你当前正在访问 Microsoft Azure Global Edition 技术文档网站。 如果需要访问由世纪互联运营的 Microsoft Azure 中国技术文档网站,请访问 https://docs.azure.cn。
教程:在 Azure Notebook 中使用个性化体验创建服务
重要
从 2023 年 9 月 20 日开始,将无法创建新的个性化体验创建服务资源。 个性化体验创建服务将于 2026 年 10 月 1 日停用。
本教程在 Azure Notebook 中运行一个个性化体验创建服务循环,以此演示个性化体验创建服务循环的端到端生命周期。
该循环为客户建议要订购哪种类型的咖啡。 用户及其偏好存储在用户数据集中。 有关咖啡的信息存储在咖啡数据集中。
用户和咖啡
笔记本(用于模拟用户与网站的交互)从数据集中选择随机用户、当日时间和天气类型。 用户信息摘要如下:
| 客户 - 上下文特征 | 当日时间 | 天气状况 |
|---|---|---|
| Alice Bob Cathy Dave |
上午 下午 晚上 |
晴 下雨 下雪 |
为帮助个性化体验创建服务不断学习,系统还会详细了解每个人的咖啡选择习惯。
| 咖啡 - 操作特征 | 温度类型 | 来源地 | 烘培 | 有机 |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 卡布奇诺 | 热 | 肯尼亚 | 深色 | 有机 |
| 冷泡 | 冷 | 巴西 | 浅色 | 有机 |
| 加冰摩卡 | 冷 | 埃塞俄比亚 | 浅色 | 非有机 |
| 拿铁 | 热 | 巴西 | 深色 | 非有机 |
个性化体验创建服务循环的作用是尽量在用户与咖啡之间找到最佳匹配。
本教程的代码已在个性化体验创建服务示例 GitHub 存储库中提供。
模拟的工作原理
在最初运行系统时,个性化体验创建服务的建议成功率仅为 20% 到 30%。 由发送回个性化体验创建服务奖励 API 的奖励(通过分数 1)来指示该成功。 在进行一些排名和奖励调用后,系统会改善。
在初始请求后,运行脱机评估。 这样,个性化体验创建服务便可以评审数据,并建议更好的学习策略。 应用新的学习策略,并使用上一请求计数的 20% 再次运行笔记本。 使用新学习策略后,循环的表现会改善。
排名和奖励调用
对于数千个个性化体验创建服务服务调用中的每个调用,Azure Notebook 会向 REST API 发送“排名”请求:
- 排名/请求事件的唯一 ID
- 上下文特征 - 用户、天气和当日时间的随机选择 - 模拟网站或移动设备上的用户
- 带特征的操作 - 所有咖啡数据 - 个性化体验创建服务基于这些数据提供建议
系统接收请求,然后将该预测结果与用户在相同的当日时间和天气状况下所做的已知选择进行比较。 如果已知的选择与预测的选择相同,则向个性化体验创建服务发回奖励评分 1。 否则,发送回的奖励评分为 0。
备注
这只是一种模拟,因此奖励算法非常简单。 在真实场景中,该算法应使用业务逻辑,并可能需要权衡客户体验的各个方面来确定奖励评分。
先决条件
- 一个 Azure Notebook 帐户。
- 一个 Azure AI 个性化体验创建服务资源。
- 如果你已使用个性化体验创建服务资源,请确保在该资源的 Azure 门户中清除数据。
- 将此示例的所有文件上传到 Azure Notebook 项目。
文件说明:
- Personalizer.ipynb 是用于本教程的 Jupyter 笔记本。
- 用户数据集存储在某个 JSON 对象中。
- 咖啡数据集存储在某个 JSON 对象中。
- 示例请求 JSON 是发送到排名 API 的 POST 请求的预期格式。
配置个性化体验创建服务资源
在 Azure 门户中配置个性化体验创建服务资源:将“更新模型频率”设置为 15 秒,将“奖励等待时间”设置为 10 分钟。 这些值可在“配置”页面上找到 。
| 设置 | 值 |
|---|---|
| 更新模型频率 | 15 秒 |
| 奖励等待时间 | 10 分钟 |
为了显示本教程中的变化,这些值的持续时间非常短。 在未验证这些值能否实现个性化体验创建服务循环的目标的情况下,不应在生产方案中使用这些值。
设置 Azure Notebook
- 将“内核”更改为
Python 3.6。 - 打开
Personalizer.ipynb文件。
运行 Notebook 单元
运行每个可执行单元,并等待它返回。 该单元运行完成时,其旁边的方括号中会显示数字而不是 *。 以下部分解释了每个单元在编程方面的作用及其预期的输出。
包括 Python 模块
包括所需的 Python 模块。 该单元不提供输出。
import json
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
import random
import requests
import time
import uuid
设置个性化体验创建服务资源密钥和名称
在 Azure 门户中,在个性化体验创建服务资源的“快速启动”页上找到你的密钥和终结点。 将 <your-resource-name> 的值更改为个性化体验创建服务资源的名称。 将 <your-resource-key> 的值更改为个性化体验创建服务密钥。
