Troubleshoot Kubernetes Compute
In this article, you learn how to troubleshoot common workload errors on the Kubernetes compute. Common errors include training jobs and endpoint errors.
Inference guide
The common Kubernetes endpoint errors on Kubernetes compute are categorized into two scopes: compute scope and cluster scope. The compute scope errors are related to the compute target, such as the compute target isn't found, or the compute target isn't accessible. The cluster scope errors are related to the underlying Kubernetes cluster, such as the cluster itself isn't reachable, or the cluster isn't found.
Kubernetes compute errors
The following are common error types in compute scope that you might encounter when using Kubernetes compute to create online endpoints and online deployments for real-time model inference. You can trouble shoot by following the linked sections for guidelines:
- ERROR: GenericComputeError
- ERROR: ComputeNotFound
- ERROR: ComputeNotAccessible
- ERROR: InvalidComputeInformation
- ERROR: InvalidComputeNoKubernetesConfiguration
ERROR: GenericComputeError
The error message is as:
Failed to get compute information.
This error should occur when system failed to get the compute information from the Kubernetes cluster. You can check the following items to troubleshoot the issue:
- Check the Kubernetes cluster status. If the cluster isn't running, you need to start the cluster first.
- Check the Kubernetes cluster health.
- You can view the cluster health check report for any issues, for example, if the cluster is not reachable.
- You can go to your workspace portal to check the compute status.
- Check if the instance types are information is correct. You can check the supported instance types in the Kubernetes compute documentation.
- Try to detach and reattach the compute to the workspace if applicable.
Note
To trouble shoot errors by reattaching, please guarantee to reattach with the exact same configuration as previously detached compute, such as the same compute name and namespace, otherwise you may encounter other errors.
ERROR: ComputeNotFound
The error message is as follows:
Cannot find Kubernetes compute.
This error should occur when:
- The system can't find the compute when create/update new online endpoint/deployment.
- The compute of existing online endpoints/deployments have been removed.
You can check the following items to troubleshoot the issue:
- Try to recreate the endpoint and deployment.
- Try to detach and reattach the compute to the workspace. Pay attention to more notes on reattach.
ERROR: ComputeNotAccessible
The error message is as follows:
The Kubernetes compute is not accessible.
This error should occur when the workspace MSI (managed identity) doesn't have access to the AKS cluster. You can check if the workspace MSI has the access to the AKS, and if not, you can follow this document to manage access and identity.
ERROR: InvalidComputeInformation
The error message is as follows:
The compute information is invalid.
There is a compute target validation process when deploying models to your Kubernetes cluster. This error should occur when the compute information is invalid. For example, the compute target is not found, or the configuration of Azure Machine Learning extension has been updated in your Kubernetes cluster.
You can check the following items to troubleshoot the issue:
- Check whether the compute target you used is correct and existing in your workspace.
- Try to detach and reattach the compute to the workspace. Pay attention to more notes on reattach.
ERROR: InvalidComputeNoKubernetesConfiguration
The error message is as follows:
The compute kubeconfig is invalid.
This error should occur when the system failed to find any configuration to connect to cluster, such as:
- For Arc-Kubernetes cluster, there is no Azure Relay configuration can be found.
- For AKS cluster, there is no AKS configuration can be found.
To rebuild the configuration of compute connection in your cluster, you can try to detach and reattach the compute to the workspace. Pay attention to more notes on reattach.
Kubernetes cluster error
Below is a list of error types in cluster scope that you might encounter when using Kubernetes compute to create online endpoints and online deployments for real-time model inference, which you can trouble shoot by following the guideline:
ERROR: GenericClusterError
The error message is as follows:
Failed to connect to Kubernetes cluster: <message>
This error should occur when the system failed to connect to the Kubernetes cluster for an unknown reason. You can check the following items to troubleshoot the issue:
For AKS clusters:
- Check if the AKS cluster is shut down.
- If the cluster isn't running, you need to start the cluster first.
- Check if the AKS cluster has enabled selected network by using authorized IP ranges.
- If the AKS cluster has enabled authorized IP ranges, make sure all the Azure Machine Learning control plane IP ranges have been enabled for the AKS cluster. More information you can see this document.
For an AKS cluster or an Azure Arc enabled Kubernetes cluster:
- Check if the Kubernetes API server is accessible by running
kubectlcommand in cluster.
