Use predictive autoscale to scale out before load demands in virtual machine scale sets
Predictive autoscale uses machine learning to help manage and scale Azure Virtual Machine Scale Sets with cyclical workload patterns. It forecasts the overall CPU load to your virtual machine scale set, based on your historical CPU usage patterns. It predicts the overall CPU load by observing and learning from historical usage. This process ensures that scale-out occurs in time to meet the demand.
Predictive autoscale needs a minimum of seven days of history to provide predictions. The most accurate results come from 15 days of historical data.
Predictive autoscale adheres to the scaling boundaries you've set for your virtual machine scale set. When the system predicts that the percentage CPU load of your virtual machine scale set will cross your scale-out boundary, new instances are added according to your specifications. You can also configure how far in advance you want new instances to be provisioned, up to 1 hour before the predicted workload spike occurs.
Forecast only allows you to view your predicted CPU forecast without triggering the scaling action based on the prediction. You can then compare the forecast with your actual workload patterns to build confidence in the prediction models before you enable the predictive autoscale feature.
Predictive autoscale offerings
- Predictive autoscale is for workloads exhibiting cyclical CPU usage patterns.
- Support is only available for virtual machine scale sets.
- The Percentage CPU metric with the aggregation type Average is the only metric currently supported.
- Predictive autoscale supports scale-out only. Configure standard autoscale to manage to scale in actions.
- Predictive autoscale is only available for the Azure Commercial cloud. Azure Government clouds aren't currently supported.
Enable predictive autoscale or forecast only with the Azure portal
Go to the Virtual machine scale set screen and select Scaling.
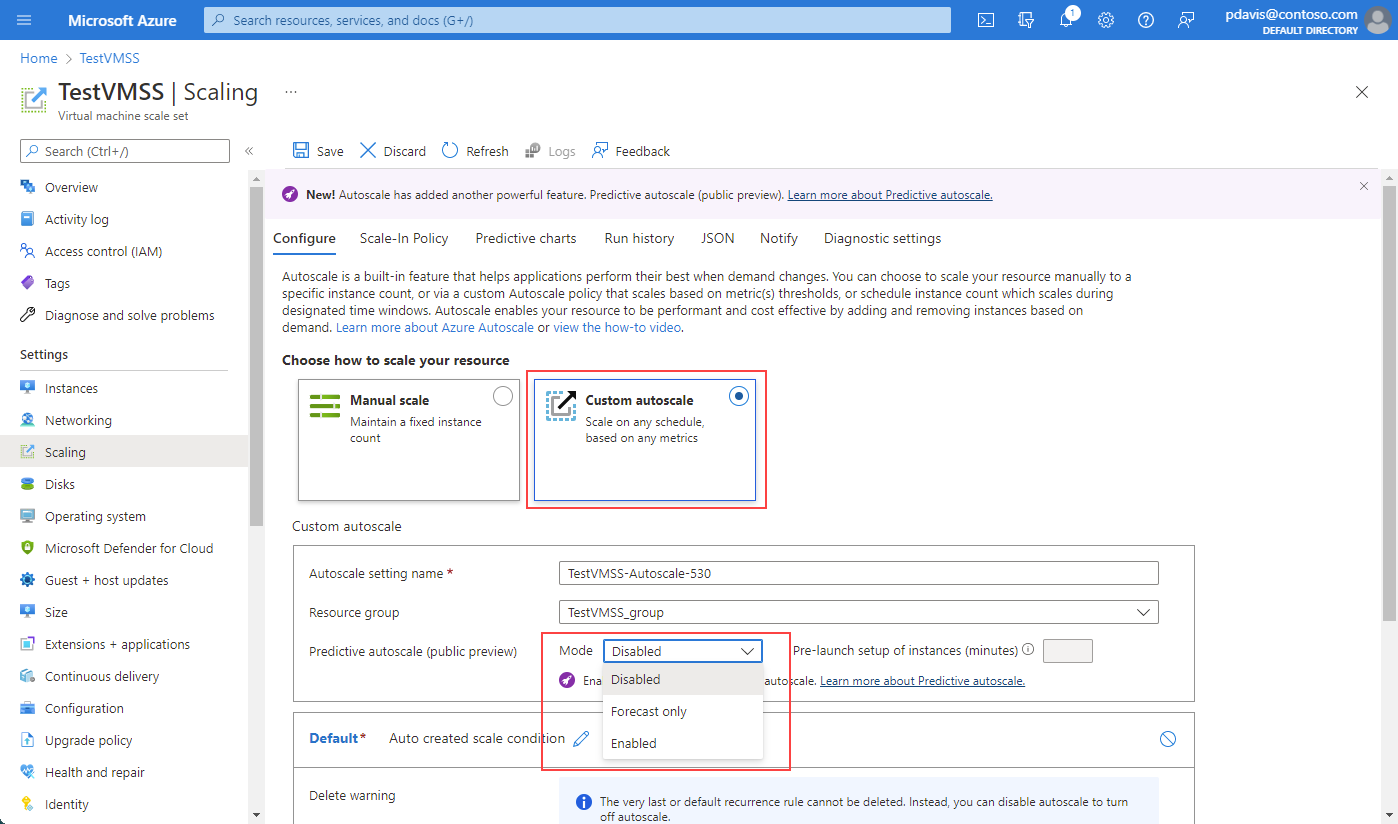
Under the Custom autoscale section, Predictive autoscale appears.
By using the dropdown selection, you can:
- Disable predictive autoscale. Disable is the default selection when you first land on the page for predictive autoscale.
- Enable forecast-only mode.
- Enable predictive autoscale.
Note
Before you can enable predictive autoscale or forecast-only mode, you must set up the standard reactive autoscale conditions.
