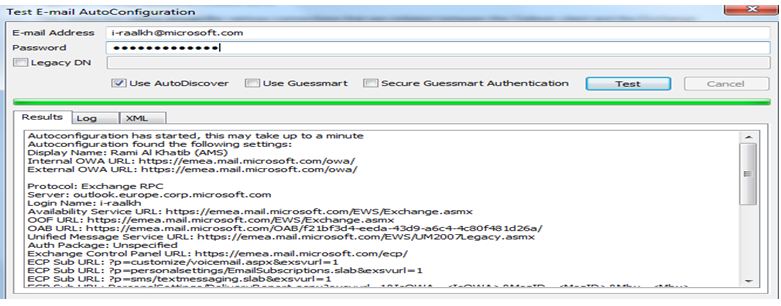
You can also use Outlook 2007 to test the AutoConfiguration information that is provided by the Autodiscover service.
- On the Test E-mail AutoConfiguration page, verify that the check box next to Use AutoDiscover is selected, and then click the Test button.
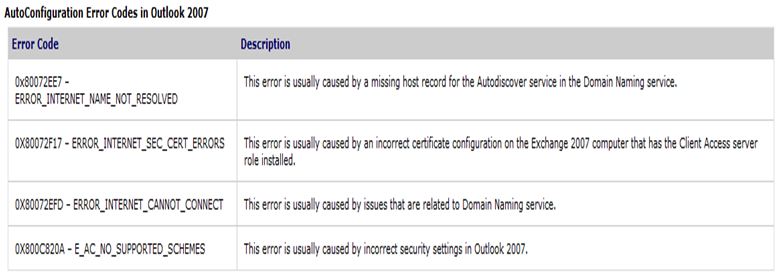
The following table provides a brief description of error codes that may occur when you test the AutoConfiguration for the Autodiscover service in Outlook 2007.
Exchange 2007 provides two ways for you to determine whether the Availability service is not functioning correctly:
1- Using the Event Log to Troubleshoot the Availability Service
2- Using the Test-OutlookWebServices Cmdlet to Troubleshoot the Availability Service as below:
Test-OutlookWebServices -id:user1@contoso.com -TargetAddress: user2@contoso.com
Troubleshooting Autodiscover service
Troubleshooting Autodiscover requires you to understand which part of autodiscover is not working. But generally, It is good practice to find out whether autodiscover working for internal clients or not. Internal clients who are belong to the same network of domain.
Following are some common procedures to check autodiscover configuration:
• Run Test-OutlookWebservices | fl
• Run Test-EmailAutoConfiguration on client to find how autodiscover is connecting and where exactly it's failing.
• Verify URL for autodiscover. Get-ClientAccessServer | fl
Check for AutodiscoverInternalServerUri attribute.
• You may also access the autodiscover url from IE and in response should get "600 invalid request".
• If autodiscover not working for external client verify authentication on Autodiscover virtual directory and if required you may recreate the virtual directory by running command:
Remove-AutodiscoverVirtualDirectory
New-AutodiscoverVirtualDirectory