ERROR: ClusterNotReachable
The error message is as follows:
The Kubernetes cluster is not reachable.
This error should occur when the system can't connect to a cluster. You can check the following items to troubleshoot the issue:
For AKS clusters:
- Check if the AKS cluster is shut down.
- If the cluster isn't running, you need to start the cluster first.
For an AKS cluster or an Azure Arc enabled Kubernetes cluster:
- Check if the Kubernetes API server is accessible by running
kubectlcommand in cluster.
ERROR: ClusterNotFound
The error message is as follows:
Cannot found Kubernetes cluster.
This error should occur when the system cannot find the AKS/Arc-Kubernetes cluster.
You can check the following items to troubleshoot the issue:
- First, check the cluster resource ID in the Azure portal to verify whether Kubernetes cluster resource still exists and is running normally.
- If the cluster exists and is running, then you can try to detach and reattach the compute to the workspace. Pay attention to more notes on reattach.
Tip
More troubleshoot guide of common errors when creating/updating the Kubernetes online endpoints and deployments, you can find in How to troubleshoot online endpoints.
Identity error
ERROR: RefreshExtensionIdentityNotSet
This error occurs when the extension is installed but the extension identity is not correctly assigned. You can try to reinstall the extension to fix it.
Please notice this error is only for managed clusters
How to check sslCertPemFile and sslKeyPemFile is correct?
In order to allow for any known errors to be surfaced, you can use the commands to run a baseline check for your cert and key. Expect the second command to return "RSA key ok" without prompting you for password.
openssl x509 -in cert.pem -noout -text
openssl rsa -in key.pem -noout -check
Run the commands to verify whether sslCertPemFile and sslKeyPemFile are matched:
openssl x509 -in cert.pem -noout -modulus | md5sum
openssl rsa -in key.pem -noout -modulus | md5sum
For sslCertPemFile, it is the public certificate. It should include the certificate chain which includes the following certificates and should be in the sequence of the server certificate, the intermediate CA certificate and the root CA certificate:
- The server certificate: the server presents to the client during the TLS handshake. It contains the server’s public key, domain name, and other information. The server certificate is signed by an intermediate certificate authority (CA) that vouches for the server’s identity.
- The intermediate CA certificate: the intermediate CA presents to the client to prove its authority to sign the server certificate. It contains the intermediate CA’s public key, name, and other information. The intermediate CA certificate is signed by a root CA that vouches for the intermediate CA’s identity.
- The root CA certificate: the root CA presents to the client to prove its authority to sign the intermediate CA certificate. It contains the root CA’s public key, name, and other information. The root CA certificate is self-signed and trusted by the client.
Training guide
When the training job is running, you can check the job status in the workspace portal. When you encounter some abnormal job status, such as the job retried multiple times, or the job has been stuck in initializing state, or even the job has eventually failed, you can follow the guide to troubleshoot the issue.
Job retry debugging
If the training job pod running in the cluster was terminated due to the node running to node OOM (out of memory), the job is automatically retried to another available node.
To further debug the root cause of the job try, you can go to the workspace portal to check the job retry log.
- Each retry log is recorded in a new log folder with the format of "retry-<retry number>"(such as: retry-001).
Then you can get the retry job-node mapping information, to figure out which node the retry-job has been running on.