To enable forecast-only mode, select it from the dropdown. Define a scale-out trigger based on Percentage CPU. Then select Save. The same process applies to enable predictive autoscale. To disable predictive autoscale or forecast-only mode, select Disable from the dropdown.
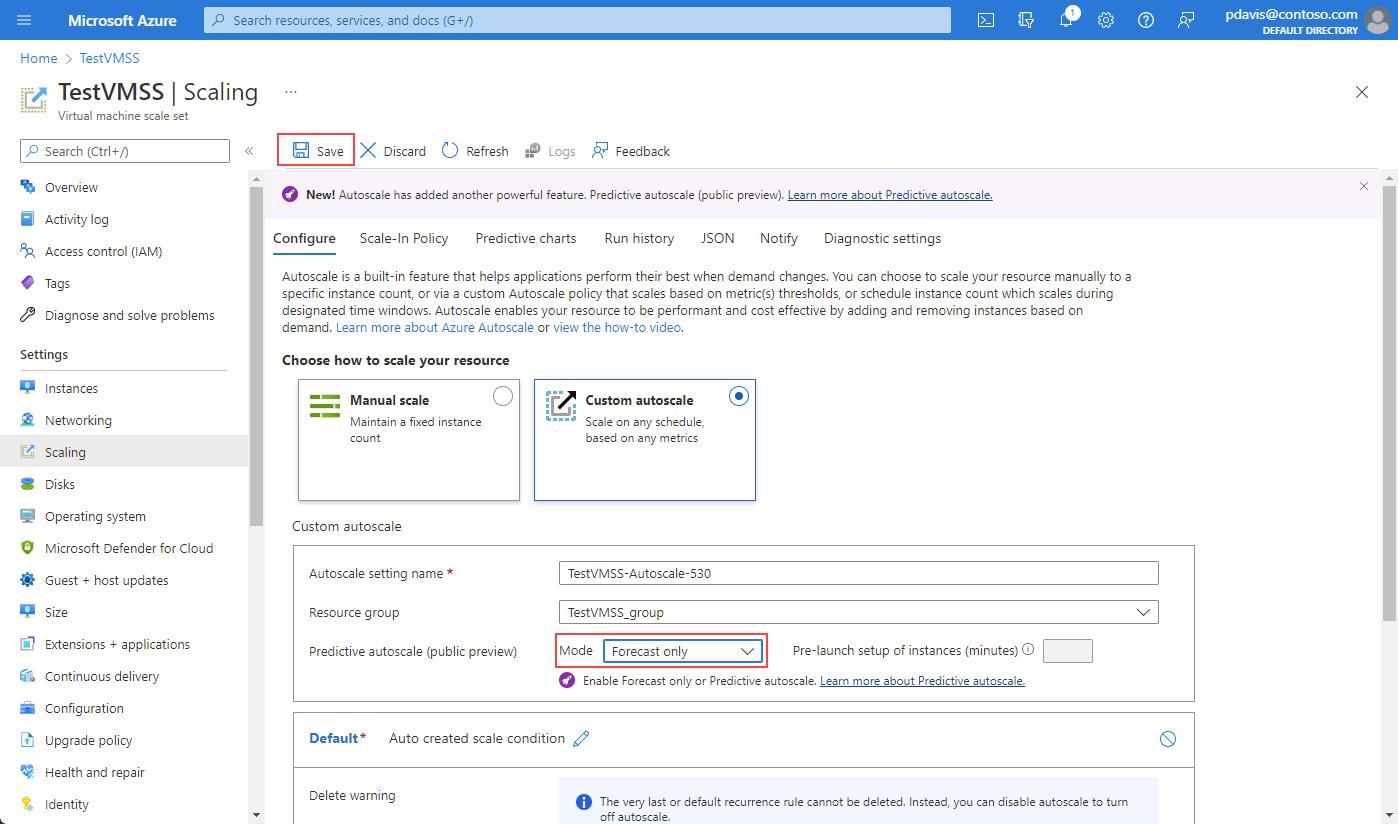
If desired, specify a prelaunch time so the instances are fully running before they're needed. You can prelaunch instances between 5 and 60 minutes before the needed prediction time.
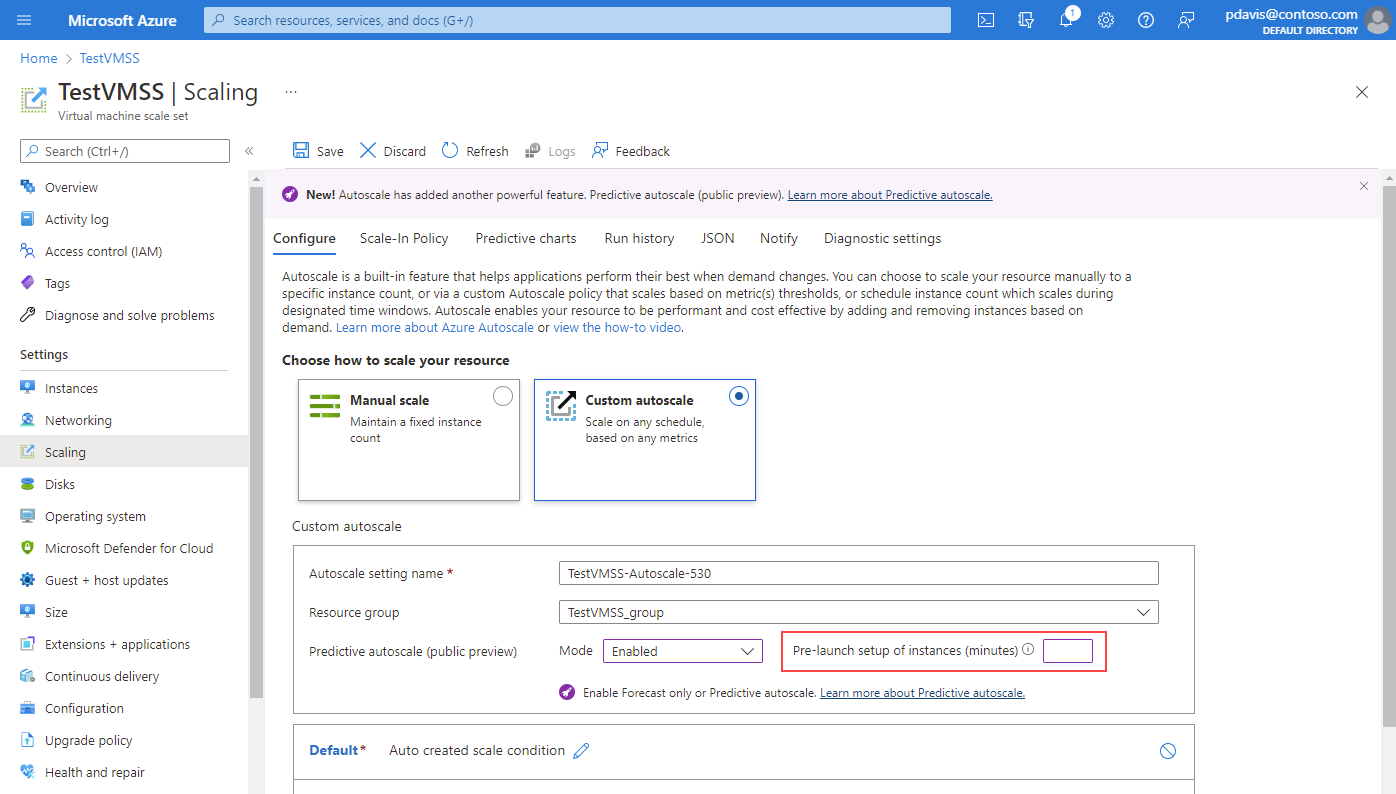
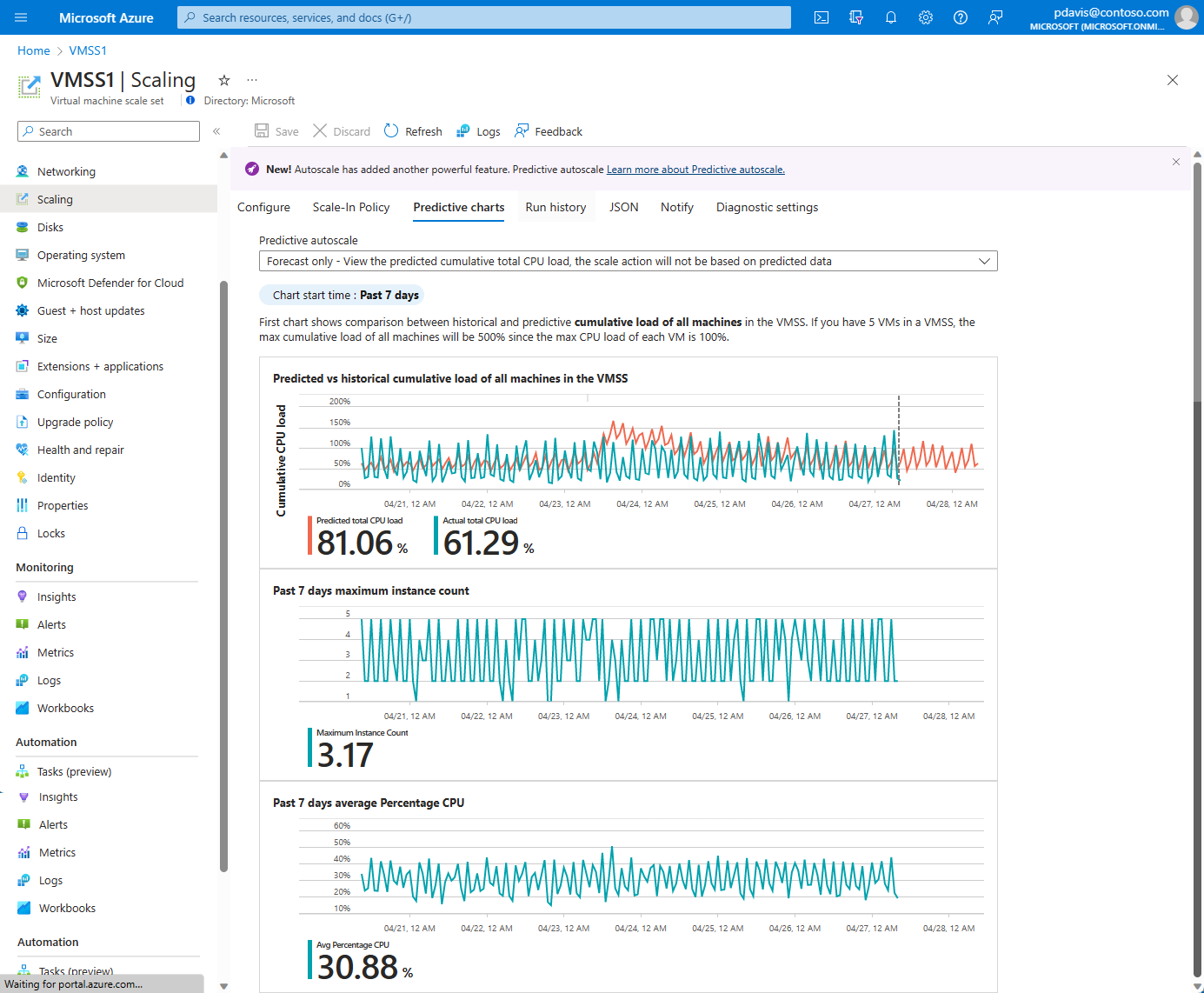
After you've enabled predictive autoscale or forecast-only mode and saved it, select Predictive charts.
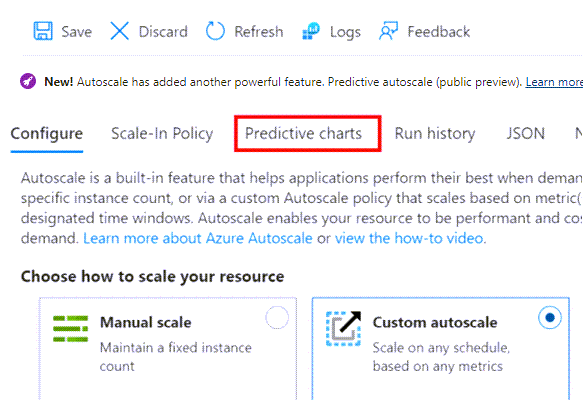
You see three charts:
- The top chart shows an overlaid comparison of actual versus predicted total CPU percentage. The time span of the graph shown is from the last seven days to the next 24 hours.
- The middle chart shows the maximum number of instances running over the last seven days.
- The bottom chart shows the current Average CPU utilization over the last seven days.
Enable using an Azure Resource Manager template
Retrieve the virtual machine scale set resource ID and resource group of your virtual machine scale set. For example: /subscriptions/e954e48d-abcd-abcd-abcd-3e0353cb45ae/resourceGroups/patest2/providers/Microsoft.Compute/virtualMachineScaleSets/patest2
Update the autoscale_only_parameters file with the virtual machine scale set resource ID and any autoscale setting parameters.