# Replace 'personalization_base_url' and 'resource_key' with your valid endpoint values.
personalization_base_url = "https://<your-resource-name>.cognitiveservices.azure.com/"
resource_key = "<your-resource-key>"
输出当前日期和时间
使用此函数可以记下迭代函数的迭代开始和结束时间。
这些单元不提供输出。 调用该函数时,它会输出当前日期和时间。
# Print out current datetime
def currentDateTime():
currentDT = datetime.datetime.now()
print (str(currentDT))
获取上次模型更新时间
调用 get_last_updated 函数时,它会输出更新的模型的上次修改日期和时间。
这些单元不提供输出。 调用该函数时,它会输出模型的上次训练日期。
该函数使用 GET REST API 来获取模型属性。
# ititialize variable for model's last modified date
modelLastModified = ""
def get_last_updated(currentModifiedDate):
print('-----checking model')
# get model properties
response = requests.get(personalization_model_properties_url, headers = headers, params = None)
print(response)
print(response.json())
# get lastModifiedTime
lastModifiedTime = json.dumps(response.json()["lastModifiedTime"])
if (currentModifiedDate != lastModifiedTime):
currentModifiedDate = lastModifiedTime
print(f'-----model updated: {lastModifiedTime}')
获取策略和服务配置
使用这两个 REST 调用来验证服务的状态。
这些单元不提供输出。 调用该函数时,它会输出服务值。
def get_service_settings():
print('-----checking service settings')
# get learning policy
response = requests.get(personalization_model_policy_url, headers = headers, params = None)
print(response)
print(response.json())
# get service settings
response = requests.get(personalization_service_configuration_url, headers = headers, params = None)
print(response)
print(response.json())
构造 URL 并读取 JSON 数据文件
此单元
- 生成 REST 调用中使用的 URL
- 使用个性化体验创建服务资源密钥设置安全性标头
- 设置排名事件 ID 的随机种子
- 读入 JSON 数据文件
- 调用
get_last_updated方法 - 示例输出中已删除学习策略 - 调用
get_service_settings方法
该单元包含调用 get_last_updated 和 get_service_settings 函数后生成的输出。
# build URLs
personalization_rank_url = personalization_base_url + "personalizer/v1.0/rank"
personalization_reward_url = personalization_base_url + "personalizer/v1.0/events/" #add "{eventId}/reward"
personalization_model_properties_url = personalization_base_url + "personalizer/v1.0/model/properties"
personalization_model_policy_url = personalization_base_url + "personalizer/v1.0/configurations/policy"
personalization_service_configuration_url = personalization_base_url + "personalizer/v1.0/configurations/service"
headers = {'Ocp-Apim-Subscription-Key' : resource_key, 'Content-Type': 'application/json'}
# context
users = "users.json"
# action features
coffee = "coffee.json"