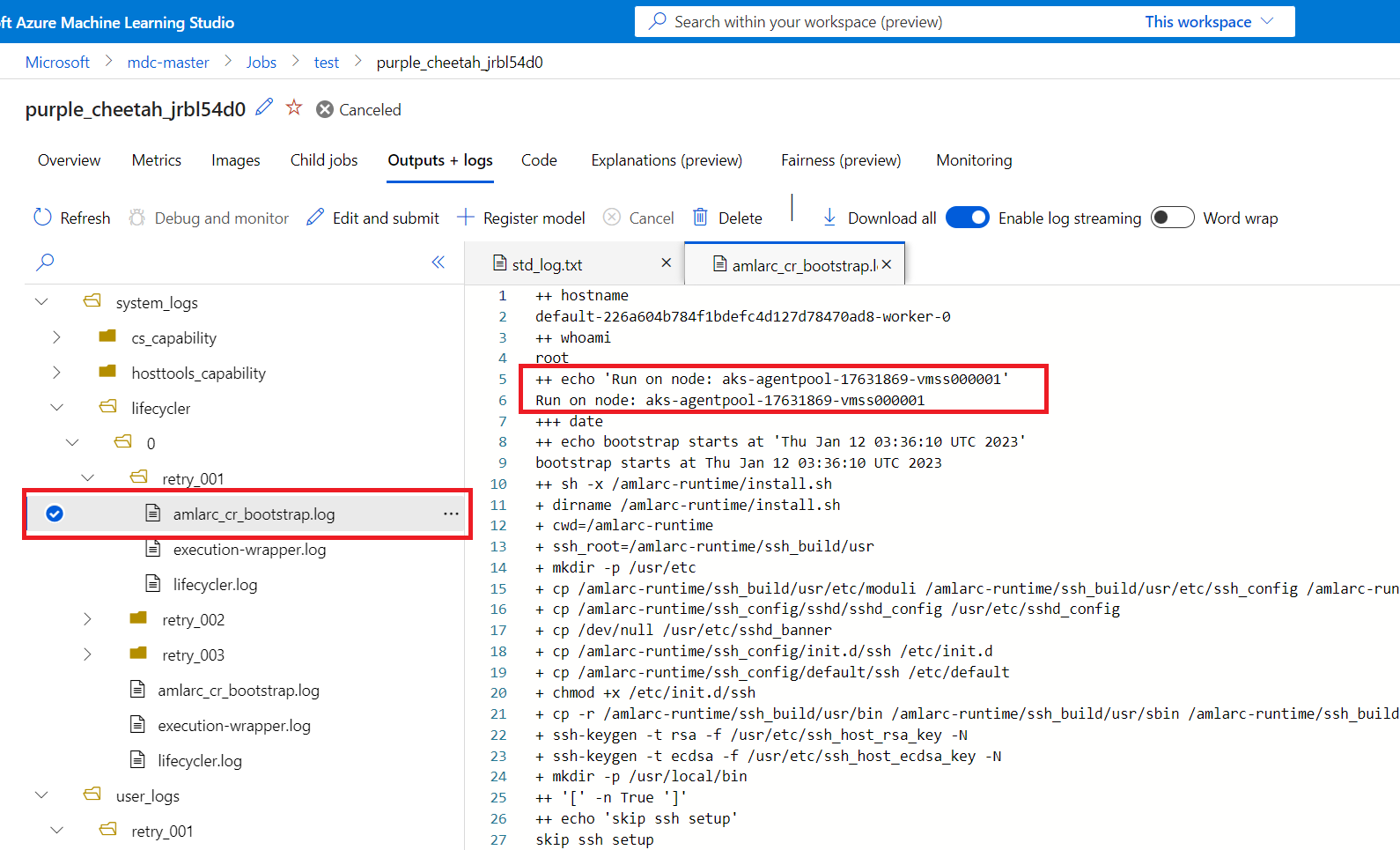
You can get job-node mapping information from the amlarc_cr_bootstrap.log under system_logs folder.
The host name of the node, which the job pod is running on is indicated in this log, for example:
++ echo 'Run on node: ask-agentpool-17631869-vmss0000"
"ask-agentpool-17631869-vmss0000" represents the node host name running this job in your AKS cluster. Then you can access the cluster to check about the node status for further investigation.
Job pod get stuck in Init state
If the job runs longer than you expected and if you find that your job pods are getting stuck in an Init state with this warning Unable to attach or mount volumes: *** failed to get plugin from volumeSpec for volume ***-blobfuse-*** err=no volume plugin matched, the issue might be occurring because Azure Machine Learning extension doesn't support download mode for input data.
To resolve this issue, change to mount mode for your input data.
Common job failure errors
Below is a list of common error types that you might encounter when using Kubernetes compute to create and execute a training job, which you can trouble shoot by following the guideline:
- Job failed. 137
- Job failed. E45004
- Job failed. 400
- Give either an account key or SAS token
- AzureBlob authorization failed
Job failed. 137
If the error message is:
Azure Machine Learning Kubernetes job failed. 137:PodPattern matched: {"containers":[{"name":"training-identity-sidecar","message":"Updating certificates in /etc/ssl/certs...\n1 added, 0 removed; done.\nRunning hooks in /etc/ca-certificates/update.d...\ndone.\n * Serving Flask app 'msi-endpoint-server' (lazy loading)\n * Environment: production\n WARNING: This is a development server. Do not use it in a production deployment.\n Use a production WSGI server instead.\n * Debug mode: off\n * Running on http://127.0.0.1:12342/ (Press CTRL+C to quit)\n","code":137}]}
Check your proxy setting and check whether 127.0.0.1 was added to proxy-skip-range when using az connectedk8s connect by following this network configuring.