Use a PowerShell command to deploy the template that contains the autoscale settings. For example:
PS G:\works\kusto_onboard\test_arm_template> new-azurermresourcegroupdeployment -name binzAutoScaleDeploy -resourcegroupname cpatest2 -templatefile autoscale_only.json -templateparameterfile autoscale_only_parameters.json
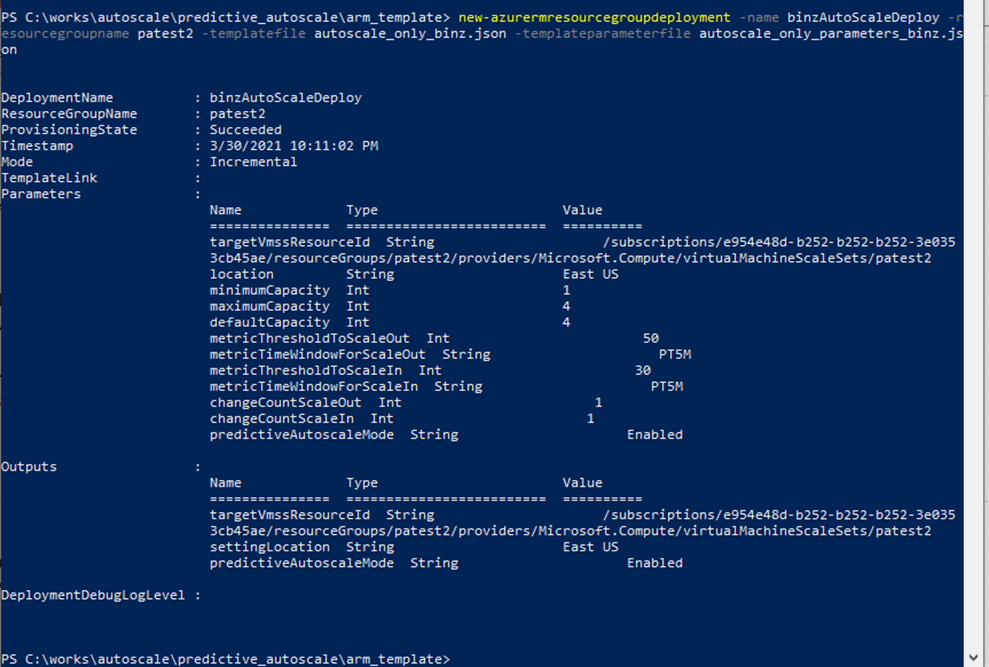
autoscale_only.json
{
"$schema": "https://schema.management.azure.com/schemas/2019-04-01/deploymentTemplate.json#",
"contentVersion": "1.0.0.0",
"parameters": {
"targetVmssResourceId": {
"type": "string"
},
"location": {
"type": "string"
},
"minimumCapacity": {
"type": "Int",
"defaultValue": 2,
"metadata": {
"description": "The minimum capacity. Autoscale engine will ensure the instance count is at least this value."
}
},
"maximumCapacity": {
"type": "Int",
"defaultValue": 5,
"metadata": {
"description": "The maximum capacity. Autoscale engine will ensure the instance count is not greater than this value."
}
},
"defaultCapacity": {
"type": "Int",
"defaultValue": 3,
"metadata": {
"description": "The default capacity. Autoscale engine will preventively set the instance count to be this value if it can not find any metric data."
}
},
"metricThresholdToScaleOut": {
"type": "Int",
"defaultValue": 30,
"metadata": {
"description": "The metric upper threshold. If the metric value is above this threshold then autoscale engine will initiate scale out action."
}
},
"metricTimeWindowForScaleOut": {
"type": "string",
"defaultValue": "PT5M",
"metadata": {
"description": "The metric look up time window."
}
},
"metricThresholdToScaleIn": {
"type": "Int",
"defaultValue": 20,
"metadata": {
"description": "The metric lower threshold. If the metric value is below this threshold then autoscale engine will initiate scale in action."
}
},
"metricTimeWindowForScaleIn": {
"type": "string",
"defaultValue": "PT5M",
"metadata": {
"description": "The metric look up time window."
}
},
"changeCountScaleOut": {
"type": "Int",
"defaultValue": 1,
"metadata": {
"description": "The instance count to increase when autoscale engine is initiating scale out action."
}
},
"changeCountScaleIn": {
"type": "Int",
"defaultValue": 1,
"metadata": {
"description": "The instance count to decrease the instance count when autoscale engine is initiating scale in action."
}
},
"predictiveAutoscaleMode": {
"type": "String",
"defaultValue": "ForecastOnly",
"metadata": {
"description": "The predictive Autoscale mode."