# empty JSON for Rank request
requestpath = "example-rankrequest.json"
# initialize random
random.seed(time.time())
userpref = None
rankactionsjsonobj = None
actionfeaturesobj = None
with open(users) as handle:
userpref = json.loads(handle.read())
with open(coffee) as handle:
actionfeaturesobj = json.loads(handle.read())
with open(requestpath) as handle:
rankactionsjsonobj = json.loads(handle.read())
get_last_updated(modelLastModified)
get_service_settings()
print(f'User count {len(userpref)}')
print(f'Coffee count {len(actionfeaturesobj)}')
验证输出的 rewardWaitTime 是否设置为 10 分钟,modelExportFrequency 是否设置为 15 秒。
-----checking model
<Response [200]>
{'creationTime': '0001-01-01T00:00:00+00:00', 'lastModifiedTime': '0001-01-01T00:00:00+00:00'}
-----model updated: "0001-01-01T00:00:00+00:00"
-----checking service settings
<Response [200]>
{...learning policy...}
<Response [200]>
{'rewardWaitTime': '00:10:00', 'defaultReward': 0.0, 'rewardAggregation': 'earliest', 'explorationPercentage': 0.2, 'modelExportFrequency': '00:00:15', 'logRetentionDays': -1}
User count 4
Coffee count 4
排查首次 REST 调用的问题
这前一个单元是调用个性化体验创建服务的第一个单元。 请确保输出中的 REST 状态代码为 <Response [200]>。 如果收到错误(例如 404),但你确信资源密钥和名称正确,请重新加载笔记本。
确保咖啡和用户的计数均为 4。 如果收到错误,请检查是否上传了所有 3 个 JSON 文件。
在 Azure 门户中设置指标图表
稍后在本教程中,处理 10,000 个请求的长时间运行的进程将在浏览器中通过一个不断更新的文本框显示。 该长时间运行的进程结束时,以图表或总和形式显示信息可能更易于查看。 若要查看此信息,请使用随资源一起提供的指标。 完成向服务发送请求后,可以创建图表,然后在该进程长时间运行过程中定期刷新该图表。
在 Azure 门户中选择你的个性化体验创建服务资源。
在资源导航栏中,选择“监视”下的“指标”。
在图表中选择“添加指标”。
资源和指标命名空间已设置。 只需选择“成功的调用”的指标,以及“总和”中的聚合结果。
将时间筛选器更改为过去 4 小时。
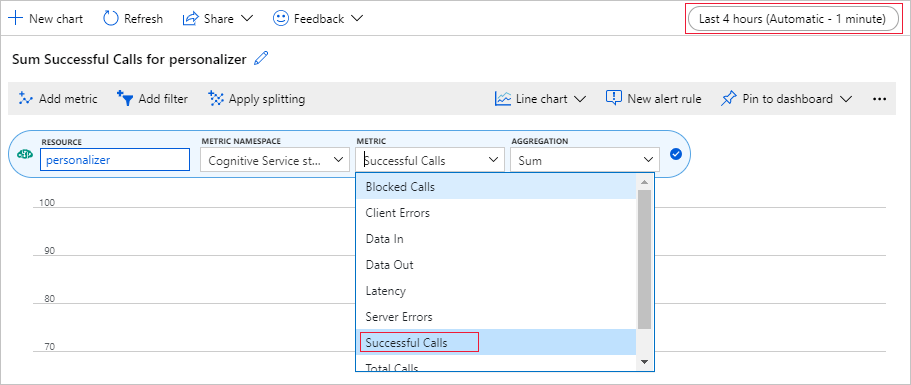
应会在图表中看到三个成功的调用。
生成唯一的事件 ID
此函数为每个排名调用生成唯一的 ID。 该 ID 用于标识排名和奖励调用信息。 此值可以来自业务流程,例如 Web 视图 ID 或事务 ID。
该单元不提供输出。 调用该函数时,它会输出唯一的 ID。
def add_event_id(rankjsonobj):
eventid = uuid.uuid4().hex
rankjsonobj["eventId"] = eventid
return eventid
获取随机用户、天气和当日时间
此函数选择唯一的用户、天气和当日时间,然后将这些项添加到要发送至排名请求的 JSON 对象。
该单元不提供输出。 调用该函数时,它会返回随机用户的名称、随机天气和随机的当日时间。
包含 4 个用户及其偏好的列表 - 为简洁起见,此处只显示了一部分偏好:
{
"Alice": {
"Sunny": {
"Morning": "Cold brew",
"Afternoon": "Iced mocha",
"Evening": "Cold brew"
}...
},
"Bob": {
"Sunny": {
"Morning": "Cappucino",
"Afternoon": "Iced mocha",
"Evening": "Cold brew"
}...
},
"Cathy": {
"Sunny": {
"Morning": "Latte",
"Afternoon": "Cold brew",
"Evening": "Cappucino"
}...
},
"Dave": {
"Sunny": {
"Morning": "Iced mocha",
"Afternoon": "Iced mocha",
"Evening": "Iced mocha"
}...