Job failed. E45004
If the error message is:
Azure Machine Learning Kubernetes job failed. E45004:"Training feature is not enabled, please enable it when install the extension."
Check whether you have enableTraining=True set when doing the Azure Machine Learning extension installation. More details could be found at Deploy Azure Machine Learning extension on AKS or Arc Kubernetes cluster
Job failed. 400
If the error message is:
Azure Machine Learning Kubernetes job failed. 400:{"Msg":"Encountered an error when attempting to connect to the Azure Machine Learning token service","Code":400}
You can follow Private Link troubleshooting section to check your network settings.
Give either an account key or SAS token
If you need to access Azure Container Registry (ACR) for Docker image, and to access the Storage Account for training data, this issue should occur when the compute is not specified with a managed identity.
To access Azure Container Registry (ACR) from a Kubernetes compute cluster for Docker images, or access a storage account for training data, you need to attach the Kubernetes compute with a system-assigned or user-assigned managed identity enabled.
In the above training scenario, this computing identity is necessary for Kubernetes compute to be used as a credential to communicate between the ARM resource bound to the workspace and the Kubernetes computing cluster. So without this identity, the training job fails and reports missing account key or sas token. Take accessing storage account, for example, if you don't specify a managed identity to your Kubernetes compute, the job fails with the following error message:
Unable to mount data store workspaceblobstore. Give either an account key or SAS token
The cause is machine learning workspace default storage account without any credentials is not accessible for training jobs in Kubernetes compute.
To mitigate this issue, you can assign Managed Identity to the compute in compute attach step, or you can assign Managed Identity to the compute after it has been attached. More details could be found at Assign Managed Identity to the compute target.
AzureBlob authorization failed
If you need to access the AzureBlob for data upload or download in your training jobs on Kubernetes compute, then the job fails with the following error message:
Unable to upload project files to working directory in AzureBlob because the authorization failed.
The cause is the authorization failed when the job tries to upload the project files to the AzureBlob. You can check the following items to troubleshoot the issue:
- Make sure the storage account has enabled the exceptions of “Allow Azure services on the trusted service list to access this storage account” and the workspace is in the resource instances list.
- Make sure the workspace has a system assigned managed identity.
Private link issue
We could use the method to check private link setup by logging into one pod in the Kubernetes cluster and then check related network settings.
Find workspace ID in Azure portal or get this ID by running
az ml workspace showin the command line.Show all azureml-fe pods run by
kubectl get po -n azureml -l azuremlappname=azureml-fe.Sign in into any of them run
kubectl exec -it -n azureml {scorin_fe_pod_name} bash.If the cluster doesn't use proxy run
nslookup {workspace_id}.workspace.{region}.api.azureml.ms. If you set up private link from VNet to workspace correctly, then the internal IP in VNet should be responded through the DNSLookup tool.If the cluster uses proxy, you can try to
curlworkspace
curl https://{workspace_id}.workspace.westcentralus.api.azureml.ms/metric/v2.0/subscriptions/{subscription}/resourceGroups/{resource_group}/providers/Microsoft.MachineLearningServices/workspaces/{workspace_name}/api/2.0/prometheus/post -X POST -x {proxy_address} -d {} -v -k
When the proxy and workspace are correctly set up with a private link, you should observe an attempt to connect to an internal IP. A response with an HTTP 401 status code is expected in this scenario if a token isn't provided.
Other known issues
Kubernetes compute update doesn't take effect
At this time, the CLI v2 and SDK v2 don't allow updating any configuration of an existing Kubernetes compute. For example, changing the namespace doesn't take effect.
Workspace or resource group name end with '-'
A common cause of the "InternalServerError" failure when creating workloads such as deployments, endpoints, or jobs in a Kubernetes compute, is having the special characters like '-' at the end of your workspace or resource group name.
Next steps
Feedback
Coming soon: Throughout 2024 we will be phasing out GitHub Issues as the feedback mechanism for content and replacing it with a new feedback system. For more information see: https://aka.ms/ContentUserFeedback.
Submit and view feedback for