}
}
},
"variables": {
},
"resources": [{
"type": "Microsoft.Insights/autoscalesettings",
"name": "cpuPredictiveAutoscale",
"apiVersion": "2022-10-01",
"location": "[parameters('location')]",
"properties": {
"profiles": [{
"name": "DefaultAutoscaleProfile",
"capacity": {
"minimum": "[parameters('minimumCapacity')]",
"maximum": "[parameters('maximumCapacity')]",
"default": "[parameters('defaultCapacity')]"
},
"rules": [{
"metricTrigger": {
"metricName": "Percentage CPU",
"metricNamespace": "",
"metricResourceUri": "[parameters('targetVmssResourceId')]",
"timeGrain": "PT1M",
"statistic": "Average",
"timeWindow": "[parameters('metricTimeWindowForScaleOut')]",
"timeAggregation": "Average",
"operator": "GreaterThan",
"threshold": "[parameters('metricThresholdToScaleOut')]"
},
"scaleAction": {
"direction": "Increase",
"type": "ChangeCount",
"value": "[parameters('changeCountScaleOut')]",
"cooldown": "PT5M"
}
}, {
"metricTrigger": {
"metricName": "Percentage CPU",
"metricNamespace": "",
"metricResourceUri": "[parameters('targetVmssResourceId')]",
"timeGrain": "PT1M",
"statistic": "Average",
"timeWindow": "[parameters('metricTimeWindowForScaleIn')]",
"timeAggregation": "Average",
"operator": "LessThan",
"threshold": "[parameters('metricThresholdToScaleIn')]"
},
"scaleAction": {
"direction": "Decrease",
"type": "ChangeCount",
"value": "[parameters('changeCountScaleOut')]",
"cooldown": "PT5M"
}
}
]
}
],
"enabled": true,
"targetResourceUri": "[parameters('targetVmssResourceId')]",
"predictiveAutoscalePolicy": {
"scaleMode": "[parameters('predictiveAutoscaleMode')]"
}
}
}
],
"outputs": {
"targetVmssResourceId" : {
"type" : "string",
"value" : "[parameters('targetVmssResourceId')]"
},
"settingLocation" : {
"type" : "string",
"value" : "[parameters('location')]"
},
"predictiveAutoscaleMode" : {
"type" : "string",
"value" : "[parameters('predictiveAutoscaleMode')]"
}
}
}
autoscale_only_parameters.json
{
"$schema": "https://schema.management.azure.com/schemas/2019-04-01/deploymentTemplate.json#",
"contentVersion": "1.0.0.0",
"parameters": {
"targetVmssResourceId": {
"value": "/subscriptions/e954e48d-b252-b252-b252-3e0353cb45ae/resourceGroups/patest2/providers/Microsoft.Compute/virtualMachineScaleSets/patest2"
},
"location": {
"value": "East US"
},
"minimumCapacity": {
"value": 1
},
"maximumCapacity": {
"value": 4
},
"defaultCapacity": {
"value": 4
},
"metricThresholdToScaleOut": {
"value": 50
},
"metricTimeWindowForScaleOut": {
"value": "PT5M"
},
"metricThresholdToScaleIn": {
"value": 30
},
"metricTimeWindowForScaleIn": {
"value": "PT5M"
},
"changeCountScaleOut": {
"value": 1
},
"changeCountScaleIn": {
"value": 1
},
"predictiveAutoscaleMode": {
"value": "Enabled"
}
}
}
For more information on Azure Resource Manager templates, see Resource Manager template overview.
Frequently asked questions
This section answers frequently asked questions.
Why is CPU percentage over 100 percent on predictive charts?
The predictive chart shows the cumulative load for all machines in the scale set. If you have 5 VMs in a scale set, the maximum cumulative load for all VMs will be 500%, that is, five times the 100% maximum CPU load of each VM.
What happens over time when you turn on predictive autoscale for a virtual machine scale set?
Prediction autoscale uses the history of a running virtual machine scale set. If your scale set has been running less than seven days, you'll receive a message that the model is being trained. For more information, see the no predictive data message. Predictions improve as time goes by and achieve maximum accuracy 15 days after the virtual machine scale set is created.