}
}
def add_random_user_and_contextfeatures(namesoption, weatheropt, timeofdayopt, rankjsonobj):
name = namesoption[random.randint(0,3)]
weather = weatheropt[random.randint(0,2)]
timeofday = timeofdayopt[random.randint(0,2)]
rankjsonobj['contextFeatures'] = [{'timeofday': timeofday, 'weather': weather, 'name': name}]
return [name, weather, timeofday]
添加所有咖啡数据
此函数将整个咖啡列表添加到要发送至排名请求的 JSON 对象。
该单元不提供输出。 调用该函数时,它会更改 rankjsonobj。
下面是单个咖啡特征的示例:
{
"id": "Cappucino",
"features": [
{
"type": "hot",
"origin": "kenya",
"organic": "yes",
"roast": "dark"
}
}
def add_action_features(rankjsonobj):
rankjsonobj["actions"] = actionfeaturesobj
将预测结果与已知用户偏好进行比较
对于每个迭代,将在调用排名 API 之后调用此函数。
此函数将用户在特定时间和天气状况下的咖啡偏好,与个性化体验创建服务根据这些筛选器提供的建议进行比较。 如果建议匹配,则返回评分 1,否则返回评分 0。 该单元不提供输出。 调用该函数时,它会输出评分。
def get_reward_from_simulated_data(name, weather, timeofday, prediction):
if(userpref[name][weather][timeofday] == str(prediction)):
return 1
return 0
循环排名和奖励调用
下一个单元是 Notebook 的主要工作,它会获取随机用户,获取咖啡列表,然后将两者发送到排名 API。 将预测结果与用户的已知偏好进行比较,然后将奖励发回到个性化体验创建服务服务。
该循环将运行 num_requests 次。 个性化体验创建服务需要调用排名和奖励几千次才能创建一个模型。
下面是发送到排名 API 的 JSON 示例。 为简洁起见,此处的咖啡列表并不完整。 可以在 coffee.json 中查看完整的 JSON。
发送到排名 API 的 JSON:
{
'contextFeatures':[
{
'timeofday':'Evening',
'weather':'Snowy',
'name':'Alice'
}
],
'actions':[
{
'id':'Cappucino',
'features':[
{
'type':'hot',
'origin':'kenya',
'organic':'yes',
'roast':'dark'
}
]
}
...rest of coffee list
],
'excludedActions':[
],
'eventId':'b5c4ef3e8c434f358382b04be8963f62',
'deferActivation':False
}
来自排名 API 的 JSON 响应:
{
'ranking': [
{'id': 'Latte', 'probability': 0.85 },
{'id': 'Iced mocha', 'probability': 0.05 },
{'id': 'Cappucino', 'probability': 0.05 },
{'id': 'Cold brew', 'probability': 0.05 }
],
'eventId': '5001bcfe3bb542a1a238e6d18d57f2d2',
'rewardActionId': 'Latte'
}
最后,每个循环将显示随机选择的用户、天气、当日时间和确定的奖励。 奖励评分 1 表示个性化体验创建服务资源根据给定的用户、天气和当日时间选择了正确的咖啡类型。
1 Alice Rainy Morning Latte 1
该函数使用:
def iterations(n, modelCheck, jsonFormat):
i = 1
# default reward value - assumes failed prediction
reward = 0
# Print out dateTime
currentDateTime()
# collect results to aggregate in graph
total = 0
rewards = []
count = []
# default list of user, weather, time of day
namesopt = ['Alice', 'Bob', 'Cathy', 'Dave']
weatheropt = ['Sunny', 'Rainy', 'Snowy']
timeofdayopt = ['Morning', 'Afternoon', 'Evening']
while(i <= n):
# create unique id to associate with an event
eventid = add_event_id(jsonFormat)
# generate a random sample
[name, weather, timeofday] = add_random_user_and_contextfeatures(namesopt, weatheropt, timeofdayopt, jsonFormat)
# add action features to rank
add_action_features(jsonFormat)
# show JSON to send to Rank
print('To: ', jsonFormat)
# choose an action - get prediction from Personalizer
response = requests.post(personalization_rank_url, headers = headers, params = None, json = jsonFormat)
# show Rank prediction
print ('From: ',response.json())
# compare personalization service recommendation with the simulated data to generate a reward value
prediction = json.dumps(response.json()["rewardActionId"]).replace('"','')
reward = get_reward_from_simulated_data(name, weather, timeofday, prediction)
# show result for iteration
print(f' {i} {currentDateTime()} {name} {weather} {timeofday} {prediction} {reward}')
# send the reward to the service
response = requests.post(personalization_reward_url + eventid + "/reward", headers = headers, params= None, json = { "value" : reward })
# for every N rank requests, compute total correct total
total = total + reward
# every N iteration, get last updated model date and time
if(i % modelCheck == 0):
print("**** 10% of loop found")
get_last_updated(modelLastModified)
# aggregate so chart is easier to read
if(i % 10 == 0):
rewards.append( total)
count.append(i)
total = 0
i = i + 1
# Print out dateTime
currentDateTime()
return [count, rewards]
针对 10,000 个迭代运行
针对 10,000 个迭代运行个性化体验创建服务循环。 这是一个长时间运行的事件。 请不要关闭运行笔记本的浏览器。 定期刷新 Azure 门户中的指标图表,以查看调用服务的总次数。 针对循环的每个迭代调用排名和奖励大约 20,000 次后,迭代即告完成。
# max iterations
num_requests = 200
# check last mod date N% of time - currently 10%
lastModCheck = int(num_requests * .10)
jsonTemplate = rankactionsjsonobj
# main iterations
[count, rewards] = iterations(num_requests, lastModCheck, jsonTemplate)
在图表结果中查看改善情况
基于 count 和 rewards 创建图表。
def createChart(x, y):
plt.plot(x, y)
plt.xlabel("Batch of rank events")
plt.ylabel("Correct recommendations per batch")
plt.show()
运行 10,000 个排名请求的图表
运行 createChart 函数。
createChart(count,rewards)
阅读图表
此图表显示当前默认学习策略的模型成功率。
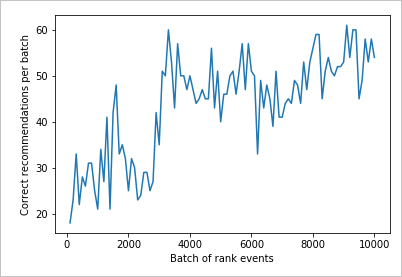
测试结束时,循环的理想目标是平均成功率接近 100% 减去探索率。 探索率的默认值为 20%。
100-20=80
在 Azure 门户中个性化体验创建服务资源的“配置”页上可以找到此探索率值 。
若要根据提供给排名 API 的数据找出更好的学习策略,请在门户中针对个性化体验创建服务循环运行脱机评估。
运行脱机评估
在 Azure 门户中,打开个性化体验创建服务资源的“评估”页。
选择“创建评估”。
输入评估名称的所需数据,以及循环评估的日期范围。 该日期范围应仅包括你要重点评估的日期。

运行此脱机评估的目的是确定是否有适用于此循环中使用的特征和操作的更好学习策略。 若要找出更好的学习策略,请确保已启用“优化发现”。
选择“确定”开始评估。
此“评估”页将列出新的评估及其当前状态。 此评估可能需要一段时间,具体取决于现有的数据量。 在几分钟后,可以返回此页查看结果。
评估完成后,请选择该评估,然后选择“不同学习策略的比较”。 此时会显示可用的学习策略,及其处理数据的行为。
选择表中最上面的学习策略,然后选择“应用”。 这会将最佳的学习策略应用到模型,并重新训练。
将更新模型频率更改为 5 分钟
- 仍在 Azure 门户中的个性化体验创建服务资源上,选择“配置”页 。
- 将“模型更新频率”和“奖励等待时间”更改为 5 分钟,然后选择“保存”。
#Verify new learning policy and times
get_service_settings()
验证输出的 rewardWaitTime 和 modelExportFrequency 是否都设置为 5 分钟。
-----checking model
<Response [200]>
{'creationTime': '0001-01-01T00:00:00+00:00', 'lastModifiedTime': '0001-01-01T00:00:00+00:00'}
-----model updated: "0001-01-01T00:00:00+00:00"
-----checking service settings
<Response [200]>
{...learning policy...}
<Response [200]>
{'rewardWaitTime': '00:05:00', 'defaultReward': 0.0, 'rewardAggregation': 'earliest', 'explorationPercentage': 0.2, 'modelExportFrequency': '00:05:00', 'logRetentionDays': -1}
User count 4
Coffee count 4
验证新学习策略
返回到 Azure Notebooks 文件,然后继续运行同一个循环,但这一次仅针对 2,000 个迭代运行。 定期刷新 Azure 门户中的指标图表,以查看调用服务的总次数。 针对循环的每个迭代调用排名和奖励大约 4,000 次后,迭代即告完成。
# max iterations
num_requests = 2000
# check last mod date N% of time - currently 10%
lastModCheck2 = int(num_requests * .10)
jsonTemplate2 = rankactionsjsonobj
# main iterations
[count2, rewards2] = iterations(num_requests, lastModCheck2, jsonTemplate)
运行 2,000 个排名请求的图表
运行 createChart 函数。
createChart(count2,rewards2)
查看第二个图表
第二个图表应会直观显示排名预测准确度有提升,预测结果与用户的偏好相符。

清理资源
如果你不打算继续学习本教程系列,请清理以下资源:
- 删除 Azure Notebook 项目。
- 删除个性化体验创建服务资源。
后续步骤
个性化体验创建服务的 GitHub 存储库中提供了本示例使用的 Jupyter 笔记本和数据文件。