If changes to the workload pattern occur but remain periodic, the model recognizes the change and begins to adjust the forecast. The forecast improves as time goes by. Maximum accuracy is reached 15 days after the change in the traffic pattern happens. Remember that your standard autoscale rules still apply. If a new unpredicted increase in traffic occurs, your virtual machine scale set will still scale out to meet the demand.
What if the model isn't working well for me?
The modeling works best with workloads that exhibit periodicity. We recommend that you first evaluate the predictions by enabling "forecast only," which will overlay the scale set's predicted CPU usage with the actual, observed usage. After you compare and evaluate the results, you can then choose to enable scaling based on the predicted metrics if the model predictions are close enough for your scenario.
Why do I need to enable standard autoscale before I enable predictive autoscale?
Standard autoscaling is a necessary fallback if the predictive model doesn't work well for your scenario. Standard autoscale will cover unexpected load spikes, which aren't part of your typical CPU load pattern. It also provides a fallback if an error occurs in retrieving the predictive data.
Which rule takes effect if both predictive and standard autoscale rules are set?
Standard autoscale rules are used if there's an unexpected spike in the CPU load, or an error occurs when retrieving predictive data
We use the threshold set in the standard autoscale rules to understand when you’d like to scale out and by how many instances. If you want your Virtual Machine Scale Set to scale out when the CPU usage exceeds 70% and actual or predicted data shows that CPU usage is or will be over 70%, then a scale out will occur.
Errors and warnings
This section addresses common errors and warnings.
Didn't enable standard autoscale
You receive the following error message:
To enable predictive autoscale, create a scale out rule based on 'Percentage CPU' metric. Click here to go to the 'Configure' tab to set an autoscale rule.

This message means you attempted to enable predictive autoscale before you enabled standard autoscale and set it up to use the Percentage CPU metric with the Average aggregation type.
No predictive data
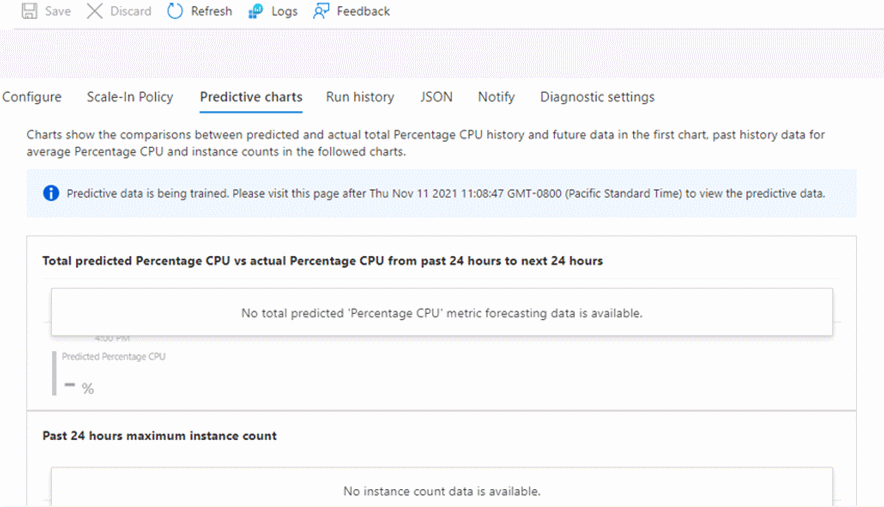
You won't see data on the predictive charts under certain conditions. This behavior isn't an error, it's the intended behavior.
When predictive autoscale is disabled, you instead receive a message that begins with "No data to show..." You then see instructions on what to enable so that you can see a predictive chart.

When you first create a virtual machine scale set and enable forecast-only mode, you receive the message "Predictive data is being trained..." and a time to return to see the chart.
Next steps
Learn more about autoscale in the following articles:
Feedback
Coming soon: Throughout 2024 we will be phasing out GitHub Issues as the feedback mechanism for content and replacing it with a new feedback system. For more information see: https://aka.ms/ContentUserFeedback.
Submit and view feedback for